Static interval K small
Give a length sequence a[1], a[2],... a[N], the number of decimal K in the interval of [L, R] for each query?
We can build a weight segment tree, which stores the number of occurrences of a weight.
For [L, R] interval (a [L]~a [R]), the line segment tree is constructed.
The following example refers to blog: https://www.cnblogs.com/LiuRunky/p/Sustainable_Segment_Tree.html
For example, the sequence a={10,20,30,20,50,10,60,40} is discretized and b={1,2,3,2,5,1,6,4} is obtained.
For each discretized number in a sequence, we establish a numerical-based interval and segment tree to count its occurrence times.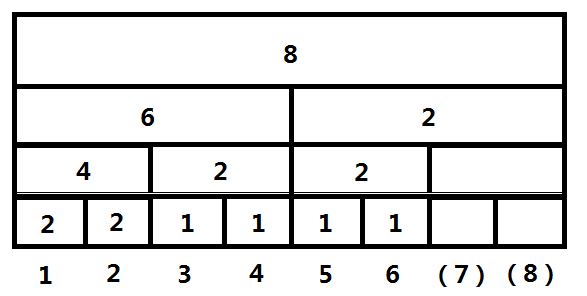
(7 and 8 are used to occupy space and can be ignored)
In this way, we can find the smallest k by the idea of similar dichotomy, and the node of the segment tree has helped us to split the interval half-way.
Suppose we want to find interval 7 small:
step 1: Numbers in interval [1,4] appear six times, so we can go directly to another interval [5,8] and find the first smallest one in this interval.
step 2: Numbers in intervals [5,6] appear twice, so the first smallest in [5,8] must be the first smallest in [5,6].
step 3: Numbers in intervals [5, 5] appear once, so 5 is the first smallest in [5, 6], that is, the seventh smallest in the whole query interval.
Then how to get the segment tree of interval [L, R]? Here we need to use the President Tree. First, we build an empty tree with zero occurrences, and then update and add a[1], a[2],... a[N], then we get N versions of the weight line segment tree (which can be seen as a prefix and a tree).
For any node, only the segment tree of version R and L-1 is subtracted from the same location node, and the value added from L-1 to R is the value of the segment tree of [L, R].
Template questions: POJ2104 - K-th Number
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define LL long long using namespace std; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; const int maxn=1e5+50; int n,m,N,a[maxn],b[maxn],root[maxn]; int t[maxn<<5],ls[maxn<<5],rs[maxn<<5],cnt=0; int build(int l,int r) { int rt=++cnt; if(l==r) { t[rt]=0; return rt; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; ls[rt]=build(l,mid); rs[rt]=build(mid+1,r); t[rt]=t[ls[rt]]+t[rs[rt]]; return rt; } int updata(int l,int r,int pos,int pre) { int rt=++cnt; if(l==r) { //Number of occurrences + 1 t[rt]=t[pre]+1; //Note that it's not t[rt]++. return rt; } ls[rt]=ls[pre],rs[rt]=rs[pre]; int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(pos<=mid) ls[rt]=updata(l,mid,pos,ls[pre]); else rs[rt]=updata(mid+1,r,pos,rs[pre]); t[rt]=t[ls[rt]]+t[rs[rt]]; return rt; } int query(int l,int r,int rt1,int rt2,int K) { if(l==r) return l; //Returns the corresponding weight int suml=t[ls[rt2]]-t[ls[rt1]]; //Sum of occurrence times of left subtree int mid=(l+r)>>1; if(suml>=K) return query(l,mid,ls[rt1],ls[rt2],K); //The rt of L-1 tree and R tree should be updated together else return query(mid+1,r,rs[rt1],rs[rt2],K-suml); //Note the change to K-suml } void init() { for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) b[i]=a[i]; sort(b+1,b+n+1); N=unique(b+1,b+n+1)-(b+1); //Number of different numbers after discretization for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) //That is to say, after discretization, it becomes 1 ~ N. a[i]=lower_bound(b+1,b+N+1,a[i])-b; } int main() { scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); init(); //Discretization root[0]=build(1,N); //Build an empty tree first for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) root[i]=updata(1,N,a[i],root[i-1]); //Update and join in turn for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { int L,R,K; scanf("%d %d %d",&L,&R,&K); printf("%d\n",b[query(1,N,root[L-1],root[R],K)]); } return 0; }