The control statements used to implement branch structure in c language mainly include if statement and switch statement.
Relational operator
| operator | meaning |
| > | greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| < | less than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| == | be equal to |
| != | Not equal to |
Relational expression:
The formula linking two expressions with relational operators is called relational expression. The general form of relational expression is:
Expression 1 relational operator expression
Function: compare the size of two expressions and return a logical value.
"=" is an assignment operator and "= =" is a relational operator
Since there is no data of logical type in c language, "1" represents "true" and "0" represents "false"
Logical operator
| operator | ! | && | || |
| name | Logical non | Logic and | Logical or |
| Associativity | Right combination | Left combination | Left combination |
| priority | high | > | low |
Logical operator
| x | y | !x | x&&y | x||y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | Not 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Not 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Not 0 | Not 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
The order of precedence of various operators from high to low
| operator | ! | Arithmetic operator | Relational operator | &&And|| | Assignment Operators |
| Associativity | Right combination | Left combination | Left combination | Left combination | Right combination |
| priority | high | > | > | > | low |
Conditional operators and conditional expressions
Conditional operator: composed of "?" and ":" symbols, it is used for conditional evaluation. It is a ternary operator and requires three operands.
Conditional expression: the formula connecting three expressions is called conditional expression, and its general form is:
Expression 1? Expression 2: expression 3
If else statement
1. Double branch if statement Its general form is:
if (expression)
Statement 1;
else
Statement 2;
2. Single branch if statement Its general form is:
if (expression)
sentence;
3. Multi branch if statement
if (expression 1)
Statement 1;
else if (expression 2)
Statement 2;
...
else if (expression n-1)
Statement n-1;
else
Statement n;
General form of switch statement:
switch (expression)
{ case constant expression 1: statement 1; break;
case constant expression 2: Statement 2; break;
....
case constant expression n: statement n; break;
default: statement n+1; break;
}
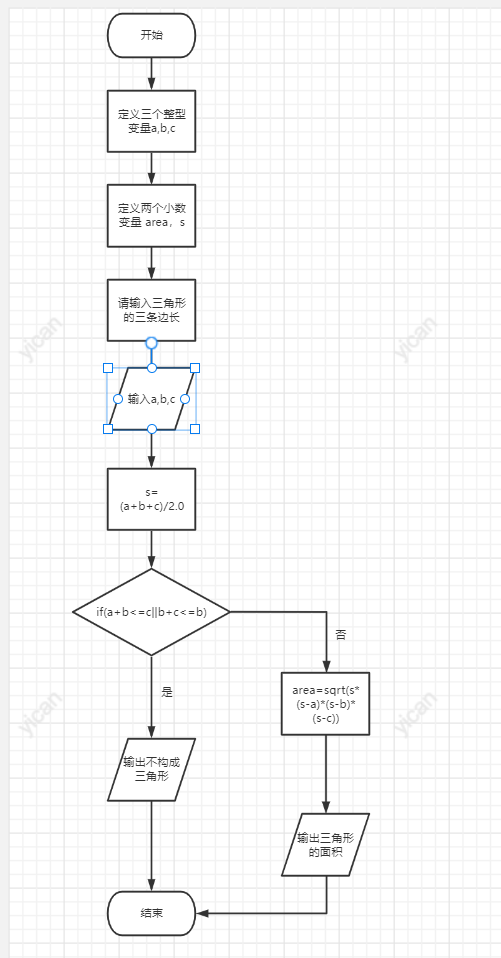
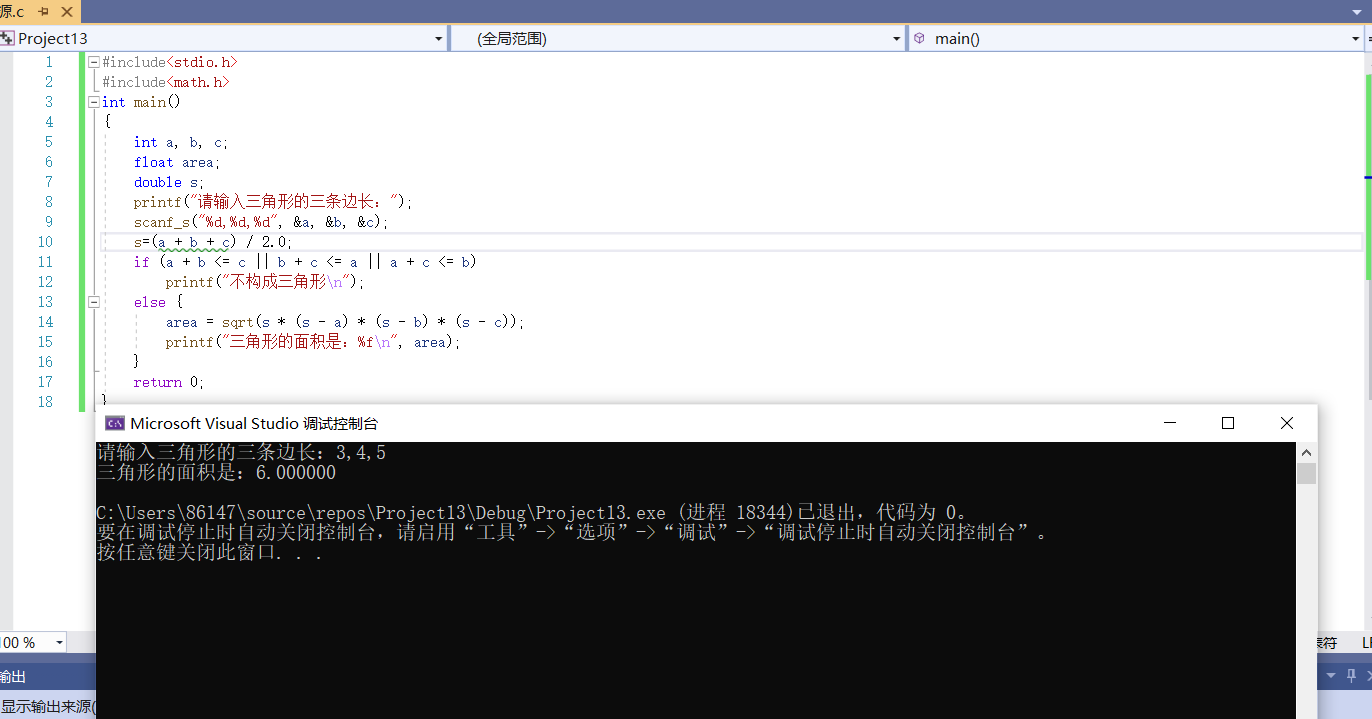
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int a, b, c;
float area;
double s;
printf("Please enter the three sides of the triangle:");
scanf_s("%d,%d,%d", &a, &b, &c);
s=(a + b + c) / 2.0;
if (a + b <= c || b + c <= a || a + c <= b)
printf("Does not form a triangle\n");
else {
area = sqrt(s * (s - a) * (s - b) * (s - c));
printf("The area of the triangle is:%f\n", area);
}
return 0;
}
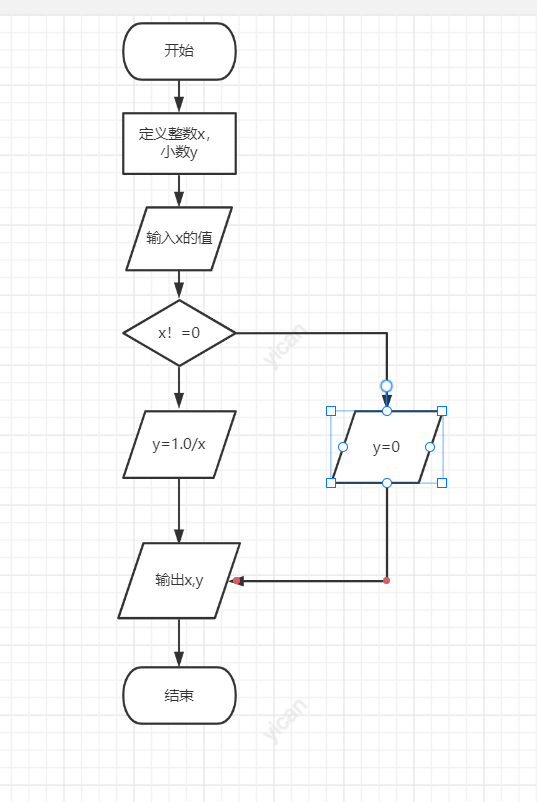
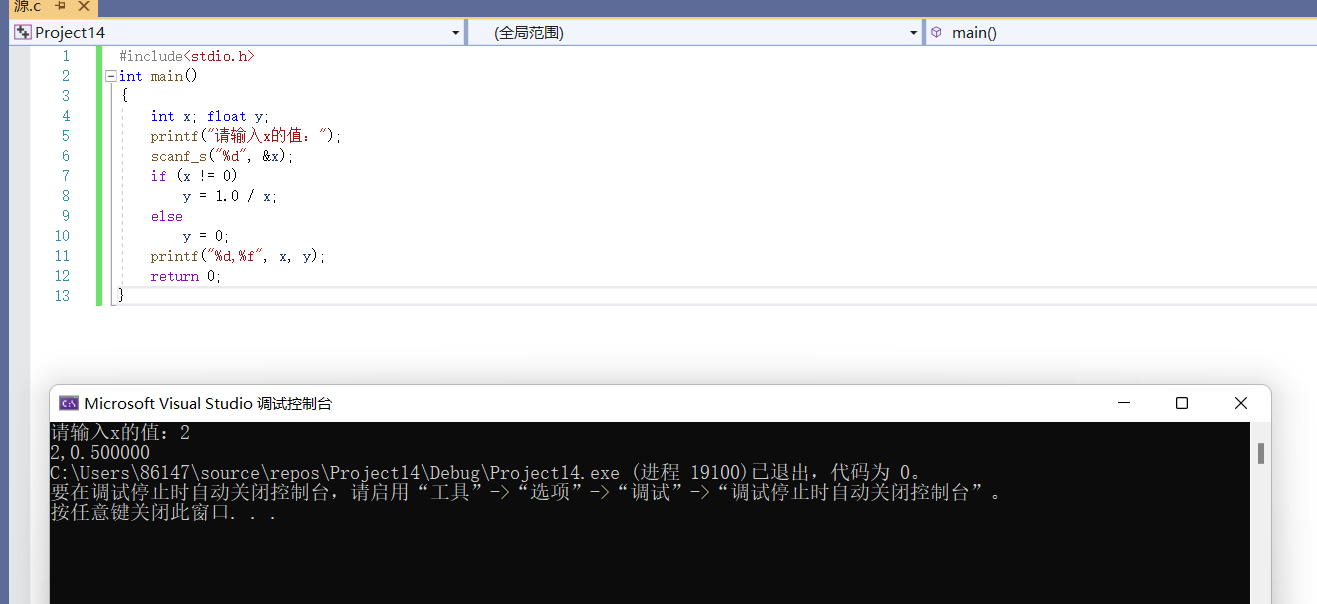
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x; float y;
printf("Please enter x Value of:");
scanf_s("%d", &x);
if (x != 0)
y = 1.0 / x;
else
y = 0;
printf("%d,%f", x, y);
return 0;
}
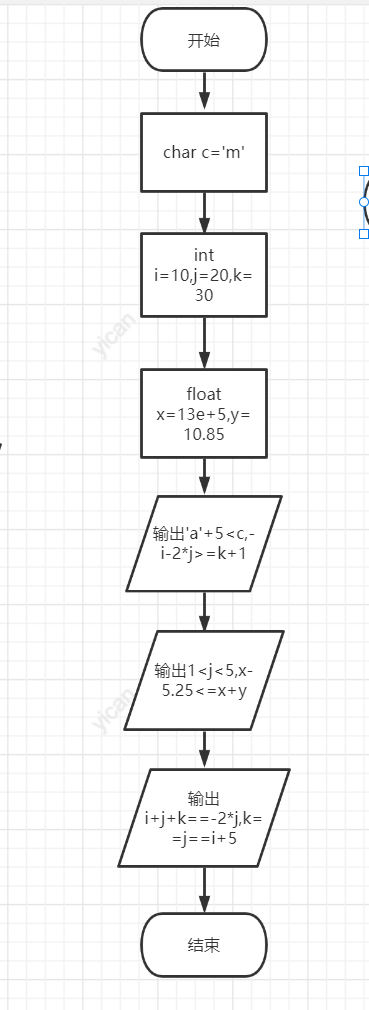
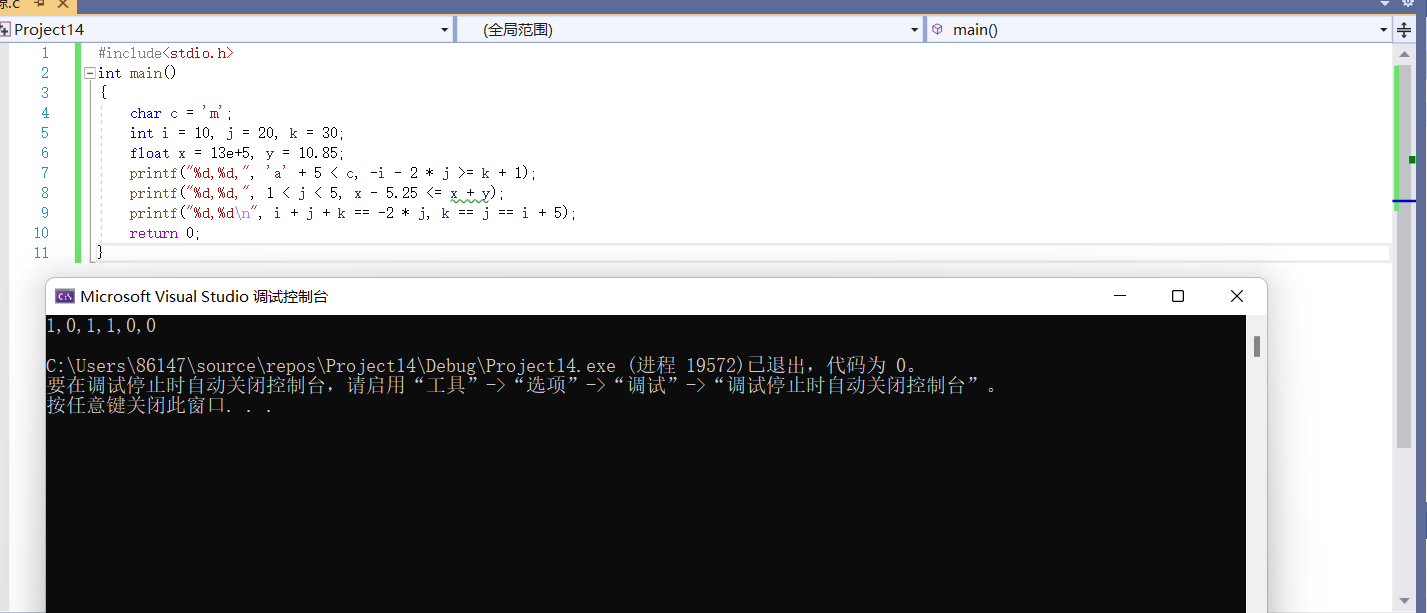
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char c = 'm';
int i = 10, j = 20, k = 30;
float x = 13e+5, y = 10.85;
printf("%d,%d,", 'a' + 5 < c, -i - 2 * j >= k + 1);
printf("%d,%d,", 1 < j < 5, x - 5.25 <= x + y);
printf("%d,%d\n", i + j + k == -2 * j, k == j == i + 5);
return 0;
}
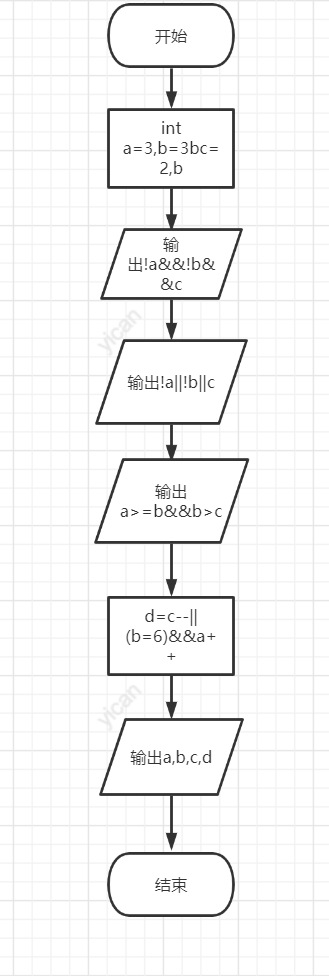
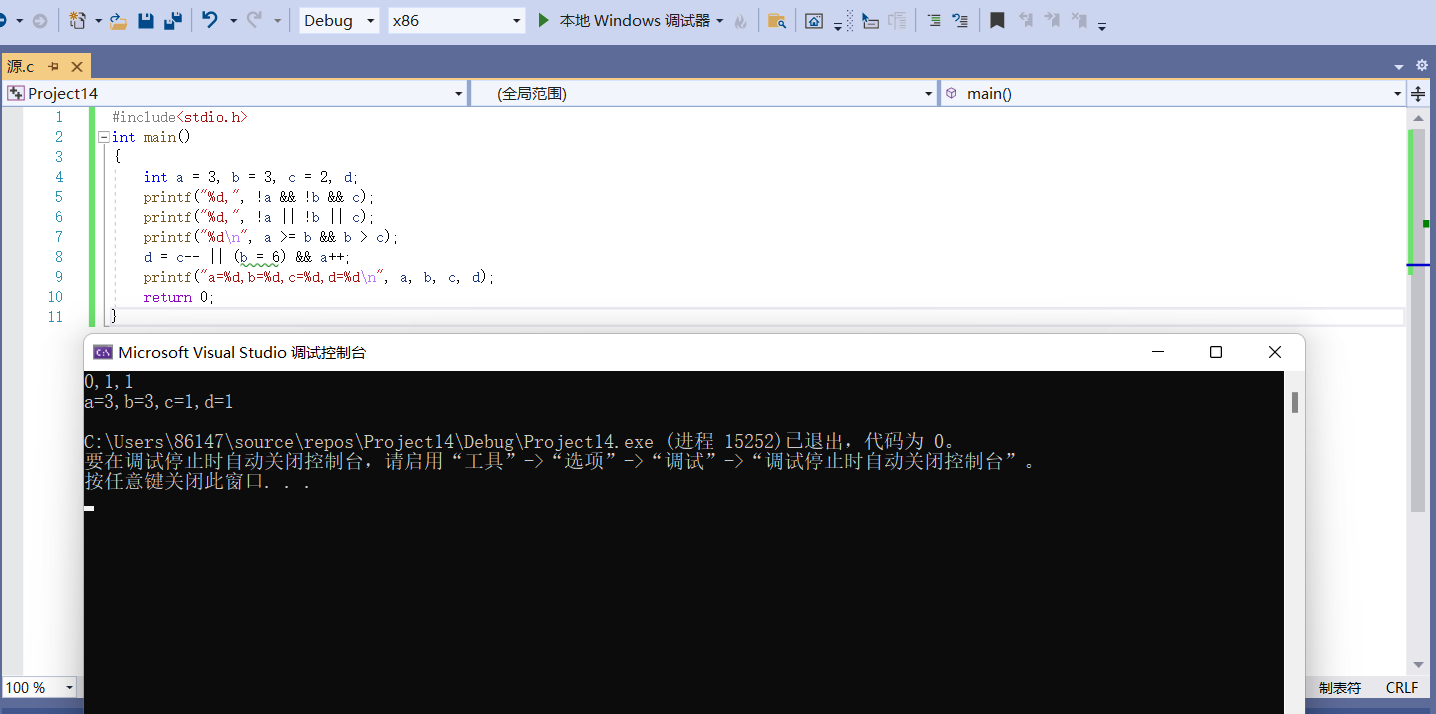
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 3, b = 3, c = 2, d;
printf("%d,", !a && !b && c);
printf("%d,", !a || !b || c);
printf("%d\n", a >= b && b > c);
d = c-- || (b = 6) && a++;
printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d,d=%d\n", a, b, c, d);
return 0;
}
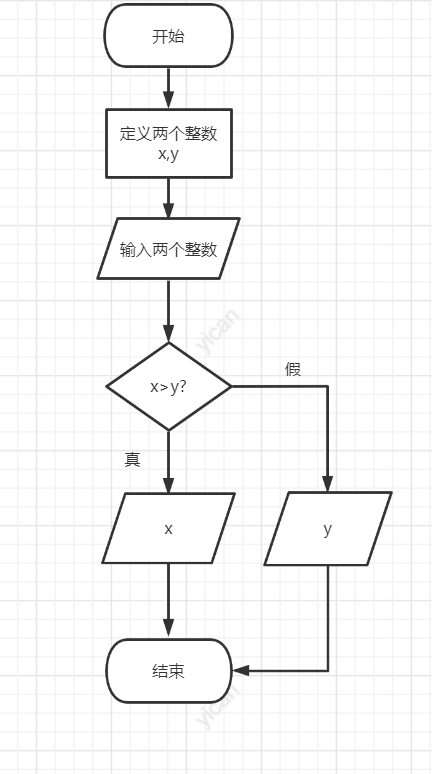
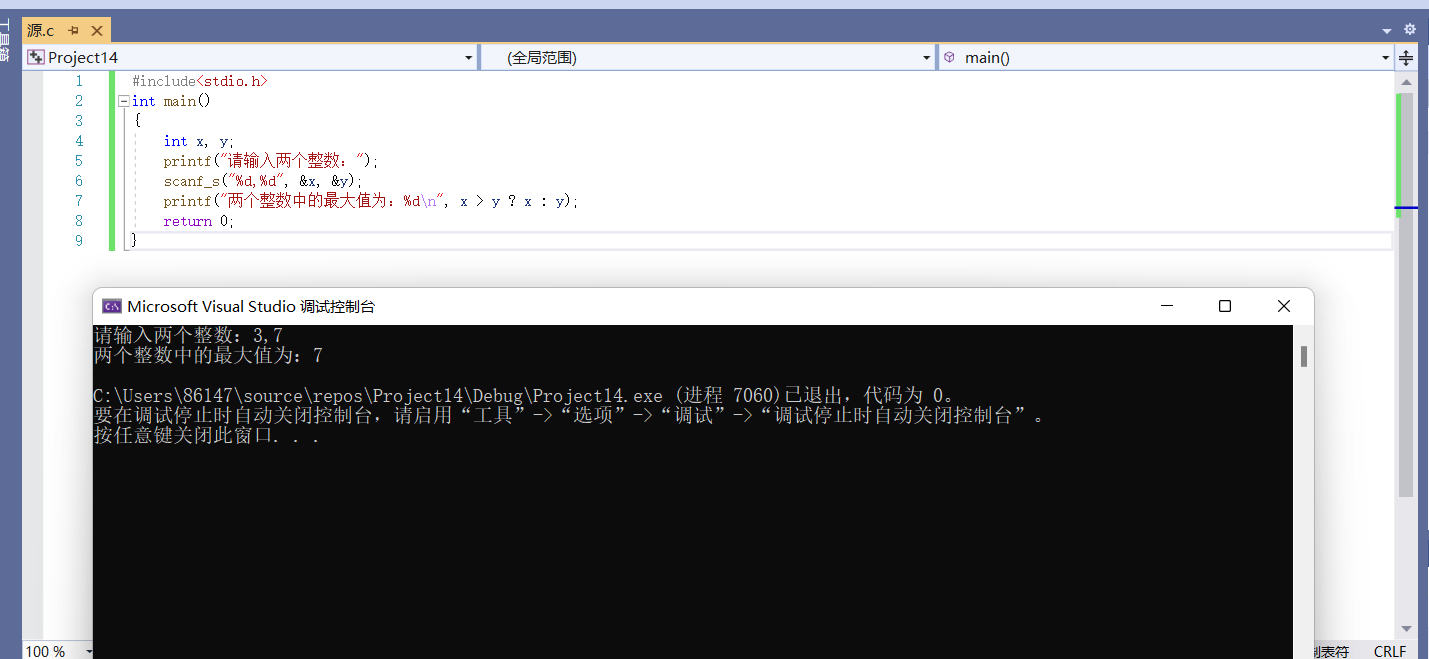
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x, y;
printf("Please enter two integers:");
scanf_s("%d,%d", &x, &y);
printf("The maximum of the two integers is:%d\n", x > y ? x : y);
return 0;
}
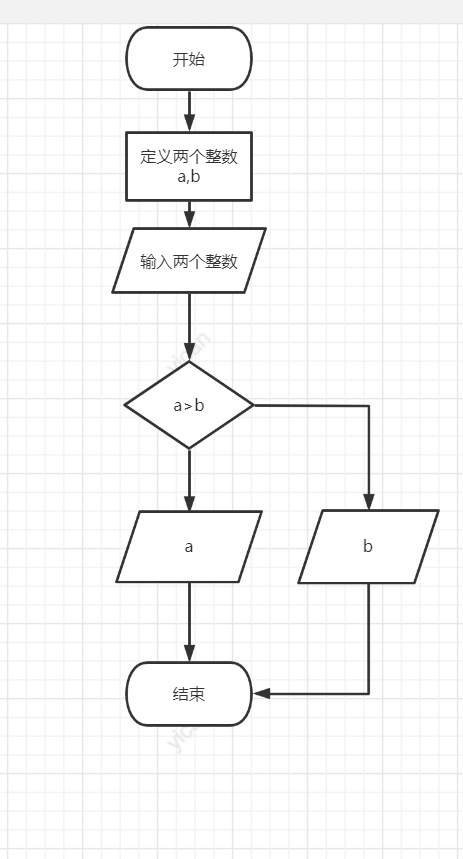
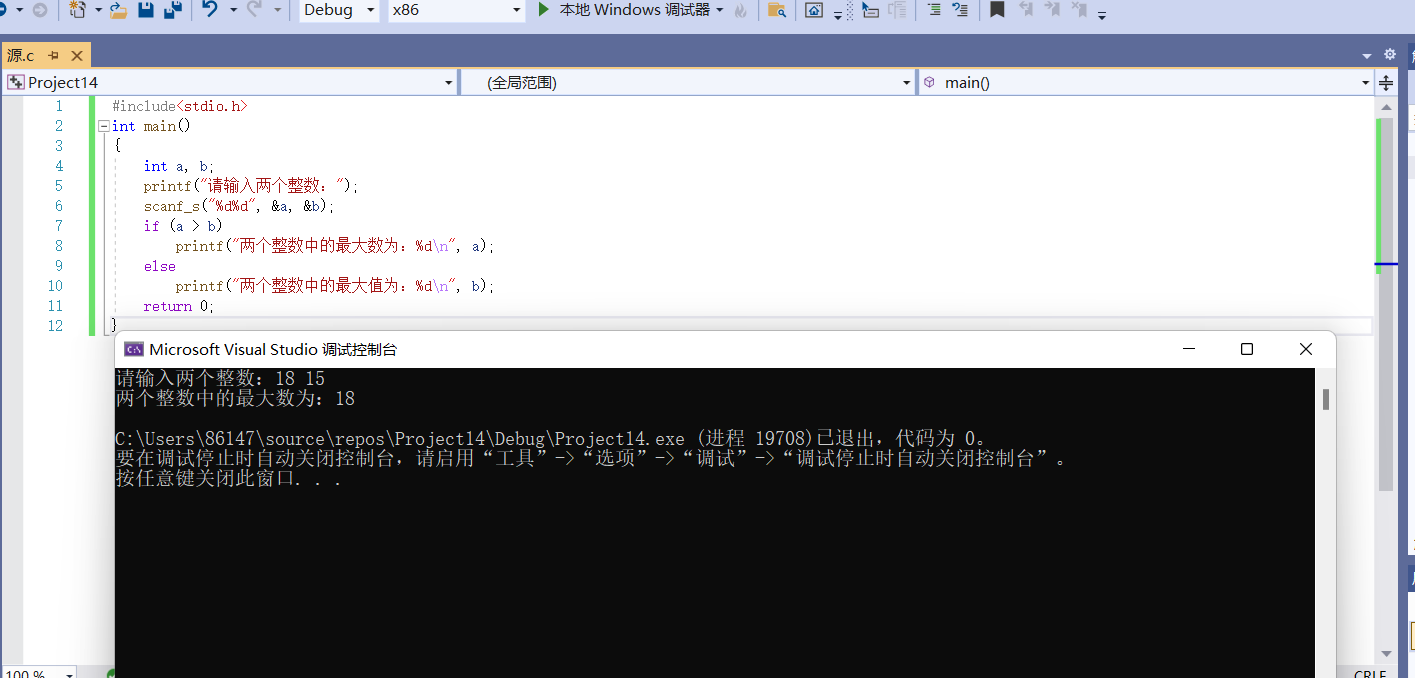
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a, b;
printf("Please enter two integers:");
scanf_s("%d%d", &a, &b);
if (a > b)
printf("The maximum number of two integers is:%d\n", a);
else
printf("The maximum of the two integers is:%d\n", b);
return 0;
}
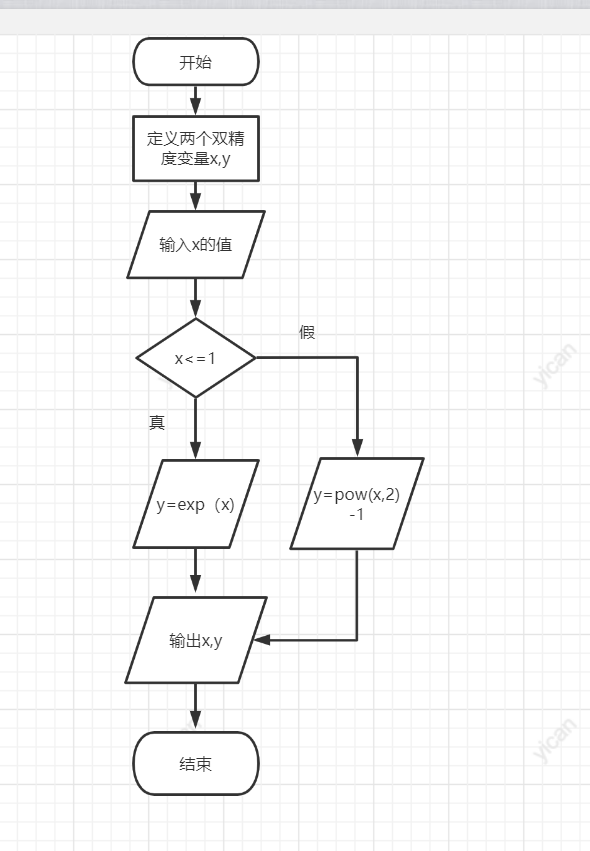
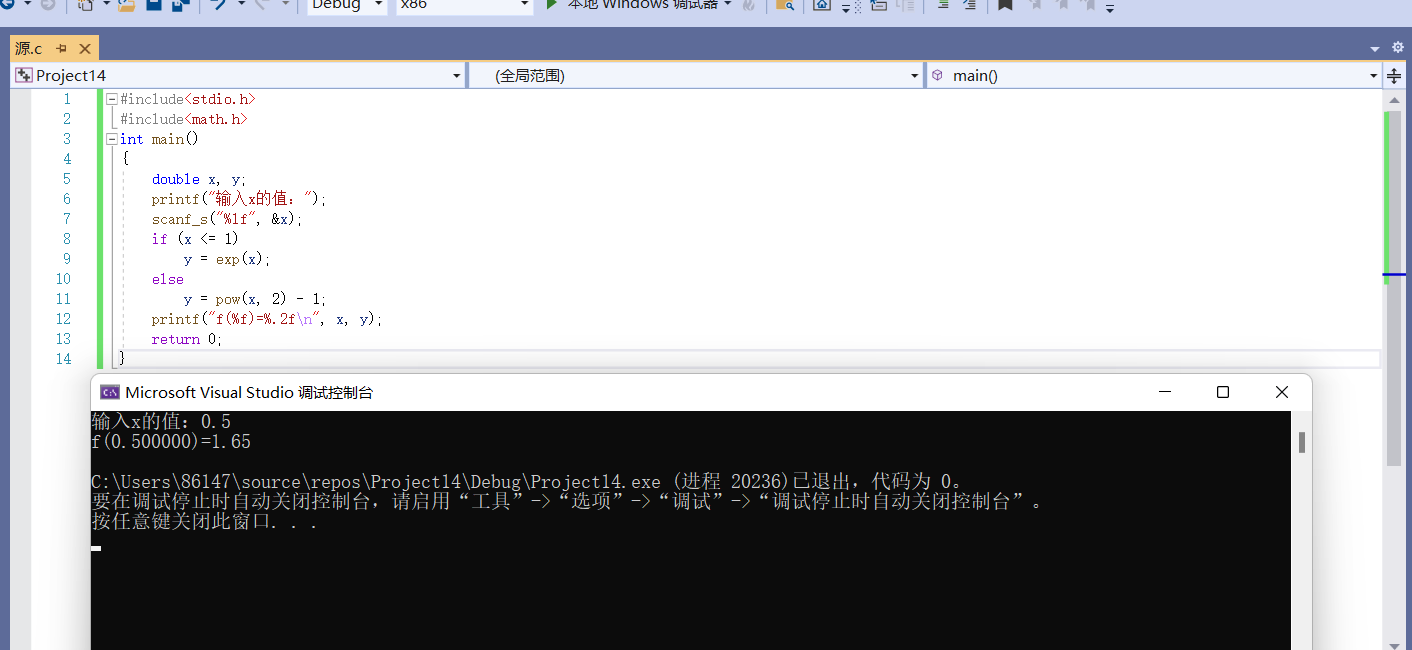
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x, y;
printf("input x Value of:");
scanf_s("%lf", &x);
if (x <= 1)
y = exp(x);
else
y = pow(x, 2) - 1;
printf("f(%f)=%.2f\n", x, y);
return 0;
}
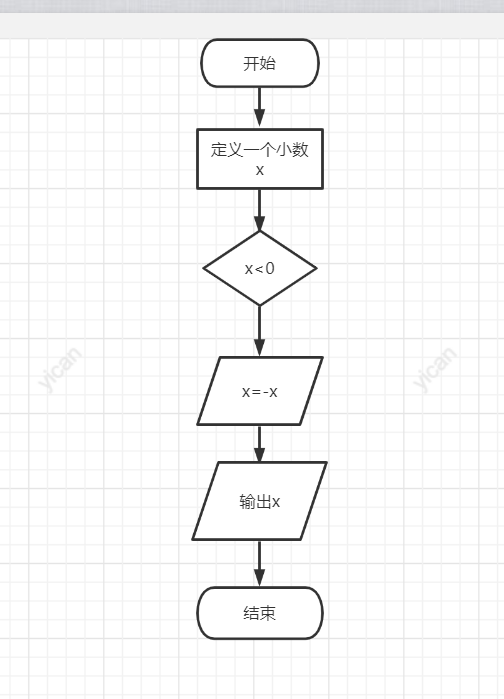
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
float x;
scanf_s("%f", &x);
if (x < 0)
x = -x;
printf("%f", x);
return 0;
}
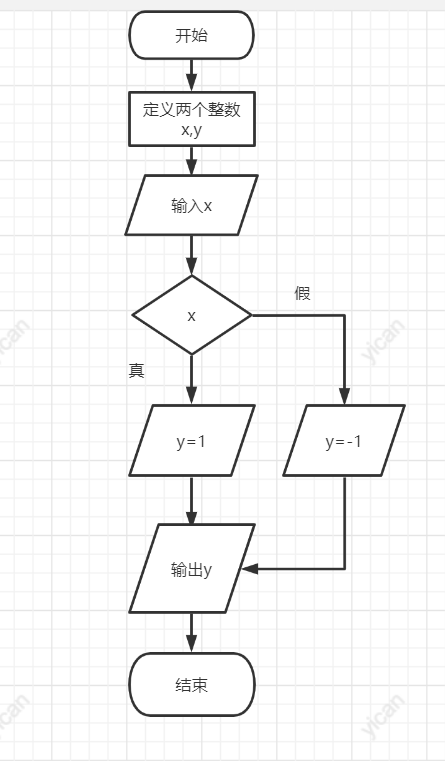
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x, y;
printf("x=");
scanf_s("%d", &x);
if (x)
y = 1;
else
y = -1;
printf("y=%d", y);
return 0;
}
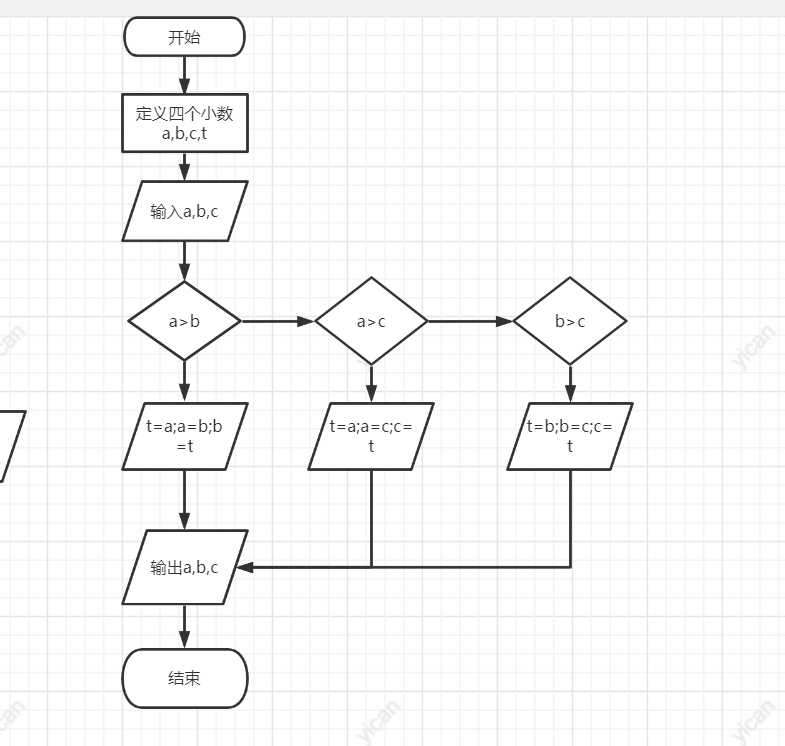
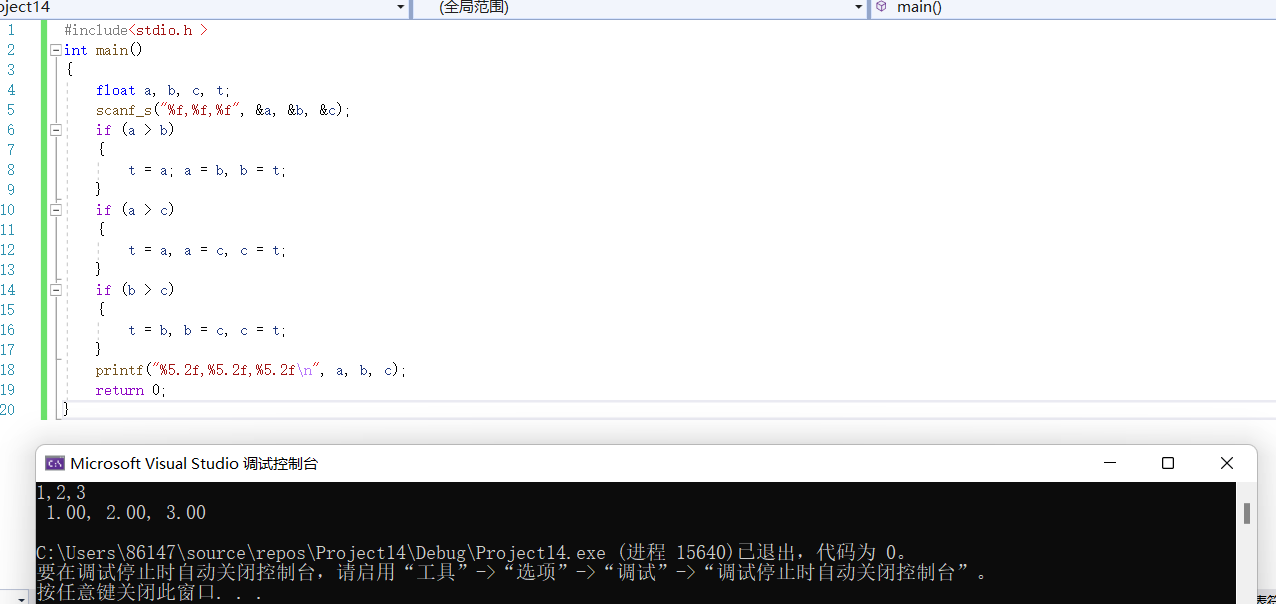
#include<stdio.h >
int main()
{
float a, b, c, t;
scanf_s("%f,%f,%f", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
{
t = a; a = b, b = t;
}
if(a>c)
{
t = a, a = c, c = t;
}
if(b>c)
{
t = b, b = c, c = t;
}
printf("%5.2f,%5.2f,%5.2f\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
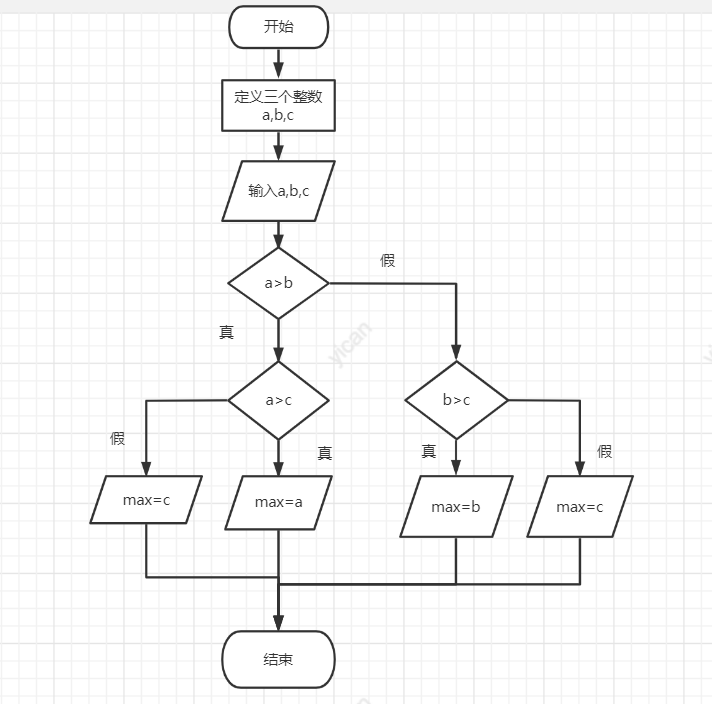
#include<stdio.h >
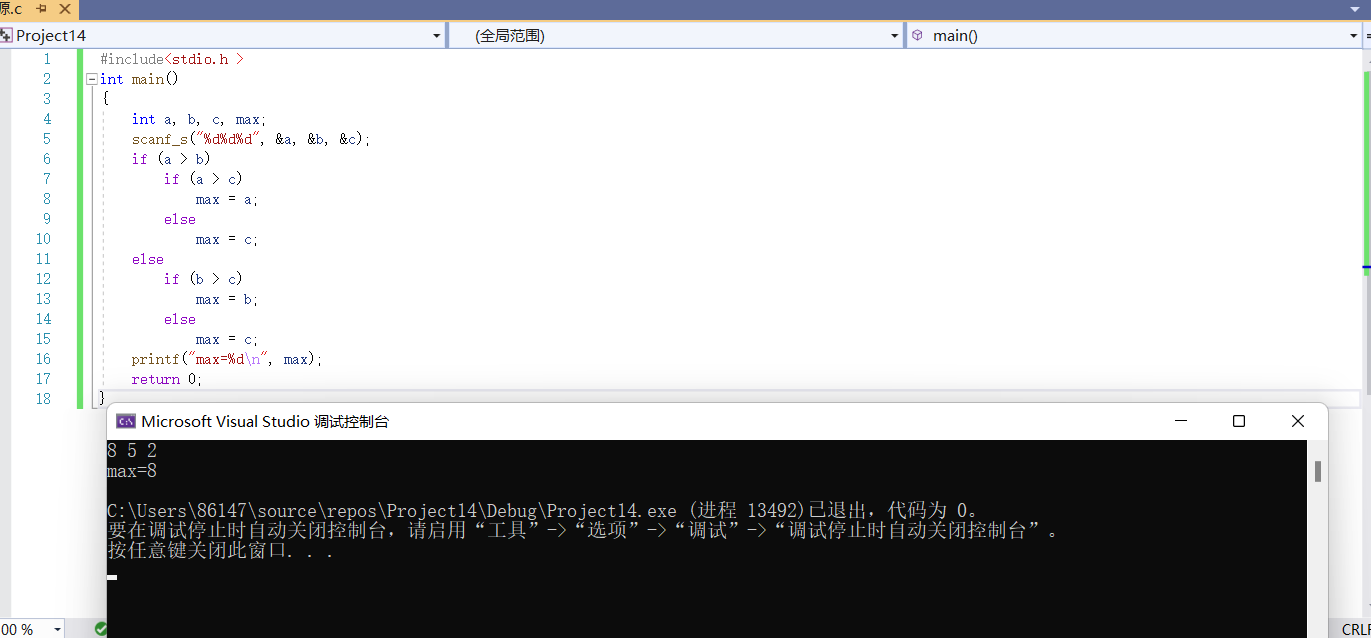
int main()
{
int a, b, c, max;
scanf_s("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
if (a > b)
if (a > c)
max = a;
else
max = c;
else
if (b > c)
max = b;
else
max = c;
printf("max=%d\n", max);
return 0;
}