What is a complete binary tree
Method 1
Depth first search, first search the left subtree, then the right subtree. When the traversing node is a leaf node, the depth of the leaf node is stored in the array, and finally judge whether the number is like a shape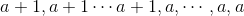 Or like
Or like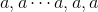 If so, then this tree is a complete binary tree, otherwise, it is not a complete binary tree. Take the following tree as an example. The code is as follows:
If so, then this tree is a complete binary tree, otherwise, it is not a complete binary tree. Take the following tree as an example. The code is as follows:
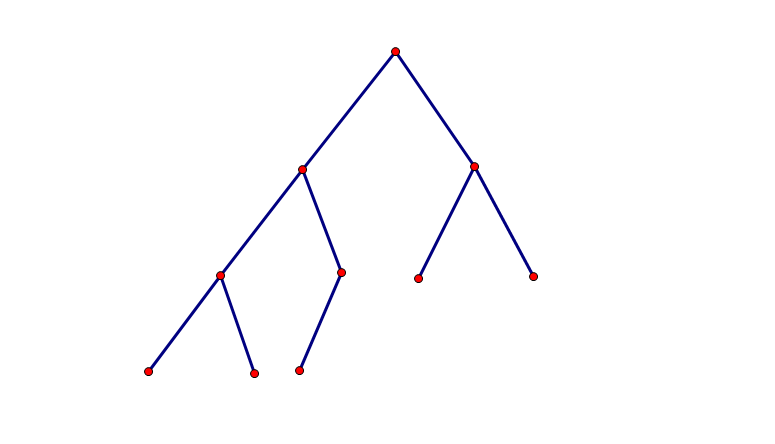
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct node
{
node* left;
node* right;
}*tree[1005], *root;
int deep[1005], cnt;
//Initialize tree building
void Init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1005; i++)
{
tree[i] = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
tree[i]->left = NULL;
tree[i]->right = NULL;
}
root = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root = tree[1];
root->left = tree[2];
root->right = tree[3];
tree[2]->left = tree[4];
tree[2]->right = tree[5];
tree[3]->left = tree[6];
tree[3]->right = tree[7];
tree[4]->left = tree[8];
tree[4]->right = tree[9];
tree[5]->left = tree[10];
}
//Depth first search for leaves
void Dfs(node* root, int dep)
{
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
deep[cnt++] = dep;
return;
}
if (root->left != NULL)
Dfs(root->left, dep + 1);
if (root->right != NULL)
Dfs(root->right, dep + 1);
}
//Output deep array
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
printf("%d%c", deep[i], i == cnt - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
//Determine whether the binary tree is complete
bool Check()
{
int f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++)
{
if (deep[i - 1] != deep[i])
{
if (deep[i - 1] == deep[i] + 1)
f++;
else
return false;
}
}
if (f <= 1)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
Init();
Dfs(root, 1);
Print();
puts(Check() ? "Yes" : "No");
}Method 2:
Breadth first search, layer by layer search. When the traversed node is a leaf node, the depth of the leaf node is stored in the array, and finally the number is judged to be the shape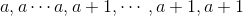 Or like
Or like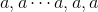 If so, then this tree is a complete binary tree, otherwise, it is not a complete binary tree.
If so, then this tree is a complete binary tree, otherwise, it is not a complete binary tree.
Take the tree above as an example and the code is as follows:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Pair pair<node*,int>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct node
{
node* left;
node* right;
}*tree[1005], *root;
int deep[1005], cnt;
//Initialize tree building
void Init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1005; i++)
{
tree[i] = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
tree[i]->left = NULL;
tree[i]->right = NULL;
}
root = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
root = tree[1];
root->left = tree[2];
root->right = tree[3];
tree[2]->left = tree[4];
tree[2]->right = tree[5];
tree[3]->left = tree[6];
tree[3]->right = tree[7];
tree[4]->left = tree[8];
tree[4]->right = tree[9];
tree[5]->left = tree[10];
}
//Depth first search for leaves
void Bfs(node* root)
{
queue<Pair>q;
q.push(Pair{ root,1 });
while (!q.empty())
{
Pair temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp.first->left == NULL && temp.first->right == NULL)
deep[cnt++] = temp.second;
if (temp.first->left != NULL)
q.push(Pair{ temp.first->left ,temp.second + 1 });
if (temp.first->right != NULL)
q.push(Pair{ temp.first->right ,temp.second + 1 });
}
}
//Output deep array
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
printf("%d%c", deep[i], i == cnt - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
}
//Determine whether the binary tree is complete
bool Check()
{
int f = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++)
{
if (deep[i - 1] != deep[i])
{
if (deep[i - 1] + 1 == deep[i])
f++;
else
return false;
}
}
if (f <= 1)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
Init();
Bfs(root);
Print();
puts(Check() ? "Yes" : "No");
}