catalogue
Header file and macro definition to be referenced in advance
Other data structures needed (chain stack and chain queue)
The structure of the binary tree used (binary linked list)
Decompose a binary tree T into three parts: root, left subtree and right subtree
Preorder traversal binary tree
Middle order traversal binary tree
Postorder traversal binary tree
Returns the depth of the binary tree
Count the leaves of binary tree T with count
Construction of binary tree by preorder
Preordered non recursive traversal
Medium order non recursive traversal
Postorder non recursive traversal
Header file and macro definition to be referenced in advance
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> // using namespace std; #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define OVERFLOW -1 #define UNSUCCESS 0 #define SUCCESS 1
Other data structures needed (chain stack and chain queue)
//Chain stack
typedef struct LSNode {
ElemType data;
struct LSNode* next;
}LSNode,*LStack;
void InitStack_LS(LStack& S); //Initialize chain stack
void DestroyStack_LS(LStack& S); //Destroy chain stack
Status StackEmpty_LS(LStack S); //Judge whether the stack is empty. If it is empty, return TRUE; otherwise, return FALSE
Status Push_LS(LStack& S, ElemType e); //Push element e onto stack
Status Pop_LS(LStack& S, ElemType& e); //The top element of stack S is out of the stack and returned with e
Status GetTop_LS(LStack S, ElemType& e); //Take the top element of stack S and return it with e
typedef struct LQNode {
ElemType data;
struct LQNode* next;
}LQNode,*QueuePtr;
typedef struct {
QueuePtr front; //Queue head pointer
QueuePtr rear; //Tail pointer
}LQueue;
void InitQueue_LQ(LQueue& Q); //Initialize queue Q
void DestroyQueue_LQ(LQueue& Q); //Destroy queue Q
Status EnQueue_LQ(LQueue& Q, ElemType e); //Insert element e at the end of queue Q
Status DeQueue_LQ(LQueue& Q, ElemType& e); //If the queue Q is not empty, delete the queue header element, use e to return its value, and return OK, otherwise ERROR;If you want to see the implementation of these two data structures, you can see
Data structure learning, chain queue
Data structure learning, chain stack
The structure of the binary tree used (binary linked list)
typedef struct BITNode {
TElemType data; //Data domain
struct BITNode* lchild; //Left child
struct BITNode* rchild; //Right child
}BiTNode, * BiTree, * ElemType;Its basic operation interface
void InitBiTree(BiTree& T); //Create an empty binary tree BiTree MakeBiTree(TElemType e, BiTree L, BiTree R); //Create a binary tree, where the value of the root node is e, and L and R are the left subtree and right subtree respectively void DestroyBitree(BiTree& T); //Destroy binary tree Status BiTreeEmpty(BiTree T); //Empty binary tree Status BreakBiTree(BiTree& T, BiTree& L, BiTree& R);//Decompose a binary tree T into three parts: root, left subtree and right subtree Status ReplaceLeft(BiTree& T, BiTree& LT); //Replace the left subtree. If t is not empty, replace the left subtree of T with LT and return the original left subtree of T with Lt Status ReplaceRight(BiTree& T, BiTree& RT); //Replace the right subtree. If t is not empty, replace the right subtree of T with RT, and return the original right subtree of T with RT //Advanced operation Status visit(TElemType a); //Recursive traversal Status PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //Preorder Status InOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //Middle order Status PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //Post order int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T); //Returns the depth of the binary tree void CountLeaf(BiTree T, int& count); //Count the leaves of binary tree T with count BiTree CreateBiTree(char* defBT, int& i); //Construction of binary tree by preorder //Non recursive traversal void LevelOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //level traversal Status PreOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //Preorder non recursive Status InOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType)); //Medium order non recursive Status PostOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType));//Postorder non recursive
basic operation
Create an empty binary tree
void InitBiTree(BiTree& T)
{
T = NULL;
}Create a binary tree, where the value of the root node is e, and L and R are the left subtree and right subtree respectively
BiTree MakeBiTree(TElemType e, BiTree L, BiTree R)
{
BiTree T;
T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
if (T != NULL)
{
T->data = e;
T->lchild = L;
T->rchild = R;
return T;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}Destroy binary tree
void DestroyBitree(BiTree& T)
{
if (T != NULL)//Simple and crude recursion
{
DestroyBitree(T->lchild);
DestroyBitree(T->rchild);
free(T);
}
}Empty binary tree
Status BiTreeEmpty(BiTree T)
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return TRUE;
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}Decompose a binary tree T into three parts: root, left subtree and right subtree
Status BreakBiTree(BiTree& T, BiTree& L, BiTree& R)
{
if (T != NULL)
{
L = T->lchild;
R = T->rchild;
T->lchild = NULL;
T->rchild = NULL;
return OK;
}
else
{
return OVERFLOW;
}
}Replace the left subtree. If t is not empty, replace the left subtree of T with LT and return the original left subtree of T with Lt
Status ReplaceLeft(BiTree& T, BiTree& LT)
{
BiTree temp;
if (T != NULL)
{
temp = T->lchild;
T->lchild = LT;
LT = temp;
return OK;
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}Replace the right subtree. If t is not empty, replace the right subtree of T with RT, and return the original right subtree of T with RT
Status ReplaceRight(BiTree& T, BiTree& RT)
{
BiTree temp;
if (T != NULL)
{
temp = T->rchild;
T->rchild = RT;
RT = temp;
return OK;
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}Advanced operation
//Access function
Status visit(TElemType a)
{
if (a != '#')
{
printf("%c", a);
return OK;
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}Recursive traversal
Preorder traversal binary tree
Status PreOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return OK;
}
if (visit(T->data) == ERROR)//root
{
return ERROR;
}
if (PreOrderTraverse(T->lchild, visit) == ERROR)//Left
{
return ERROR;
}
if (PreOrderTraverse(T->rchild, visit) == ERROR)//right
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}Middle order traversal binary tree
Status InOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return OK;
}
if (InOrderTraverse(T->lchild, visit) == ERROR)//Left
{
return ERROR;
}
if (visit(T->data) == ERROR)//root
{
return ERROR;
}
if (InOrderTraverse(T->rchild, visit) == ERROR)//right
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}Postorder traversal binary tree
Status PostOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
if (T == NULL)
{
return OK;
}
if (PostOrderTraverse(T->lchild, visit) == ERROR)//Left
{
return ERROR;
}
if (PostOrderTraverse(T->rchild, visit) == ERROR)//right
{
return ERROR;
}
if (visit(T->data) == ERROR)//root
{
return ERROR;
}
return OK;
}Returns the depth of the binary tree
int BiTreeDepth(BiTree T)
{
int depthLeft, depthRight;
if (T == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
depthLeft = BiTreeDepth(T->lchild);
depthRight = BiTreeDepth(T->rchild);
return 1 + (depthLeft > depthRight ? depthLeft : depthRight);
}
}Count the leaves of binary tree T with count
void CountLeaf(BiTree T, int& count)
{
if (T != NULL)
{
if (T->lchild == NULL && T->rchild == NULL)
{
count++;
}
CountLeaf(T->lchild, count);
CountLeaf(T->rchild, count);
}
}Construction of binary tree by preorder
BiTree CreateBiTree(char* defBT, int& i)
{
BiTree T;
TElemType ch;
ch = defBT[i++];
if (ch == '#')
{
InitBiTree(T);
}
else
{
T = MakeBiTree(ch, NULL, NULL);
T->lchild = CreateBiTree(defBT, i);
T->rchild = CreateBiTree(defBT, i);
}
return T;
}Non recursive traversal
level traversal
void LevelOrderTraverse(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
if (T != NULL)
{
LQueue Q;
InitQueue_LQ(Q);
BiTree p = T;
visit(p->data);
EnQueue_LQ(Q, p);
while (DeQueue_LQ(Q, p) == OK)
{
if (p->lchild != NULL)
{
visit(p->lchild->data);
EnQueue_LQ(Q, p->lchild);
}
if (p->rchild != NULL)
{
visit(p->rchild->data);
EnQueue_LQ(Q, p->rchild);
}
}
DestroyQueue_LQ(Q);
}
}The following three non recursive traversals can be seen
I can only say that this is a big man https://blog.csdn.net/Benja_K/article/details/88389039
https://blog.csdn.net/Benja_K/article/details/88389039
Preordered non recursive traversal
Status PreOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
BiTree p;
p = T;
LStack S;
InitStack_LS(S);
while (p != NULL || StackEmpty_LS(S) != TRUE)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
Push_LS(S, p);
visit(p->data);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
Pop_LS(S, p);
p = p->rchild;
}
}
DestroyStack_LS(S);
return OK;
}Medium order non recursive traversal
Status InOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
BiTree p;
p = T;
LStack S;
InitStack_LS(S);
while (p != NULL || StackEmpty_LS(S) != TRUE)
{
if (p != NULL)
{
Push_LS(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
Pop_LS(S, p);
visit(p->data);
p = p->rchild;
}
}
DestroyStack_LS(S);
return OK;
}Postorder non recursive traversal
Status PostOrderTraverse_U(BiTree T, Status(*visit)(TElemType))
{
LStack S;
InitStack_LS(S);
int top = -1;
int Stack[15];
BiTNode* p = T;
while (p != NULL || StackEmpty_LS(S) != TRUE)
{
if (p != NULL) {
Push_LS(S, p);
top++;
Stack[top] = 1;
p = p->lchild;
}
else
{
if (Stack[top] == 1)
{
GetTop_LS(S, p);
Stack[top] = 2;
p = p->rchild;
}
else
{
Pop_LS(S, p);
top--;
visit( p->data);
p = NULL;
}
}
}
DestroyStack_LS(S);
return OK;
}Testing of some interfaces
The binary tree tested is
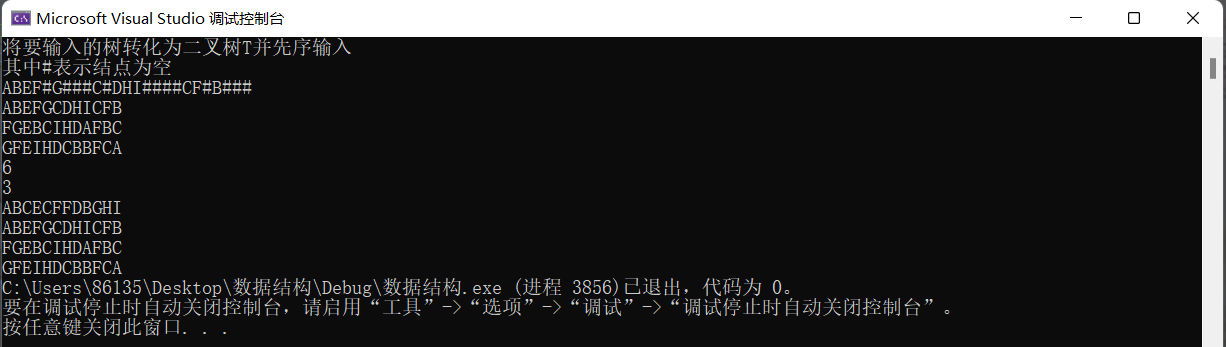
int main()
{
//ABEF#G###C#DHI####CF#B#### / / preamble
char defBT[100] = { '#' };
if (defBT != NULL)
{
printf("Convert the tree to be imported into a binary tree T And input in sequence\n");
printf("among#Indicates that the node is empty. \ n "");
//scanf("%s", defBT);
cin >> defBT;
getchar();
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
BiTree T;
int i = 0;
T = CreateBiTree(defBT, i);
PreOrderTraverse(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
InOrderTraverse(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
PostOrderTraverse(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
cout << BiTreeDepth(T) << endl;
int j = 0;
CountLeaf(T, j);
cout << j << endl;
LevelOrderTraverse(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
PreOrderTraverse_U(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
InOrderTraverse_U(T, visit);
cout << "\n";
PostOrderTraverse_U(T, visit);
}
There are many operations for binary tree, such as the copy of binary tree, the search of binary tree, how many nodes the binary tree has, and whether the binary tree is a complete binary tree, which is left to you to realize by yourself.