1. Introduction to databases
What is a database?(https://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/articles/5950372.html)
A Database is a warehouse that organizes, stores, and manages data according to its structure.
Each database has one or more different API s for creating, accessing, managing, searching, and replicating stored data.
We can also store data in files, but reading and writing data in files is relatively slow.
So now we use relational database management systems (RDBMS) to store and manage large amounts of data.The so-called relational database is a database based on the relational model, which processes the data in the database with the help of mathematical concepts and methods such as set algebra.
RDBMS is the feature of Relational Database Management System:
1. Data appears in tabular form
2. Record names per behavior
3. The data field for each column that corresponds to the record name
4. Many rows and columns form a form
5. Several forms form a database
The following figure is a database
RDBMS terminology
Before we start learning about MySQL databases, let's look at some terms for RDBMS:
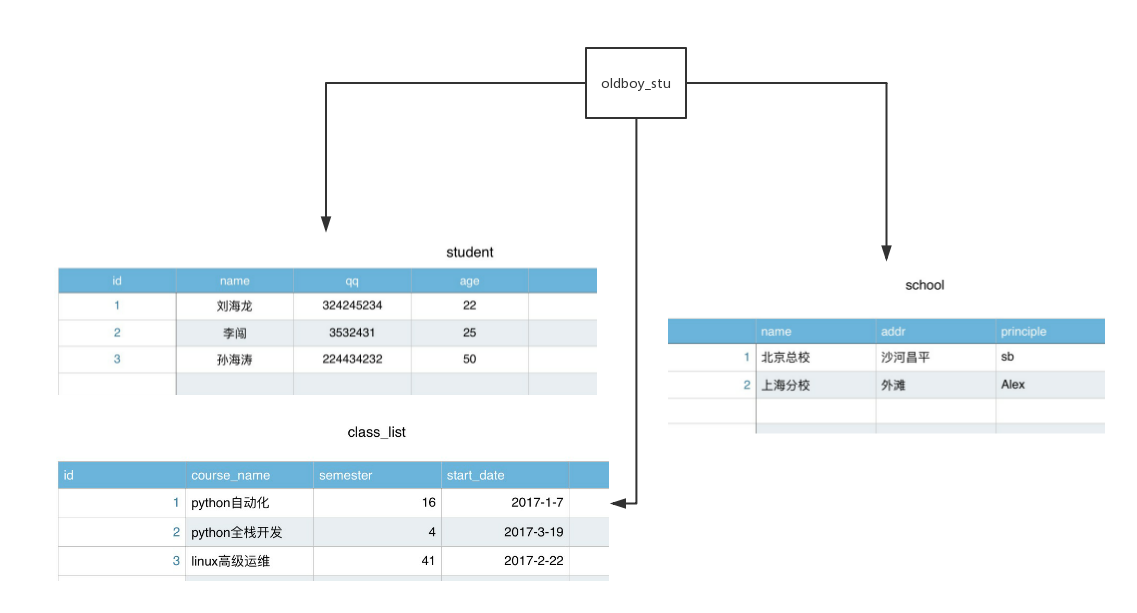
Database: A database is a collection of related tables;
Datasheet: A table is a matrix of data.A table in a database looks like a simple spreadsheet;
Column: A column (data element) contains the same data, such as postal code data;
Line: A row (=tuple, or record) is a set of related data, such as a user-subscribed data
Redundancy: Stores twice as much data. Redundancy can make your system faster.(The more normalized the table, the more relationships between tables; join queries may often be required between multiple tables; and join operations can slow down queries.For example, student information is stored in the student table, and department information is stored in the Department table.Associate with the Department table through the dept_id field in the student table.If you want to query the name of a department in which a student resides, you must look up the number (dept_id) of the Department in which the student resides from the student table, and then use that number to department to find the name of the department.Join queries can waste a lot of time if this is often needed.So you can add a redundant field, dept_name, to the student table to store the name of the Department in which the student resides.This saves you from having to connect every time.)
Primary key: The primary key is unique.A data table can contain only one primary key.You can use the primary key to query data;
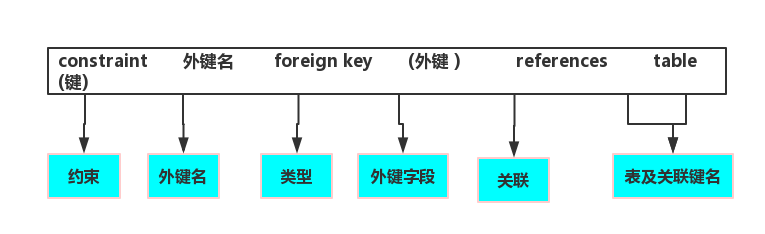
Foreign keys: Foreign keys are used to associate two tables;
Composite keys: Composite keys (composite keys) use multiple columns as an index key and are generally used for composite indexes.
Index: Use an index to quickly access specific information in a database table.An index is a structure that sorts the values of one or more columns in a database table.A catalogue similar to a book;
Referential Integrity: Referential Integrity requires that references to non-existent entities not be allowed in a relationship.Integrity and entity integrity are the integrity constraints that the relationship model must satisfy in order to ensure data consistency.
Mysql Database
Mysql is the most popular relational database management system, and MySQL is one of the best RDBMS(Relational Database Management System) applications for WEB applications.Developed by Swedish MySQL AB and currently owned by Oracle.MySQL is an associated database management system that increases speed and flexibility by keeping data in different tables instead of all in one large warehouse.
Mysql is open source, so you don't have to pay extra fees;
2.Mysql supports large databases.Can handle large databases with tens of millions of records;
3.MySQL uses the standard form of SQL data language;
Mysql can be allowed on multiple systems and supports multiple languages.These programming languages include C, C++, Python, Java, Perl, PHP, Eiffel, Ruby, Tcl, etc.
5.Mysql has good support for PHP, which is currently the most popular Web development language;
MySQL supports large databases, data warehouses with 50 million records, 32-bit system tables can support up to 4GB, 64-bit systems can support up to 8TB;
7.Mysql is customizable and uses the GPL protocol, so you can modify the source code to develop your own Mysql system.
2. Installation and use of MYSQ database
* Install Mysql on Linux/UNIX
RPM packages are recommended for installing Mysql on Linux platforms, and MySQL AB provides download addresses for the following RPM packages:
1.MySQL - MySQL Server.You need this option unless you only want to connect to a MySQL server running on another machine;
2.MySQL-client - MySQL client program for connecting to and operating Mysql servers;
3.MySQL-devel-library and include files, if you want to compile other MySQL clients, such as Perl modules, you need to install the RPM package;
4.MySQL-shared - This package contains shared libraries (libmysqlclient.so*) that some languages and applications need to load dynamically and uses MySQL;
5. Benchmarking and performance testing tools for MySQL-bench-MySQL database servers.
The following example of installing Mysql RMP is on a SuSE Linux system, although this installation step is also appropriate for other RPM-enabled Linux systems, such as Centos.
The installation steps are as follows:
* Log on to your Linux system using root users.
Download the Mysql RPM package at: MySQL Download.
* Perform the Mysql installation with the following commands, rpm packages downloaded for you:
[root@host]# rpm -i MySQL-5.0.9-0.i386.rpm
The above process of installing the mysql server creates a mysql user and creates a mysql configuration file, my.cnf.
You can find all MySQL-related binaries in / usr/bin and / usr/sbin.All tables and databases will be created in the / var/lib/mysql directory.
Following are some installation procedures for mysql optional packages that you can install as needed:
[root@host]# rpm -i MySQL-client-5.0.9-0.i386.rpm [root@host]# rpm -i MySQL-devel-5.0.9-0.i386.rpm [root@host]# rpm -i MySQL-shared-5.0.9-0.i386.rpm [root@host]# rpm -i MySQL-bench-5.0.9-0.i386.rpm
* Install Mysql on Window s
* Installing Mysql on Window s is relatively easy, you only need to load it MySQL Download Download the mysql installation package for the window version and unzip the installation package.
Double-click the setup.exe file. Next, all you need to do is install the default configuration and click next. By default, the installation information will be in the C:\mysql directory.
Next you can switch to the C:\mysql\bin directory at the command prompt by typing the cmd command= in the search box with Start= and type a command:
mysqld.exe --console
The above commands will output some mysql startup and InnoDB information if the installation is successful.
* Verify Mysql installation
After a successful installation of Mysql, some basic tables are initialized, and after the server starts, you can verify that Mysql is working properly through a simple test.
* Use the mysqladmin tool to get the server status:
Check the version of the server using the mysqladmin command and the binary on linux at / usr/bin on linux and on window s at C:\mysql\bin.
[root@host]# mysqladmin --version
The command on linux will output the following results based on your system information:
mysqladmin Ver 8.23 Distrib 5.0.9-0, for redhat-linux-gnu on i386
If you did not enter any information after executing the above command, your Mysql installation was not successful.
Using MySQL Client(Mysql client) to execute simple SQL commands
You can use the mysql command to connect to the mysql server in the MySQL Client(Mysql client). By default, the password of the mysql server is empty, so no password is required for this example.
The commands are as follows:
[root@host]# mysql
The above command will output a MySQL > prompt when executed, which indicates that you have successfully connected to the Mysql server. You can execute the SQL command at the MySQL > prompt:
mysql> SHOW DATABASES; +----------+ | Database | +----------+ | mysql | | test | +----------+ 2 rows in set (0.13 sec)
What Mysql needs to do after installation
After successful Mysql installation, the default root user password is empty. You can use the following command to create the root user password:
[root@host]# mysqladmin -u root password "new_password";
You can now connect to the Mysql server using the following commands:
[root@host]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:*******
Note: When entering a password, the password will not be displayed, you can enter it correctly.
Start MySQL at Linux system startup
If you need to start the MySQL server at Linux system startup, you need to add the following commands to the / etc/rc.local file:
/etc/init.d/mysqld start
Similarly, you need to add the mysqld binary to the / etc/init.d/directory.
3. mysql management
Start and shut down MySQL server
First, we need the following commands to check whether the MySQL server is started:
ps -ef | grep mysqld
If MySql is started, the above command will output a list of MySQL processes. If MySQL is not started, you can use the following command to start the MySQL server:
root@host# cd /usr/bin
./mysqld_safe &
If you want to shut down the currently running MySQL server, you can execute the following commands:
1 root@host# cd /usr/bin
2 ./mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown
3 Enter password: ******
MySQL User Settings
If you need to add MySQL users, you only need to add new users to the user table in the MySQL database.
The following is an example of adding a user with the user name guest and password guest123, and authorizing the user to perform SELECT, INSERT, and UPDATE operations:
root@host# mysql -u root -p Enter password:******* mysql> use mysql; #Enter Database Directive Database changed mysql> INSERT INTO user (host, user, password, select_priv, insert_priv, update_priv) VALUES ('localhost', 'guest', PASSWORD('guest123'), 'Y', 'Y', 'Y'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.20 sec) mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> SELECT host, user, password FROM user WHERE user = 'guest'; +-----------+---------+------------------+ | host | user | password | +-----------+---------+------------------+ | localhost | guest | 6f8c114b58f2ce9e | +-----------+---------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
When adding users, be aware to use the PASSWORD() function provided by MySQL to encrypt passwords.You can see in the above example that the user password is encrypted as: 6f8c114b58f2ce9e.
Note: The password of the user table in MySQL 5.7 has been replaced with authentication_string.
Note: Be aware that the FLUSH PRIVILEGES statement needs to be executed.This command will reload the authorization form when executed.
If you do not use this command, you will not be able to connect to the mysql server using the newly created user unless you restart the mysql server.
mysql> use mysql; #Enter mysql database Database changed mysql> show tables; #Tables in mysql database +---------------------------+ | Tables_in_mysql | +---------------------------+ | columns_priv | | db | | engine_cost | | event | | func | | general_log | | gtid_executed | | help_category | | help_keyword | | help_relation | | help_topic | | innodb_index_stats | | innodb_table_stats | | ndb_binlog_index | | plugin | | proc | | procs_priv | | proxies_priv | | server_cost | | servers | | slave_master_info | | slave_relay_log_info | | slave_worker_info | | slow_log | | tables_priv | | time_zone | | time_zone_leap_second | | time_zone_name | | time_zone_transition | | time_zone_transition_type | | user | +---------------------------+ 31 rows in set (0.01 sec)
There are databases and tables in the database. If there are tables in the database, the database is equivalent to a workbook and the tables are equivalent to a worksheet.
Desc table #Display information inside the sheet to view table data
mysql> desc servers; #Displays the information in the worksheet servers, how many columns are there, and the names of the columns are as follows +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Server_name | char(64) | NO | PRI | | | | Host | char(64) | NO | | | | | Db | char(64) | NO | | | | | Username | char(64) | NO | | | | | Password | char(64) | NO | | | | | Port | int(4) | NO | | 0 | | | Socket | char(64) | NO | | | | | Wrapper | char(64) | NO | | | | | Owner | char(64) | NO | | | | +-------------+----------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Fields in the database, Field, Type (field type), Null (empty), key (primary key), Default (default), Extra
Select * from table\G; view the data in the worksheet, \G is to have the data displayed in columns, too much data is displayed in confusion in the operating system
mysql> select * from user\G; #Display information in database tables *************************** 1. row *************************** Host: localhost User: root Select_priv: Y Insert_priv: Y Update_priv: Y Delete_priv: Y Create_priv: Y Drop_priv: Y Reload_priv: Y Shutdown_priv: Y Process_priv: Y File_priv: Y Grant_priv: Y References_priv: Y Index_priv: Y Alter_priv: Y Show_db_priv: Y Super_priv: Y Create_tmp_table_priv: Y Lock_tables_priv: Y Execute_priv: Y Repl_slave_priv: Y Repl_client_priv: Y Create_view_priv: Y Show_view_priv: Y Create_routine_priv: Y Alter_routine_priv: Y Create_user_priv: Y Event_priv: Y Trigger_priv: Y Create_tablespace_priv: Y ssl_type: ssl_cipher: x509_issuer: x509_subject: max_questions: 0 max_updates: 0 max_connections: 0 max_user_connections: 0 plugin: auth_socket authentication_string: password_expired: N password_last_changed: 2017-09-23 11:09:00 password_lifetime: NULL account_locked: N *************************** 2. row *************************** Host: localhost User: mysql.session Select_priv: N Insert_priv: N Update_priv: N Delete_priv: N Create_priv: N Drop_priv: N Reload_priv: N Shutdown_priv: N Process_priv: N File_priv: N Grant_priv: N References_priv: N Index_priv: N Alter_priv: N Show_db_priv: N Super_priv: Y Create_tmp_table_priv: N Lock_tables_priv: N Execute_priv: N Repl_slave_priv: N Repl_client_priv: N Create_view_priv: N Show_view_priv: N Create_routine_priv: N Alter_routine_priv: N Create_user_priv: N Event_priv: N Trigger_priv: N Create_tablespace_priv: N ssl_type: ssl_cipher: x509_issuer: x509_subject: max_questions: 0 max_updates: 0 max_connections: 0 max_user_connections: 0 plugin: mysql_native_password authentication_string: *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE password_expired: N password_last_changed: 2017-09-23 11:09:04 password_lifetime: NULL account_locked: Y *************************** 3. row *************************** Host: localhost User: mysql.sys Select_priv: N Insert_priv: N Update_priv: N Delete_priv: N Create_priv: N Drop_priv: N Reload_priv: N Shutdown_priv: N Process_priv: N File_priv: N Grant_priv: N References_priv: N Index_priv: N Alter_priv: N Show_db_priv: N Super_priv: N Create_tmp_table_priv: N Lock_tables_priv: N Execute_priv: N Repl_slave_priv: N Repl_client_priv: N Create_view_priv: N Show_view_priv: N Create_routine_priv: N Alter_routine_priv: N Create_user_priv: N Event_priv: N Trigger_priv: N Create_tablespace_priv: N ssl_type: ssl_cipher: x509_issuer: x509_subject: max_questions: 0 max_updates: 0 max_connections: 0 max_user_connections: 0 plugin: mysql_native_password authentication_string: *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE password_expired: N password_last_changed: 2017-09-23 11:09:04 password_lifetime: NULL account_locked: Y *************************** 4. row *************************** Host: localhost User: debian-sys-maint Select_priv: Y Insert_priv: Y Update_priv: Y Delete_priv: Y Create_priv: Y Drop_priv: Y Reload_priv: Y Shutdown_priv: Y Process_priv: Y File_priv: Y Grant_priv: Y References_priv: Y Index_priv: Y Alter_priv: Y Show_db_priv: Y Super_priv: Y Create_tmp_table_priv: Y Lock_tables_priv: Y Execute_priv: Y Repl_slave_priv: Y Repl_client_priv: Y Create_view_priv: Y Show_view_priv: Y Create_routine_priv: Y Alter_routine_priv: Y Create_user_priv: Y Event_priv: Y Trigger_priv: Y Create_tablespace_priv: Y ssl_type: ssl_cipher: x509_issuer: x509_subject: max_questions: 0 max_updates: 0 max_connections: 0 max_user_connections: 0 plugin: mysql_native_password authentication_string: *F9509400A27C5FF86A2809919526D0679EF9F15C password_expired: N password_last_changed: 2017-09-23 11:09:11 password_lifetime: NULL account_locked: N 4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
MySQL User Settings
If you need to add MySQL users, you only need to add new users to the user table in the MySQL database.
The following is an example of adding a user with the username guest and password guest123, and authorizing the user to perform SELECT, INSERT, and UPDATE operations:
root@host# mysql -u root -p Enter password:******* mysql> use mysql; Database changed mysql> INSERT INTO user (host, user, password, select_priv, insert_priv, update_priv) VALUES ('localhost', 'guest', PASSWORD('guest123'), 'Y', 'Y', 'Y'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.20 sec) mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> SELECT host, user, password FROM user WHERE user = 'guest'; +-----------+---------+------------------+ | host | user | password | +-----------+---------+------------------+ | localhost | guest | 6f8c114b58f2ce9e | +-----------+---------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
When adding users, be aware to use the PASSWORD() function provided by MySQL to encrypt passwords.You can see in the above example that the user password is encrypted as: 6f8c114b58f2ce9e.
Note: The password of the user table in MySQL 5.7 has been replaced with authentication_string;
Note: Be aware that the FLUSH PRIVILEGES statement needs to be executed.This command will reload the authorization table when executed.
If you do not use this command, you will not be able to connect to the mysql server using the newly created user unless you restart the mysql server.
You can assign permissions to users when they are created. In the corresponding permissions column, set to'Y'in the insert statement. The list of user permissions is as follows:
Select_priv,Insert_priv,Update_priv,Delete_priv,Create_priv,Drop_priv,Reload_priv,Shutdown_priv,Process_priv,
File_priv,Grant_priv;
Another way to add users is through the SQL GRANT command, which adds user Zara with password zara123 to the specified database TUTORIALS.
root@host# mysql -u root -p password; Enter password:******* mysql> use mysql; Database changed mysql> GRANT SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,CREATE,DROP -> ON TUTORIALS.* -> TO 'zara'@'localhost' -> IDENTIFIED BY 'zara123';
* etc/my.cnf file configuration
In general, you do not need to modify the configuration file, which is configured as follows by default:
[mysqld] datadir=/var/lib/mysql socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock [mysql.server] user=mysql basedir=/var/lib [safe_mysqld] err-log=/var/log/mysqld.log pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
Commands to manage MySQL
The following lists the commands commonly used in using Mysql databases:
1.USE Database Name: Select the Mysql database you want to operate on, and all Mysql commands will only target that database after using this command;
SHOW DATABASES: List the databases of the MySQL database management system;
SHOW TABLES: #Displays all tables of the specified database, you need to use the use command to select the database you want to operate on before using this command;
4.SHOW COLUMNS FROM data table: #Display the attributes, attribute types, primary key information, whether NULL, default values and other information of the data table;
5.create database testdb charset "utf8"; #create a database called testdb and make it support Chinese;
Drop database testdb; #delete database;
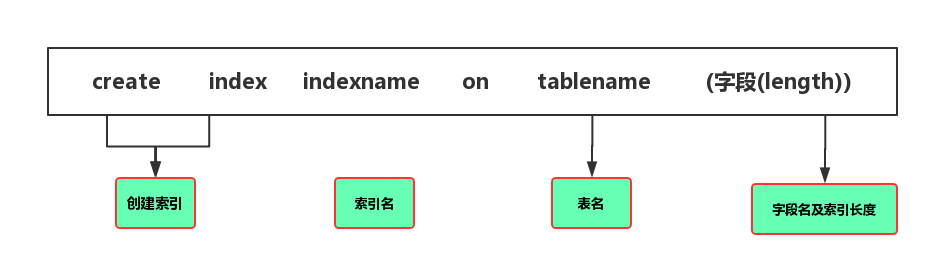
SHOW INDEX FROM data table: Displays detailed index information of the data table, including PRIMARY KEY (primary key);
Create a database using create database as follows:
mysql> create database oldboydb; #Create a database so that it cannot be written in Chinese by default. There is a character set latin1 in it which is Latin by default and does not support Chinese Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show create database oldboydb; #View information about the created database +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ | oldboydb | CREATE DATABASE `oldboydb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET latin1 */ | +----------+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
When creating a database, set the string utf8 as follows:
mysql> create database oldboydb charset "utf8"; #Default database table can be Chinese, utf8 level Query OK, 1 row affected (0.04 sec) mysql> show create database oldboydb; +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Database | Create Database | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ | oldboydb | CREATE DATABASE `oldboydb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */ | +----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4. MySQL data types
The types of data fields defined in MySQL are important for optimizing your database.
MySQL supports many types and can be roughly divided into three categories: numeric, date/time, and string (character) types.
- Numeric type
MySQL supports all standard SQL numeric data types
These include strict numeric data types (INTEGER, SMALLINT, DECIMAL, and NUMERIC) and approximate numeric data types (FLOAT, REAL, and DOUBLE PRECISION).
The keyword INT is synonymous with INTEGER and the keyword DEC is synonymous with DECIMAL.
The BIT data type holds bit field values and supports MyISAM, MEMORY, InnoDB, and BDB tables.
MySQL also supports integer types TINYINT, MEDIUMINT, and BIGINT as extensions to the SQL standard.The following table shows the storage and extent of each integer type required.
* Date and time type
The date and time types that represent time values are DATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIME, and YEAR.
Each time type has a valid range of values and a "zero" value, which is used when specifying values that are not represented by illegal MySQL.
The TIMESTAMP type has a unique automatic update feature that will be described later.
* String type
String types refer to CHAR, VARCHAR, BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB, TEXT, ENUM, and SET.This section describes how these types work and how to use them in queries.
| type | Size | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR | 0-255 Bytes | Fixed-length string |
| VARCHAR | 0-65535 Bytes | Variable length string |
| TINYBLOB | 0-255 Bytes | A binary string of no more than 255 characters |
| TINYTEXT | 0-255 Bytes | Short text string |
| BLOB | 0-65 535 bytes | Long text data in binary form |
| TEXT | 0-65 535 bytes | Long Text Data |
| MEDIUMBLOB | 0-16 777 215 bytes | Medium-length text data in binary form |
| MEDIUMTEXT | 0-16 777 215 bytes | Medium-length text data |
| LONGBLOB | 0-4 294 967 295 bytes | Maximum text data in binary form |
| LONGTEXT | 0-4 294 967 295 bytes | Very large text data |
CHAR and VARCHAR types are similar, but they are saved and retrieved in different ways.Their maximum length and whether trailing spaces are retained vary.There is no case conversion during storage or retrieval.
The BINARY and VARBINARY classes are similar to CHAR and VARCHAR except that they contain binary strings rather than non-binary strings.That is, they contain byte strings instead of character strings.This means they have no character set and sort and compare numeric values based on column value bytes.
BLOB is a binary large object that can hold a variable amount of data.There are four types of BLOB: TINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and LONGBLOB.They differ only in the maximum length that can hold values.
There are four types of TEXT: TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, and LONGTEXT.These correspond to four BLOB types with the same maximum length and storage requirements.
5. Common MySQL commands
MySQL Create Data Table
Grammar
create table table_name(column_name column_type);
Create a student table
create table student( stu_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name CHAR(32) NOT NULL, age INT NOT NULL, register_date DATE, PRIMARY KEY ( stu_id ) );
Create databases, database operations, transform databases for creation;
mysql> create table student(stu_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> name char(32) not null, -> age int not null, -> register_date date not null, -> primary key (stu_id)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.04 sec) mysql> show tables -> ; +--------------------+ | Tables_in_oldboydb | +--------------------+ | student | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Display the created database information:
mysql> desc student; #Show information about the created student table +---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | stu_id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(32) | NO | | NULL | | | age | int(11) | NO | | NULL | | | register_date | date | NO | | NULL | | +---------------+----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.10 sec)
Instance resolution:
1. If you don't want the field to be NULL, you can set the field's property to NOT NULL. When you operate a database, you will get an error if you enter NULL for the field's data.
2.AUTO_INCREMENT defines columns as self-increasing attributes, typically used for primary keys, with values automatically added by 1;
3. The PRIMARY KEY keyword is used to define a column as the primary key.You can use multiple columns to define the primary key, separated by commas.
MySQL Insert Data
Grammar
INSERT INTO table_name ( field1, field2,...fieldN )
VALUES
( value1, value2,...valueN );
Insert data:
mysql> insert into student (name,age,register_date) values ("alex li",22,"2016-03-4") -> ; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 1 | alex li | 22 | 2016-03-04 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Insert data into the stuedent table as follows:
mysql> insert into student (name,age,register_date) values ("wupeiqi",28,"2017-5-20"); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.22 sec) mysql> select * from student; +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 1 | alex | 22 | 2017-01-18 | | 2 | wupeiqi | 28 | 2017-05-20 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL Query Data
Grammar
1 SELECT column_name,column_name 2 FROM table_name 3 [WHERE Clause] 4 [LIMIT M ][OFFSET N] #Offset offset rows, starting with M rows, LIMIT shows the number N.
1. You can use one or more tables in a query statement, use commas (,) to split tables, and use WHERE statements to set query conditions;
2. The SELECT command can read one or more records;
3. You can use asterisks (*) instead of other fields, and the SELECT statement returns all the field data of the table.
4. You can use the WHERE statement to contain any conditions;
5. You can specify the data offset from which the SELECT statement begins the query through OFFSET.By default, the offset is 0;
6. You can use the LIMIT property to set the number of records returned;
mysql> select * from student limit 3 offset 2; +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 3 | alex li | 24 | 2016-03-04 | | 4 | alex li | 24 | 2016-03-01 | | 5 | alex li | 24 | 2016-03-02 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) For example, with this SQL, limit is followed by three pieces of data, offset is followed by reading from Article 3 mysql> select * from student limit 3 ,1; +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 4 | alex li | 24 | 2016-03-01 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) This SQL, followed by a limit, reads from Article 3, reading one piece of information.
mysql> select * from student where name = "alex"; +--------+------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+------+-----+---------------+ | 1 | alex | 22 | 2017-01-18 | +--------+------+-----+---------------+ 1 row in set (0.08 sec)
Select * from table (worksheet name) limit n offset m, limit the output first, then where to start the query, offset must be used with limit, but limit does not have to be with offset, as follows:
mysql> select * from student limit 5 offset 3; #First determine the output, where to start the query +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 4 | wupeiqi | 28 | 2017-05-20 | | 5 | chunyun | 26 | 2016-05-16 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student limit 2 #limit can be used without offset; -> ; +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | stu_id | name | age | register_date | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ | 1 | alex | 22 | 2017-01-18 | | 2 | wupeiqi | 28 | 2017-05-20 | +--------+---------+-----+---------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student offset 2; #But offset must be used with limit;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax;
check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '2' at line
MySQL where clause
Grammar
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN FROM table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE condition1 [AND [OR]] condition2.....
The following is a list of operators that can be used in a WHERE clause.
The examples in the table below assume that A is 10B and 20
Like fuzzy query; where name like "sheet%"
| Operator | describe | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equal sign, checks if two values are equal, returns true if they are equal | (A = B) returns false. |
| <>, != | Not equal, detects if two values are equal, returns true if they are not equal | (A!= B) Returns true. |
| > | Greater than sign, detects if the value on the left is greater than the value on the right, returns true if the value on the left is greater than the value on the right | (A > B) returns false. |
| < | Less than sign, detects if the value on the left is less than the value on the right, returns true if the value on the left is less than the value on the right | (A < B) returns true. |
| >= | Greater than or equal to sign, detects if the value on the left is greater than or equal to the value on the right, returns true if the value on the left is greater than or equal to the value on the right | (A >= B) returns false. |
| <= | Less than or equal to sign, detects if the value on the left is less than or equal to the value on the right, and returns true if the value on the left is less than or equal to the value on the right | (A <= B) Returns true. |
Primary keys are very fast for conditional queries as WHERE clauses.
select * from student where register_date > '2016-03-04';
select * from student where register date like "2016-06%"; #Fuzzy Query, Date June 2016
MySQL UPDATE Query
Grammar
UPDATE table_name SET field1=new-value1, field2=new-value2
[WHERE Clause]