1, Database introduction
1.1 related concepts
There are many types of databases, including relational database and non relational database. MySQL database (relational) is introduced here
Related concepts
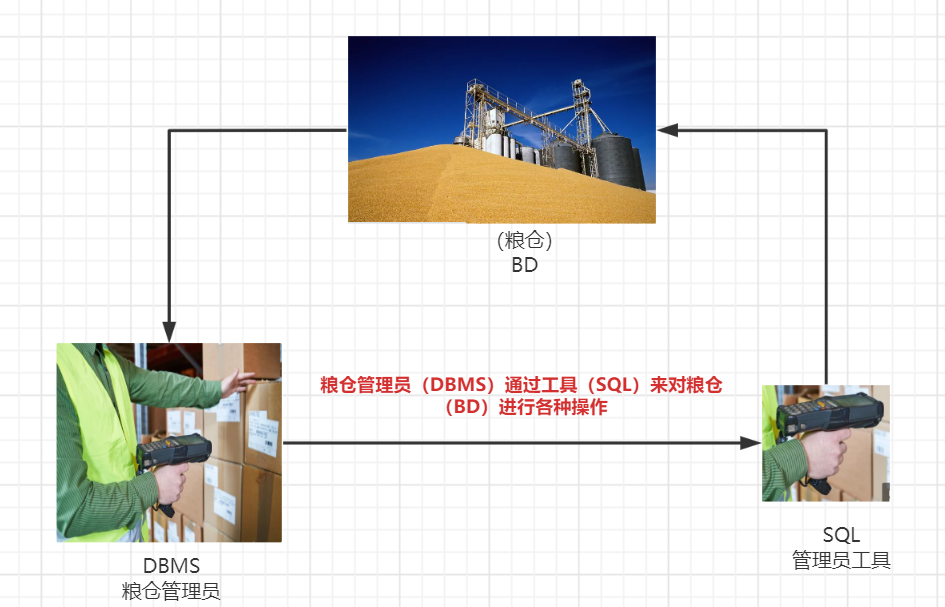
one ️⃣ DB (database): a "warehouse" for storing data. It holds a series of organized data.
two ️⃣ DBMS (database management system): the database is added, deleted and searched through the database management system
three ️⃣ SQL (structure query language): Structured Query Language
We can understand the relationship between the three with a picture
Characteristics of data stored in database:

2.2 relevant orders
When installing and configuring the database software, we need to start MySQL Service can only be used
1. Start and stop of MySQL service:
#cmd start / stop MySQL net start/stop MySQL name
2. Database login and logout:
#data base logging mysql -h locahost -P 3306 -u root(root User login) -p(If you enter the password directly, p The following password cannot be followed by a space) #Database exit exit
3. View all current databases
show databases;
4. Open the specified library
use Library name;
5. View table structure
desc Table name;
2, DQL statement (Data Query Language)
Data Query Language
Query database data, such as SELECT statement.
Simple single table query or multi table complex query and nested query.
It is the most core and important statement in database language.
The most frequently used statement.
2.1 basic query
1. Syntax:
select Query list from Table name (The query list can be fields, constant values, expressions and functions in the table, and the result is a virtual table eg: select 100; #constant select 100%98; #expression select version;AS(Alias the field, AS (can be replaced by a space) #function select distinct XX from Table name ; #duplicate removal select concat(a,b,c,) #Splicing ifnull #(expression, return value) judge whether it is empty
2. Usage of + sign
+Sign: in MySQL, the + sign is an operator. If there is a character type, the character type will be converted to a number type. If the conversion is successful, the operation will be carried out. If the conversion fails, the character is assigned to 0, and if one of them is null. The final result is null
2.2 query criteria
format
select Query list from Table name where Screening conditions;
1. Filter by conditional expression:
Conditional operation: > < =! < > =<=
select ID>0 from Table name where Screening conditions;
2. Filter by logical expression:
&&And and: both conditions are true, and vice versa
||And or: as long as one condition is true, the result is true, and vice versa
! Or not: if the connection condition is false, the result is true; otherwise, it is false
select name not null from Table name where Screening conditions;
- Specific situations will have specific applications in different scenarios
2. Filter by fuzzy query
like:
like is usually used to judge characters, so it is generally used with wildcards
Wildcard:
1.% any number of characters, including 0 characters
2._ Any single character
#For example, if there is a field name in the employee table, you need to search the data with e in the name select name from employee where name like '%e%';
between and
#Query the employee name with salary greater than 1000 and less than 2000 in the employee table select name from employee where salary between 1000 and 2000;
in
#Query the name and job number of employees belonging to the IT department in the employee table select name,id from employee where job_id in (IT);
Sort query
order by asc(Ascending order) |desc(Descending order) Query list order by Usually at the end of the sentence( limit (except)
2.3 common functions
1. Character function
length()Gets the number of bytes of the parameter value concat() Splice string upper() Convert parameter values to uppercase lower() Convert parameter values to lowercase substr() Intercepts the string and returns #The database index starts at 1 instr(Large string, substring)Returns the starting index position of the substring in the large string. If it is not found, it returns 0 trim()Remove the string before and after the string lpad() Fill the specified length with the specified character rpad() Fill the specified length with the specified character replace ()replace
2. Mathematical function
round() rounding ceil()Round up and return>=The minimum integer for this parameter truncate()Truncate several decimal places mod() Surplus
3. Date function
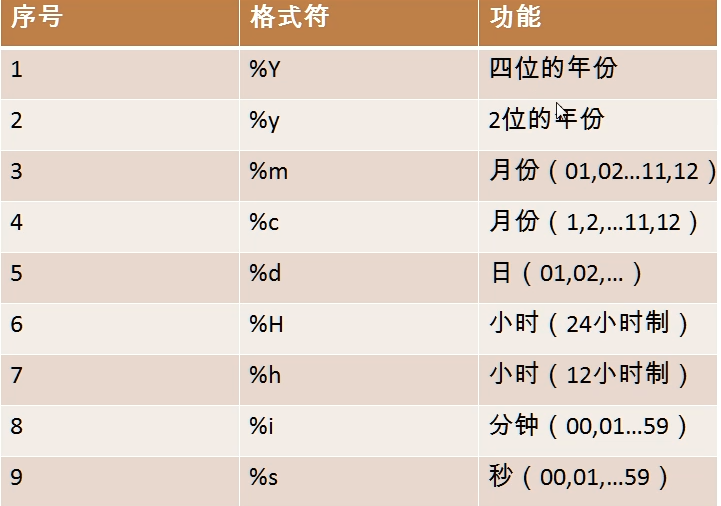
now () Return system date+time curdate() Returns the current system date, excluding time curtime() Returns the current system date, excluding time datadiff() The number of days to find the difference between two dates monthname()Return month in English
Time < - > string


Time correspondence format
4. Aggregate function
sum() Summation function avg() Average function max() Maximum function min() Minimum function count() Function of finding number
2.4 connection query
1. Internal connection
inner join
grammar
select Query list from Table 1 aliases inner join Table 2 aliases
2. External connection
Application scenario:
Used to query records in one table but not in another
characteristic:
1. The query result of external connection is all records in the main table
If there is a matching from the table, the matching value is displayed. If there is no matching from the table, null is displayed
External join query result = internal join result + records in the main table but not in the slave table. The left join is the main table, the right external join is the main table, and the right join is the main table
3 the same effect can be achieved by exchanging the order of the two tables outside the left and right
4 total external connection = results of internal connection + those in Table 1 but not in Table 2 + those in Table 2 but not in Table 1
grammar

select Query list from Table 1 aliases [line type] on Connection conditions [where Screening conditions] [group by grouping] [having Screening conditions] [order by Sort list]
eg

3. Cross connection
Cross connection is also called Cartesian product
eg

2.5 sub query
By where the subquery appears
select After:
Only scalar subqueries are supported
from After:
Support sub query
where or having After:
scalar subquery
Column subquery
Row subquery
exists Later (related sub query)

eg

2.6 paging query
Application scenario:
When the data to be displayed is incomplete on one page, you need to submit sql requests in pages
Syntax:
select query list from table
[join type join table 2 on connection conditions where filter conditions
group by grouping field having grouped filtering order by sorted field] limit offset,size;
offset the starting element index of the item to be displayed (starting element index starts from 0) size the number of items to be displayed
select Query list from surface [join type join Table 2 on Connection conditions where Screening conditions group by Grouping field having Filtering after grouping order by Sorted fields] limit offset,size; offset The starting element of the entry to display(The starting element starts from 0) size Number of entries to display
eg
2.7 joint query
Merge multiple query statements into one result

grammar
Query statement 1 union Query statement 2 union ...
eg
