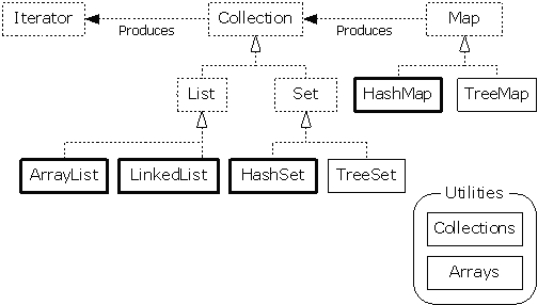
Collection framework
- A collection of interfaces and classes
- In Java Util package
Set framework system
Collection interface:
- Stores a non unique, unordered set of objects
List interface:
- Store objects with = = not unique (value repeatable), ordered (insertion order) = =
Set interface:
- Store a set of unique (values cannot be repeated) and unordered objects
Map interface:
- Store a set of = key value = object, and provide the image from key to value (key: key value: value)
Collection
| Method name | explain |
|---|---|
| clear() | Empty all elements in the collection |
| isEmpty() | Judge whether a set is empty |
| Iterator() | Gets the iterator that traverses a collection |
| toArray() | Transform a set into a sequence |
List
Implementation class:
- ArrayList:
- Variable length array, continuous
- Efficient traversal and random access to elements
- LinkedList:
- Linked list storage mode
- The efficiency of inserting and deleting elements is high
ArrayList
//Creator of news headlines
public class NewTitle {
private int id;
private String title;
private String author;
public NewTitle() {
}
public NewTitle(int id, String title, String author) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
//Storage and operation of news headlines (ArrayList)
public class NewsMgr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create News Title Object
NewTitle title1 = new NewTitle(1,"The Forbidden City, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title2 = new NewTitle(2,"The Great Wall, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title3 = new NewTitle(3,"Beihai, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title4 = new NewTitle(4,"Summer Palace, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title5 = new NewTitle(5,"Tiananmen Square, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
//Create a collection object and add news headlines to the collection
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(title1);//Equivalent to list[0] = title1 in the array;
list.add(title2);
list.add(title3);
list.add(title4);
list.add(title5);
//Get the total number of news headlines
//The size() method of ArrayList is equivalent to the length attribute of array
System.out.println("There are news headlines"+list.size()+"strip");
//Print the name of news headlines one by one
//Method 1: traverse the position of ArrayList element (subscript)
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//list.get(i);// Equivalent to list[i], but the return value is Object
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)list.get(i);//Data type conversion
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
//Method 2: enhanced for
for (Object obj:
list) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)obj;
System.out.println(title.getTitle());
}
}
}
| Method name | explain |
|---|---|
| boolean add(Object o) | Add elements sequentially at the end of the list, starting at 0 |
| void add(int index,Object o) | Adds an element at the specified index position, which must be between 0 and the number of elements in the list= |
| int size() | Returns the number of elements in the list |
| Object get(int index) | Returns the element at the specified index position. The extracted element is of Object type, and forced type conversion is required before use |
| boolean contains(Object o) | Determine whether the specified element exists in the list |
| boolean remove(Object o) | Remove element from list |
| Object remove(int index) | Removes the specified location element from the list, starting at 0 |
LinkedList
| Method name | explain |
|---|---|
| void addFirst(Object o) | Add an element at the beginning of the list |
| void addLast(Object o) | Add an element at the end of the list |
| Object getFirst() | Returns the first element in the list |
| Object getLast() | Returns the last element in the list |
| Object removeFirst() | Deletes and returns the first element in the list |
| Object removeLast() | Deletes and returns the last element in the list |
import java.util.LinkedList;
//Storage and operation of news headlines (ArrayList)
public class NewsMgr2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create News Title Object
NewTitle title1 = new NewTitle(1,"The Forbidden City, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title2 = new NewTitle(2,"The Great Wall, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title3 = new NewTitle(3,"Beihai, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title4 = new NewTitle(4,"Summer Palace, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title5 = new NewTitle(5,"Tiananmen Square, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
//Create a collection object and add news headlines to the collection
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add(title1);//Equivalent to list[0] = title1 in the array;
list.add(title2);
list.add(title3);
list.add(title4);
//Inserts a specific element at a specified location
list.add(1,title5);
//Insert headline
NewTitle title6 = new NewTitle(6,"National Museum of popular scenic spots in Beijing","Li Hua");
list.addFirst(title6);//Add at the top of the list
//Get the total number of news headlines
//The size() method of ArrayList is equivalent to the length attribute of array
System.out.println("There are news headlines"+list.size()+"strip");
//Print the name of news headlines one by one
//Method 1: traverse the position of ArrayList element (subscript)
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//list.get(i);// Equivalent to list[i], but the return value is Object
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)list.get(i);//The return value is Object, which needs to be cast
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
//Method 2: enhanced for
for (Object obj: list) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)obj;
System.out.println(title.getTitle());
}
//Get headlines / last news
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
NewTitle titleFirst = (NewTitle)list.getFirst();
System.out.println("Headline information:"+titleFirst.getTitle());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
NewTitle titleLast = (NewTitle)list.getLast();
System.out.println("Last news information:"+titleLast.getTitle());
//Delete headlines
list.removeFirst();
System.out.println("Number of deleted entries:"+list.size());
for (Object obj:
list) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)obj;
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
}
}
You can use the parent class to reference the methods of the child class (list = new LinkedList), but you can only call the methods shared by the parent and child classes, and the methods unique to the child class cannot be called
Set
Implementation class: HashSet
Because the Set interface is unique and unordered, it cannot be output through get.
- Reference of object stored in Set
import java.util.*;
//The reference of the object is stored in the Set
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
String s1 = new String("java");
String s2 = s1;
String s3 = new String("JAVA");
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
System.out.println(set.size());//2
}
}
- The Set interface uses the equals() method of the object to compare whether two objects are equal
import java.util.*;
//Set if the corresponding values are the same
public class SetDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
String s1 = new String("java");
String s2 = s1;
String s3 = new String("java");
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
System.out.println(set.size());//1
}
}
Traverse Set set method:
-
(1) Enhanced for loop
-
(2) Iterator Iterator
- Get the Iterator: Collection interface and iterator() method
- Iterator method
- boolean hasNext(): judge whether there is another accessible element
- Object next(): returns the next element to access
import java.util.*; //Storage and operation of news headlines (ArrayList) public class NewsMgr3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create News Title Object NewTitle title1 = new NewTitle(1,"The Forbidden City, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author"); NewTitle title2 = new NewTitle(2,"The Great Wall, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author"); //Create a collection object and add news headlines to the collection Set set = new HashSet(); //Set--Collection(add(Object)) set.add(title1); set.add(title2); //Get the total number of news headlines System.out.println("There are news headlines"+set.size()+"strip"); //Print the title of the news item by item System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------"); //Method 1: enhance for for (Object obj : set) { NewTitle title = (NewTitle)obj; System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());//Disorder } System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------"); //Method 2: Iterator //(1) Get iterator object Iterator itor = set.iterator(); //(2) Determine whether the next element exists while(itor.hasNext()){ //(3) Returns the next element to access NewTitle title = (NewTitle)itor.next(); System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor()); } } }
Map
Implementation class: HashMap
(key,value): key is unique and unordered; Value is repeatable
There is no inheritance relationship between map and Collection. Map is not a sub interface of Collection.
Operations on data:
- put(key,value)
- get(key)
- size():
| Method name | explain |
|---|---|
| Object put(Object key, Object val) | Stored as a key value pair |
| Object get(Object key) | Returns the associated value according to the key, or null if the specified key does not exist |
| Object remove(Object key) | Delete = key value pair mapped by the specified key== |
| int size() | Returns the number of elements |
| Set keySet() | Returns a collection of keys |
| Collection values() | Returns a collection of values |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | Returns true if there is a key value pair mapped by the specified key |
Traverse Map:
- Traverse key through key = > value
- Traversal through Iterator
- Enhanced for loop
- Traverse key value pairs (the data type is Map.Entry)
import java.util.*;
public class CountriesInfo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create a collection object and put the country information key value pair into the collection
Map countries = new HashMap();
countries.put("China","China");
countries.put("USA","U.S.A");
countries.put("Japan","Japan");
countries.put("France","France");
//Gets the number of storage elements in the collection
System.out.println(countries.size());
//Get the specific key and value in the collection. The return value type of object needs forced data type conversion
String country = (String)countries.get("China");
System.out.println(country);
//If not found, null is returned
String country2 = (String)countries.get("Australia");
System.out.println(country2);
//Determine whether a country exists in the set
System.out.println("Does it exist china"+countries.containsKey("China"));
//Delete the country corresponding to a specific key
System.out.println("Does it exist USA: "+countries.containsKey("USA"));
countries.remove("USA");
System.out.println("Does it exist USA: "+countries.containsKey("USA"));
System.out.println(countries.size());
//Get the set of keys, values, and key value pairs
System.out.println(countries.keySet());
System.out.println(countries.values());
System.out.println(countries);
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------");
//Idea 1 of traversing Map: traversing key(Set) through key = > value
Set keys = countries.keySet();//Get all key s in the Map
//Method 1: enhanced for traversing key (Set)
for (Object obj:
keys) {
String key = (String)obj;//Get every key in the Map
String value = (String)countries.get(key);//Get the corresponding value according to each key in the Map
System.out.println(key+"--"+value);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------");
//Method 2: Iterator iterator traverses key (Set)
Iterator itor = keys.iterator();
while (itor.hasNext()){
String key = (String)itor.next();//Each key in the Map is obtained
String value = (String)countries.get(key);//Get the corresponding value according to each key in the Map
System.out.println(key+"--"+value);
}
//Traverse Map idea 2: get all key value pairs in the Map, and then get key and value in the key value pairs respectively
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------------------");
Set set = countries.entrySet();//Get key value pairs in Map
//Traverse the set of key value pairs and put each key value pair (obj) --- map Entry (type of key value pair)
for (Object obj:set) {
Map.Entry me = (Map.Entry)obj;
String key = (String)me.getKey();//Get the value from the key pair
String value = (String)me.getValue();//Get the value in the key value pair
System.out.println(key+"--"+value);
}
}
}
example:
//Student type: name and gender
public class Student {
private String name;
private String sex;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
import java.util.*;
//Student information management (student English name) to obtain the corresponding student details
public class StudentInfoMgr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu1 = new Student("Zhang San","male");
Student stu2 = new Student("Li Hua","male");
Student stu3 = new Student("Xiao Hua Wang","female");
Map stuMap = new HashMap();
stuMap.put("Buck",stu1);
stuMap.put("Jack",stu2);
stuMap.put("Jession",stu3);
//A total of several students have entered foreign enterprises
System.out.println("Altogether"+stuMap.size()+"Students entered foreign enterprises");
System.out.println("------------------------ta We are----------------------");
Set set = stuMap.entrySet();
for (Object obj : set) {
Map.Entry me = (Map.Entry)obj;
String key = (String)me.getKey();
Student student = (Student)me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"-"+student.getName()+"-"+student.getSex());
}
//Achieve the student information under the characteristic English name
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//String name = "Jack";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the English name of the student you want to find:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
if (stuMap.containsKey(name)){
//If the corresponding key is found in the Map, the corresponding value is obtained according to the key
Student student = (Student)stuMap.get(name);
System.out.println("The student information is as follows:");
System.out.println(name+"-"+student.getName()+"-"+student.getSex());
}else {
System.out.println("Sorry, there is no such student");
}
}
}
Collections algorithm class:
The Collections class defines a series of static methods for manipulating Collections
-
Common static methods:
- sort(): sort (ascending)
- binarySearch(): find
- max()\min(): find the maximum and minimum values
- reverse(): inverts the array of elements
-
import java.util.*; //Common methods of Collections public class CollectionsUseDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("ant"); list.add("bear"); list.add("pen"); list.add("zoo"); list.add("apple"); list.add("candy"); list.add("zookeeper"); System.out.println("-------------------------"); for (String s: list) { System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("-------------------------"); //Use Collections to sort Collections in ascending order Collections.sort(list); for (String s: list) { System.out.println(s); } System.out.println("-------------------------"); //Find the maximum and minimum values in the set System.out.println("The largest elements in the collection are:"+Collections.max(list)); System.out.println("The smallest elements in the set are:"+Collections.min(list)); //Find specific elements in the collection and sort them first System.out.println(Collections.binarySearch(list,"candy")); //Invert collection elements Collections.reverse(list); for (String s: list) { System.out.println(s); } } } -
Custom element sorting
- Implement Comparable interface
- Override compareTo() method
public class Student implements Comparable { private int no; private String name; private String sex; public Student() { } public Student(int no, String name, String sex) { this.no = no; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } //Rewrite method to define the comparison rules of student objects //Comparison rules: students with large student numbers shall be arranged backward //Comparison object: the current student object (this) and Object o public int compareTo(Object o) { Student student = (Student)o; if (this.no == student.no){ return 0;//Same student number }else if (this.no > student.no){ return 1;//The current student number is greater than the comparative student number }else { return -1;//The current student number is less than the comparative student number } } }import java.util.*; //Common methods of Collections public class CollectionsUseDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>(); Student stu1 = new Student(1,"Zhang San","male"); Student stu2 = new Student(7,"Li Si","male"); Student stu3 = new Student(3,"Xiao Hua Wang","female"); Student stu4 = new Student(9,"Wang Wu","male"); list.add(stu1); list.add(stu2); list.add(stu3); list.add(stu4); System.out.println("-------------------------"); for (Student stu : list) { System.out.println(stu.getNo()+"-"+stu.getName()+"-"+stu.getSex()); } System.out.println("-------------------------"); //Use Collections to sort Collections in ascending order Collections.sort(list); for (Student stu: list) { System.out.println(stu.getNo()+"-"+stu.getName()+"-"+stu.getSex()); } System.out.println("-------------------------"); } }
generic paradigm
<>
Specify the type of the object as a parameter to other classes or methods to ensure the safety and stability of type conversion
- Is essentially a parametric type
- When using generic definitions, you do not need to cast types
- A generic collection can constrain the element type of the collection, such as ArrayList student, which means that only E element type is allowed in the student collection.
import java.util.*;
public class NewsMgr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NewTitle title1 = new NewTitle(1,"The Forbidden City, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
NewTitle title2 = new NewTitle(2,"The Great Wall, a popular scenic spot in Beijing","author");
ArrayList<NewTitle> list = new ArrayList<NewTitle>();
list.add(title1);//Equivalent to list[0] = title1 in the array;
list.add(title2);
//Generics restrict the security of elements added by the collection framework. Elements of wrong types are not added at compile time
//list.add("aaa");
//Method 1: traverse the position of ArrayList element (subscript)
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//list.get(i);// Equivalent to list[i], but the return value is Object
//NewTitle title = (NewTitle)list.get(i);// Data type conversion
NewTitle title = list.get(i);//After adding a generic type, the return value is NewTitle
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
//Method 2: enhanced for
/*for (Object obj: list) {
NewTitle title = (NewTitle)obj;
System.out.println(title.getTitle());
}*/
for (NewTitle title: list) {
System.out.println(title.getTitle());
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------------");
//Method 3: Iterator
System.out.println("iterator ");
Iterator<NewTitle> itor = list.iterator();
while (itor.hasNext()){
NewTitle title = itor.next();
System.out.println(title.getTitle()+"-"+title.getAuthor());
}
- Generic nesting: < map Entry<key,value>>
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> set = countries.entrySet();//Get key value pairs in Map
//Traverse the set of key value pairs and put each key value pair (obj) --- map Entry (type of key value pair)
for (Map.Entry<String,String> me:set) {
String key = me.getKey();//Get the value from the key pair
String value = me.getValue();//Get the value in the key value pair
System.out.println(key+"--"+value);
}