3 interface instructions
3.1 data definition interface (DDL)
3.1.1 create database
3.1.1.1 create database
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/settingService/{dbName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | PUT | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| Return value | CreateDBResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the create database operation |
| explain | Create a database named dbName. Here, database is a logical concept, which can correspond to a physical database in sql database or a logical database in nosql. |
3.1.1.2 example code
The DataSongClient driver package is introduced and implemented as follows:
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port); boolean result = dataSongClient.createDB(dbName); System.out.println(result);
Note: dbName can only contain letters or numbers and cannot start with a number
3.1.2 create data table
3.1.2.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/settingService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | PUT | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| Return value | CreateTableResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the create data table operation |
| explain | Create an sql data table or nosql data table in the database dbName. |
3.1.2.2 example code
The DataSongClient driver package is introduced and implemented as follows:
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port); dataSongClient.setDatabaseName(dbName);//Note that you need to specify a database boolean result = dataSongClient.createTable(Student.class); System.out.println(result);
Note 1: when you use the dataSongClient instance for the first time, you need to specify the database for operation once.
Note 2: the table can be created automatically through class. Student is defined as follows:
@DSStoreType(StoreType.Fulltext)//Specify the storage type of the table, such as fulltext, sql, etc
@DSTableName(value = "student")//Specify the database name, but not specified. The class name will be used automatically by default
public class Student extends DataSongBean {
@DSFulltextIndexType(FulltextIndexType.None)//Set storage only, not index, that is, it can not be retrieved as a condition, saving storage space
private String classid;
@DSFulltextIndexType(FulltextIndexType.None)
private Date createtime;
@DSFulltextIndexType(FulltextIndexType.Whitespace)//Set space participle
private String interest;
@DSFulltextIndexType (FulltextIndexType.IK) //Set Chinese word segmentation
private String name;
private int age;//Not set, retrievable by default
@DSFulltextIndexType(FulltextIndexType.None)
private Date birth;
}
1) An internal unique id is built into the DataSongBean_ id, that is, all DataSong tables will have a built-in unique id.
2) All annotations of DataSong start with "DS" and are divided into class level and attribute level, as shown in the following figure:
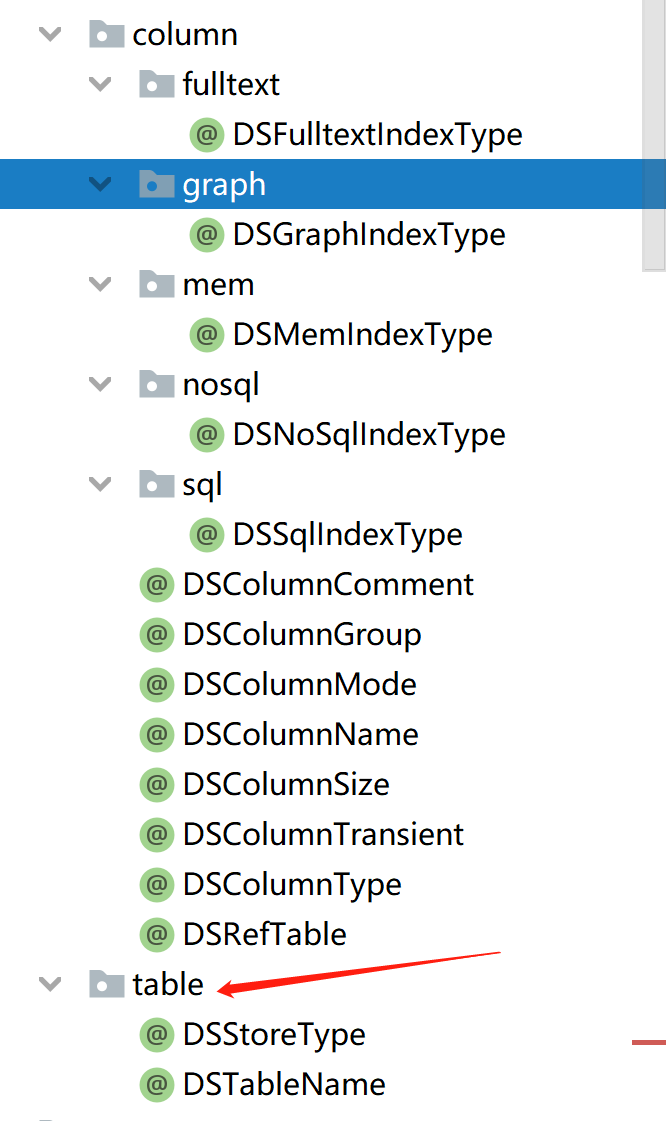
Different storage types (DSStoreType) should correspond to different index types (DSFulltextIndexType, DSGraphIndexType, dsmmemindextype, DSNoSqlIndexType, DSSqlIndexType). Other attribute level annotations do not distinguish between storage types.
3.1.3 delete data table
3.1.3.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/settingService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | DELETE | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| Return value | DeleteTableResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the delete data table operation |
| explain | Deletes a specified data table. |
3.1.3.2 example code
The DataSongClient driver package is introduced and implemented as follows:
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port); dataSongClient.setDatabaseName(dbName);//Note that you need to specify a database boolean result = dataSongClient.deleteTable(Student.class); System.out.println(result);
Note: this deletion is a physical deletion. Once deleted, it cannot be restored.
3.1.4 delete database
3.1.4.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/settingService/{dbName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | DELETE | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| Return value | DeleteDBResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the delete database operation |
| explain | Delete a specified database and delete the data tables contained in the database. |
3.1.4.2 example code
The DataSongClient driver package is introduced and implemented as follows:
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port); boolean result = dataSongClient.deleteDB(dbName); System.out.println(result);
Note: this deletion is a physical deletion. Once deleted, it cannot be restored.
3.2 data operation interface (DML)
3.2.1 data query interface
3.2.1.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/data/v2/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | POST | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| requestbody |
{"search": {"NAME": "bool","must": [{"column": "satelliteTime","NAME": "range","from": "from_time","to":"to_time"}, {"column": "channel","NAME": "term","value": channel_id}]},"sort": {"satelliteTime": "ASC"},"columns": ["satelliteTime", value_id],"size": 10000,"statistic": {"NAME": "metric", "column": value_id}}
| |
| Return value | DeleteTableResponse |
{"status":200,"info":"search data ok","tookInMillis": 30,"total": 425327,"items": "[{"satelliteTime":"2019-01-01 00:08:28.634","_id":"2_1_20190101000828","M001CG044":0.0,"status":0},{"satelliteTime":"2019-01-01 00:16:31.635","_id":"2_1_20190101001631","M001CG044":3.0,"status":0},...],"statistic": [{"key": "metric", "value": {"sum_of_squares": 1497218.0, "min": 0.0, "avg": 1.508034994251482, "max": 3.0, "variance": 1.2459878879242219, "count": 425327, "std_deviation": 1.116238275604372, "sum": 641408.0}, "children": None}]}
|
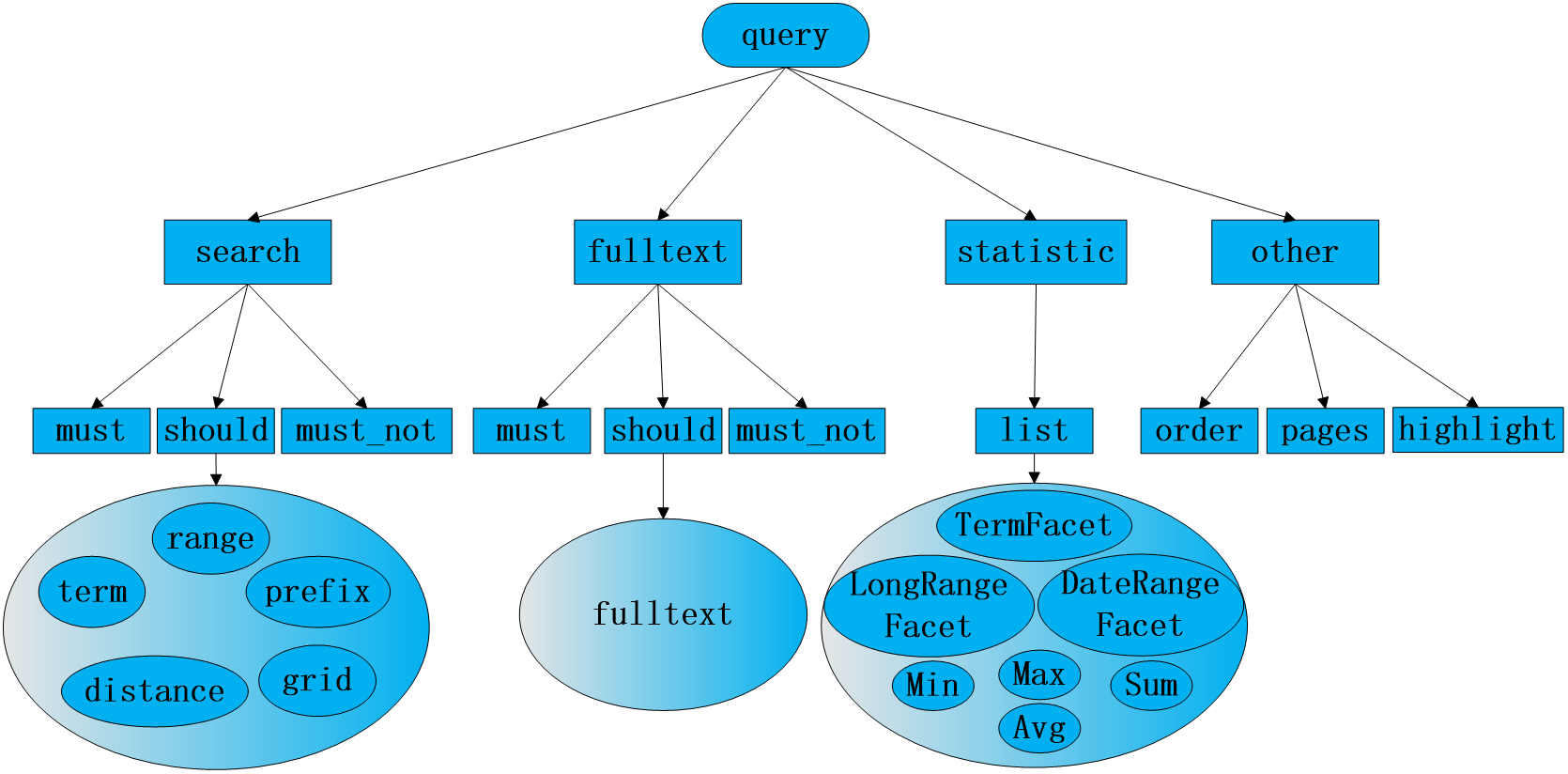
| explain | In Parameter Description: dbName and tablaName are variable parameters, corresponding to specific model name and telemetry package name; requestbody is the specific content of the query request parameter object in JSON format, and the red object is the optional query content. Where channel_ The id field describes the channel name of the remote measurement source; value_id: represents the specific name of the remote measurement to be queried; Statistical: the object describes whether to perform basic data statistical analysis, where value_ The id field describes the specific name of the remote measurement to be statistically analyzed. Among the return values: Items: describes the returned results obtained by the query_ id is the corresponding data id; Statistical: describes the statistical field information of the query remote measurement results. |
The internal query system is as follows:
3.2.1.2 example code
(1) Query condition construction
Exact match condition:
//Writing method 1.1
TermSearchCondition term = new TermSearchCondition();
term.setValue(new int[]{ 6, 7});
term.setColumn("age");
//Writing 1.2
TermSearchCondition ageTermSearchCondition = ConditionBuilder.termCondition("age", 7);
//Writing 2.1
TermSearchCondition interestTermSearchCondition = ConditionBuilder.termCondition("interest", new String[]{"high jump","Basketball"});
//Writing 2.2
TermSearchCondition interestTermSearchCondition = ConditionBuilder.termCondition("interest", "High jump basketball");//The query criteria will also be automatically segmented
Range query criteria
//Writing method 1
RangeSearchCondition rangeSearchCondition = new RangeSearchCondition();
rangeSearchCondition.setFrom("2021-02-07 18:25:04");
// rangeSearchCondition.setTo("2021-02-07 18:25:05.6");// You can set limits on only one side
rangeSearchCondition.setColumn("createtime");
//Writing method 2
RangeSearchCondition createtimeRangeSearchCondition = ConditionBuilder.rangeCondition("createtime","2021-03-06 8:25", "2021-03-06 18:25:05.6");
Bool query criteria
BoolSearchCondition boolSearchCondition = new BoolSearchCondition();
boolSearchCondition.must(rangeSearchCondition);//.must(ageTermSearchCondition).must(createtimeRangeSearchCondition);
(2) Construction of statistical conditions
Note: statistics the distribution of data in the dataset that meets the query criteria. Basic single value statistics cannot be cascaded at multiple levels. Grouping statistics supports multi-level cascading, which can be compared with SQL query. The statistical result is returned in the form of table, which can also be compared with SQL query. All statistics need to set an alias. Alias cannot be repeated for multiple conditions in the same query.
Mean statistics
//Writing method 1
AvgStatisticCondition avgStatisticCondition = new AvgStatisticCondition();
avgStatisticCondition.setAlias("avg");
avgStatisticCondition.setColumn("age");
//Writing method 2
AvgStatisticCondition c1 = ConditionBuilder.avgStatisticCondition("age", "Average statistics");
Summation statistics
//Writing method 1
SumStatisticCondition sumStatisticCondition = new SumStatisticCondition();
sumStatisticCondition.setAlias("sum");
sumStatisticCondition.setColumn("age");
//Writing method 2
SumStatisticCondition c2 = ConditionBuilder.sumStatisticCondition("age", "Summation statistics");
Count statistics
CountStatisticCondition c4 = ConditionBuilder.countStatisticCondition("age", "count Statistics");
Group statistics by date interval - setting the next level is supported
//For the createtime column, statistics are grouped by day
DateRangeStatisticCondition dateRangeStatisticCondition = ConditionBuilder.dateRangeStatisticCondition("createtime", "time_statistic", DateInterval.Day);
//Next level statistics can be set for date range
dateRangeStatisticCondition.addChild(c4);
dateRangeStatisticCondition.addChild(c5);
Group statistics by type - supports setting the next level
//For the interest column, group statistics
TermStatisticCondition termStatisticCondition = ConditionBuilder.termStatisticCondition
termStatisticCondition.setColumn("interest");
termStatisticCondition.setAlias("alias");
termStatisticCondition.addChild(c4);
termStatisticCondition.addChild(sumStatisticCondition);
(3) Inquiry
SearchDataRequest searchDataRequest = new SearchDataRequest();
//Set query criteria
searchDataRequest.setSearch(boolSearchCondition);
//Adding statistical conditions allows multiple statistical conditions to be set in parallel, and the index adopts the add method
searchDataRequest.addStatistic(c3);
//Set paging
searchDataRequest.setStart(0);
searchDataRequest.size(5);
//Set sort
searchDataRequest.sort("birth", SortOrder.ASC);
searchDataRequest.sort("createtime", SortOrder.DESC);
//Set the columns to be fetched
searchDataRequest.setColumns(new String[] {"interest"});//Return all columns without setting default
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip, port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName(dbName);
DataSongSearchResult response = dataSongClient.getDataService().searchData(Student.class ,searchDataRequest);//If you set an entity class, it will be flipped automatically
//Total hits
System.out.println("Total number of qualified articles:"+response.getTotal());
//Parse query results (if any)
for(int i = 0 ; i <response.getItems().size(); i++) {
System.out.println(DataSongJsonUtils.toJson(response.getItems().get(i)));
}
//Parse Statistics (if any)
//The return structure is encapsulated into the same structure (i.e. table structure) as the ResultSet in the jdbc protocol
for(int index = 0 ; index < response.getStatistics().size() ; index++){
DataSongResultSet resultSet = (DataSongResultSet) response.getStatistics().get(index);
//Header resolution, that is, user-defined alias
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = resultSet.getMetaData();
for (int i = 1; i <= rsmd.getColumnCount(); i++) {
System.out.print(rsmd.getColumnName(i)+"\t\t");
}
System.out.println();
//Structural analysis
while(resultSet.next()){
for(int i=1;i<=rsmd.getColumnCount();i++){
System.out.print(resultSet.getObject(i));
System.out.print("\t\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
3.2.1 data insertion and modification
3.2.1.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/dataService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | PUT | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| requestbody | Data entity | |
| Return value | PutDataResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the insertion or modification operation execution result. |
| explain | DataSong data storage middleware assigns a globally unique id number to all data records. If the data submitted by the user contains id, the data with the same id number in the system will be automatically overwritten. Otherwise, the system will automatically assign a unique id number and return the id number to the user. |
3.2.1.2 example code
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
StudentBean studentBean = new StudentBean();
// studentBean.set_id("1"); // Not required
studentBean.setAge(2);
studentBean.setClassid("sdf");
studentBean.setCreatetime(new Date());
studentBean.setName("sdfssdfdf");
studentBean.setInterest("Football basketball table tennis");
dataSongClient.getDataService().saveData("StudentBean",studentBean); //For the same_ id data will be overwritten directly. Therefore, when modifying data, you need to bring the fields that do not need to be modified and follow the rest specification.
//Batch insert
List<StudentBean> datas = new ArrayList<>();
dataSongClient.getDataService().batchSaveData( datas);
Note: the table name is not required to be displayed during insertion. The corresponding table name can be automatically resolved according to the data type.
3.2.2 data deletion
3.2.2.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/dataService/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | DELETE | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | The data primary key can be separated by multiple commas | |
| Return value | DeleteDataResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the deletion operation execution result |
| explain | Data deletion is performed by specifying a unique piece of data by database name, data table name and data id. |
3.2.2.2 example code
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
boolean result = dataSongClient.getDataService().deleteData(StudentBean.class, "11"); //The table name can be a class or a string
System.out.println(result);
//Batch deletion is written as follows:
List<String> ids = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"11","12","13"});
long result = dataSongClient.getDataService().batchDeleteData(StudentBean.class, ids); //The library name can be a class or a string
3.2.3 data retrieval
The old version interface has more functions and is cumbersome to use. It is not recommended.
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/dataService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | POST | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| requestbody | Query request | |
| Return value | SearchDataResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code and data of the query operation execution result |
| explain | Data retrieval includes basic query of data and statistical query of data. Different query Json strings are constructed through the query condition entity class shown in Figure 4-2. |
3.2.4 data acquisition
3.2.4.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/dataService/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | GET | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | The data primary key can be separated by multiple commas | |
| Return value | GetDataResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code and data of the query operation execution result |
| explain | Uniquely specify a piece of data through the database, data table and id, and return it according to the established format. If the data does not exist, the user will be reminded through the status code and status field. |
3.2.4.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");//Real database name
StudentBean result = dataSongClient.getDataService().getData(StudentBean.class, "1"); //The table name can be a class or a string. If it is a string, the json format is returned
System.out.println( DataSongJsonUtils.toJson(result));
//For batch acquisition, write as follows
List<String> ids = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"1","2","3"});
List<StudentBean> result = dataSongClient.getDataService().batchGetData(StudentBean.class, ids); //The table name can be a class or a string
3.2.5 data clearing
3.2.5.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:8080/datasong/dataService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | DELTE | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| Return value | ClearDataResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the emptying operation |
| explain | Specify a unique data table (sql data table or Nosql data table) through the database and data table, and clear the data. |
3.2.5.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
boolean result = dataSongClient.getDataService().clearData(StudentBean.class); //The table name can be a class or a string
System.out.println( result);
3.3 document operation interface
3.3.1 local file upload
3.3.1.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:15680/datasong/fileService/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | PUT | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| requestbody | File description | |
| Return value | PutFileResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the file upload operation |
| explain | Upload a local file. As a piece of data, the file logically belongs to a specified data table. |
3.3.1.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
String id = dataSongClient.getFileService().uploadFile(StudentBean.class,"D:\\New text document.txt"); //For the same_ id data will be directly overwritten
System.out.println( id);
3.3.2 file deletion
3.3.2.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1: 15680/datasong/fileService/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | DELETE | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | File primary key | |
| Return value | DeleteFileResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the file deletion operation |
| explain | A file is uniquely determined and deleted according to the id number of the database, data table and data file. |
3.3.2.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
boolean id = dataSongClient.getFileService().deleteFile(StudentBean.class,"dddddddd");
System.out.println( id);
3.3.3 file download
3.3.3.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1: 15680/datasong/fileService/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | GET | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | File primary key | |
| Return value | GetFileResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the file download operation |
| explain | According to the configuration file, download the file to the locally specified cache directory. |
3.3.3.1 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
boolean id = dataSongClient.getFileService().downloadFile(StudentBean.class,"dddddddd","d://ddd.txt");
System.out.println( id);
3.3.4 file streaming upload
3.3.4.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1: 15680/datasong/fileService/stream/{dbName}/{tableName} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | POST | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| requestbody | File stream | |
| Return value | PutFileResponse | Returns the operation response structure, including the status code of the execution result of the file streaming upload operation |
| explain |
3.3.4.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\New text document.txt"));//The stream can also be obtained through the stream returned by the browser
String id = dataSongClient.getFileService().uploadFile(StudentBean.class,"New text document.txt",inputStream); //For the same_ id data will be directly overwritten
System.out.println( id);
3.3.5 file streaming Download
3.3.5.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1: 15680/datasong/fileService/stream/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | GET | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | File id | |
| Return value | Response | File stream |
| explain | Find the specified file according to the user's request and return it in streaming mode. It supports direct parsing by the browser. |
3.3.5.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
InputStream inputStream = dataSongClient.getFileService().downloadFileStream(StudentBean.class,"dddddddd");
System.out.println( inputStream);
3.3.6 document preview
3.3.6.1 interface description
| Service interface | http://127.0.0.1:15680/datasong/fileService/preview/{dbName}/{tableName}/{id} | |
|---|---|---|
| Operator | GET | |
| Parameter description | dbName | Logical database name |
| tablaName | Logical table name | |
| id | File id | |
| Return value | Response | File stream |
| explain | Find the specified file preview according to the user's request and return it in streaming mode. It supports direct parsing by the browser. |
3.3.6.2 code example
DataSongClient dataSongClient = DataSongHttpClient.getInstance(ip,port);
dataSongClient.setDatabaseName("test");
boolean result = dataSongClient.getFileService().previewFile(StudentBean.class,"dddddddd", servletResponse);
System.out.println( result);