Personal blog portal, welcome to visit
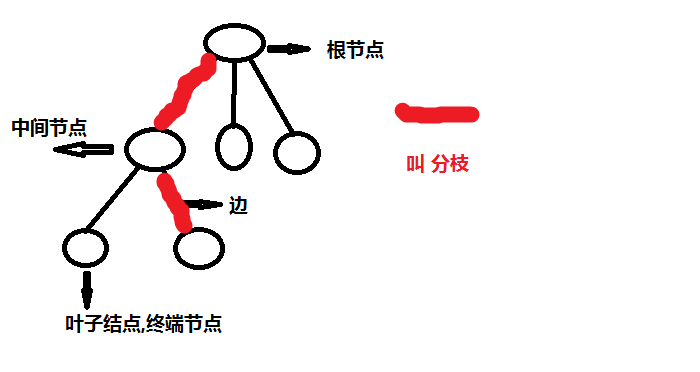
Tree:
Definition: a tree has at most one root node. The terminal of each path is called terminal node, also known as leaf node. A node that is neither a root nor a leaf is called an intermediate node, and the line between the node and the node is called an edge. From bottom to top, it is called height * *, and from top to bottom, it is called * * * depth * * *.
PS: the overall height and depth of the tree are the maximum.
Degree: if the current node has n child nodes, it is called n degree.
Binary tree
Definition: each node in the tree is allowed to have at most two nodes.
Full binary tree
Definition: each layer is a binary tree with full nodes (2 nodes) except the last layer.
Complete binary tree
Definition: only the last layer is allowed to have vacancies, and the vacancy mode is a right to left binary tree.
ps: full binary tree is a special situation of complete binary tree.
balanced binary tree
Definition: for any node in the tree, the height difference between the left and right subtrees shall not exceed 1.
ps: a complete binary tree must be a balanced binary tree.
Sorted binary tree
Definition: the value of the left child is smaller than that of the father, and the value of the right node is larger than that of the parent node.
Properties of binary tree
- k k K-layer full binary tree, the number of leaf nodes is $2^{k-1}$
- k k The k-layer full binary tree has a total number of nodes 2 k − 1 2^{k}-1 2k−1
- For any binary tree, the node with degree 0 is one less than the node with degree 2. ( n 0 = n 2 + 1 n_0=n_2+1 n0 = n2 + 1),PS: for a complete binary tree, there is at most one node with degree 1.
- One has n n A complete binary tree with n nodes. Its depth is $K=\lfloor log2^{n}\rfloor +1 $(rounded down). For example, 3.33 takes 3
- Yes, one n n A complete binary tree with n nodes, starting from 1 and numbering from top to bottom and from left to right,
- i = 1 i=1 i=1 is the root node.
- $2i<=n $ , i i i has left subtree, otherwise not.
- 2 i + 1 < = n 2i+1<=n 2I + 1 < = n, i i i has a right subtree, otherwise not.
- from 1 1 1 ~ $\displaystyle\frac{n}2 of between of section spot all yes father section spot , All nodes between are parent nodes, The parent nodes of \ n \ frayst are all rounded down to $display 2}.
Traversal of binary tree
- Depth (recursive version)
- Preorder traversal: left and right roots
- Middle order traversal: left root right
- Post order traversal: left and right roots
- Traverse the sequence from top to bottom, from left to right:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int nValue;
struct Node *pLeft;
struct Node *pRight;
}BinaryTree;
typedef struct node3
{
BinaryTree *nValue;
struct node3 *pNext;
}MyQueue;
typedef struct node4
{
int nCount;
MyQueue* pHead;
MyQueue *pTail;
}Queue;
BinaryTree * CreateTree();
void RecPreOrderTraversal(BinaryTree *pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
//Preorder traverses around the root
printf("%d ",pRoot->nValue);
RecPreOrderTraversal(pRoot->pLeft);
RecPreOrderTraversal(pRoot->pRight);
}
void RecInOrderTraversal(BinaryTree *pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
//Middle order traversal left root right
RecInOrderTraversal(pRoot->pLeft);
printf("%d ",pRoot->nValue);
RecInOrderTraversal(pRoot->pRight);
}
void RecLastOrderTraversal(BinaryTree *pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
//Postorder traversal of left and right roots
RecLastOrderTraversal(pRoot->pLeft);
RecLastOrderTraversal(pRoot->pRight);
printf("%d ",pRoot->nValue);
}
void q_Init(Queue **pQueue)
{
if(pQueue == NULL)return;
*pQueue = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
(*pQueue)->nCount = 0;
(*pQueue)->pHead = NULL;
(*pQueue)->pTail = NULL;
}
void q_Push(Queue *pQueue,BinaryTree *nNum)
{
MyQueue *pTemp = NULL;
if(pQueue == NULL)return;
pTemp = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
pTemp->nValue = nNum;
pTemp->pNext = NULL;
if(pQueue->pHead == NULL)
{
pQueue->pHead = pTemp;
}
else
{
pQueue->pTail->pNext = pTemp;
}
pQueue->pTail = pTemp;
pQueue->nCount++;
}
BinaryTree* q_Pop(Queue *pQueue)
{
MyQueue *pDel = NULL;
BinaryTree *Temp = NULL;
if(pQueue == NULL || pQueue->pHead == NULL)return NULL;
pDel = pQueue->pHead;
Temp = pDel->nValue;
pQueue->pHead = pQueue->pHead->pNext;
free(pDel);
pDel = NULL;
pQueue->nCount--;
if(pQueue->nCount == 0)
{
pQueue->pTail = NULL;
}
return Temp;
}
int q_IsEmpty(Queue *pQueue)
{
if(pQueue == NULL )return -1;
return pQueue->nCount ? 0:1;
}
void EveryTravelsalTree(BinaryTree *Tree)
{
//level traversal
Queue *M_Queue = NULL;
BinaryTree *Temp = NULL;
if(Tree == NULL)return;
q_Init(&M_Queue);
q_Push(M_Queue,Tree);
while(!q_IsEmpty(M_Queue))
{
Temp = q_Pop(M_Queue);
printf("%d ",Temp->nValue);
if(Temp->pLeft != NULL)
{
q_Push(M_Queue,Temp->pLeft);
}
if (Temp->pRight != NULL)
{
q_Push(M_Queue,Temp->pRight);
}
}
}
Example binary tree
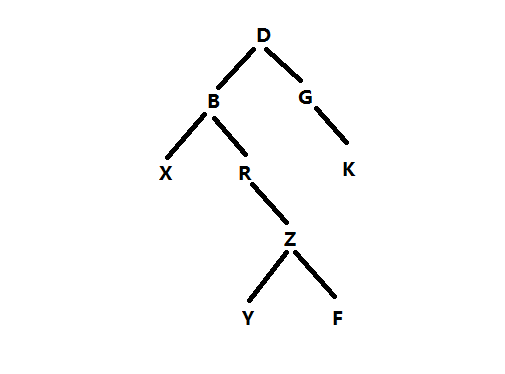
Preamble: X Y F X R B K G D
Middle order: X B R Y Z F D G K
Later: X Y F Z R B K G D
Creation of binary tree
Manually create binary tree, the slowest and most basic zero technology creation method
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int nValue;
struct Node *pLeft;
struct Node *pRight;
}BinaryTree;
BinaryTree * CreateTree()
{
BinaryTree *pRoot = NULL;
pRoot = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot ->nValue = 1;
//Left 2 of root
pRoot->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot->pLeft->nValue = 2;
//Left left 4
pRoot->pLeft->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot->pLeft->pLeft->nValue = 4;
pRoot->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft = NULL;
pRoot->pLeft->pLeft->pRight = NULL;
//Left right 5
pRoot->pLeft->pRight = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot->pLeft->pRight->nValue = 5;
pRoot->pLeft->pRight->pLeft = NULL;
pRoot->pLeft->pRight->pRight = NULL;
//Right 3 of root
pRoot->pRight = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot->pRight->nValue = 3;
pRoot->pRight->pRight = NULL;
//Right left 6
pRoot->pRight->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pRoot->pRight->pLeft->nValue = 6;
pRoot->pRight->pLeft->pLeft = NULL;
pRoot->pRight->pLeft->pRight = NULL;
return pRoot;
}
Create binary tree recursively (reverse sequence creates binary tree)
The binary tree is created according to the characteristics of sequence traversal
void DynamicRecPreOrder(BinaryTree **Temp)
{
//The dynamic creation of binary tree in the preamble is called recursive creation of binary tree or deserialization creation of binary tree
int j;
scanf_s("%d",&j);
if(Temp==NULL)return;
if(j == 0)return;
*Temp = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*Temp)->nValue = j;
(*Temp)->pLeft = NULL;
(*Temp)->pRight = NULL;
DynamicRecPreOrder(&((*Temp)->pLeft));
DynamicRecPreOrder(&((*Temp)->pRight));
return;
}
Dynamic creation of binary tree (using the situation of array)
According to the properties of binary tree 5
BinaryTree *DynamicArryCreateTree(int Temp[],int Num)
{
BinaryTree *Templ = NULL;
int i = 0;
int m = 0;
Templ = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree)*Num);
for(;i<Num;i++)
{
Templ[i].nValue = Temp[i];
Templ[i].pLeft = NULL;
Templ[i].pRight = NULL;
}
for (m = 0; m <= (Num/2) - 1 ; m++)
{
if(2*m+1<Num)
{
Templ[m].pLeft = &Templ[2*m+1];
}
if(2*m+2<Num)
{
Templ[m].pRight = &Templ[2*m+2];
}
}
return Templ;
}
Cyclic advanced traversal of binary tree (non recursive)
Narrative process
- Application stack
- Inspection parameters
- (preamble: print node) node stacking
- Judge whether the node has left
- Yes, repeat 3 4
- No, next step (middle order: print node)
- Pop up the top of the stack. Check whether the pop-up top is empty
- Yes, it's over
- None, repeat 5
- Judge whether the pop-up node has right
- Yes, turn the right node into the current node, and then repeat 3 and 4
- None, repeat 5
Using loop to realize preorder traversal
void OnRecTraversal(BinaryTree* Temp)
{
Stack *m_Stack = NULL;
if(Temp == NULL)return;
s_Init(&m_Stack);
while(1)
{
while (Temp)
{
printf("%d\n",Temp->nValue);
s_Push(m_Stack,Temp);
Temp = Temp->pLeft;
}
//Stack top pop-up
Temp = s_Pop(m_Stack);
//Judge whether the node is empty
if(Temp == NULL)return;
//Right processing
Temp = Temp->pRight;
}
}
Using loop to realize middle order traversal
void MidTraversal(BinaryTree* Temp)
{
Stack *m_Stack = NULL;
if(Temp == NULL)return;
s_Init(&m_Stack);
while(1)
{
while (Temp)
{
s_Push(m_Stack,Temp);
Temp = Temp->pLeft;
}
//Stack top pop-up
Temp = s_Pop(m_Stack);
//Judge whether the node is empty
if(Temp == NULL)return;
printf("%d\n",Temp->nValue);
//Right processing
Temp = Temp->pRight;
}
}
Using loop to realize post order traversal
void RecLastOrderTraversal(BinaryTree* Temp)
{
Stack *m_Stack = NULL;
BinaryTree* pTemp = 0;
if(Temp == NULL)return;
s_Init(&m_Stack);
while(1)
{
while (Temp)
{
s_Push(m_Stack,Temp);
Temp = Temp->pLeft;
}
if(m_Stack->pTop == NULL)return;
if(m_Stack->pTop->nValue->pRight == NULL||m_Stack->pTop->nValue->pRight == pTemp)
{
pTemp = s_Pop(m_Stack);
printf("%d\n",pTemp->nValue);
}else
{
Temp = m_Stack->pTop->nValue->pRight;
}
}
return;
}
Insert a node into a binary tree
First, write a search API
Find a node in a binary tree
BinaryTree * Chop(BinaryTree *pRoot,int nNum)
{
Queue *pQueue = NULL;
BinaryTree *pTemp = NULL;
if(pRoot == NULL)return NULL;
q_Init(&pQueue);
//Root in the team
q_Push(pQueue,pRoot);
while(!q_IsEmpty(pQueue))
{
pTemp = q_Pop(pQueue);
if(pTemp->nValue == nNum)
{
//Remember to clear the queue
return pTemp;
}
//Join the team left and right
if(pTemp->pLeft != NULL)
{
q_Push(pQueue,pTemp->pLeft);
}
if(pTemp->pRight != NULL)
{
q_Push(pQueue,pTemp->pRight);
}
}
return NULL;
}
Insert a node in a binary tree, input direction and value
//The incoming tree is placed under the node, and the value and direction are put in
void InsertNode(BinaryTree **pRoot,int nNum,int nValue,int nDirection)
{
BinaryTree *pNode = NULL;
BinaryTree *pTemp = NULL;
if(pRoot == NULL || *pRoot == NULL)return;
//lookup
pNode = Chop(*pRoot,nNum);
//testing
//non-existent
if(pNode == NULL)
{
printf("Value does not exist~~~\n");
return;
}
//existence
pTemp = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pTemp->nValue = nValue;
pTemp->pLeft = NULL;
pTemp->pRight = NULL;
//Inserted direction
if(nDirection == LEFT)
{
pTemp->pLeft = pNode->pLeft;
pNode->pLeft = pTemp;
return;
}
if(nDirection == RIGHT)
{
pTemp->pRight = pNode->pRight;
pNode->pRight = pTemp;
return;
}
}
Create a sort binary tree
Create process
- Put value into node
- Check whether the tree is an empty tree. If it is an empty node, the new node is the root and ends
- If the tree is not empty
Compare node values
If the value is larger than the node value, go to the right subtree
- Empty tree: put into node
- Non empty tree: go to the right and repeat step 3
If the value is smaller than the node value, go to the left subtree
- Empty tree: put into node
- Non empty tree: go left and repeat step 3
If the value is the same, it violates the steps of sorting binary tree, releases the new node space, and ends
void InsertNode(BinaryTree **pRoot,int nNum)
{
BinaryTree *pTemp = NULL;
BinaryTree *pMark = NULL;
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
pTemp = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
pTemp->nValue = nNum;
pTemp->pLeft = NULL;
pTemp->pRight = NULL;
//Empty tree
if(*pRoot == NULL)
{
*pRoot = pTemp;
return;
}
//Marker root
pMark = *pRoot;
while(1)
{
//The value of the new node is small
if(nNum < pMark->nValue)
{
//left indent
if(pMark->pLeft == NULL)
{
pMark->pLeft = pTemp;
return;
}
//Non empty left
pMark = pMark->pLeft;
}
//The value of the new node is large
else if(nNum > pMark->nValue)
{
//right indent
if(pMark->pRight == NULL)
{
pMark->pRight = pTemp;
return;
}
//Non empty right
pMark = pMark->pRight;
}
//The new value already exists, which violates the end of nature
else
{
free(pTemp);
pTemp = NULL;
return;
}
}
}
BinaryTree *CreateSrtTree(int arr[],int nLength)
{
BinaryTree *pRoot = NULL;
int i;
if(arr == NULL || nLength <=0)return NULL;
for(i = 0;i<nLength;i++)
{
InsertNode(&pRoot,arr[i]);
}
return pRoot;
}
Delete a node from a sorted binary tree
Deleted process
- Leaf node, delete directly
- If there is a child (that is, there is only one left subtree or right subtree), delete the current node and replace it with a child
- For two children, find the leftmost node on the right or the rightmost node on the left, overwrite the value of the found node with the value of the deleted node, and then proceed to steps 1 and 2
The code to find a node in a sorted binary tree
//Parameters: tree, searched value, address of deleted node, father of deleted node
void Search(BinaryTree *pTree,int nNum,BinaryTree **pDel,BinaryTree **pDelFather)
{
if(pTree == NULL)return;
while(pTree)
{
//End of finding and remembering the deleted location
if(pTree->nValue == nNum)
{
*pDel = pTree;
return;
}
//The search value is smaller than that of the current node. Remember the father of the deleted node and go left
else if(pTree->nValue > nNum)
{
*pDelFather = pTree;
pTree = pTree->pLeft;
}
//The search value is larger than that of the current node. Remember the father of the deleted node and go to the right
else
{
*pDelFather = pTree;
pTree = pTree->pRight;
}
}
//After the search, the pointer of the parent of the empty flag deletion node was not found
*pDelFather = NULL;
return ;
}
Delete a node code in the sorted binary tree
void DelOneChild(BinaryTree **pRoot, BinaryTree *pDel,BinaryTree *pDelFather)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
//The deleted node is the root
if(pDelFather == NULL)
{
*pRoot = pDel->pLeft ? pDel->pLeft:pDel->pRight;
free(pDel);
pDel = NULL;
return;
}
//Detect whether the deleted node is the father's left or right
if(pDel == pDelFather->pLeft)
{
//Associate the child whose node is not empty with pdelfather
pDelFather->pLeft = pDel->pLeft ? pDel->pLeft:pDel->pRight;
free(pDel);
pDel = NULL;
return;
}
if(pDel == pDelFather->pRight)
{
pDelFather->pRight = pDel->pLeft ? pDel->pLeft:pDel->pRight;
free(pDel);
pDel = NULL;
return;
}
}
void DelNode(BinaryTree **pTree,int nNum)
{
BinaryTree *pDel = NULL;
BinaryTree *pDelFather = NULL;
BinaryTree *pMark =NULL;
if(pTree == NULL || *pTree == NULL)return;
//lookup
Search(*pTree,nNum,&pDel,&pDelFather);
//Can't find
if(pDel == NULL)return;
//find
//There are two children looking right for the youngest
if(pDel->pLeft!= NULL && pDel->pRight != NULL)
{
pMark = pDel;
//Move to right
pDelFather = pDel;
pDel = pDel->pRight;
//Find the leftmost one on the right
while(pDel->pLeft)
{
pDelFather = pDel;
pDel = pDel->pLeft;
}
//Value override
pMark->nValue = pDel->nValue;
}
//Delete those with or without children
DelOneChild(pTree,pDel,pDelFather);
}
A sort binary tree is converted into a sort bidirectional linked list
technological process
- According to the characteristics of middle order traversal, the left root is right
- Take the left of the binary tree as the upper pointer of the linked list, and the right of the binary tree as the lower pointer of the linked list
- Traverse the output position in the middle order, and turn the binary tree into a linked list connection
code
void SortTreeToList(BinaryTree *pRoot, BinaryTree **pHead,BinaryTree **pTail)
{
if(pRoot == NULL)return;
if(pHead == NULL || pTail == NULL)return;
//Find left
SortTreeToList(pRoot->pLeft,pHead,pTail);
//Add node to tail
if(*pHead == NULL)
{
*pHead = pRoot;
}
else
{
//Bidirectional pointing Association
//left = previous pre
//right = next
(*pTail)->pRight = pRoot;
pRoot->pLeft = *pTail;
}
*pTail = pRoot;
//Find the right side
SortTreeToList(pRoot->pRight,pHead,pTail);
}
Two rotations of balanced binary tree
Depth of ordinary binary tree: the number of elements in the stack after traversal
Turn the one-step balanced binary tree into a balanced binary tree
Dextral
Add a father's pointer to the original binary tree
Add a node F to the left subtree of the left subtree for right rotation
Break off the long side of the intersection of A and B - D - F
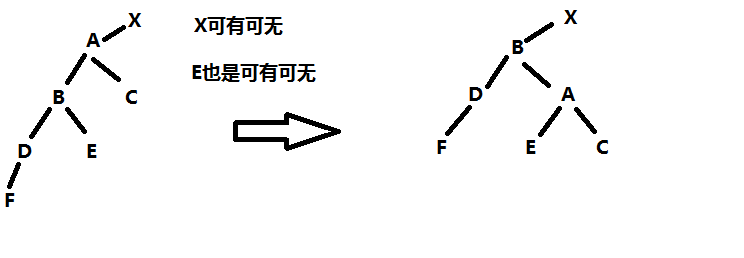
Two steps:
Note: a - > peleft = pmark
Deal with your son first:
- A ->Father->left = pmark
- pmark->right = A
- pmark = pmark->right
Father: - pmark ->father = A->father
- A->father = pmark
- pmark->right->father = A
Sinistral
Opposite to right rotation
Create an unbalanced binary tree
void CreateBiTree(BinaryTree **root)
{
if(root == NULL)return;
(*root) = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->nValue = 1;
(*root)->pFather = NULL;
//Left subtree
(*root)->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->pLeft->nValue = 2;
(*root)->pLeft->pFather = *root;
//Right subtree
(*root)->pRight = NULL;
//Left left
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->nValue = 3;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pFather = (*root)->pLeft;
//Left left left
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft->nValue = 5;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft->pFather = (*root)->pLeft->pLeft;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft = NULL;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pLeft->pRight = NULL;
//Left left right
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pRight = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pRight ->nValue = 6;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pRight ->pFather = (*root)->pLeft->pLeft;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pRight ->pLeft = NULL;
(*root)->pLeft->pLeft->pRight ->pRight = NULL;
//Left right
(*root)->pLeft->pRight = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
(*root)->pLeft->pRight->nValue = 4;
(*root)->pLeft->pRight->pFather = (*root)->pLeft;
(*root)->pLeft->pRight->pLeft = NULL;
(*root)->pLeft->pRight->pRight = NULL;
}
Right hand, left hand code
void RightRotate(BinaryTree **pTree)
{
BinaryTree *pMark = NULL;
if(pTree == NULL)return;
//Right hand mark left
pMark = (*pTree)->pLeft;
//Dealing with son relationship
(*pTree)->pLeft = pMark->pRight;
pMark->pRight = *pTree;
//Does the fulcrum father exist
if((*pTree)->pFather != NULL)
{
//Associate the left of the fulcrum with the father of the fulcrum
((*pTree)->pFather->pLeft == *pTree)?((*pTree)->pFather->pLeft = pMark):((*pTree)->pFather->pRight= pMark);
}
//Related father
//Does the left of the fulcrum exist
if((*pTree)->pLeft != NULL)
{
(*pTree)->pLeft->pFather = *pTree;
}
pMark->pFather = (*pTree)->pFather;
(*pTree)->pFather = pMark;
//The fulcrum is the root node that changes after rotation
if(pMark->pFather == NULL)
{
*pTree = pMark;
}
}
void LeftRotate(BinaryTree **pTree)
{
BinaryTree *pMark = NULL;
if(pTree == NULL)return;
//Right hand mark left
pMark = (*pTree)->pRight;
//Dealing with son relationship
(*pTree)->pRight = pMark->pLeft;
pMark->pLeft = *pTree;
//Does the fulcrum father exist
if((*pTree)->pFather != NULL)
{
//Associate the left of the fulcrum with the father of the fulcrum
((*pTree)->pFather->pLeft == *pTree)?((*pTree)->pFather->pLeft = pMark):((*pTree)->pFather->pRight= pMark);
}
//Related father
//Does the left of the fulcrum exist
if((*pTree)->pRight != NULL)
{
(*pTree)->pRight->pFather = *pTree;
}
pMark->pFather = (*pTree)->pFather;
(*pTree)->pFather = pMark;
//The fulcrum is the root node that changes after rotation
if(pMark->pFather == NULL)
{
*pTree = pMark;
}
}