Introduction to Config
In the micro-service system, there are many services. The same configuration, such as database information, caching, parameters, will appear on different services. If a configuration changes, many service configurations need to be modified. spring cloud provides a configuration center to solve this scenario problem.
The general configuration in the system is stored at the same address: GitHub,Gitee, local configuration service, etc. Then the configuration center reads the configuration and publishes it restful ly. Other services can call the interface to get configuration information.
2. Configuration of Server
1. Project structure

- Core Note: @EnableConfigServer
2. Core Dependence
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>3. Core Profile
Note the configuration of the read file here
- active: native, read the local configuration;
- active: git, read network warehouse configuration;
server:
port: 9001
spring:
application:
name: config-server-9001
profiles:
# Read Local
# active: native
# Read Git
active: git
cloud:
config:
server:
native:
search-locations: classpath:/config
git:
# Read the warehouse address
uri: https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/spring-cloud-config.git
# Read under the warehouse specified folder
search-paths: /cloudbaseconfig
# Login Account for Private Requirements
username:
password:
label: master4. Read configuration content
The results read in different environments are different.
info: date: 20190814 author: cicada sign: develop version: V1.0
Configuration of Client
1. Core Dependence
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Core Profile
In the configuration center above, the configuration reads Git resources, so the configuration here is to read Git resources.
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: config-client-8001
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
config:
# Read local configuration
#uri: http://localhost:9001
## Read Policy: Fast Failure
#fail-fast: true
## Read File Name: No Suffix
#name: client-8001
## Read Configuration Environment
#profile: dev # client-8001-dev.yml
# ----------------------------------------
# Resource names on github
name: client-8001
# Read Configuration Environment
profile: dev
label: master
# After the micro-service is started, the GitHub configuration file is obtained through the configuration center 6001 service.
uri: http://localhost:9001
# ----------------------------------------3. Test Interface
@RestController
public class ClientController {
@Value("${info.date}")
private String date ;
@Value("${info.author}")
private String author ;
@Value("${info.sign}")
private String sign ;
@Value("${info.version}")
private String version ;
/**
* Get configuration information
*/
@RequestMapping("/getConfigInfo")
public String getConfigInfo (){
return date+"-"+author+"-"+sign+"-"+version ;
}
}IV. Eureka-based configuration
The above pattern, through the service center, gets the configuration directly. Now add the registry Eureka.
1. Project structure
The order of start-up is also as follows:
node06-eureka-7001 config-server-9001 config-client-8001
2. Modifying configuration items
- Add config-server-9001 to the registry;
- Configure config-client-8001 to read the registry;
After completing the Eureka Registry rendering, the starting sequence is as follows:
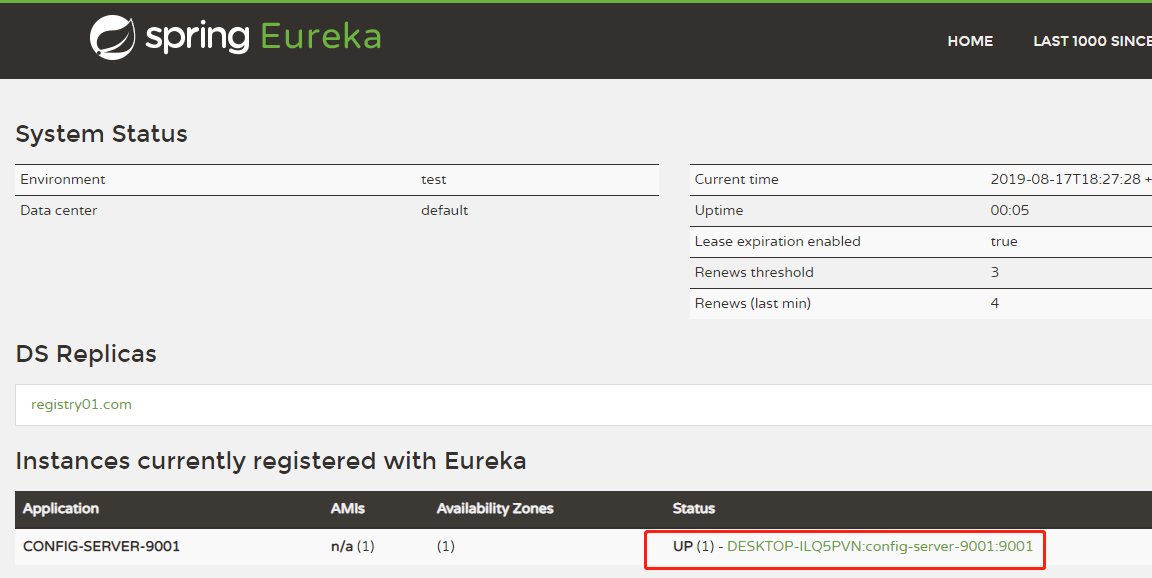
3. Modify client configuration
Get services through the registry and avoid using URI addresses.
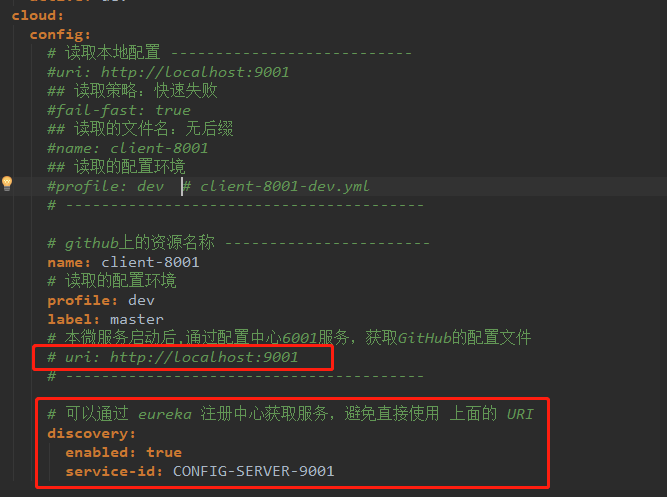
After testing, it is correct.
- Reminder: If you read the git configuration in China, you may often go out and can not load the problem. This case uses Gitee's address.
5. Source code address
GitHub Address: Know a smile https://github.com/cicadasmile/spring-cloud-base Code Yun Address: Know a smile https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/spring-cloud-base