Database Constraints
not null - > non NULL constraint
When creating a table, specify that a column is not empty (null);
give an example:
Create a student table structure and specify that the id is not empty;
mysql> create table student(
-> id int not null,
-> sn int,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
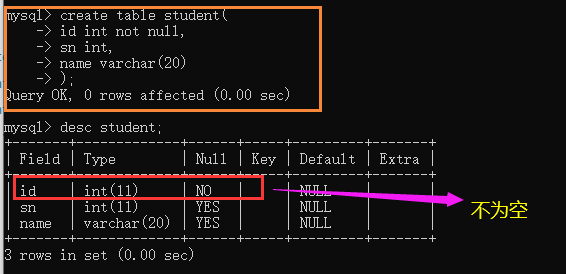
After a non NULL constraint is specified, you cannot insert null. Otherwise, an error is reported;
Unique ---- > unique constraint
Specify that a column is unique and not duplicate;
give an example:
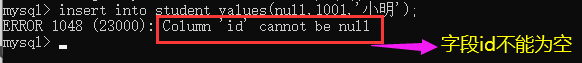
Create a student table structure, the specified id is not empty, and the student number is unique;
mysql> create table student(
-> id int not null,
-> sn int unique,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );

After a unique constraint is specified, duplicate data cannot be added to the table, otherwise an error will be reported;
Default ----- > default value constraint
Specifies that when inserting data, if a column is empty, it defaults to unkown:
give an example:
Setting: when the name column is empty, the default value is unknown;
mysql> create table student(
-> id int not null,
-> sn int unique,
-> name varchar(20) default 'unknown'
-> );

be careful:
- Insert four pieces of data. The display of empty string ('') is different from that of empty (null)~
mysql> insert into student values
-> (1,1001,null),
-> (2,1002,'floret'),
-> (3,1003,''),
-> (4,1004,'Little pig');
Query results:
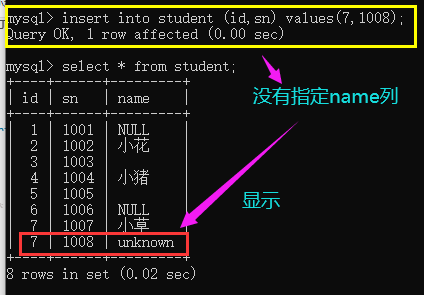
- When inserting, the default value can be displayed only if this field is not specified. If it is specified, even null will be inserted, as shown above;
mysql> insert into student (id,sn) values(7,1008);
Query results:
Primary key - > primary key constraint
The combination of not null and unique ensures that a column (multiple columns) has a unique identification, which is convenient for querying, deleting and modifying data;
give an example:
Create a student table structure with id as the primary key;
mysql> create table student(
-> id int primary key,
-> sn int unique,
-> name varchar(20) default 'unknown'
-> );
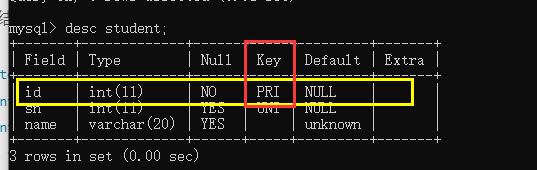
For integer type primary keys, auto is often used_ Increase to use; Indicates that it is self incremented from 1, but when inserting data, do not specify the primary key field;
Scenario:
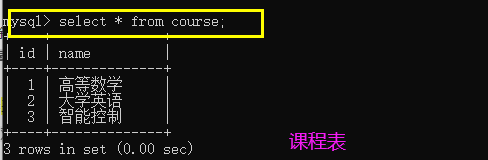
Create a curriculum with id as the primary key of the integer number, as shown below:
mysql> create table course(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Insert data without specifying the primary key field:
mysql> insert into course(name) values
-> ('Advanced mathematics'),
-> ('College English'),
-> ('intelligent control');
Query results:

Foreign key - > foreign key constraint
foreign key: used to associate the primary key or unique key of other tables;
Syntax:
foreign key (field name of this table) references (table name of associated table) (associated field name)
give an example:
- Create class table classes with id as the primary key;
- Create a student table. One student corresponds to one class and one class corresponds to multiple students. Use id as the primary key and classes as the primary key_ id is the foreign key, associated with the class table id;
mysql> create table classes(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(20)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql>
mysql> drop table if exists student;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create table student(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> sn int unique,
-> name varchar(20) default 'unknown',
-> classes_id int,
-> foreign key (classes_id) references classes(id)
-> );
Insert data:
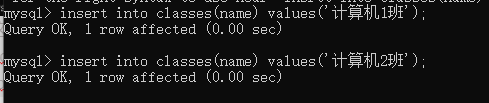
- (1) Insert class information

Query results:
- (2) Insert student information
mysql> insert into student (sn,name,classes_id) values
-> (1001,'Li Ning',1),
-> (1002,'Zhang Wei',1),
-> (1003,'Jordan',2);
Query results:
Li Ning and Zhang Wei are in computer class 1, and Jordan is in computer class 2;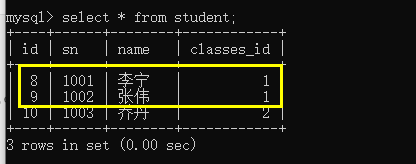
Table design
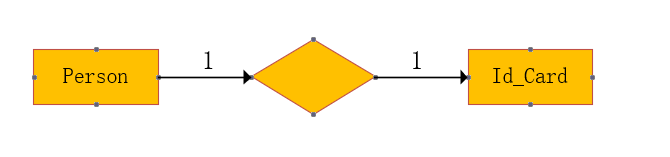
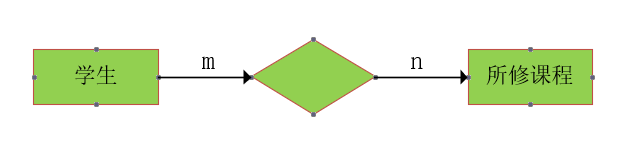
one-on-one
- One person corresponds to one ID card information
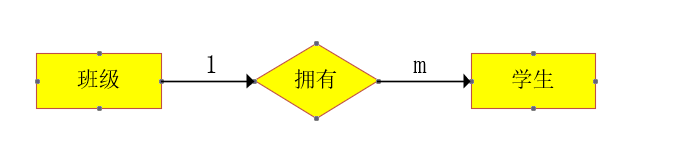
One to many
- A class has multiple students
Many to many
- One student has to take many courses
be careful:
- The direct relationship between tables is only: 1 to 1 and 1 to many;
- The many to many relationship is the intermediate relationship generated by the intermediate table;
give an example:
There are three tables in total: class table, student table and test score table. After the test scene occurs, there will be a many to many correspondence between students and courses!
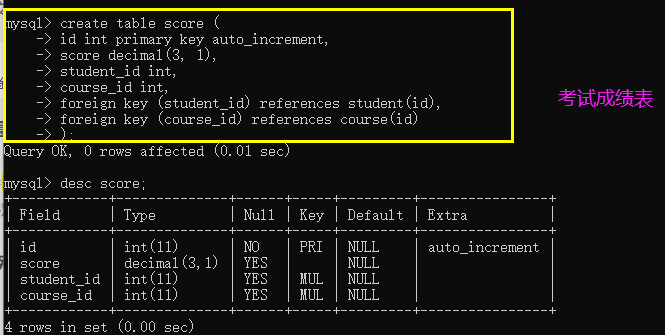
- Examination result sheet
- Class Schedule Card
- Class table
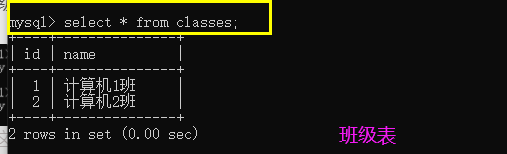
Insert data:
mysql> insert into score values
-> (null,59,8,1),
-> (null,70,8,2),
-> (null,87,9,2),
-> (null,69,10,1),
-> (null,99,8,1);
Result query: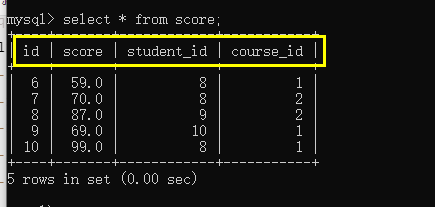
Content summary
| Constraint type | explain |
|---|---|
| not null | Indicates that a column cannot store null values |
| unique | Ensure that each row of a column must have a unique value |
| default | Specifies the default value when no value is assigned to the column |
| primary key | Combination of not null and unique |
| foreign key | Ensure referential integrity that data in one table matches values in another table |