The sixth chapter
- Example 6.1 assign 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 to ten array elements in turn, and output them in reverse order
- Example 6.2 solving Fibonacci sequence problem with array
- Example 6.3 there are ten areas, which are required to be arranged in the order of small to large
- Example 6.4 interchange the elements of a two-dimensional array row and column and store them in another two-dimensional array
- Example 6.5 has a 3 x 4 matrix, which requires the program to find out the value of the element with the largest value, as well as the row number and column number
Example 6.1 assign 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 to ten array elements in turn, and output them in reverse order
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,a[10]; for(i=0;i<=9;i++) a[i]=i; for(i=9;i>=0;i--) printf("%d ",a[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: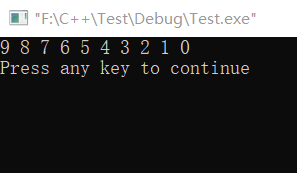
Example 6.2 solving Fibonacci sequence problem with array
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i; int f[20]={1,1}; for(i=2;i<20;i++) f[i]=f[i-2]+f[i-1]; for(i=0;i<20;i++) { if(i%5==0) printf("\n"); printf("%12d",f[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: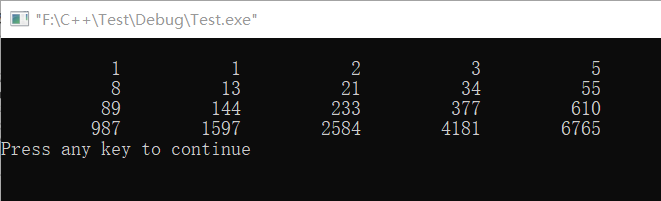
Example 6.3 there are ten areas, which are required to be arranged in the order of small to large
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a[10]; int i,j,t; printf("input 10 numbers:\n"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); printf("\n"); for(j=0;j<9;j++) for(i=0;i<9-j;i++) if(a[i]>a[i+1]) {t=a[i];a[i]=a[i+1];a[i+1]=t;} printf("the sorted numbers:\n"); for(i=0;i<10;i++) printf("%d ", a[i]); printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: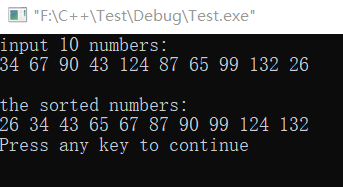
Example 6.4 interchange the elements of a two-dimensional array row and column and store them in another two-dimensional array
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}; int b[3][2],i,j; printf("array a:\n"); for(i=0;i<=1;i++) { for(j=0;j<=2;j++) { printf("%5d",a[i][j]); b[j][i]=a[i][j]; } printf("\n"); } printf("array b:\n"); for(i=0;i<=2;i++) { for(j=0;j<=1;j++) { printf("%5d",b[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } printf("\n"); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: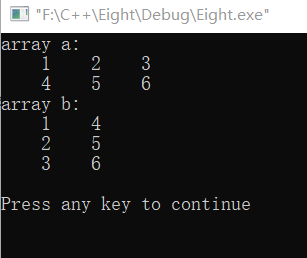
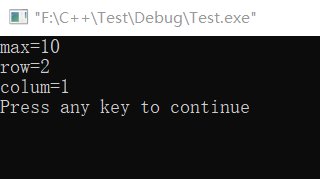
Example 6.5 has a 3 x 4 matrix, which requires the program to find out the value of the element with the largest value, as well as the row number and column number
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,row=0,colum=0,max; int a[4][5]={{1,2,3,4},{9,8,7,6},{-10,10,-5,2}}; max=a[0][0]; for(i=0;i<=2;i++) for(j=0;j<=3;j++) if(a[i][j]>max) { max=a[i][j]; row=i; colum=j; } printf("max=%d\nrow=%d\ncolum=%d\n",max,row,colum); return 0; }
The operation results are as follows: