Catalog
What is a heap?
Heap is a data structure that can be used to implement priority queues
Big root pile
Big root heap, as the name implies, is the largest root node. First, we use the process of building small root heap to learn the idea of heap.
Heap
The following figure shows the process of small root piling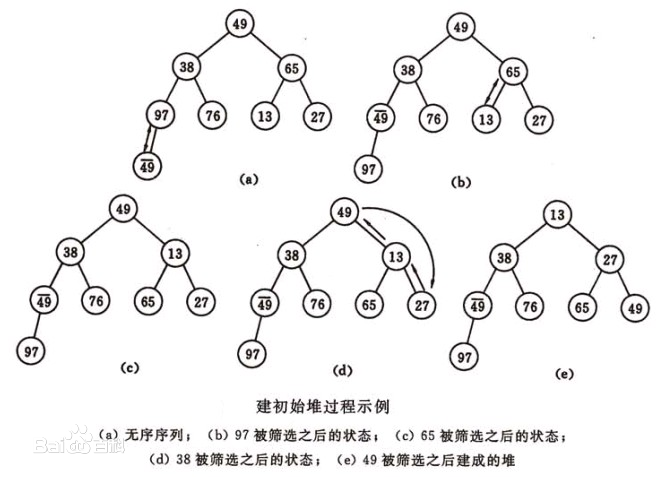
Heap operation
- Go up
- Sink
- insert
- Eject
- Crest
-
Heap sort
STL heap
include in Library
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int x,int y)
{
return x>y;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> a;
int num,n=10;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
num = rand()%(233*2);
a.push_back(num);
}
for(vector<int>::iterator i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
{
cout<<*i<<ends;
}cout<<endl<<endl;
make_heap(a.begin(),a.end());//Default big root heap
for(vector<int>::iterator i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
{
cout<<*i<<ends;
}cout<<endl<<endl;
make_heap(a.begin(),a.end(),cmp);//Homemade little root pile
for(vector<int>::iterator i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
{
cout<<*i<<ends;
}cout<<endl<<endl;
a.push_back(2333);
push_heap(a.begin(),a.end(),cmp);//Add new elements to the heap
for(vector<int>::iterator i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
{
cout<<*i<<ends;
}cout<<endl<<endl;
a.pop_back(); //Delete tail
for(vector<int>::iterator i=a.begin();i!=a.end();i++)
{
cout<<*i<<ends;
}cout<<endl<<endl;
getchar();getchar();getchar();getchar();
return 0;
}STL queue
include in Library
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct student{
int grade;
string name;
};
struct cmp{
bool operator() (student s1,student s2){
return s1.grade < s2.grade;
}
};
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int n=10,num;
/*
1. push [Join the team and get to the end of the team]
2. pop [Team leader element out of the team]
3. size [Return the number of elements in the queue]
4. front [Return the first element in the queue]
5. back [Return the last element in the queue]
6. empty [Judge whether the queue is empty]
*/
//Cout < < queue: < endl;
queue<int> a;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
num = rand()%233;
a.push(num);
}
//Sequence length
cout<<a.size()<<endl;
//Sequence header element
cout<<a.front()<<endl;
//Sequence tail element
cout<<a.back()<<endl;
//Whether the sequence is empty
while(!a.empty()){
cout<<a.front()<<ends;
a.pop();
}cout<<endl<<endl;
priority_queue<int> pq_1;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
num = rand()%233;
pq_1.push(num);
}
//By default, the highest value is at the head of the team (descending)
while(!pq_1.empty()){
//Note that the access header element here is. top
cout<<pq_1.top()<<ends;
pq_1.pop();
}cout<<endl;
//In the following cases, the smaller one is at the head of the team (ascending)
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > pq_2;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
num = rand()%233;
pq_2.push(num);
}
while(!pq_2.empty()){
//Note that the access header element here is. top
cout<<pq_2.top()<<ends;
pq_2.pop();
}cout<<endl;cout<<endl;
//Operator overloading
priority_queue<student,vector<student>,cmp> q;
student s1,s2,s3;
s1.grade = 90;
s1.name = "Tom";
s2.grade = 80;
s2.name = "Jerry";
s3.grade = 100;
s3.name = "Kevin";
q.push(s1);
q.push(s2);
q.push(s3);
while(!q.empty()){
cout<<q.top().name<<":"<<q.top().grade<<endl;
q.pop();
}
getchar();
return 0;
}