!!!!! Container can only be created with image!!!!! , write it down, take the test!
Download a centos image before you talk about the container operation command (this command is available in the previous "common Docker image operation command". Students who don't know can go to see it)
//First check centos. [root@iz Two ze0lvzs71710m0jegmsz ~]# docker search centos NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED centos The official build of CentOS. 5627 [OK] ansible/centos7-ansible Ansible on Centos7 125 [OK] jdeathe/centos-ssh OpenSSH / Supervisor / EPEL/IUS/SCL Repos - ... 114 [OK] consol/centos-xfce-vnc Centos container with "headless" VNC session... 99 [OK] centos/mysql-57-centos7 MySQL 5.7 SQL database server 63 imagine10255/centos6-lnmp-php56 centos6-lnmp-php56 57 [OK] tutum/centos Simple CentOS docker image with SSH access 44 centos/postgresql-96-centos7 PostgreSQL is an advanced Object-Relational ... 39 kinogmt/centos-ssh CentOS with SSH 29 [OK] centos/httpd-24-centos7 Platform for running Apache httpd 2.4 or bui... 26 pivotaldata/centos-gpdb-dev CentOS image for GPDB development. Tag names... 10 guyton/centos6 From official centos6 container with full up... 9 [OK] drecom/centos-ruby centos ruby 6 [OK] centos/tools Docker image that has systems administration... 4 [OK] darksheer/centos Base Centos Image -- Updated hourly 3 [OK] pivotaldata/centos Base centos, freshened up a little with a Do... 3 mamohr/centos-java Oracle Java 8 Docker image based on Centos 7 3 [OK] miko2u/centos6 CentOS6 Japanese environment 2 [OK] pivotaldata/centos-mingw Using the mingw toolchain to cross-compile t... 2 pivotaldata/centos-gcc-toolchain CentOS with a toolchain, but unaffiliated wi... 2 indigo/centos-maven Vanilla CentOS 7 with Oracle Java Developmen... 1 [OK] blacklabelops/centos CentOS Base Image! Built and Updates Daily! 1 [OK] pivotaldata/centos7-dev CentosOS 7 image for GPDB development 0 smartentry/centos centos with smartentry 0 [OK] pivotaldata/centos6.8-dev CentosOS 6.8 image for GPDB development 0 //Select the image you want and the image version (the default is last if you don't write the version), and pull it down (I've done it before) [root@iz2ze0lvzs71710m0jegmsz ~]# docker pull centos Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/centos 729ec3a6ada3: Already exists Digest: sha256:f94c1d992c193b3dc09e297ffd54d8a4f1dc946c37cbeceb26d35ce1647f88d9 Status: Downloaded newer image for centos:latest docker.io/library/centos:latest //Take a look at the local image [root@iz2ze0lvzs71710m0jegmsz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE xiaowang/mytomcat 1.2 49733849ab9f 18 hours ago 507MB mongo latest 191b28dbfefe 28 hours ago 363MB tomcat latest 882487b8be1d 6 days ago 507MB centos latest 0f3e07c0138f 3 weeks ago 220MB hello-world latest fce289e99eb9 9 months ago 1.84kB
I. command to create and start a container
Syntax and common parameters:
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE(Can be mirrored image id It can also be mirrored REPOSITORY) [COMMAND] OPTIONS Some are a minus sign, some are two minus signs --name="Container new name": Specify a name for the container; -d: Run the container in the background and return to the container ID,That is, start the guard container; -i: Run the container in interactive mode, usually with -t At the same time; -t: Reassign a pseudo input terminal to the container, usually with -i Simultaneous use; -P: Random port mapping; -p: There are four formats for specifying port mapping ip:hostPort:containerPort ip::containerPort hostPort:containerPort containerPort
for instance:
//Start a container. The container is running centos system. #docker run -it centos //Use image centos:latest to start a container in interactive mode and execute the / bin/bash command inside the container. #docker run -it centos /bin/bash //Use the image tomcat:latest to start a container in interactive mode, host port 7777, docker container port 8080 (at this time, you can directly visit localhost:7777 to enter the tomcat home page) #docker run -it -p 7777:8080 tomcat
2. List all currently running containers
Syntax and common parameters:
docker ps [OPTIONS] OPTIONS Description (common): -a :List all currently running containers+Run in history -l :Show recently created containers. -n: Recent display n Containers created. -q :In silent mode, only the container number is displayed. --no-trunc :Output is not truncated.
3. Exit the container
There are two ways to exit:
Exit container stops and exits (do it yourself: create a centos container in interactive mode, enter exit, and then docker ps) ctrl+p+q container does not stop exiting (do it yourself: create a centos container in interactive mode, press ctrl+p+q, and then docker ps)
IV. starting container
docker start container ID or container name
V. restart the container
docker restart container ID or container name
Vi. stop the container
docker stop container ID or container name
VII. Forced stop of container
docker kill container ID or container name
VIII. Delete stopped containers
docker rm -f ${docker ps -a -q} docker ps -a -q | xargs docker rm
Key content:
1. Start the daemonic container: docker run -d container name
//Use centos:latest to start a container in backend mode #docker run -d centos //Then the docker ps -a will check and find that the container has exited #docker ps -a
So to summarize:
There must be a foreground process for Docker container to run in the background.
If the commands that the container runs are not those that have been suspended (such as running top and tail), they will exit automatically.
This is the mechanism of docker, such as your web container. We take nginx as an example. Normally, we only need to start the response service to configure the startup service.
For example, service nginx start
However, in this way, nginx runs in the background process mode, which results in no application running in the docker foreground.
After the container is started in the background, he will commit suicide immediately because he thinks he has nothing to do.
Therefore, the best solution is to run the program you want to run as a previous process.
2. View the container log: docker logs -f -t --tail container ID
-t is add time stamp
-f is printed with the latest log
--tail number shows the last number
3. View the processes running in the container
docker top container ID
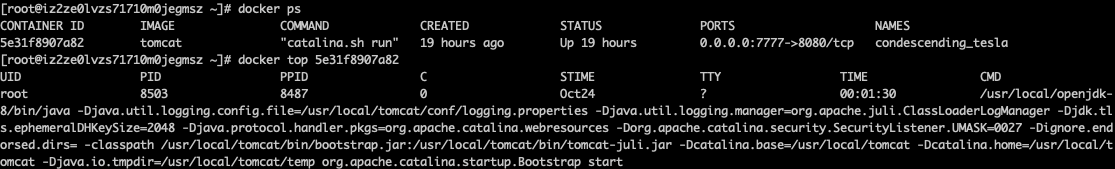
4. Check the details inside the container
Docker inspection container ID
5. Enter the running container and interact with the command line (important, remember to tap)
docker exec -it container ID bashShell
[root@iz2ze0lvzs71710m0jegmsz ~]# docker exec -it 0a6da2eccfb4 ls -l /tmp total 8 -rwx------ 1 root root 1379 Sep 27 17:13 ks-script-0n44nrd1 -rwx------ 1 root root 671 Sep 27 17:13 ks-script-w6m6m_20 Reenter: docker attach container ID The difference between the above two: Attach - > directly enter the terminal of the container start command. No new process will start : exec ---- is to open a new terminal in the container and start a new process.
6. Copy files from the container to the host
docker cp container ID: path inside container destination host path
[root@iz2ze0lvzs71710m0jegmsz ~]# docker cp 0a6da2eccfb4:/root/test.txt /root/o.txt