📋 Personal profile
- 💖 About the author: Hello, I'm Daniel 😜
- 📝 Personal homepage: Hall owner a Niu🔥
- 🎉 Support me: like 👍+ Collection ⭐ Email + message 📝
- 📣 Series column: web development🍁
- 💬 Maxim: so far, all life is written with failure, but it doesn't prevent me from moving forward! 🔥

🍒 preface
Today, I'd like to summarize the data types in javascript. I hope you can gain something.
🍊 other
🍇 Input and output statements in js
| method | explain | ascription |
|---|---|---|
| alert(msg) | Browser pop-up alert box | browser |
| console.log(msg) | Browser console printout information | browser |
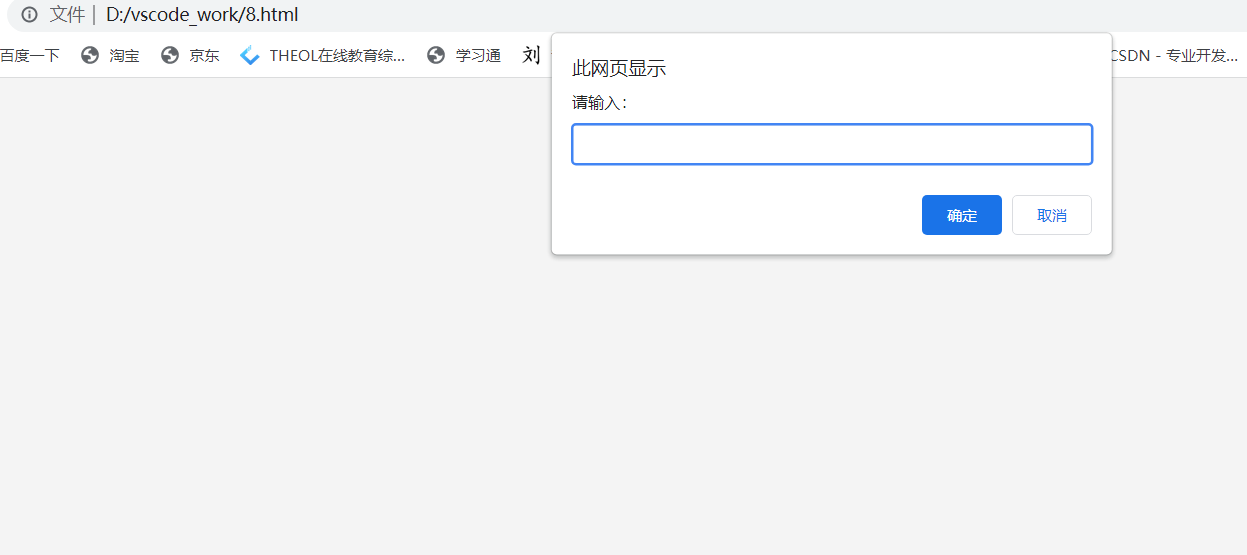
| prompt(info) | The browser pops up an input box, which can be entered by the user | browser |
Note: the input obtained by prompt(info) is of string type, which is similar to input() in python.
<script>
prompt("Please enter:");
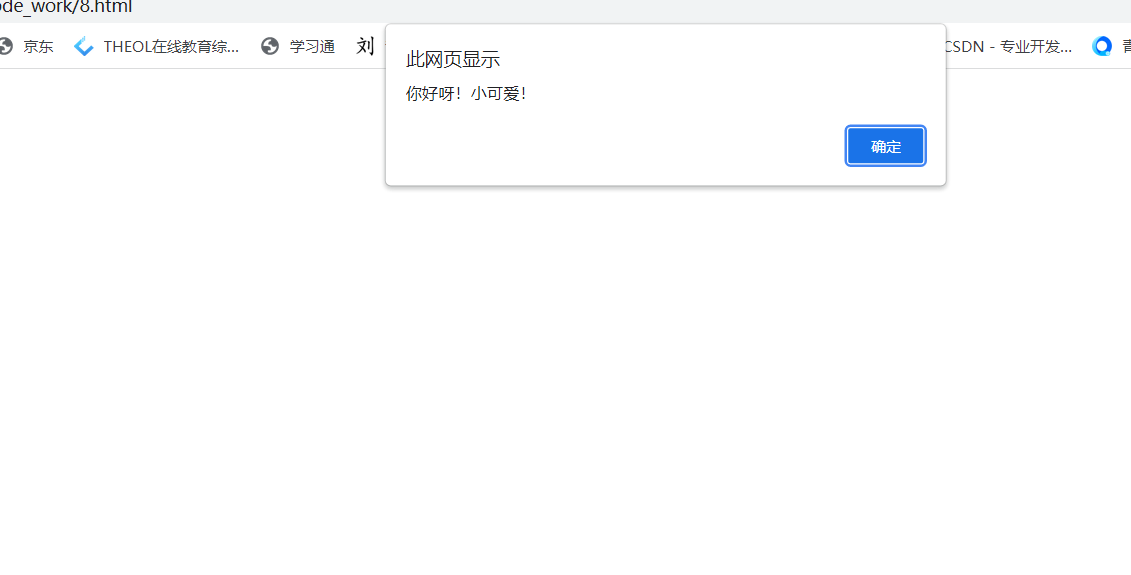
alert('How do you do! Cutie!');
console.log('Daniel is the most handsome!');
</script>

🍇 Comments in js
| Single-Line Comments | multiline comment |
|---|---|
| // | /* */ |
Note: the comments in css are / * * /. It doesn't matter if you can't remember the comments in various languages. Just remember the shortcut key ctrl + /. Most editors support this shortcut key, which is applicable to most languages. Just select the content to be commented and ctrl + /.
🍇 Name variable in js
1. js to declare a variable with the keyword var
//Declare variable var age ; // Declare a variable named age age = 18; var name = 'aniu' //Initialization of variables
- var is a JS keyword used to declare variables (the meaning of variable variable). After using this keyword to declare a variable, the computer will automatically allocate memory space for the variable, which does not need to be managed by the programmer.
- age is the variable name defined by the programmer. We need to access the space allocated in memory through the variable name.
2. Special case of declared variables
| situation | explain | result |
|---|---|---|
| var age ; console.log ( age ); | Only declaration without assignment | undefined |
| console.log ( age ) | No declaration, no assignment, direct use | report errors |
| age =10; console.log ( age ); | No declaration, only assignment | 10 |
3. Variable naming convention
- Consists of letters (A - Za - z), numbers (0-9), underscores () Dollar sign ($), such as usrage, num01_ name.
- Strictly case sensitive. var app ; And VaR app; Are two variables.
- Cannot start with a number. 18age is wrong.
- Cannot be keyword or reserved word. For example: var, for, while
- Variable names must be meaningful.
- Follow the hump nomenclature. The first letter is lowercase, and the first letter of the following word needs to be capitalized. myName
🍊 Basic data types in js
Variables are where values are stored. They have names and data types. The data type of the variable determines how the bits representing these values are stored in the computer's memory. JavaScript is a weakly typed or dynamic language. This means that there is no need to declare the type of variable in advance, and the type will be determined automatically during the operation of the program.
var age =18; I //This is a numeric type var ok ='yes; //This is a string
When the code is running, the data type of the variable is determined by the JS engine according to the data type of the variable value on the right. After running, the variable determines the data type.
| Simple data type | explain | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Numeric type, including integer and floating-point values, such as 12 and 0.82 | 0 |
| Boolean | Boolean value types, such as true and false, are equivalent to 1 and 0 | false |
| String | String type, such as "Zhang San". Note that the strings in js are quoted | " " |
| Undefined | var a ; Variable a is declared but no value is given. At this time, a = undefined | undefined |
| Null | var a = nul ; Declared that variable a is null | null |
🍇 Digital Number
- Digital hexadecimal
The most common base systems are binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal.
// Octal digit sequence range: 0 ~ 7 var num1=07; //Corresponding to decimal 7 var num2=018; //18 corresponding to decimal var num3=08; //8 corresponding to decimal // Hexadecimal digit sequence range: 0 ~ 9 and A ~ F var num =0xA; //10 corresponding to decimal
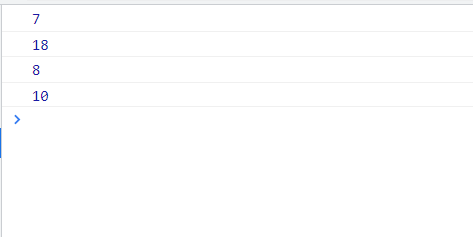
We just need to remember that in js, 0 is added before octal and 0x is added before hexadecimal.
- Digital range
1. The maximum and minimum values of values in JavaScript.
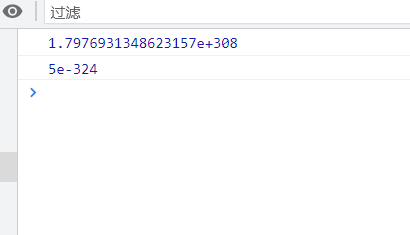
console.log(Number.MAX_VALUE);//1.7976931348623157e+308 console.log(Number.MIN_VALUE);//5e-324
Maximum value: number MAX_ Value, the value is 1.7976931348623157e+308
Minimum value: number MIN_ Value: 5e-32
2. Infinitesimal, infinity, non numeric.
console.log (Number.MAX_VALUE *2);// Infinity infinity
console.log(-Number.MAX_VALUE *2);//-Infinity infinitesimal
console.log('aniu' - 100); // NaN Not a Number
// isNaN() this method is used to judge non numbers and return a value. If it is a number, it returns false. If it is not a number, it returns true
console.log(isNaN(12));// false
console.log(isNaN('aniu')); // true

🍇 Boolean type
For example, true and false are equivalent to 1 and 0
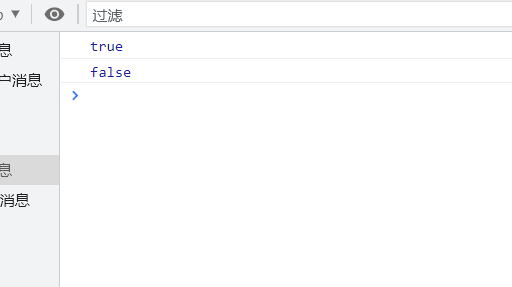
var flag = true; var flag1 = false; console.log(flag); console.log(flag1);
🍇 String type string
- Escape string in js

- Other knowledge points of string.
Multiple strings can be spliced with +. The splicing method is string + any type = new string after splicing. Before splicing, any type added with the string will be converted into a string, and then spliced into a new string.
// 1. Find the length of the string
var str = 'a niu';
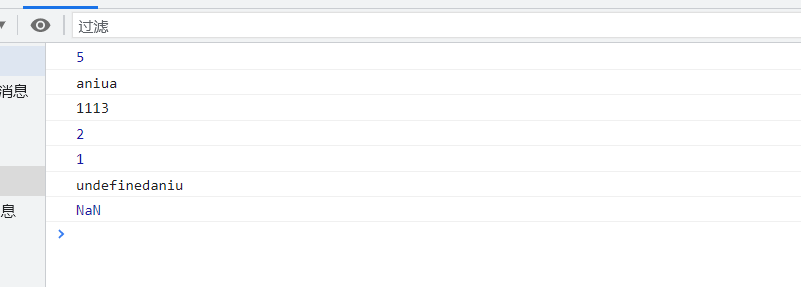
console.log(str.length); //The length method finds the length of the string
// 2. String splicing+
console.log('aniu'+'a'); // aniua
console.log('11'+13); // 1113
var flag = true;
var flag1 = false;
console.log(flag+1); // 2
console.log(flag1+1); // 1
var s = undefined;
console.log(s + 'aniu'); // underfinedaniu
console.log(s + 1); //undefined is added to the number and the result is NaN
🍇 Undefined and Null
- A variable that is not assigned after the declaration will have a default value of undefined (pay attention to the result if connecting or phase)
var m ;
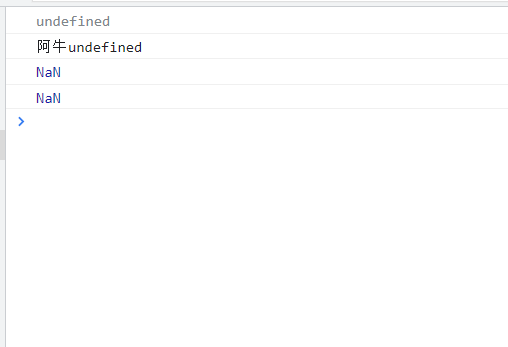
console.log (m); //undefined
console.log ('A Niu'+ m);//Daniel undefined
console.log (11+m); // NaN
console.log (true + m); // NaN
- A declared variable is given a null value, and the value stored in it is null (when learning objects, we continue to study null)
var m = null;
console.log (m); // null
console.log ('A Niu'+ m);//A Niu null
console.log (11+m); // 11
console.log (true + m); // 1

🍒 epilogue
Today's knowledge is summarized here. The next chapter brings the data type conversion in js.
Here is the first part: 👉 Getting to know javascript (unveiling the mystery of javascript)