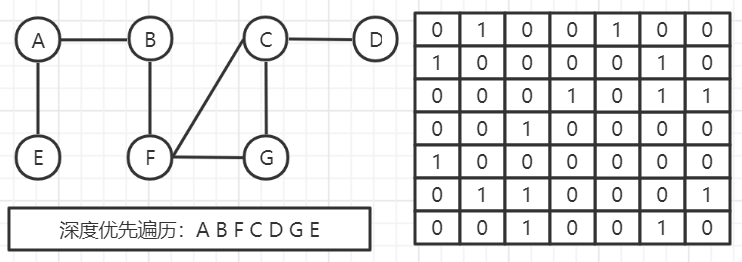
Depth first search
- Unlike breadth first search, depth first search (DFS) is similar to the prior traversal of a tree. As the name implies, the search strategy followed by this search algorithm is to search a graph as "deep" as possible.
- Its basic idea is as follows: first access a starting vertex v in the graph, and then start from V to access any vertex adjacent to V and not accessed w 1 w_1 w1, revisit and w 1 w_1 w1) any vertex that is adjacent and not accessed w 2 w_2 w2... Repeat the above process. When the downward access can no longer be continued, it will return to the recently accessed vertex in turn. If it has adjacent vertices that have not been accessed, the above search process will continue from this point until all vertices in the graph have been accessed.
Code implementation (adjacency matrix method)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MaxVertenNum 100 / / maximum number of vertices
#define NodeNum 7 / / number of vertices
typedef char VertexType; //Data type of vertex
typedef int EdgeType; //Store vertex information
typedef struct
{
VertexType Vex[MaxVertenNum]; //Vertex table
EdgeType Edge[MaxVertenNum][MaxVertenNum]; //adjacency matrix
int vexnum, edgenum; //The current number of vertices and edges of a graph
}MGraph;
void InitG(MGraph& g) //initialization
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < MaxVertenNum; i++)
{
g.Vex[i] = '\0';
}
for (i = 0; i < MaxVertenNum; i++)
for (j = 0; j < MaxVertenNum; j++)
g.Edge[i][j] = 0;
g.vexnum = NodeNum;
}
void CreateVex(MGraph &g) //Create vertex information
{
VertexType ch;
printf("Enter the vertices of the graph:");
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf("%c", &ch);
g.Vex[i] = ch;
}
}
void CreateEdge(MGraph& g) //Create adjacency matrix information
{
EdgeType b;
int i, j = 0;
printf("Enter adjacency matrix information:\n");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
for (j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &b);
g.Edge[i][j] = b;
}
}
void Info(MGraph& g) //The number of vertices and edges of a graph
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++)
if (g.Edge[i][j] == 1) count++;
g.edgenum = count / 2;
}
int CountDegree(MGraph g, VertexType point) //Count the degree of each vertex
{
int j, k, count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (g.Vex[i] == point) j = i;
for (int k = 0; k < g.vexnum; k++) if (g.Edge[j][k] == 1) count++;
return count;
}
void PrintG(MGraph g) //Output the connection of each vertex
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++)
if (g.Edge[i][j] == 1) printf("%c->%c ", g.Vex[i], g.Vex[j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int FirstNeighbor(MGraph g,VertexType x) //Find the first adjacent node of vertex x in graph G, and return the vertex number if any. If x has no adjacency point or X does not exist in the graph, - 1 is returned.
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (x == g.Vex[i]) j = i;
if (j >= g.vexnum) return -1; //There is no vertex with value x in the graph
else
{
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (g.Edge[j][i] == 1) return i; //Return vertex number
if (i >= g.vexnum) return -1; //x has no adjacency points
}
}
int NextNeighbor(MGraph g, VertexType x, VertexType y)
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
if (g.Vex[i] == x) j = i;
if (g.Vex[i] == y) k = i;
}
if (j >= g.vexnum || k >= g.vexnum) return false; //There is no vertex x or vertex y
else
{
for (i = k+1; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
if (g.Edge[j][i] == 1) return i; //Return vertex number
}
if (i >= g.vexnum) return -1; //x has no adjacency points
}
}
void PrintMatrix(MGraph g) //Output adjacency matrix
{
int i, j;
printf("Output adjacency matrix:\n");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
printf("\t%c", g.Vex[i]);
printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
printf("%c", g.Vex[i]);
for (j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++)
printf("\t%d", g.Edge[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
bool visited[MaxVertenNum]; //Access tag array
void DFS(MGraph g, VertexType ch) //Starting from the vertex, depth first traverses the graph
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (g.Vex[i] == ch) j = i;
printf("%c ", ch); //Access vertex
visited[j] = true; //Set accessed flag
for (i = FirstNeighbor(g, g.Vex[j]); i >= 0; i = NextNeighbor(g, g.Vex[j], g.Vex[i]))
if (!visited[i]) DFS(g, g.Vex[i]); //Adjacent vertices that have not been accessed
}
void DFSTraverse(MGraph g) //Depth first traversal of figure G
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) visited[i] = false; //Initialize access tag data
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) //Starting from vertex 0, depth first traverses graph G
if (!visited[i]) DFS(g, g.Vex[i]);
}
int main()
{
MGraph g;
VertexType Vex[MaxVertenNum];
EdgeType Edge[MaxVertenNum][MaxVertenNum];
InitG(g);
CreateVex(g);
CreateEdge(g);
Info(g);
printf("\n Undirected graph G There are:%d A vertex,%d Strip edge\n", g.vexnum, g.edgenum);
PrintMatrix(g);
printf("Output undirected graph G Connection of vertices in:\n");
PrintG(g);
printf("\n");
int sumdegree = 0, i;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
int degree;
degree = CountDegree(g, g.Vex[i]);
printf("vertex%c The degree of is:%d\n", g.Vex[i], degree);
sumdegree = sumdegree + degree;
}
printf("Undirected graph G The sum of the degrees of all vertices in the is:%d\n", sumdegree);
printf("\n Output depth first search results:");
DFSTraverse(g);
return 0;
}
Operation results
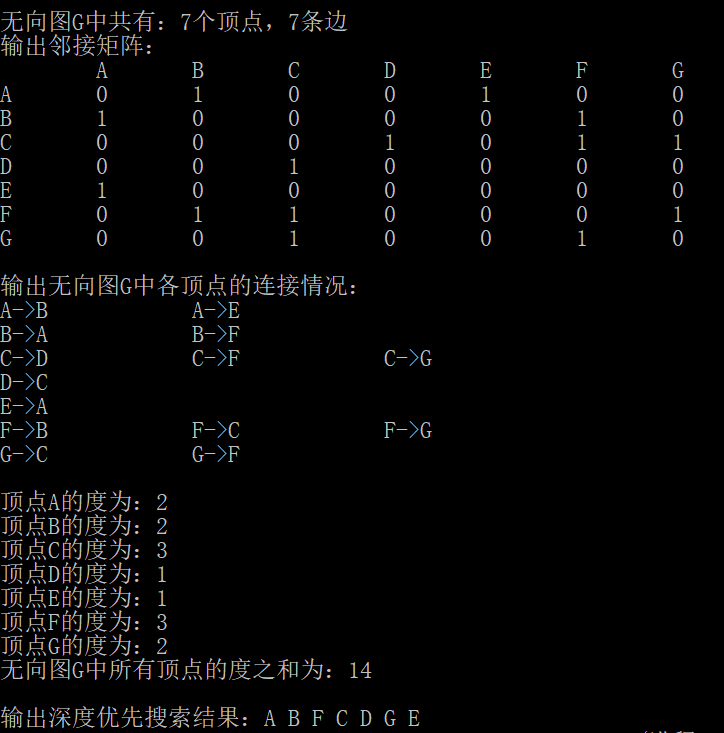
Program analysis
- Space complexity: from the function call stack. In the worst case, the recursion depth is O(|V|); At best, O(1).
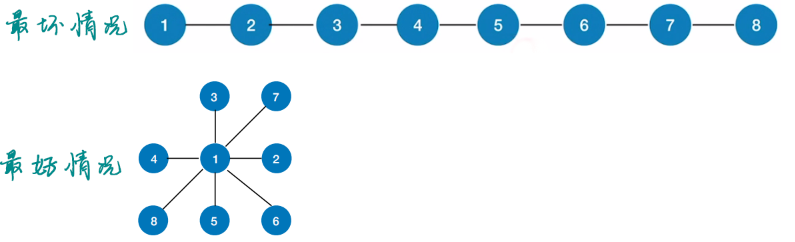
- Time complexity = time required to access each node + time required to explore each edge.
- When the adjacency matrix storage method is adopted: it takes O(|V|) time to access | V vertices, and it takes O(|V|) time to find the adjacency point of each vertex. There are | V vertices in total, so the time complexity = O(|V)| 2 ^2 2).
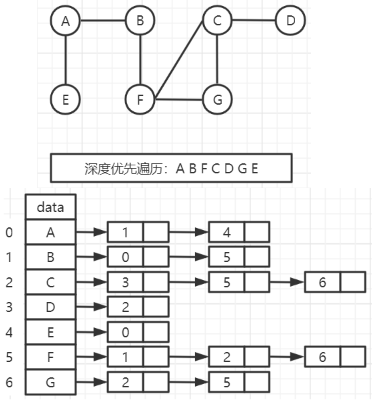
Code implementation (adjacency table method)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define NodeNum 7 / / number of vertices
typedef char VertexType;
//Type declaration of graph
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjvex; //The number of adjacent points of the edge
struct ArcNode* nextarc; //Pointer to next edge
//int weight; / / information about the edge, such as weight
}ArcNode; //Type of edge node
typedef struct VNode
{
VertexType data; //Vertex information
ArcNode* firstarc; //Point to the first edge node
}VNode;
typedef struct
{
VNode adjlist[MaxVertexNum]; //Head node array of adjacency table
int vexnum, edgenum; //Number of vertices and edges in a graph
}AdjGraph; //Complete graph adjacency table type
void InitG(AdjGraph& g)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MaxVertexNum; i++)
{
g.adjlist[i].data = '\0';
g.adjlist[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
g.vexnum = NodeNum;
}
void CreateVNde(AdjGraph& g)
{
int i;
char ch;
printf("Enter vertex information:");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
scanf("%c", &ch);
g.adjlist[i].data = ch;
g.adjlist[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
}
void CreateANode(AdjGraph& g, VertexType ch, int num)
{
ArcNode* p, * r = g.adjlist[0].firstarc;
int i, j, k;
while (num--)
{
p = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
p->nextarc = NULL;
printf("Enter the number of vertices:");
scanf("%d", &i);
for (j = 0; j < g.vexnum; j++)
if (g.adjlist[j].data == ch) k = j;
if (i != k)
{
p->adjvex = i;
if (g.adjlist[k].firstarc == NULL)
{
g.adjlist[k].firstarc = p;
r = p;
}
else
{
r->nextarc = p;
r = p;
}
}
}
}
int FirstNeighbor(AdjGraph& g, VertexType x)
//Find the first adjacent node of vertex x in graph G. if there is, return the vertex number. If x has no adjacent point or X does not exist in the graph, return - 1
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (g.adjlist[i].data == x) j = i;
if (j >= g.vexnum) return -1; //x does not exist in the diagram
ArcNode* p = g.adjlist[j].firstarc;
if (p == NULL) return -1; //If x has no adjacency
else return p->adjvex; //Return vertex number
}
int NextNeighbor(AdjGraph& g, VertexType x, VertexType y)
//Find the first adjacent node of vertex x in graph G. if there is, return the vertex number. If x has no adjacent point or X does not exist in the graph, return - 1
{
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
if (g.adjlist[i].data == x) j = i;
if (g.adjlist[i].data == y) k = i;
}
if (j >= g.vexnum || k >= g.vexnum) return -1; //There is no vertex x or vertex y
else
{
ArcNode* p = g.adjlist[j].firstarc;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->adjvex == k)
{
if (p->nextarc != NULL) return p->nextarc->adjvex;
else return -1;
}
else p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}
void CountDegree(AdjGraph &g)
{
ArcNode* p;
int sumdegree = 0;
printf("Output degrees of each vertex:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
p = g.adjlist[i].firstarc;
int degree = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
degree++;
p = p->nextarc;
}
sumdegree += degree;
printf("vertex%c The degree of is:%d\n", g.adjlist[i].data, degree);
}
printf("Undirected graph G The sum of the degrees of all vertices in the is:%d", sumdegree);
g.edgenum = sumdegree / 2;
}
void PrintG(AdjGraph g)
{
int i;
ArcNode* p;
printf("Output the connection of each vertex:\n");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
p = g.adjlist[i].firstarc;
printf("%d(%c) ", i, g.adjlist[i].data);
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("-%d(%c) ", p->adjvex, g.adjlist[p->adjvex].data);
p = p->nextarc;
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
bool visited[MaxVertexNum]; //Access tag array
void DFS(AdjGraph g, VertexType ch)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
if (g.adjlist[i].data == ch) j = i;
printf("%c ", ch); //Access vertex
visited[j] = true; //Set accessed flag
for (i = FirstNeighbor(g,g.adjlist[j].data); i >= 0; i = NextNeighbor(g, g.adjlist[j].data, g.adjlist[i].data))
if (!visited[i]) DFS(g, g.adjlist[i].data); //Adjacent vertices that have not been accessed
}
void DFSTraverse(AdjGraph g) //Depth first traversal of G
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) visited[i] = false; //Initialize accessed tag data
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++) //Traverse from vertex 0
if (!visited[i]) DFS(g, g.adjlist[i].data);
}
int main()
{
AdjGraph g;
VertexType ch;
int i, num;
ArcNode* p;
InitG(g);
CreateVNde(g);
printf("\n");
for (i = 0; i < g.vexnum; i++)
{
printf("Create vertex%c Edge node of\n", g.adjlist[i].data);
printf("Enter the number of edge nodes to create:");
scanf("%d", &num);
CreateANode(g, g.adjlist[i].data, num);
printf("\n");
}
PrintG(g);
CountDegree(g);
printf("\n");
printf("\n Undirected graph G The number of vertices is:%d,The number of sides is:%d\n", g.vexnum, g.edgenum);
printf("\n Output depth first search results:");
DFSTraverse(g);
return 0;
}
Operation results
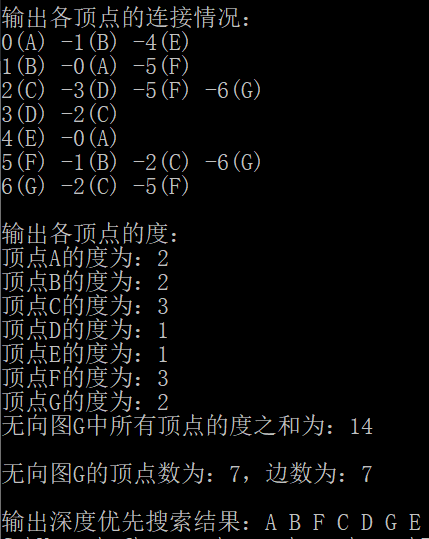
Program analysis
- Space complexity: from the function call stack. In the worst case, the recursion depth is O(|V|); in the best case, O(1).

- Time complexity = time required to access each node + time required to explore each edge.
- When the adjacency table storage method is adopted: it takes O(|V|) time to access | V vertices, and it takes O(|E|) time to find the adjacency points of each vertex. The time complexity = O(|V|+|E|).