catalogue
Characteristics of creative mode
① Hungry Han formula (static constant)
② Hungry Chinese (static code block)
④ Lazy (thread safety, synchronization method)
⑤ Lazy (thread safe, synchronous code block)
Characteristics of creative mode
- Concern: creating objects and separating the creation and use of objects can reduce the coupling of code
Create pattern classification
Singleton pattern, factory pattern, abstract factory pattern, builder pattern, prototype model
Singleton Pattern
Single case introduction
definition:
Ensure that a class has only one instance and provide a global access point to access it
Single example class diagram:
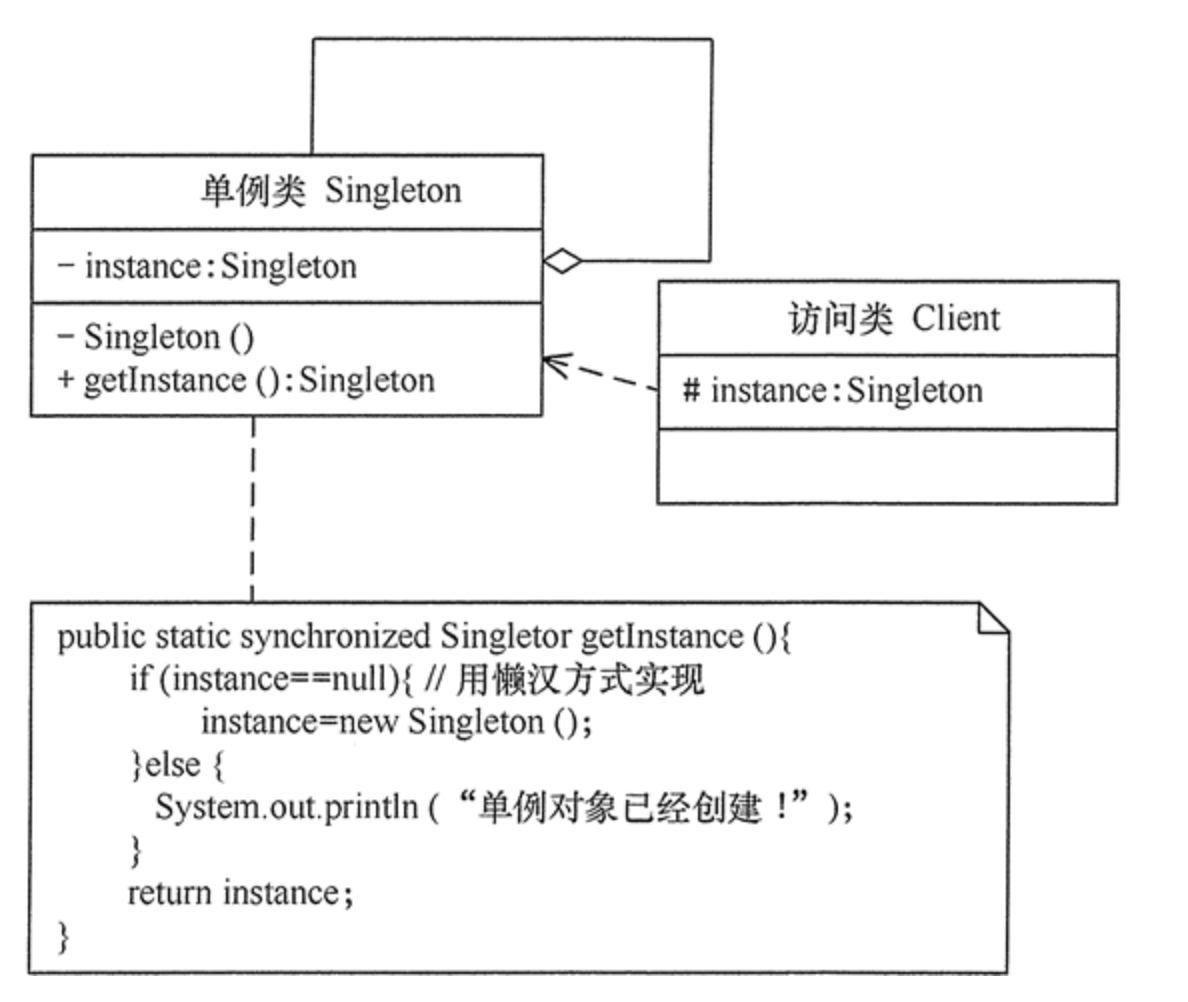
Roles included in the singleton:
Singleton class: contains an instance and can create the instance class by itself
Singleton Pattern features:
1. A singleton class has only one instance.
2. A single class must create its own unique instance.
3. A singleton class must provide this instance to all other instances.
Code demonstration
There are 8 implementations of singleton
Hungry Han formula (static constant)
Hungry Chinese (static code block)
Lazy (thread unsafe)
Lazy (locked)
Lazy (optimized locking)
Lazy (double check)
Static inner class
enumeration
① Hungry Han formula (static constant)
/**
* Hungry Han formula (static variable)
* Thread safe. After the class is recorded in memory, the JVM ensures thread safety
* Simple, recommended implementation
*/
public class Singleton1 {
//Constructor Privatization (prevent new)
private Singleton1() {}
//This class creates objects and static variables internally
private final static Singleton1 single = new Singleton1();
//Provide a public static method to return the instance object and provide it for external use
public static Singleton1 getInstance() {
return single;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: simple writing
Class instantiation has been completed during class loading to ensure thread safety
Disadvantages: instantiation is completed during class loading (lazy loading is not implemented). If this instance is not used, memory will be wasted
② Hungry Chinese (static code block)
/**
* Hungry Chinese (static code block)
*/
public class Singleton2 {
//Constructor privatization
private Singleton2(){}
//Create an object instance inside the class
private static Singleton2 single;
//In a static code block, create a singleton object
static {
single = new Singleton2();
}
//Provide public access points
public static Singleton2 getInstance(){
return single;
}
}The advantages and disadvantages are the same as hungry Chinese static variables.
Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: simple writing
Class instantiation has been completed during class loading to ensure thread safety
Disadvantages: instantiation is completed during class loading (lazy loading is not implemented). If this instance is not used, memory will be wasted
③ Lazy (thread unsafe)
/**
* Lazy (thread unsafe)
*/
public class Singleton3 {
private static Singleton3 single;
private Singleton3 (){}
//Provide a static public access. When called, an instance is created, that is, lazy
public static Singleton3 getInstance() {
if (single == null) {
single = new Singleton3();
}
return single;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: easy to implement
The effect of lazy loading is realized, but it can only be used in a single thread
Disadvantages: under multithreading, there is thread insecurity
④ Lazy (thread safety, synchronization method)
/**
* Lazy style
*/
public class Singleton4 {
private static Singleton4 single;
private Singleton4 (){}
//Provide a static public access. When called, an instance is created, that is, lazy
public static synchronized Singleton4 getInstance() {
if (single == null) {
single = new Singleton4();
}
return single;
}
}Key point of thread safety: synchronized
Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: easy to implement
Solve thread safety problems through thread safety keywords
Implement lazy loading
Disadvantages: low efficiency. When each thread obtains an instance, it needs to synchronize the execution of getInstance. The synchronization efficiency of the method is too low
⑤ Lazy (thread safe, synchronous code block)
/**
* Lazy style
*/
public class Singleton5 {
private static Singleton5 single;
private Singleton5() {
}
//Provide a static public access. When called, an instance is created, that is, lazy
public static Singleton5 getInstance() {
if (single == null) {
synchronized (Singleton5.class) {
single = new Singleton5();
}
}
return single;
}
}Some optimization has been made for locking (the lock is a code block), and the overall advantages and disadvantages are consistent with the above.
Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: easy to implement
Implement lazy loading
Solve thread safety problems through thread safety keywords
Disadvantages: low efficiency. When each thread obtains an instance, it needs to synchronize the execution of getInstance. The synchronization efficiency of the method is too low, but the two codes are locked tightly. If two threads enter the if judgment statement at the same time, one of them will execute and the other will wait for the execution to be completed, Then two instances are created, so there is no guarantee that only one object will be created. Therefore, the following double check is introduced
⑥ Double check
/**
* Double test
*/
public class Singleton6 {
private static Singleton6 single;
private Singleton6() {
}
//Provide a static public access. When called, an instance is created, that is, lazy
public static Singleton6 getInstance() {
if (single == null) {
synchronized (Singleton6.class) {
if (single == null) {
single = new Singleton6();
}
}
}
return single;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: lazy loading
Thread safety, double check, if (single == null) check twice to ensure thread safety and high efficiency
Disadvantages: difficult to implement
Recommended use
⑦ Static inner class
/**
* Static inner class
* Static internal attribute, which is initialized when the class is loaded to ensure thread safety
* Using static inner class to realize delayed loading
*/
public class Singleton7 {
private Singleton7() {
}
//Provides a static inner class with a static property
private static class SingleHoler{
private static final Singleton7 instance = new Singleton7();
}
//Provide a static public access and directly return singleholder instance
public static Singleton7 getInstance() {
return SingleHoler.instance;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Thread safety: the essence is to ensure thread safety through class loading
Lazy loading: class initialization is triggered only when it is actually used. It is also a form of lazy loading
High efficiency: no lock mechanism is used
Recommended use
⑧ Enumeration mode
/**
* Implementation of singleton by enumeration
*/
public enum Singleton8 {
INSTANCE;//attribute
//Provide a static public access and directly return singleholder instance
public static Singleton8 getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}Advantages and disadvantages: (Evaluation: whether lazy loading is realized, whether thread safety is achieved, and difficulty of implementation)
Advantages: easy to implement
Thread safety
Disadvantages: lazy loading is not implemented
Recommended use
Single case re exploration
advantage:
The singleton mode ensures that there is only one instance in memory, which reduces the memory overhead
It avoids multiple occupation of resources
Setting global access points for a single instance can optimize and share resource access
Disadvantages:
The singleton mode generally has no interface and is difficult to expand. If you want to expand, you need to modify the code, which violates the opening and closing principle
Applicable scenarios:
For some classes that need to be created frequently, the application of singleton can reduce the memory pressure of the system and reduce GC
Some object instances occupy a lot of resources, or the instances are time-consuming and frequently used. The singleton form is adopted
Java application
1. Singleton in spring
In spring, Bean can be defined into two patterns: singleton (single instance) and Prototype (multiple instances), and the pattern in spring adopts single instance