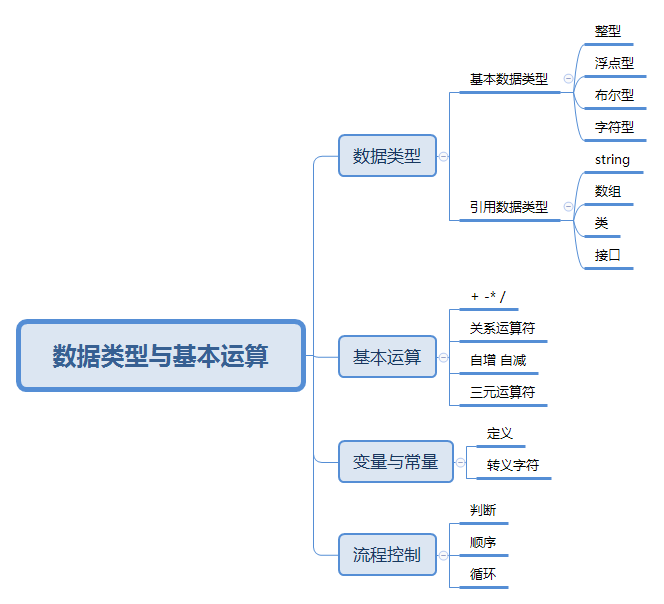
1, Data type
1. Basic data type:
(1) Integer: byte short int long
(2) Floating point type: float double
(3) Boolean: bool
(4) Character type: cahr
2. Reference data type:
string array class interface
2, Constants and variables
1. Variables
(1) Variable definition: data type variable name;
(2) Variable assignment: variable name = value;
(3) Use of variables: first define, then assign, and then use
eag: int a=10;
2... Constant
(1) . constant definition: (const) data type constant name;
(2) . constant assignment: constant name = value;
(3) . use of constants: first define, then assign, and then use
eag:(const) int b=100;
3, Naming rules
Camel / hump naming method: the first letter of the word is lowercase, and the first letter of each other word is uppercase. It is mostly used to name variables: myStudent
Pascal: each word is capitalized, distinguished from lowercase, multi-user and named MiddleSchool for methods or classes
4, Type conversion
1. Display conversion (forced conversion): byte < – short (char) < – int < – long < – float < – double
Format: (force conversion of data type) variable name
/* int a = 10; float b; b = a; //print(a+"\t"+b);//10
Other conversion methods: int.Parse(); Convert.ToInt(); Convert.ToString();…
2. Implicit conversion (automatic type conversion): byte – > short (char) – > int – > long – > float – > double
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{//Using Convert type conversion, you will succeed if you succeed, and throw an exception if you fail
// int a = Convert.ToInt32("da5555");
//If you succeed, you will succeed, and if you fail, you will throw exceptions
// int b = int.Parse("dadad2121");
//Try to convert a string to type int
#region int.TryParse summary
/*
Summary:
public static Int32 Parse(string s, NumberStyles style);
Converts the string representation of a number to its 32-bit signed integer equivalent. A return value indicating whether the conversion was successful.
Parameters:
s:
A string containing the number to convert
When this method returns, if the conversion is successful, it contains a 32-bit unsigned integer value equivalent to the number contained in s; If the conversion fails, zero is included. If the s parameter is null or System.String.Empty, the format is incorrect, or the number represented is less than
System.Int32.MinValue Or greater than System.Int32.MaxValue, the conversion fails. This parameter is passed without initialization; Initially in result
Any value provided in is overwritten.
s if true is successfully converted; Otherwise, it is false.
*/
#endregion
int number = 110;
bool c= int.TryParse("123", out number);
//If the conversion succeeds, enter number and return the value of c. if the conversion fails, return the value of number to 0 and return the value of c
Console.WriteLine(c);
Console.WriteLine(number);
}
}
5, Escape character
Escape character: a \ plus a special character to form a character with special meaning
\n: Line feed
\b: Backspace
\: backslash
\t: Tab
": double quotation marks
@Symbol:
1. Cancel the escape function of \ in the string
2. Keep the original format output
Use of plus sign:
1. Connection: when one side of the + sign is a string
2. Addition: both sides are numbers
6, Basic operation
1.+ - * / %
2. Relational operator: > > = < < = ==
3. Self increase and self decrease:
Whether it is before + + or after + +, the final result is to add 1 to this variable
In the expression: if it is the first + +, first add 1 to the variable itself, and then take the value after 1 to participate in the operation
If it is post + +, take the original value to participate in the operation. After the operation, add 1 to the variable itself
The deduction is the same as above
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{//++The original value of number is added after, and then number is added by 1
//++Add number+1 before, and then number+1
int number = 10;
// int result = 10 + ++number;// number 11 result 21
/* number++;
int result = 10 + number;*/
int result = 10 + number++;// number 11 result 20
/*int result=10+number;
number++;
*/
Console.WriteLine("number The values are:{0},result The values are:{1}", number,result);
int a = 5;
int b = a++ + ++a * 2 + --a + a++;
/* 5 6
7*2 7
6 6
6 7
*/
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",b,a);
}
}
7, Logical operator
Logical and: & & true (1) false (0) multiplication
Logical or: | true (1) false (0) addition 1 + 1 = 1
Logical non:! 1 becomes 0 becomes 1
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Xiao Su, please enter your Chinese score");
int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Xiao Su, please enter your math score");
int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
bool c = a > 90 && b > 90;
Console.WriteLine(c);
//Judge leap year
Console.WriteLine("Please enter the year to judge");
int d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
//The year can be divided by 400 (2000)
//Year can be divided by 4 but not 100 (2008)
bool e = (d % 400 == 0) || (d % 4 == 0 && d % 100 != 0);// Logic takes precedence over logic or
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
8, VS common shortcut keys
Ctrl + s save
Ctrl + c copy
Ctrl + v paste
Ctrl + x cut
Ctrl + z undo
Ctrl + k +d quick alignment code
Ctrl + k + c quick comment selection
Ctrl + k + u to quickly de annotate the selected annotation content
9, Ternary operator
/// <summary> /// ///Expression 1? Expression 2: expression 3 ///Expression 1 is generally a relational expression. Any formula using if else can use a relational expression ///Note: expression 2 and expression 3 must be consistent with the expression result type /// bool a5 = false; /// string s = a5 ? "Yes" : "No"; /// </summary>
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculate the ratio of two numbers and find the maximum value
//Console.WriteLine("please enter the first number:");
//int a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
//Console.WriteLine("please enter the second number:");
//int b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
//int c = a > b ? a : b;
//Console.WriteLine(c);
//if (a > b)
//{
// Console.WriteLine(a);
//}
//else { Console.WriteLine(b); }
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.Add("Zhang San");
al.Add(1);
al.Add('d');
al.Add(true);
// al.Remove(1); / / delete a single element. Delete whoever writes it
al.RemoveAt(2);//Delete elements according to Subscripts
al.Insert(1, "Inserted");// Inserts an element before the specified location
//al.Sort();
al.Add("Big boy");
if (!al.Contains("Big boy"))//Determines whether an element is in System.Collections.ArrayList
{
al.Add("Big boy");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Already");
}
foreach (object item in al)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
List<string> list = new List<string>();
list.Add("Zhang San");
list.Add("Li Si");
list.Add("Wang Wu");
list.Add("Tian Liu");
list.Add("Zhao Qi");
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("for Cycle:" + list[i]);
}
list.RemoveAt(0);
foreach (string item in list)
{
Console.WriteLine("foreach Iteration:" + item);
}
}
}