Dear friends, happy new year.
Hash table is essentially an array, and chain address is the array that stores the linked list.
The hash function is used to properly calculate a number to obtain the hash value of the number, and the hash table is searched, inserted and deleted according to the hash value.
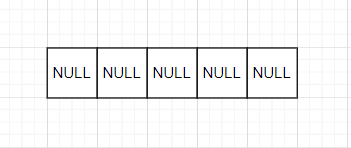
Suppose this is a hash table H with a capacity of 5 and a length of 0; All five pointers are NULL;
First, we have a number: 3; Assume that the hash value obtained is 2, as shown in the figure:
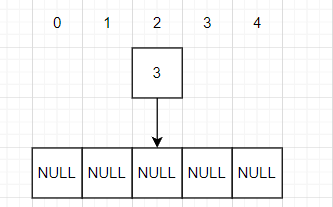
Then make 3 the first node of the third linked list in the array storing the five linked lists.
As shown in the figure:
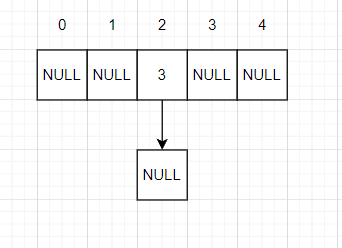
This is the operation of inserting and deleting. You can also learn from the operation of single linked list.
Let's see how to achieve it
catalogue
Header file and macro definition to be referenced in advance
The structure of the hash table used
Header file and macro definition to be referenced in advance
#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> // //using namespace std; #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define OVERFLOW -1 #define UNSUCCESS 0 #define SUCCESS 1 typedef int ElemType; typedef int Status; typedef int KeyType;
The structure of the hash table used
//(chain address)
typedef struct {
KeyType Key;
//Other data can be stored here
}RecordType, RcdType;
typedef struct Node { //In fact, this pointer is a linked list
RcdType r;
struct Node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct {
Node** rcd; //Pointer to array
int size; //Capacity of hash table
int count; //Number of records contained in the current table
int(*hash)(KeyType key, int hashSize); //Function pointer variable, select hash function
}HashTable;Hash function used
int hash(int key, int hashSize)
{//Hash function, hashSize is the length of address space (the capacity of hash table)
return (3 * key) % hashSize;
}There are many kinds of hash functions
1. Direct addressing method. Your number is 98. Go directly to H.rcd[98]. hash = 98
2. In addition to the remainder method, hash = keyword% (a number you like (generally the capacity of the hash table)) is also my choice.
3. Digital analysis method,
4. Folding method,
5. Square middle method,
Wait. 3, 4, 5 if you are interested, just search it. I won't talk about it.
Its basic operation interface
Status InitHash(HashTable& H, int size, int(*hash)(KeyType, int)); //Initialize hash table Status DestroyHash(HashTable& H); //Destroy hash table Node* SearchHash(HashTable H, KeyType key); //lookup Status InsertHash(HashTable& H, RcdType e); //insert Status DeleteHash(HashTable& H, KeyType key, RcdType& e); //delete void HashTraverse(HashTable H); //ergodic
Initialize hash table
Status InitHash(HashTable& H, int size, int(*hash)(KeyType, int))
{
H.rcd = (Node**)malloc(size*sizeof(Node*));
if (H.rcd != NULL)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
H.rcd[i] = NULL;
}
H.size = size;
H.hash = hash;
H.count = 0;
return OK;
}
else
{
return OVERFLOW;
}
}Destroy hash table
Status DestroyHash(HashTable& H)
{
if (H.rcd != NULL)
{
Node* np, * nt;
for (int i = 0; i < H.size; i++)
{
np = H.rcd[i];
while (np != NULL)
{
nt = np;
np = np->next;
free(nt);
}
}
H.size = 0;
H.count = 0;
H.hash = NULL;
return OK;
}
else
{
return OVERFLOW;
}
}lookup
Node* SearchHash(HashTable H, KeyType key)
{
int p = H.hash(key, H.size);
Node* np;
for (np = H.rcd[p]; np != NULL; np = np->next)
{
if (np->r.Key == key)return np;
}
return NULL;
}insert
Status InsertHash(HashTable& H, RcdType e)
{
int p;
Node* np;
np = SearchHash(H, e.Key);
if (np == NULL)
{
p = H.hash(e.Key, H.size);
np = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (np != NULL)
{
np->r = e;
np->next = H.rcd[p];
H.rcd[p] = np;
H.count++;
return OK;
}
else
{
return OVERFLOW;
}
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}delete
Status DeleteHash(HashTable& H, KeyType key, RcdType& e)
{
Node* n;
n = SearchHash(H, key);
if (n != NULL)
{
int p = H.hash(key, H.size);
Node* np, * nq;
np = H.rcd[p];
nq = NULL;
while (np != NULL)
{
if (np->r.Key != key)
{
nq = np;
np = np->next;
}
else
{
e = np->r;
if (nq == NULL)//Header
{
H.rcd[p] = np->next;
}
else//Not a header
{
nq->next = np->next;
}
break;
}
}
H.count--;
free(np);
return OK;
}
else
{
return ERROR;
}
}ergodic
void HashTraverse(HashTable H)
{
if (H.rcd != NULL)
{
Node* np, * nq;
for (int i = 0; i < H.size; i++)
{
np = H.rcd[i];
if (np == NULL)
{
printf(" #");
}
else
{
while (np)
{
printf("%3d", np->r.Key);
np = np->next;
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}Testing of some interfaces
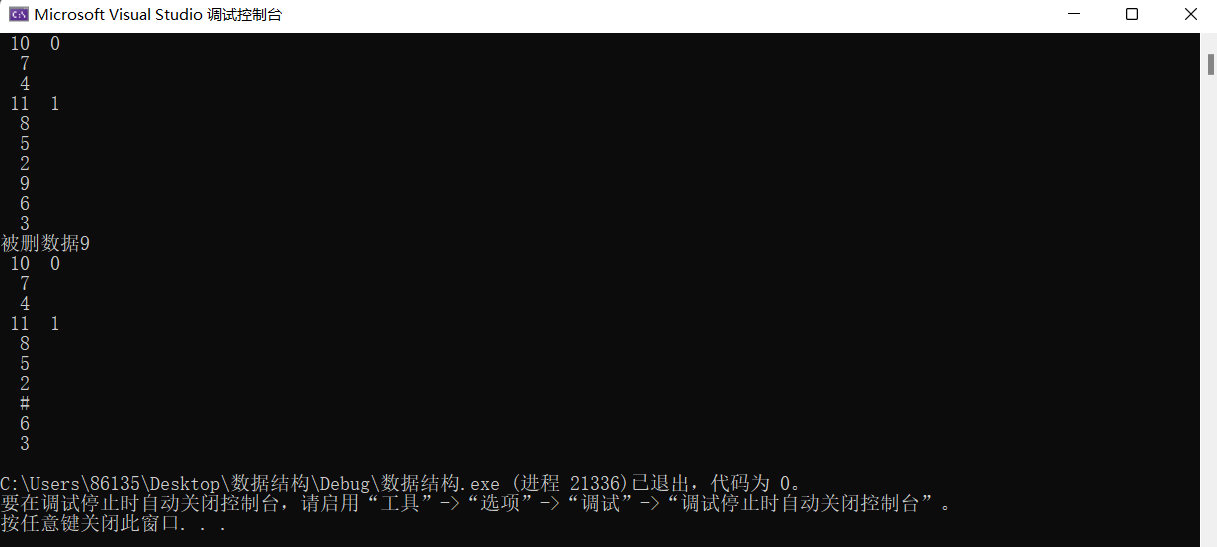
int main()
{
HashTable H;
InitHash(H, 10, hash);
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
RcdType e;
e.Key = i;
InsertHash(H, e);
}
HashTraverse(H);
RcdType e1;
DeleteHash(H, 9, e1);
printf("Deleted data%d\n", e1.Key);
HashTraverse(H);
DestroyHash(H);
}
In fact, think about it. If it's not a linked list, it's a B tree!!!, The array for storing the B tree, ha ha.