First of all, there was no interesting thinking problem after the fight. Instead, it was mainly simulated code farming problem, which was very annoying (referring to being a code farmer in the middle of the night)......
A. Square String? (violence)
Judge parity and compare violence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
string s;
void sol()
{
if (s.size()&1)
{
printf("NO\n");
return;
}
for (ll i=0;i<s.size()/2;i++)
if (s[i]!=s[s.size()/2+i])
{
printf("NO\n");
return;
}
printf("YES\n");
return;
}
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
cin>>s;
sol();
}
return 0;
}B. Squares and Cubes
For inclusion exclusion calculation, since it calculates the number of squares and cubes < = n, you can use inclusion exclusion (of course, this can also be done violently). Assuming that sol (x) is the number of x power < = n of a, the answer is sol(2)+sol(3)-sol(2*3)
PS: O was used in the race to pursue speed(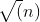 )Of course, there is a better solution, but this problem is enough
)Of course, there is a better solution, but this problem is enough
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
ll a[Ma];
ll n;
ll po(ll x,ll p)
{
ll sum=1;
while (x)
{
if (x&1)
sum*=p;
p*=p;
x>>=1;
}
return sum;
}
ll sol(ll x)
{
ll i;
for (i=1;po(x,i)<=n;i++)
continue;
return i-1;
}
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
scanf("%lld",&n);
printf("%lld\n",sol(2)+sol(3)-sol(6));
}
return 0;
}C. Wrong Addition
This question is very interesting (quite like my style in kindergarten). Just touch you from back to front. If the bit value of a is larger than that of s, you can borrow it.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
void sol(ll x,ll y)
{
ll b=0,p=1;
while (x)
{
ll a=x%10,s=y%10;
if (a>s)
{
s=y%100;
if (s-a>=10||s-a<0)
{
printf("-1\n");
return;
}
b+=(s-a)*p;
x/=10,y/=100;
}
else
{
b+=(s-a)*p;
x/=10,y/=10;
}
//cout<<a<<" "<<s<<endl;
p*=10;
}
while (y)
{
b+=p*(y%10);
y/=10;
p*=10;
}
printf("%lld\n",b);
return;
}
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
ll x,y;
scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y);
sol(x,y);
}
return 0;
}D. New Year's Problem
There should be many solutions to this problem. Here is an example of dichotomy
First, we divide the topic into two cases
1.n>m-1
In this case, we choose all. We can find the minimum value of everyone's optimal gift
2 n<=m-1
In this case, we find that there is one less thing to choose, so at least one store needs to buy two things. Therefore, we can take 0 as the lower bound and the minimum value of everyone's optimal gift as the upper bound
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
ll n,m;
vector <ll> a[Ma];
bool ask(ll x)
{
if (n>m-1)//In fact, there is no need to judge the original problem
{
for (ll i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ll add=0;
for (ll j=0;j<m;j++)
if (a[i][j]>=x)
add++;
if (add>=2)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
else
{
for (ll j=0;j<m;j++)
{
ll add=0;
for (ll i=0;i<n;i++)
if (a[i][j]>=x)
add++;
if (!add)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
void sol()
{
ll l=0,r=1e9+7;
for (ll j=0;j<m;j++)
{
ll ma=0;
for (ll i=0;i<n;i++)
ma=max(ma,a[i][j]);
r=min(ma,r);
}
while (l<=r)
{
ll mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (ask(mid))
l=mid+1;
else
r=mid-1;
}
printf("%lld\n",r);
return;
}
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
for (ll i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i].clear();
for (ll j=0;j<m;j++)
{
ll x;
scanf("%lld",&x);
a[i].push_back(x);
}
}
sol();
}
return 0;
}E. Mex and gains (touch you + priority queue)
Firstly, if x cannot be realized, x+1 must not be realized, so mark the end;
Then, for the optimal policy, we use f[i] to represent the number of times I appears in array a, and we divide it into three cases
First, let's assume that array a is the preceding empty number
Minimum number of moves ans for MEX=p-1
1.f[p]=0, we need to find the best w from array a, then the minimum number of moves of MEX=p is ans-f[p]+f[p+1]+p-w;
If a is an empty fart, then MEX=p cannot be completed;
2.f[p]=1, we don't need to move, just drive away the value at the position of p+1, that is, the minimum number of moves of MEX=p is ans-f[p]+f[p+1];
3. F [p] > 1. Similarly, we don't need to move, just drive away the value at the position of p+1, that is, the minimum number of moves of MEX=p is ans-f[p]+f[p+1], and we can put the extra p into array a;
I use the priority queue to maintain A. in fact, according to the selection, it can ensure that a is monotonic and non decreasing.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
ll a[Ma],f[Ma];
struct node
{
ll w;
bool operator <(const node &A)const{
return w<A.w;
}
};
priority_queue <node> q;
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
ll n;
scanf("%lld",&n);
for (ll i=0;i<=n;i++)
f[i]=0;
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]),f[a[i]]++;
while (!q.empty())
q.pop();
ll add=0,flag=1;
for (ll i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
if (flag)
printf("%lld ",add+f[i]);
else
printf("-1 ");
if (!f[i]&&q.empty())
flag=0;
else if (!f[i])
{
add+=i-q.top().w;
q.pop();
}
else
{
for (ll j=2;j<=f[i];j++)
q.push((node){i});
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}F. Let's Play the Hat? (thinking)
Firstly, it is found that for a given n,m, the grouping situation has been given, and what needs to be counted is ⌈ ⌉, so just put ⌈
⌉, so just put ⌈ ⌉ assign values successively, and ⌊
⌉ assign values successively, and ⌊ ⌋ fill in the blank jb, just don't match with ⌈
⌋ fill in the blank jb, just don't match with ⌈ ⌉ repeat
⌉ repeat
And for n,m, ⌈ There are n%m tables in ⌉ and ⌊
There are n%m tables in ⌉ and ⌊ ⌋ there are m-n%m tables
⌋ there are m-n%m tables
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
ll f[Ma];
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
ll n,m,k;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&k);
for (ll i=0;i<=n;i++)
f[i]=0;
ll p=0;
for (ll i=1;i<=k;i++)
{
ll u=n%m;
for (ll q=1;q<=u;q++)
{
printf("%lld ",n/m+1);
for (ll j=1;j<=n/m+1;j++)
{
f[p]=i;
printf("%lld ",p+1);
p=(p+1)%n;
}
printf("\n");
}
ll o=0;
for (ll q=1;q<=m-u;q++)
{
ll add=0;
printf("%lld ",n/m);
while (add<n/m)
{
if (f[o]!=i)
{
add++;
printf("%lld ",o+1);
}
o=(o+1)%n;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}G. Unusual Minesweeper (yard farmer + BFS + two points)
For this question, we can use the two-point answer to judge whether it is successful or not. Suppose the time is x
For the point with time < = x, it can be detonated directly
For the point with time > x and not detonated, we can find that any detonated point is equivalent (in fact, ask the number of connected blocks)
Note that time=0 can detonate a point
(there are still 40 minutes after writing F. after reading G seconds, I understood it, but I felt too tired to write, so I went to open h. as a result, H thought of using the ring for 20 minutes, but was afraid of explosion. F had no time to write. After 10 minutes after the game, his mind burst...)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ls p<<1
#define rs p<<1|1
#define Ma 1000005
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
ll v[Ma];
ll vt[Ma],va[Ma];
ll n,k;
struct node1
{
ll x,y,ti,num;
bool operator < (const node1 &A)const{
if (x==A.x)
return y<A.y;
return x<A.x;
}
}t[Ma];
struct node2
{
ll x,y,ti,num;
bool operator < (const node2 &A)const{
if (y==A.y)
return x<A.x;
return y<A.y;
}
}a[Ma];
void col(ll x)
{
v[x]=1;
ll pt=vt[x],pa=va[x];
if (pt>1&&t[pt].x==t[pt-1].x&&t[pt].y-t[pt-1].y<=k&&!v[t[pt-1].num])
col(t[pt-1].num);
if (pt<n&&t[pt].x==t[pt+1].x&&t[pt+1].y-t[pt].y<=k&&!v[t[pt+1].num])
col(t[pt+1].num);
if (pa>1&&a[pa].y==a[pa-1].y&&a[pa].x-a[pa-1].x<=k&&!v[a[pa-1].num])
col(a[pa-1].num);
if (pa<n&&a[pa].y==a[pa+1].y&&a[pa+1].x-a[pa].x<=k&&!v[a[pa+1].num])
col(a[pa+1].num);
return;
}
bool ask(ll x)
{
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
v[i]=0;
ll all=0;
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!v[i]&&t[vt[i]].ti<=x)
col(i);
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!v[i])
col(i),all++;
if (all-1<=x)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
ll tt;
scanf("%lld",&tt);
while (tt--)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&k);
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&t[i].x,&t[i].y,&t[i].ti),t[i].num=i;
a[i].x=t[i].x,a[i].y=t[i].y,a[i].ti=t[i].ti,a[i].num=t[i].num;
}
sort(t+1,t+n+1);
sort(a+1,a+n+1);
for (ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
vt[t[i].num]=va[a[i].num]=i;
ll l=0,r=n;
while (l<=r)
{
ll mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (ask(mid))
r=mid-1;
else
l=mid+1;
}
printf("%lld\n",l);
}
return 0;
}(topic G looks at the mood)