Build a database:
CREATE DATABASE `mybase`
Building tables
CREATE TABLE `t2` ( `id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `name` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT 'Full name', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
The difference between change and modify
modify Modify constraints, such as modifying the type, length, etc. of this field
alter table table name + field name + modified type
ALTER TABLE \`t2` MODIFY id INT(20);
change modifies big things, such as the name of a field (modifying a field name requires a lot of changes)
alter table table name + change field name + changed field complete statement
ALTER TABLE t2 CHANGE phone` `phone INT(30);
Modify table name:
alter table stu rename to xxx;
alter table old table name rename to new table name
Delete field from table
ALTER TABLE t2 DROP phone;
alter table table name drop field name
Foreign key syntax
alter table t1
add constrint'constraint name'foreign key (t1b column name) references t2(`field name`)
ALTER TABLE t1
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_id FOREIGN KEY (id) REFERENCES t2 (id);
Insert Syntax
insert into indicates (`field name`) values(1,2,3);
INSERT INTO grade(gradename) VALUES('Big One');
Field names can be omitted, but a one-to-one correspondence is required
Multiple data can be inserted at the same time, but values after values need to be separated by commas
INSERT INTO grade (grade name, name, id) VALUES ('big one','tom', 12);
update syntax
update table name set `field` =new value,... Other changes where id = 1;
UPDATE grade SET gradename ='preschool class'where gradeid = 1
If you do not write a condition, change all by default.
You can also change many values at once, separated by commas
update table name set column_name = val,[column = value,...] where [condition]
delete and truncate syntax
delete from table name where id = 1;
truncate from table name
If no condition is written, the entire table is deleted
truncate cannot write condition
Role: truncate is used to completely empty table data, but table structure, indexes, constraints, and so on remain unchanged;
Difference: delete does not reset self-growth, truncate does reset self-growth
After emptying the database tables with delete, restart the database service
innodb: Restart from adding columns (because it is stored in memory, power loss occurs)
myisam: Self-incrementing still starts with the last self-incrementing data (there are files, no loss)
select syntax
select field name from table name
SELECT gradename ,id FROM grade
Full Version > SELECT DISTINCT gradename AS'Age Name', id + 100 AS'Student ID'FROM grade where id = 10
Deduplicate distinct If the two lines are identical, it will deduplicate
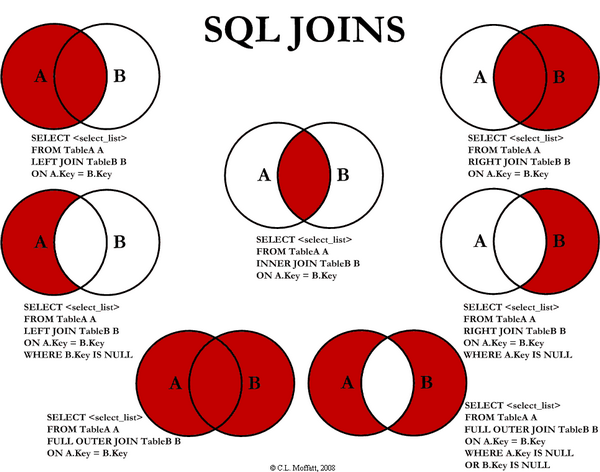
Joint Table Query
Selectect field from table inner/left/right/join Table 2 on condition
Three-table query
SELECT r.StudentNo AS 'School Number',`StudentName` AS 'Full name',sub.SubjectName,`StudentResult` AS 'Fraction' FROM result AS r LEFT JOIN student AS s ON r.StudentNo = s.studentno INNER JOIN SUBJECT AS sub ON r.subjectno = sub.subjectno
Left join (left join) returns records that include all records in the left table and those that have equal join fields in the right table
Right join (right join) returns records that include all records in the right table and those that have the same join field in the left table
Inner join only returns rows with the same join field in the two tables
Query tips:
First identify the fields you need to query and write them out.
If you have a multi-table query, start with a minimum of two tables and look up one step at a time
Find duplicate fields between tables and add conditions. Don't ambiguous. Alias whenever possible
Common Functions
| Function Name | describe |
|---|---|
| COUNT() | Returns the total number of records that meet the Select criteria, such as select count(*) [not recommended, inefficient] |
| SUM() | Returns a numeric field or expression column for statistics and the sum of a column. |
| AVG() | Usually statistics are made for numeric fields or expression columns, returning the average value of a column |
| MAX() | You can make statistics for numeric fields, character fields, or expression columns to return the maximum value. |
| MIN() | You can make statistics for numeric fields, character fields, or expression columns and return the minimum value. |
SELECT SUM(StudentResult) AS The sum FROM result; SELECT AVG(StudentResult) AS Average FROM result; SELECT MAX(StudentResult) AS Top Score FROM result; SELECT MIN(StudentResult) AS Minimum score FROM result; -- Queries can be fields,It can also be an expression
Paging and Sorting
/*============== Sort===================== Syntax: ORDER BY ORDER BY The statement is used to sort the result set according to the specified column. ORDER BY Statement defaults to sort records in ASC ascending order. If you want to sort records in descending order, you can use the DESC keyword. */ -- Query database structure-1 All test results(Number Student Name Subject Name Score) -- Sort descending by results SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,StudentResult FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON r.studentno = s.studentno INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.subjectno = sub.subjectno WHERE subjectname='database structure-1' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC /*============== Paging====================== Syntax: SELECT * FROM table LIMIT [offset,] rows | rows OFFSET offset Benefits: (User Experience, Network Transport, Query Pressure) Deduction: Page 1: limit 0,5 Page 2: limit 5,5 Page 3: limit 10,5 ...... Page N: limit (pageNo-1)*pageSzie,pageSzie [pageNo:Page number, pageSize: Number of bars per page] Rounding off the number of total/display bars is the total number of pages Take integer function ceil() Total number can be used: select count(1) from table name */ -- Display 5 pieces of data per page SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,StudentResult FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON r.studentno = s.studentno INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.subjectno = sub.subjectno WHERE subjectname='database structure-1' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC , studentno LIMIT 0,5 -- query JAVA Information about the top 10 students with scores greater than 80 in the first school year(School Number,Full name,Course Name,Fraction) SELECT s.studentno,studentname,subjectname,StudentResult FROM student s INNER JOIN result r ON r.studentno = s.studentno INNER JOIN `subject` sub ON r.subjectno = sub.subjectno WHERE subjectname='JAVA First school year' ORDER BY StudentResult DESC LIMIT 0,10
Grouping and filtering
-- Query average score for different courses,Top Score,Minimum score -- premise:Group according to different courses SELECT subjectname,AVG(studentresult) AS Average,MAX(StudentResult) AS Top Score,MIN(StudentResult) AS Minimum score FROM result AS r INNER JOIN `subject` AS s ON r.subjectno = s.subjectno GROUP BY r.subjectno HAVING Average>80; /* where Write in front of group by. Filtering after grouping To use HAVING.. Because having is filtered from the previously filtered field, where as is filtered directly from the > field in the data table */
Important: having is filtered from previously filtered fields, where as is filtered directly from > Fields in the data table
affair
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sch` ( `id` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL, `grade` INT(30) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(`id`) )ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8 INSERT INTO `sch` VALUE(2,'jerry',2),(3,'mike',3) ALTER TABLE sch CHANGE grade money INT(30) NOT NULL SET autocommit = 0 -- Close SET autocommit = 1 -- open START TRANSACTION -- Mark the start of a transaction UPDATE sch SET money = money - 500 WHERE id = 1 UPDATE sch SET money = money + 500 WHERE id = 2 INSERT -- Submit COMMIT -- RollBACK ROLLBACK -- Remember to turn on autocommit at the end of the transaction SET autocommit = 1 -- open
JDBC
Formatted writing has some drawbacks.
- Some repetitive work can be written as a tool class with static permissions
- Unsafe, risk of sql injection
package com.kuang.lesson01;
import java.awt.*;
import java.sql.*;
public class jdbcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//1. Load Driver
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// Fixed Write Load Driver
//2 User information and url
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xian?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//3. Successful connection, database object, connection represents database
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4 Object statement executing sql
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5 Execute sql object to execute sql
String sql = "select * from fir";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//The result is a list of chains
// Only queries return a linked list with executeQuery()
// Delete, update, insert all with executeUpdate(), returning the number of rows affected
while(resultSet.next())
{
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"id\") = " + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"name\") = " + resultSet.getObject("name"));
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"pwd\") = " + resultSet.getObject("pwd"));
System.out.println("==================================");
}
//6 Release the connection
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
Recommended version:
- Some fixed data is written to db. In the properties file, load using reflection
- Write a tool class jdbcUtils with driver management written as static and connection and release written as methods
- Use safer preparedStatement()
package com.kuang.lesson03;
import com.kuang.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TestSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from ? where name = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"fir");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"jack");
// int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next())
{
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"id\") = " + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"name\") = " + resultSet.getObject("name"));
System.out.println("resultSet.getObject(\"pwd\") = " + resultSet.getObject("pwd"));
System.out.println("==================================");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
}