preface
Record the recent automated test of configuration table. The idea is to combine Jenkins and local SVN to regularly see which configuration files are updated, and then execute the corresponding test cases according to the file name. This article mainly records the operation of SVN. Previously, I also wrote an article on Python operation of SVN, which is run by command line.
Tip: the following is the main content of this article. The following cases can be used for reference
environment
Win10+Python3.6
install
You need to download the command line tool first
Click here to download You can also go to its home page download
After downloading and decompressing, you can configure the variable environment
At the command line, enter:
set SVN_CMD_HOME=Decompression path\Apache-Subversion-1.14.0\bin set path=%path%;%SVN_CMD_HOME% svn help
Execute the SVN help command to output help information, and then configure it
text
1, Common SVN commands
detection
svn checkout [-depth ARG] [--ignore-externals] [-r rev] URL PATH
The depth option box is related to the - depth parameter
If you want to ignore external selection, use – ignore external selection.
If you are checking out a specific revision, use - r after the URL to specify.
to update
svn info URL_of_WC svn update [-r rev] PATH
Updating multiple projects is not an atomic operation in Subversion, so TortoiseSVN will first find the HEAD revision of the version library, and then update all projects to a specific revision to prevent working copies of mixed revisions.
If only one item is selected for update, or the selected item is from a different version library, TortoiseSVN will only be updated to HEAD.
Update to revision also implements the update command without using the command line option, but provides more options.
Update to version
svn info URL_of_WC svn update [-r rev] [-depth ARG] [--ignore-externals] PATH
The depth option box is related to the - depth parameter
If you want to ignore external selection, use – ignore external selection.
Submit
In TortoiseSVN, the submit dialog box uses the Subversion command. The first part is to check which files of the working copy may be submitted. Then you can check the list, compare with BASE, and select the projects you want to submit.
svn status -v PATH
If you select Show files that are not versioned, TortoiseSVN displays all files and folders that are not versioned in the working directory following the ignore rule. This feature has no equivalent operation in Subversion because the svn status command does not scan folders that are not versioned.
If you select files and folders that are not versioned, these items will be added to your working copy first.
svn add PATH...
When you click OK, the Subversion submission starts. If you do not modify all file check boxes, TortoiseSVN will recursively submit working copies. If you deselect some files, you must use non recursive commit (- N), and each path must be specified separately on the command line.
svn commit -m "LogMessage" [-depth ARG] [--no-unlock] PATH...
Log messages are the contents of the log edit box. It can be empty.
If hold lock is selected, use the – no unlock switch.
difference
svn diff PATH
If you use differences in the right-click menu, you will compare the modified file with the base version. The command output of the console is also to perform this operation and output the unified difference format. However, TortoiseSVN does not use this approach. TortoiseSVN uses TortoiseMerge (or the comparison difference program you choose) to visualize the full-text display of differences, so it does not have the same console operation.
You can use TortoiseSVN to compare the differences between any two files, whether they are version controlled or not. TortoiseSVN just passes the two files to the selected difference comparison program to compare the differences.
Show log
svn log -v -r 0:N --limit 100 [--stop-on-copy] PATH or svn log -v -r M:N [--stop-on-copy] PATH
By default, TortoiseSVN attempts to get 100 log messages using the – limit method. If you set it to use the old excuse, the second is to get 100 log messages.
If stop at copy / Rename is selected, use the – stop on copy switch.
Check modification
svn status -v PATH or svn status -u -v PATH
Perform the initial status check only on your working copy. If you click Check version library, you can also check the version library to see which files will be modified by the update operation. It needs the - u switch.
If you select Show files that are not versioned, TortoiseSVN displays all files and folders that are not versioned in the working directory following the ignore rule. This feature has no equivalent operation in Subversion because the svn status command does not scan folders that are not versioned.
resolved
svn resolved PATH
Rename
svn rename CURR_PATH NEW_PATH
delete
svn delete PATH
recovery
svn status -v PATH
Start with a status check to see what items in your working copy can be revoked. You can review the list of files, check the modifications of these files, and then select the items you want to undo.
When you click OK, Subversion undo begins. If you don't modify all the file check boxes, TortoiseSVN will recursively undo the modification of (- R) working copy. If you deselect some files, you must use non recursive undo, and each path must be specified separately on the command line. "
svn revert [-R] PATH...
clear
svn cleanup PATH
Acquire lock
svn status -v PATH
First, start the status check to see what items in your work copy can be locked. You can select the items you want to lock.
svn lock -m "LockMessage" [--force] PATH...
Lock information is the content of the lock edit box. It can be empty. "
If forced locking is selected, use the – force switch.
Release lock
svn unlock PATH
add to
svn add PATH...
If a folder is selected, TortoiseSVN will first recursively access the entries that can be added.
2, Execute using Python's OS module
If you do not need to return data, you can the OS module
import os
os.system('svn update path')
3, Execute using Python's subprocess module
It mainly collects the execution results of commands and extracts the desired information according to the results
import subprocess
log = subprocess.Popen('svn updata path',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.readlines()
log[0].decode('gb2312')
The returned is a list. If the returned Chinese is garbled, refer to the following method
4, Deal with Chinese garbled code
gb2312 types
# sample
>>> name = 'Game test'
>>> encode_name = name.encode('gb2312')
>>> encode_name
b'\xd3\xce\xcf\xb7\xb2\xe2\xca\xd4'
>>> encode_name.decode('gb2312')
'Game test'
utf-8 type
# sample
>>> name = 'Game test'
>>> encode_name = name.encode('utf-8')
>>> encode_name
b'\xe6\xb8\xb8\xe6\x88\x8f\xe6\xb5\x8b\xe8\xaf\x95'
>>> encode_name.decode('utf-8')
'Game test'
There are also such utf-8:% E6%B8%B8%E6%88%8F%E6%B5%8B%E8%AF%95

The above cannot be converted. Urllib is required Parse Library
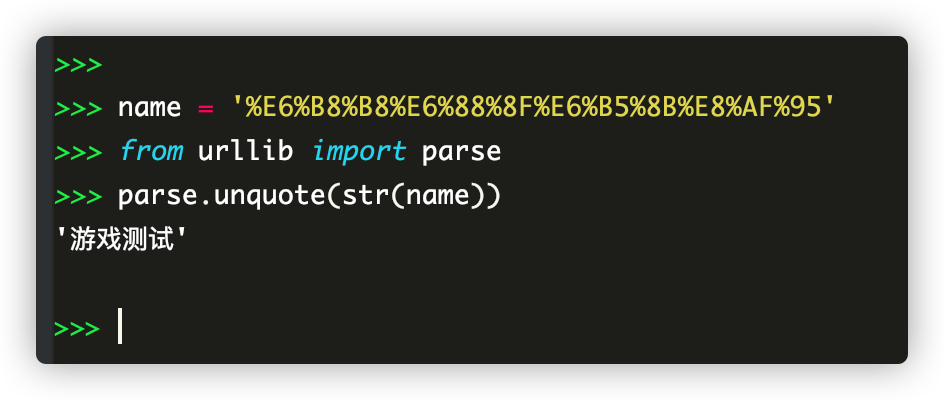
5, Extract command line data
Extract the full path of the update file
import re
import subprocess
def get_table_path():
tables = []
svn_log = subprocess.Popen('svn updata path',shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.readlines()
for f in svn_log:
file_path = re.search("Restord '(.*).xlsx'\r\n",f)
if file_path:
tables.append(file_path.group(1))
return tables
epilogue
After obtaining the updated files, the first step is completed, and the subsequent implementation only needs to test the updated files
Welcome to your little buddy WeChat official account ID:gameTesterGz
Or follow my CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32557025
Thank you for your attention and praise!
