preface:
The database used by the following MySQL functions:
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1N8uoyj0Wv6nq4zFdEnmGBw
Extraction code: 6666
1, Single line function
1. Character function
- length gets the number of bytes of the parameter value
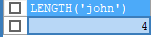
SELECT LENGTH('john');
result:
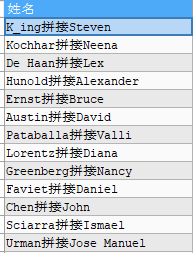
- concat splice string
SELECT CONCAT(last_name,'Splicing',first_name) full name FROM employees;
result:
- upper, lower (change case)
SELECT UPPER('john');#Change to uppercase
SELECT LOWER('JOHN');#Change to lowercase
- substr, substring (intercept specified characters)
#Intercepts all subsequent characters from the specified index
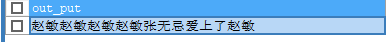
SELECT SUBSTR('Li Mochou fell in love with Lu Zhanyuan',7) out_put;
#Intercepts characters of the specified length from the specified index
SELECT SUBSTR('Li Mochou fell in love with Lu Zhanyuan',1,3) out_put;
- instr returns the index of the first occurrence of the substring. If it is not found, it returns 0
SELECT INSTR('Yang Bu regretted falling in love with Yin Liuxia','Yin Liuxia') AS out_put;
- trim removes the first and last specified characters
#Remove first aa character
SELECT TRIM('aa' FROM 'aaaaaaaaa Zhang aaaaaaaaaaaa Cuishan aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa') AS out_put;
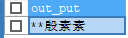
- lpad left fills the specified length with the specified character
SELECT LPAD('Yin Su Su',5,'*') AS out_put;
result:
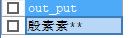
8. rpad right fills the specified length with the specified character
SELECT RPAD('Yin Su Su',5,'*') AS out_put;
result:
- Replace replace
SELECT REPLACE('Zhou Zhiruo Zhou Zhiruo Zhou Zhiruo Zhang Wuji falls in love with Zhou Zhiruo','Zhou Zhiruo','Zhao Min') AS out_put;
result:
2. Mathematical function
- Round round
SELECT ROUND(-1.55); SELECT ROUND(1.567,2); SELECT ROUND(1.400,2);
- ceil rounds up and returns > = the smallest integer of the parameter
SELECT CEIL(-1.02);
- floor rounded down and returns < = the maximum integer of the parameter
SELECT FLOOR(-9.99);
- truncate
SELECT TRUNCATE(1.69999,4);
- mod remainder
/* mod MOD(a,b) : a-a/b*b mod MOD(10,-3):10- (10)/(-3)*(-3)=1 */ SELECT MOD(10,-3); SELECT 10%3;
3. Date function
- now returns the current system date + time
SELECT NOW();
- Current date returns the current system date, excluding time
SELECT CURDATE();
- curtime returns the current time, excluding the date
SELECT CURTIME();
- You can get the specified part, year, month, day, hour, minute and second
SELECT YEAR(NOW()) year;
SELECT YEAR('1998-1-1') year;
SELECT YEAR(hiredate) year FROM employees;
SELECT MONTH(NOW()) month;
SELECT MONTHNAME(NOW()) month;
- str_to_date converts characters into dates in the specified format
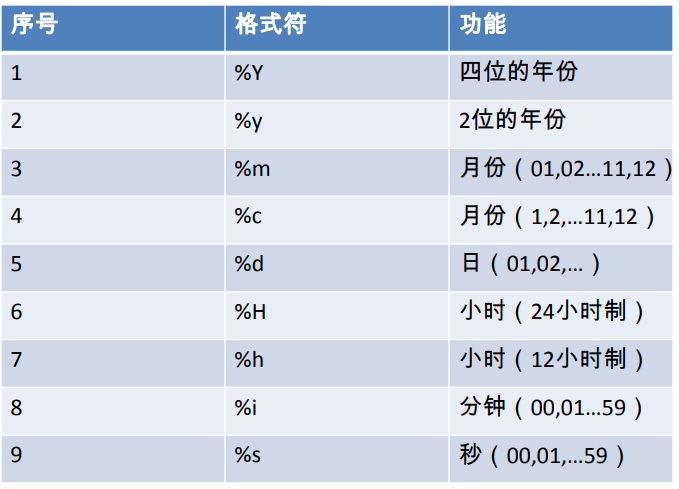
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('1998-3-2','%Y-%c-%d') AS out_put;
- Query the employee information whose employment date is 1992 – 4-3
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE hiredate = '1992-4-3';
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE hiredate = STR_TO_DATE('4-3 1992','%c-%d %Y');
- Query the number of days between two dates
SELECT DATEDIFF
#2. Query the difference days between the maximum enrollment time and the minimum enrollment time in the employee table (DIFFRENCE)
SELECT MAX(hiredate) maximum,MIN(hiredate) minimum,(MAX(hiredate)-MIN(hiredate))/1000/3600/24 DIFFRENCE
FROM employees;
SELECT DATEDIFF(MAX(hiredate),MIN(hiredate)) DIFFRENCE
FROM employees;
SELECT DATEDIFF('1995-2-7','1995-2-6');
- date_format converts the date to characters
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(),'%y year%m month%d day') AS out_put; #Query the name and employment date of the employee with bonus (xx month / xx day, xx year) SELECT last_name,DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%m month/%d day %y year') Entry date FROM employees WHERE commission_pct IS NOT NULL;
- Query the name and employment date of the employee with bonus (xx month / xx day, xx year)
// A code block var foo = 'bar';
4. Other functions
- SELECT VERSION(); Version number
- SELECT DATABASE(); view the database
- SELECT USER(); Current user
2, Grouping function
Function: used for statistics, also known as aggregate function or statistical function or group function
Classification:
sum, avg average, Max max, min Min, count
characteristic:
- sum and avg are generally used to deal with numerical types
max, min, count can handle any type - The above grouping functions ignore null values
- It can be used with distinct to realize the operation of de duplication
- For a separate introduction to the count function, count(*) is generally used to count the number of rows
- The fields queried together with the grouping function must be the fields after group by
1. Simple use
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM employees; SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees; SELECT MIN(salary) FROM employees; SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees; SELECT COUNT(salary) FROM employees; SELECT SUM(salary) and,AVG(salary) average,MAX(salary) highest,MIN(salary) minimum,COUNT(salary) number FROM employees; SELECT SUM(salary) and,ROUND(AVG(salary),2) average,MAX(salary) highest,MIN(salary) minimum,COUNT(salary) number FROM employees;
2. Detailed introduction to count function
SELECT COUNT(salary) FROM employees; #Count rows SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees; #Count rows SELECT COUNT(1) FROM employees; Efficiency: MYISAM Under the storage engine, COUNT(*)High efficiency INNODB Under the storage engine, COUNT(*)and COUNT(1)The efficiency is about the same, better than COUNT(field)Higher
3. Match with distinct (weight removal)
#The sum of salary after weight removal SELECT SUM(DISTINCT salary),SUM(salary) FROM employees; SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT salary),COUNT(salary) FROM employees;