1. Explain
There are two sorts in DataFrame: index sort and value sort.
Index sort: sort_index();
Value sorting: sort_values();
Value ranking: rank()
For index sorting, it involves the sorting of row index and column index, as well as whether it is ascending or descending. Function DF sort_ Index (axis =, ascending =, inplace =), pay special attention to these three parameters. Axis indicates whether to operate on rows or columns; Ascending indicates whether the operation is ascending or descending.
For value sorting, it also involves row and column sorting, ascending and descending sorting. Function DF sort_ Values (by =, axis =, ascending =, place =), we also need to pay special attention to these parameters, but there is an additional by operation. We need to indicate which row or column we sort according to.
Note: axis=0 indicates row operation, and axis=1 indicates column operation; ascending=True indicates ascending order, and ascending=False indicates descending order; inplace=True indicates the operation on the original DataFrame itself, so no assignment operation is required. inplace=False is equivalent to the copy of the original DataFrame. Some subsequent operations are performed on the copy file. Therefore, we need to assign a variable to save the results of the operation.
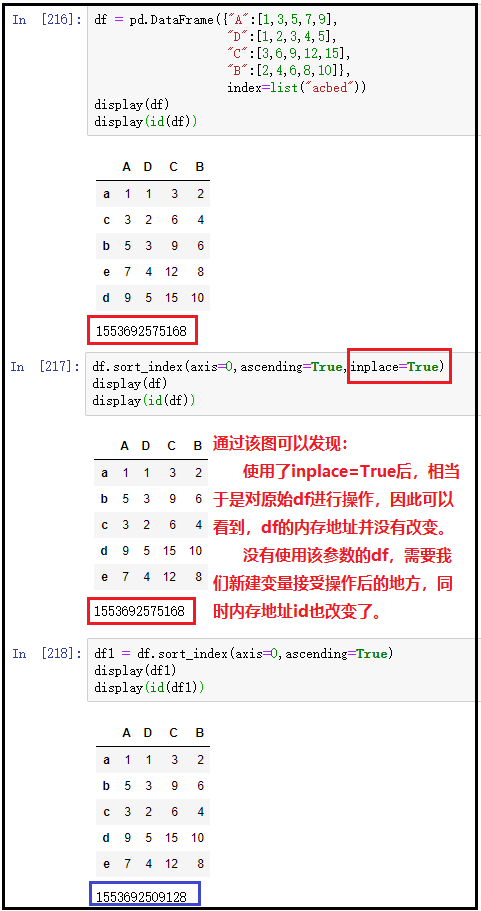
2. Index sort: DF sort_ index()
① The row index is arranged in ascending order
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1,3,5,7,9],
"D":[1,2,3,4,5],
"C":[3,6,9,12,15],
"B":[2,4,6,8,10]},
index=list("acbed"))
display(df)
display(id(df))
df.sort_index(axis=0,ascending=True,inplace=True)
display(df)
display(id(df))
df1 = df.sort_index(axis=0,ascending=True)
display(df1)
display(id(df1))
The results are as follows:
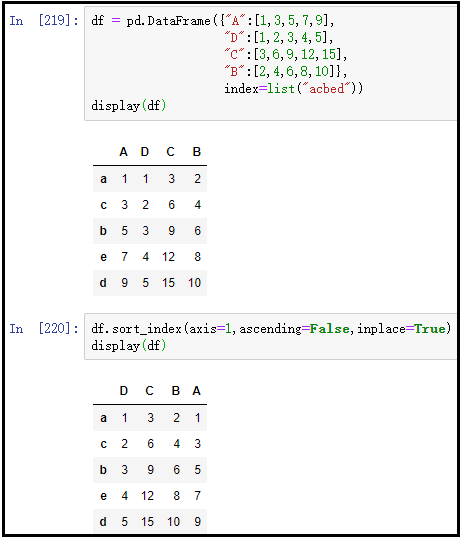
② The column indexes are arranged in descending order
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1,3,5,7,9],
"D":[1,2,3,4,5],
"C":[3,6,9,12,15],
"B":[2,4,6,8,10]},
index=list("acbed"))
display(df)
df.sort_index(axis=1,ascending=False,inplace=True)
display(df)
The results are as follows:
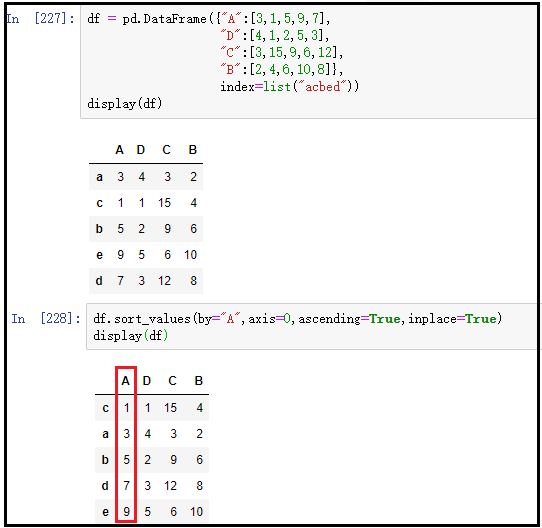
3. Value sorting: DF sort_ values()
① Sort a column in ascending order (meaningful)
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[3,1,5,9,7],
"D":[4,1,2,5,3],
"C":[3,15,9,6,12],
"B":[2,4,6,10,8]},
index=list("acbed"))
display(df)
df.sort_values(by="A",axis=0,ascending=True,inplace=True)
display(df)
The results are as follows:
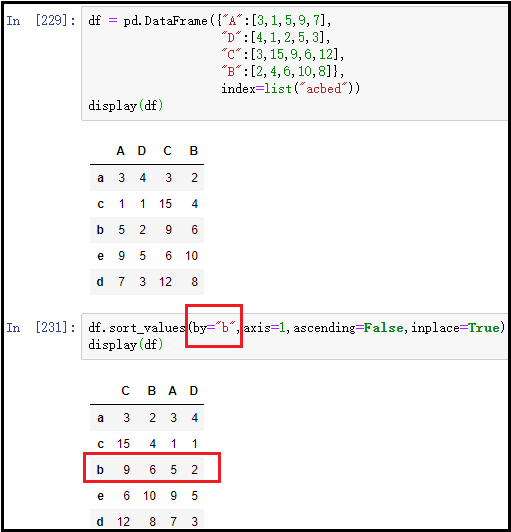
② Arrange a row in descending order (not practical)
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[3,1,5,9,7],
"D":[4,1,2,5,3],
"C":[3,15,9,6,12],
"B":[2,4,6,10,8]},
index=list("acbed"))
display(df)
df.sort_values(by="A",axis=1,ascending=False,inplace=True)
display(df)
The results are as follows:
③ Joint sorting of multiple columns (important)
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[3,1,3,9,7],
"D":[666,1,888,5,3],
"C":[3,15,9,6,12],
"B":[2,4,6,10,8]},
index=list("acbed"))
display(df)
df.sort_values(by=["A","D"],axis=0,ascending=[True,False],inplace=True)
df
The results are as follows:
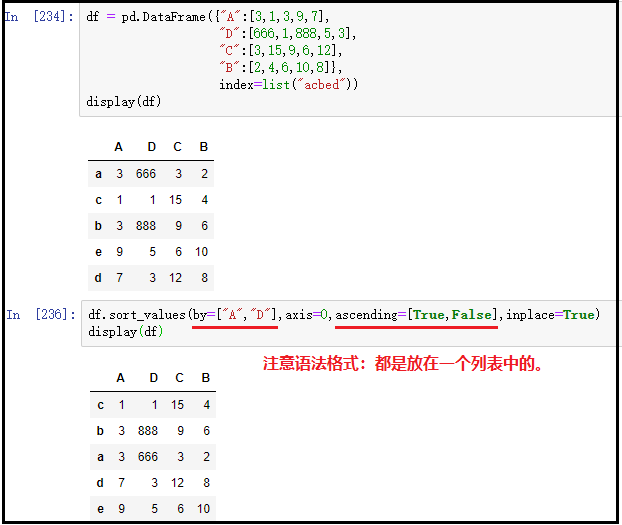
Note: in the above figure, we sort by columns A and D respectively. First, we sort by column A in ascending order. When column A has the same value, we sort by column D in descending order.
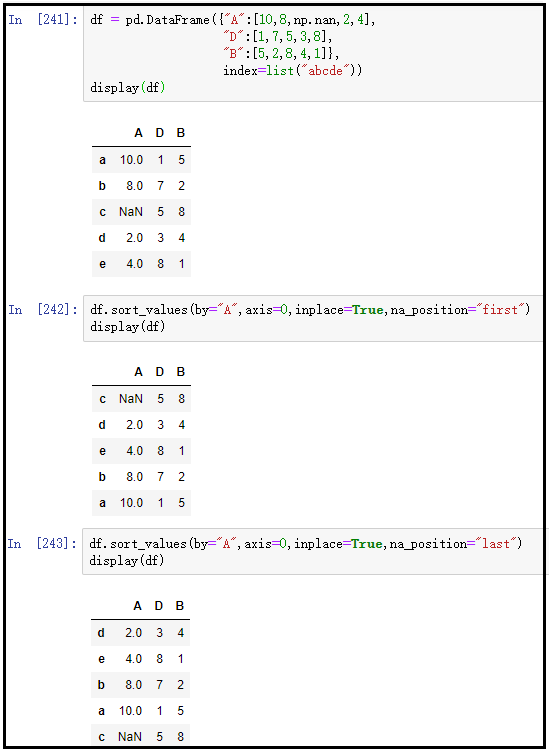
4,sort_ Na in values()_ Position parameter
na_ The position parameter is used to set the display position of the missing value. first means that the missing value is displayed in the front; last indicates that the missing value is displayed at the end.
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[10,8,np.nan,2,4],
"D":[1,7,5,3,8],
"B":[5,2,8,4,1]},
index=list("abcde"))
display(df)
df.sort_values(by="A",axis=0,inplace=True,na_position="first")
display(df)
df.sort_values(by="A",axis=0,inplace=True,na_position="last")
display(df)
The results are as follows:
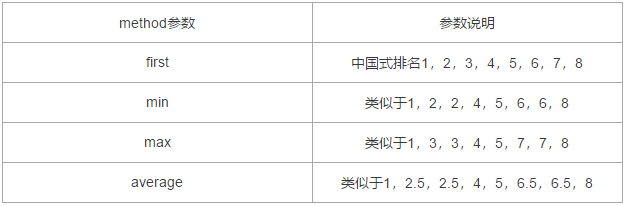
5. "Value ranking": rank() function
1) Description of common parameters of rank() function
2) Raw data
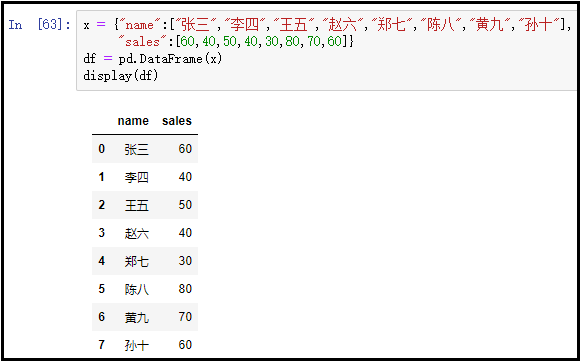
x = {"name":["Zhang San","Li Si","Wang Wu","Zhao Liu","Zheng Qi","Chen Ba","Huang Jiu","Sun Shi"],
"sales":[60,40,50,40,30,80,70,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(x)
display(df)
The results are as follows:
3) The rank() function uses the following
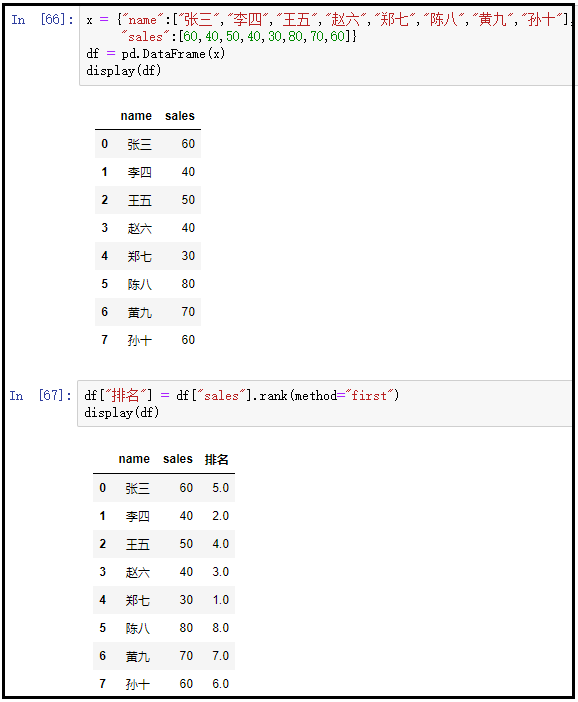
① method="first"
x = {"name":["Zhang San","Li Si","Wang Wu","Zhao Liu","Zheng Qi","Chen Ba","Huang Jiu","Sun Shi"],
"sales":[60,40,50,40,30,80,70,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(x)
display(df)
df["ranking"] = df["sales"].rank(method="first")
display(df)
The results are as follows:
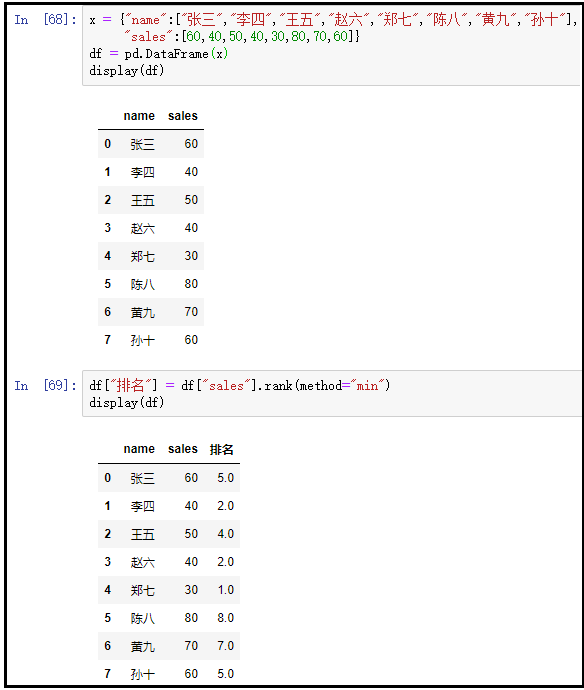
② method="min"
x = {"name":["Zhang San","Li Si","Wang Wu","Zhao Liu","Zheng Qi","Chen Ba","Huang Jiu","Sun Shi"],
"sales":[60,40,50,40,30,80,70,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(x)
display(df)
df["ranking"] = df["sales"].rank(method="min")
display(df)
The results are as follows:
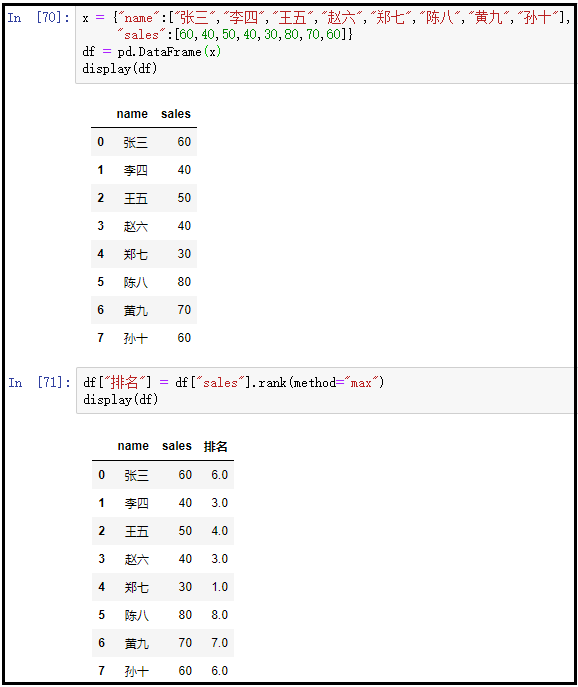
③ method="max"
x = {"name":["Zhang San","Li Si","Wang Wu","Zhao Liu","Zheng Qi","Chen Ba","Huang Jiu","Sun Shi"],
"sales":[60,40,50,40,30,80,70,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(x)
display(df)
df["ranking"] = df["sales"].rank(method="max")
display(df)
The results are as follows:
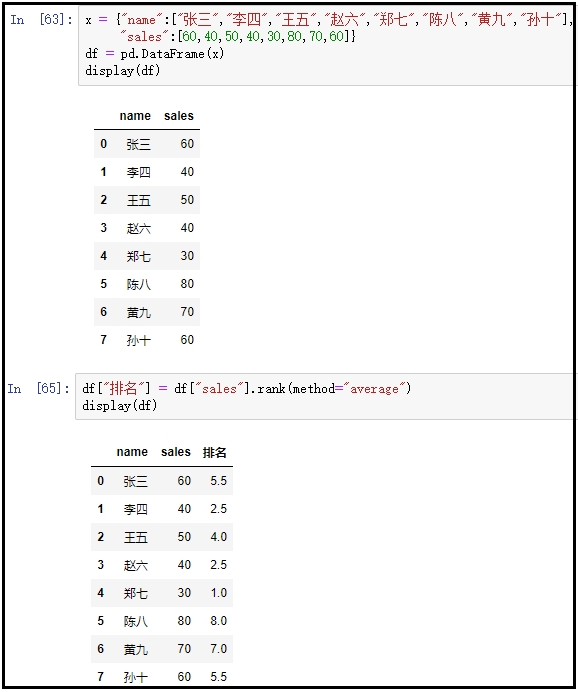
④ method="average"
x = {"name":["Zhang San","Li Si","Wang Wu","Zhao Liu","Zheng Qi","Chen Ba","Huang Jiu","Sun Shi"],
"sales":[60,40,50,40,30,80,70,60]}
df = pd.DataFrame(x)
display(df)
df["ranking"] = df["sales"].rank(method="average")
display(df)
The results are as follows: