1, Judgment statement
Python conditional statements are code blocks that determine the execution result (True or False) of one or more statements.
The following figure summarizes the execution process of conditional statements:
Format:
if + Conditions:
Action to perform
......
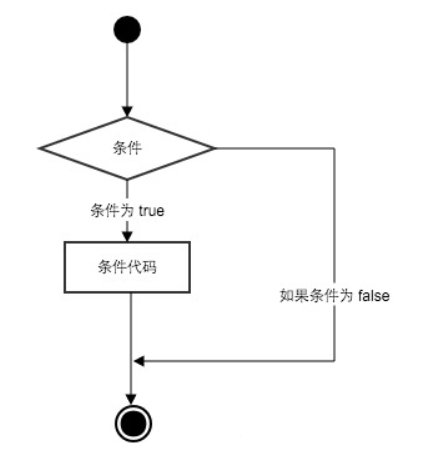
ps: if the indents are different, they represent different levels
1. Multiple judgments
if Judgment statement: Code execution elif Judgment statement: Code execution elif Judgment statement: Code execution else: Code execution
color="red"
if (color=="green"):
print("Passable")
if (color=="red"):
print("Impassable")
if (color=="yellow"):
print("Need to slow down")
print("try, python Hierarchy is related to indentation")
#----------------------------#
if color==" ":
pass #If there is no judgment content, you need to write a pass placeholder. If there is content and pass in the structure, pass can be ignored.
print("Space")
#----------------------------#
color="green"
if (color=="red"):
print("stop")
else:
print("go")
#----------------------------#
color="green"
if color=="green":
print("go")
elif color=="red":
print("stop")
elif color=="yellow":
print("slow")
else:
pass
print("End of judgment")
#----------------------------#
carType=input("Please enter the type of car:")
lightColor=input("Please enter the lamp color:")
if carType in ("jiuhu","jingche","jiuhuo"):
print("Direct passage of special vehicles")
else:
if lightColor=="green":
print("go")
elif lightColor=="red":
print("stop")
elif lightColor=="yellow":
print("slow")
else:
print("randomaction")
print("End of judgment")
#----------------------------#
score=int(input("Please enter a score:"))
if score<60:
print("fail,")
elif score>=60 and score<75:
print("pass")
elif score>=75 and score<90:
print("good")
else:
print("excellent")
2, Circular statement
1. General
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow more complex execution paths. Circular statements allow us to execute a statement or statement group multiple times. The following is the general form of circular statements in most programming languages:
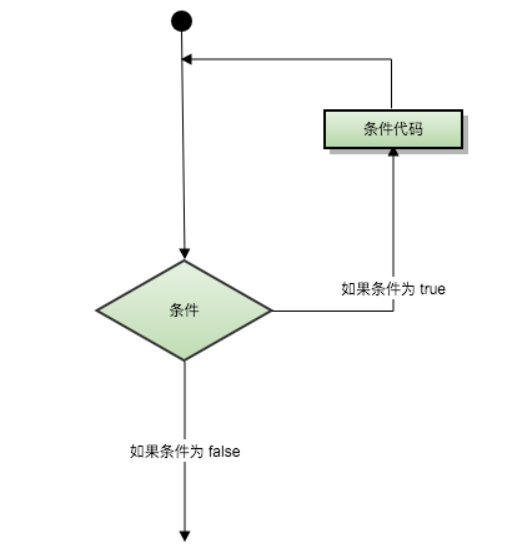
Python provides for loops and while loops (there is no do... While loop in Python)
| Cycle type | describe |
|---|---|
| while loop | Execute the loop body when the given judgment condition is true, otherwise exit the loop body. |
| for loop | Repeat statement |
| Nested loop | You can nest a for loop in the body of a while loop |
Loop control statements can change the order in which statements are executed. Python supports the following loop control statements:
| Control statement | describe |
|---|---|
| break statement | Terminates a loop during the execution of a statement block and jumps out of the entire loop |
| continue statement | During the execution of the statement block, terminate the current loop, jump out of the loop and execute the next loop. |
2.while loop
In Python programming, the while statement is used to execute a program circularly, that is, under certain conditions, execute a certain program circularly to deal with the same tasks that need to be processed repeatedly. Its basic form is:
while Conditional expression: If the conditions are met, execute the circular statement Variable value change #If the judgment condition is True, it represents an infinite loop
example:
a=1
while a<=50:
print("Print page"+str(a)+"Test papers")
a+=1
#----------#
a=1
while True:
print("Print page"+str(a)+"Test papers")
a+=1
if a==51:break
#----------#
#Judge according to the input. If you pass, end the exam. If you fail, retest
a=int(input("Please enter a number:"))
while a>=0:
if a>=60:
print("End the exam")
break
else:
print("Retest")
break
#----------#
#Judge according to the input. If you pass, end the exam. If you fail, retest
while True:
a=int(input("Please enter a score:"))
if a>=60:
print("Quit the exam,The score is:"+str(a))
break
else:
print("Fail to continue the exam,"+"Current score is:"+str(a))
continue
#----------#
while True:
a=int(input("Please enter the temperature:"))
if a>35 or (a>=-20 and a<5):
print("Please turn on the air conditioner,"+"Current temperature is:"+str(a))
break
elif a>=5 and a<=35:
print("The temperature is appropriate and there is no need to turn on the air conditioner,"+"Current temperature is:"+str(a))
break
elif a<-20:
break
#----------#
while True:
temp=int(input("Please enter the outside temperature:"))
if temp<-20:
print("It's too cold. The air conditioner is frozen")
break
elif temp>=5 and temp<=35:
print("The temperature is appropriate and there is no need to turn on the air conditioner")
else:
print("The temperature is not suitable. You need to turn on the air conditioner")
print("Program end!")
3.for loop
The Python for loop can traverse any sequence of items, such as a list or a string.
The syntax format of the for loop is as follows:
for variable in sequence
Circular statement
for i in range(51):
print("The first"+str(i)+"Test paper printing")
#----------#
for i in [1,2,3,4,5]:
print(i)
#----------#
a=(1,2,3,4,5)
for i in a:
print(i)
#----------#
#Chicken and rabbit in the same cage, 40 chickens and rabbits, 120 feet, find the number of chickens and rabbits
#Suppose there are x chickens and 40-x rabbits
for x in range(41):
b=40-x
c=2*x+4*b
if c==120:
print("The number of chickens is:"+str(x))
print("The number of rabbits is:"+str(40-x))
4.break,continue
- The break statement is used to end the whole current loop (from this execution of the current loop)
- The continue statement is used to skip this execution of the current loop (the next execution continues)
Example:
for i in range(5):
print("-----")
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
if i==3:
break
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
if i==3:
continue
print(i)
#----------#
for i in range(5):
i+=1
print("-----")
#if i==3:
#break
continue
print(i)
5.pass
Python pass is an empty statement to maintain the integrity of the program structure. Pass does nothing. It is generally used as a placeholder statement.
Example:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
# Output each letter of Python
for letter in 'Python':
if letter == 'h':
pass
print 'This is pass block'
print 'Current letter :', letter
print "Good bye!"
#result
Current letter : P
Current letter : y
Current letter : t
This is pass block
Current letter : h
Current letter : o
Current letter : n
Good bye!
3, Multiple cycles
#Single cycle printing rectangle
for i in range(5):
print("* * * * *")
#Double loop printing rectangle (print() wrap, end = 'no wrap)
for i in range(5): #Outer loop control line
for j in range(5): #Inner loop control column
print("* ",end='')
print()
#Print right triangle
##The right angle is on the lower left
for x in range(5):
for y in range(x+1):
print("* ",end='')
print()
##The right angle is on the upper left
for x in range(5):
for y in range(5-x):
print("* ",end='')
print()
##The right angle is on the top right
def num(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
if j<i:
print(' ',end=' ')
else:
print('*',end=' ')
print()
num(5)
##The right angle is at the bottom right
def num(n):
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(1,n+1):
if i+j<=n:
print(' ',end=' ')
else:
print('*',end=' ')
print()
num(5)
#Print diamond
for x in range(5):
for y in range(4-x):
print(" ",end='')
for y in range(2*x+1):
print("*",end='')
print()
for x in range(5):
for y in range(x+1):
print(" ",end='')
for y in range(7-x*2):
print("*",end='')
print()
#Print prime
lower = int(input("Enter the minimum value of the interval: "))
upper = int(input("Enter the maximum value of the interval: "))
for num in range(lower, upper + 1):
# Prime greater than 1
if num > 1:
for i in range(2, num):
if (num % i) == 0:
break
else:
print(num)
#----------------------------------
for x in range(2,101):
for y in range(2,x+1):
if x%y==0 and x!=y: #If x has a factor other than itself, then x is not prime
break
if x==y:
print("prime number:"+str(x))
break
#Find the number of daffodils for i in range(100,1000): a=int(i%10) b=int((i%100)/10) c=int(i/100) if a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==i: print(i)
#Decomposition quality factor: https://www.pianshen.com/article/962070061/
num=int(input("Please enter a positive integer:"))
son=2
print(str(num)+"=",end='')
while num!=son:
if num%son==0:
num/=son
print(str(son)+"*",end='')
else:son+=1
print(son)
#Calculate the sum, for example, enter 3, and the value is 3 + 33 + 333
a=int(input("Please enter a number:"))
n=a
sum=0
for x in range(a):
sum+=n
n=n*10+a
print(sum)