Chapter 55 SQL function% EXTERNAL
Format conversion function that returns an expression in display format.
outline
%EXTERNAL(expression) %EXTERNAL expression
parameter
- Expression - the expression to convert. A field name, an expression containing a field name, or a function whose return value is a convertible data type, such as DATE or% list. Cannot be a stream field.
describe
%EXTERNAL converts an expression to a display format, independent of the current selection mode (display mode). The display format represents the data of VARCHAR data type, no matter what data conversion the LogicalToDisplay method performs.
%EXTERNAL is usually used to select the list SELECT-ITEM. It can be used in the WHERE clause, but it is not recommended because using% EXTERNAL prevents the index from being used on the specified field.
Applying% EXTERNAL will change the column header name to a value such as "Expression_1"; Therefore, you usually need to specify a column name alias, as shown in the following example.
%Whether EXTERNAL converts a date depends on the data type returned by the date field or function.% n EXTERNAL conversion CURDATE, CURRENT_DATE, current and CURRENT_TIME value. It does not convert current_ Values for timestamp, GETDATE, getutdate, NOW, and $HOROLOG.
When% EXTERNAL converts the% List structure to display format, the displayed List elements appear to be separated by spaces. This "space" is actually two non display characters CHAR(13) and CHAR(10).
%EXTERNAL is an SQL extension.
To convert an expression to LOGICAL format regardless of the current selection mode, use the% INTERNAL function.
To convert an expression to ODBC format regardless of the current selection mode, use the% ODBC out function.
Examples
The following dynamic SQL example returns the Date of Birth (DOB) data value in the current selection mode format and uses the% EXTERNAL function to return the same data.
For demonstration purposes, in this program, the% SelectMode value is determined randomly at each call:
ClassMethod External()
{
s tStatement = ##class(%SQL.Statement).%New()
s tStatement.%SelectMode = $RANDOM(3)
if tStatement.%SelectMode = 0 {w "Select mode LOGICAL",! }
elseif tStatement.%SelectMode=1 {w "Select mode ODBC",! }
elseif tStatement.%SelectMode=2 {w "Select mode DISPLAY",! }
s myquery = 2
s myquery(1) = "SELECT TOP 5 DOB,%EXTERNAL(DOB) AS ExtDOB "
s myquery(2) = "FROM Sample.Person"
s qStatus = tStatement.%Prepare(.myquery)
s rset = tStatement.%Execute()
d rset.%Display()
w !,"End of data"
}
DHC-APP>d ##class(PHA.TEST.SQLCommand).External() Select mode DISPLAY DOB ExtDOB 04/25/1990 04/25/1990 01/02/2014 01/02/2014 01/02/2014 01/02/2014 01/28/1978 01/28/1978 5 Rows(s) Affected End of data DHC-APP>d ##class(PHA.TEST.SQLCommand).External() Select mode LOGICAL DOB ExtDOB 54536 04/25/1990 63189 01/02/2014 63189 01/02/2014 50066 01/28/1978 5 Rows(s) Affected End of data DHC-APP>d ##class(PHA.TEST.SQLCommand).External() Select mode ODBC DOB ExtDOB 1990-04-25 04/25/1990 2014-01-02 01/02/2014 2014-01-02 01/02/2014 1978-01-28 01/28/1978 5 Rows(s) Affected End of data
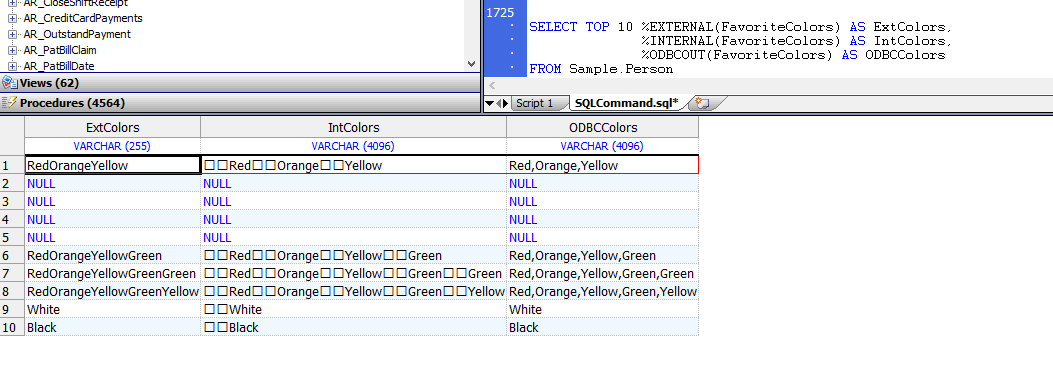
The following example shows two grammatical forms of this function;
They are the same in other respects.
They specify% external (display format),% internal (logical format), and% ODBC out (ODBC format) for the% List field:
SELECT TOP 10 %EXTERNAL(FavoriteColors) AS ExtColors,
%INTERNAL(FavoriteColors) AS IntColors,
%ODBCOUT(FavoriteColors) AS ODBCColors
FROM Sample.Person
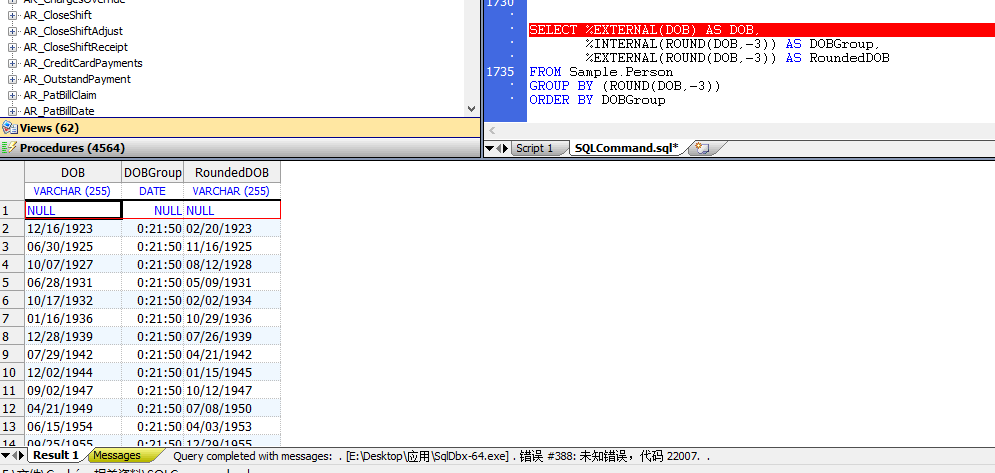
The following example converts date of birth (DOB) and rounded date of birth (DOB) values to% EXTERNAL(DISPLAY format):
SELECT %EXTERNAL(DOB) AS DOB,
%INTERNAL(ROUND(DOB,-3)) AS DOBGroup,
%EXTERNAL(ROUND(DOB,-3)) AS RoundedDOB
FROM Sample.Person
GROUP BY (ROUND(DOB,-3))
ORDER BY DOBGroup