Python wechat ordering applet course video
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/36074
Python actual combat quantitative transaction financial management system
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/35475
Deploy APIs IX gateway in K8S without using pvc
brief introduction
Because the company's project is ready for reconfiguration, now it makes technical reserves. The ocelot used in the company's project before is used as the gateway, and Ocelot is net platform is also very good, but performance issues need to be taken into account when selecting a gateway. Therefore, we abandoned Ocelot in this reconstruction and looked at apisix and kong. kong is also a very good gateway. However, because we don't know much about kong, we happen to have friends using apisix, so we chose apisix as a new gateway to avoid falling into the pit repeatedly. Not only the deployment, but also a series of plug-ins such as identity authentication using APIs IX will be used later, so update it slowly.
-
My apicix uses etcd as the data storage server. The official way of using pvc or docker compose is not very friendly to novices. This article will cover from the installation of etcd to the opening of apicix.
-
APIs IX is a server, which is used to forward network requests.
-
Apifix dashboard is his control panel for visual configuration.
-
Introduction to APIs IX
APISIX is a cloud native, high-performance and scalable microservice API gateway based on OpenResty + etcd. It is open source for Chinese people. At present, it has entered Apache for incubation. Through the plug-in mechanism, APISIX provides functions such as dynamic load balancing, authentication, current limit and speed limit. Of course, we can also develop our own plug-ins for expansion.
- Dynamic load balancing: dynamic load balancing across multiple upstream services is currently supported round-robin Polling and consistent hash algorithms. - Authentication: support key-auth,JWT,basic-auth,wolf-rbac And other authentication methods. - Current limit and speed limit: it can be limited based on the dimensions of rate, number of requests, concurrency, etc.
-
1. Deploy etcd
etcd is a distributed key value pair storage, which is designed to save key data reliably and quickly and provide access. Reliable distributed collaboration is achieved through distributed locks, leader elections and write barriers. etcd cluster is prepared for high availability, persistent data storage and retrieval.
-
ubuntu deployment etcd
-
There are two ways to deploy etcd in ubuntu:
One is to go GitHub Download the binary installation package. Another method is apt get install etcd. I have tried the second method. It may be the problem of my software source. The version is a little old, so I changed to the first method, and I also recommend the first method.
- The version downloaded from etcd I use is 3.5.2. Without much nonsense, just look at the steps:
-
1.1 copy etcd etcdctl etcdutl binary file to / usr/local/bin directory
/usr/local/bin
-
1.2. Create an etcd Conf.yml, copy the following code. I simply configured etcd here. There is no cluster, so YML is very simple.
name: etcd-1 data-dir: /home/etcd/data listen-client-urls: http://0.0.0.0:2379 advertise-client-urls: http://0.0.0.0:2379
-
1.3. Through etcd -- config file etcd The path of conf.yml runs successfully, as shown in the figure below. You can also use etcd manager client to test.
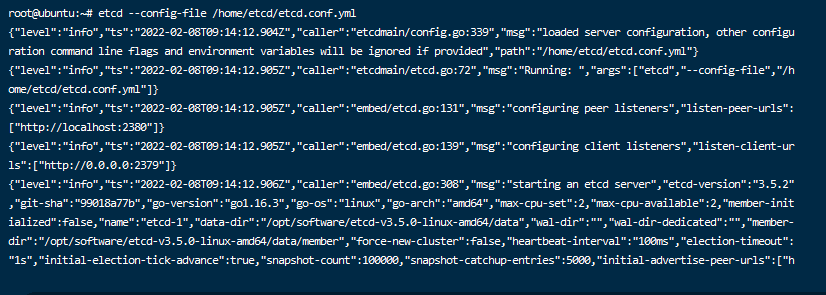
-
1.4. If you use etcd to start directly, there is no way to run in the background, so we need to create an etcd in the / etc/systemd/system directory Service to run in the background.
[Unit] Description=ETCD Server Documentation=https://github.com/coreos/etcd After=network-online.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] User=root Group=root ExecStart= etcd --config-file /home/etcd/etcd.conf.yml [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
-
1.5 after creation, the operation status can be determined through the following commands, as shown in the following figure:
# start-up sudo systemctl start etcd.service # View status sudo systemctl status etcd.service # Start and start automatically sudo systemctl enable etcd.service
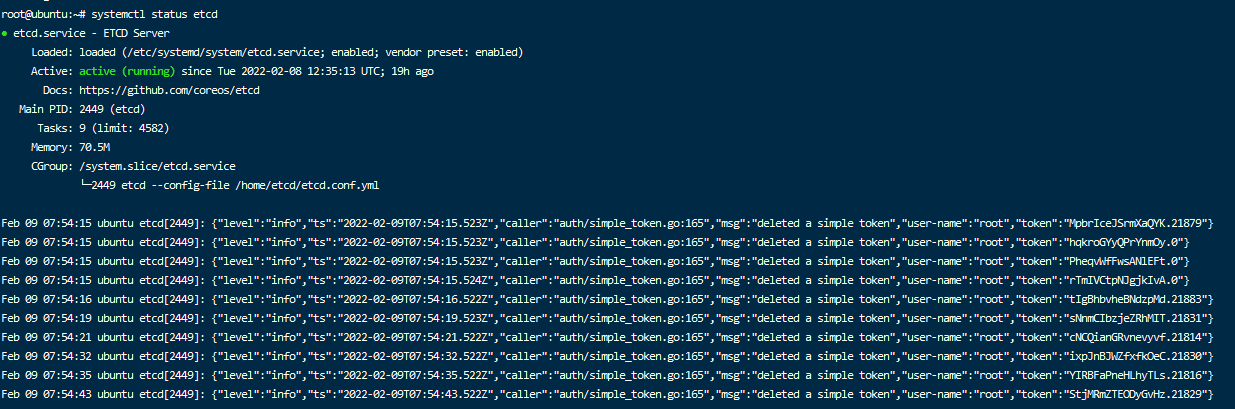
-
1.6. Set user name and password
# Set version to V3 export ETCDCTL_API=3 # Add user etcdctl user add root # Turn on authentication etcdctl auth enable
-
2. Deploy APIs IX for K8S
APIs IX gateway is divided into two parts during deployment, namely, Apis IX and APIs IX dashboard panels, so it looks rather windy. However, Apis IX uses yaml file coverage during deployment, so I store yaml in configmap to facilitate unified management. The k8s I use is microk8s produced by Ubuntu, which is mainly used because of its simple configuration.
-
2.1 deploying APIs IX
2.1.1. Create APIs IX Conf.yaml and store it in configmap,
apisix:
node_listen: 9080 # APISIX listening port
enable_ipv6: false
allow_admin: # http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_access_module.html#allow
- 0.0.0.0/0 # We need to restrict ip access rules for security. 0.0.0.0/0 is for test.
admin_key:
- name: "admin"
key: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1
role: admin # admin: manage all configuration data
# viewer: only can view configuration data
- name: "viewer"
key: 4054f7cf07e344346cd3f287985e76a2
role: viewer
enable_control: true
control:
ip: "0.0.0.0"
port: 9092
etcd:
host: # supports defining multiple etcd host addresses for an etcd cluster
- "http://192.168.31.170:2379"
user: "root" # ignore etcd username if not enable etcd auth
password: "root" # ignore etcd password if not enable etcd auth
discovery:
nacos:
host:
- "http://47.100.213.49:8848"
prefix: "/nacos/v1/"
fetch_interval: 30 # default 30 sec
weight: 100 # default 100
timeout:
connect: 2000 # default 2000 ms
send: 2000 # default 2000 ms
read: 5000 # default 5000 ms
plugin_attr:
prometheus:
export_addr:
ip: "0.0.0.0"
port: 9091
plugins:
- client-control
- ext-plugin-pre-req
- zipkin
- request-id
- fault-injection
- serverless-pre-function
- batch-requests
- cors
- ip-restriction
- ua-restriction
- referer-restriction
- uri-blocker
- request-validation
- openid-connect
- wolf-rbac
- hmac-auth
- basic-auth
- jwt-auth
- key-auth
- consumer-restriction
- authz-keycloak
- proxy-mirror
- proxy-cache
- proxy-rewrite
- api-breaker
- limit-conn
- limit-count
- limit-req
- gzip
- server-info
- traffic-split
- redirect
- response-rewrite
- grpc-transcode
- prometheus
- echo
- http-logger
- sls-logger
- tcp-logger
- kafka-logger
- syslog
- udp-logger
- serverless-post-function
- ext-plugin-post-req
stream_plugins:
- ip-restriction
- limit-conn
- mqtt-proxy
2.1.2. Create configmap with kubectl command
# Set config Yaml is stored in k8s's configmap kubectl create configmap sukt-apisix-gateway-config --from-file=config.yaml=/home/sukt-platform/apisix/apisix-gateway-config.yaml -n sukt-platform
2.1.3. Create apifix deployment yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sukt-apisix-gateway
namespace: sukt-platform
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sukt-apisix-gateway
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sukt-apisix-gateway
spec:
containers:
- name: sukt-apisix-gateway
image: apache/apisix:2.10.3-alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
securityContext:
privileged: false
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/apisix/conf/config.yaml
name: config
subPath: config.yaml
ports:
- containerPort: 9080
- containerPort: 9443
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: sukt-apisix-gateway-config
name: config
2.1.4. Create a new apifix service yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sukt-apisix-gateway-nodetype
labels:
app: sukt-apisix-gateway-nodetype
namespace: sukt-platform
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: sukt-apisix-gateway
ports:
- port: 9080
name: transfer1
targetPort: 9080
nodePort: 30107
- port: 9443
name: transfer2
targetPort: 9443
nodePort: 30108
-
2. Deploy APIs IX dashboard
2.2.1. Create apifix dashboard config Yaml and stored in configmap,
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
conf:
listen:
host: 0.0.0.0 # `manager api` listening ip or host name
port: 9000 # `manager api` listening port
allow_list: # If we don't set any IP list, then any IP access is allowed by default.
- 0.0.0.0/0
etcd:
endpoints: # supports defining multiple etcd host addresses for an etcd cluster
- "http://192.168.31.170:2379"
# yamllint disable rule:comments-indentation
# etcd basic auth info
username: "root" # ignore etcd username if not enable etcd auth
password: "root" # ignore etcd password if not enable etcd auth
mtls:
key_file: "" # Path of your self-signed client side key
cert_file: "" # Path of your self-signed client side cert
ca_file: "" # Path of your self-signed ca cert, the CA is used to sign callers' certificates
# prefix: /apisix # apisix config's prefix in etcd, /apisix by default
log:
error_log:
level: warn # supports levels, lower to higher: debug, info, warn, error, panic, fatal
file_path:
logs/error.log # supports relative path, absolute path, standard output
# such as: logs/error.log, /tmp/logs/error.log, /dev/stdout, /dev/stderr
access_log:
file_path:
logs/access.log # supports relative path, absolute path, standard output
# such as: logs/access.log, /tmp/logs/access.log, /dev/stdout, /dev/stderr
# log example: 2020-12-09T16:38:09.039+0800 INFO filter/logging.go:46 /apisix/admin/routes/r1 {"status": 401, "host": "127.0.0.1:9000", "query": "asdfsafd=adf&a=a", "requestId": "3d50ecb8-758c-46d1-af5b-cd9d1c820156", "latency": 0, "remoteIP": "127.0.0.1", "method": "PUT", "errs": []}
authentication:
secret:
secret # secret for jwt token generation.
# NOTE: Highly recommended to modify this value to protect `manager api`.
# if it's default value, when `manager api` start, it will generate a random string to replace it.
expire_time: 3600 # jwt token expire time, in second
users: # yamllint enable rule:comments-indentation
- username: admin # username and password for login `manager api`
password: P@ssW0rd
- username: user
password: P@ssW0rd
plugins: # plugin list (sorted in alphabetical order)
- api-breaker
- authz-keycloak
- basic-auth
- batch-requests
- consumer-restriction
- cors
# - dubbo-proxy
- echo
# - error-log-logger
# - example-plugin
- fault-injection
- grpc-transcode
- hmac-auth
- http-logger
- ip-restriction
- jwt-auth
- kafka-logger
- key-auth
- limit-conn
- limit-count
- limit-req
# - log-rotate
# - node-status
- openid-connect
- prometheus
- proxy-cache
- proxy-mirror
- proxy-rewrite
- redirect
- referer-restriction
- request-id
- request-validation
- response-rewrite
- serverless-post-function
- serverless-pre-function
# - skywalking
- sls-logger
- syslog
- tcp-logger
- udp-logger
- uri-blocker
- wolf-rbac
- zipkin
- server-info
- traffic-split
2.2.2. Create configmap with kubectl command
# Set config Yaml is stored in k8s's configmap kubectl create configmap sukt-apisix-dashboard-config --from-file=config.yaml=/home/sukt-platform/apisix/apisix-dashboard-config.yaml -n sukt-platform
2.2.3. Create apifix dashboard deployment yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sukt-apisix-dashboard
namespace: sukt-platform
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sukt-apisix-dashboard
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sukt-apisix-dashboard
spec:
nodeName: microk8sslave1 # Deploy to the specified node node
containers:
- name: sukt-apisix-dashboard
image: apache/apisix-dashboard:2.10.1-alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 256Mi
securityContext:
privileged: false
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/local/apisix-dashboard/conf/conf.yaml
name: config
subPath: config.yaml #This position corresponds to the name in comfigmap, not / usr / local / apifix dashboard / conf / conf.yaml
ports:
- containerPort: 9000
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext: {}
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: sukt-apisix-dashboard-config
name: config
2.2.4. Create apifix dashboard service yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sukt-apisix-dashboard-nodetype
labels:
app: sukt-apisix-dashboard-nodetype
namespace: sukt-platform
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: sukt-apisix-dashboard
ports:
- port: 9000
name: transfer1
targetPort: 9000
nodePort: 30109
-
Operation effect diagram
You can view the operation information of apifix gateway through the system information of dashboard panel
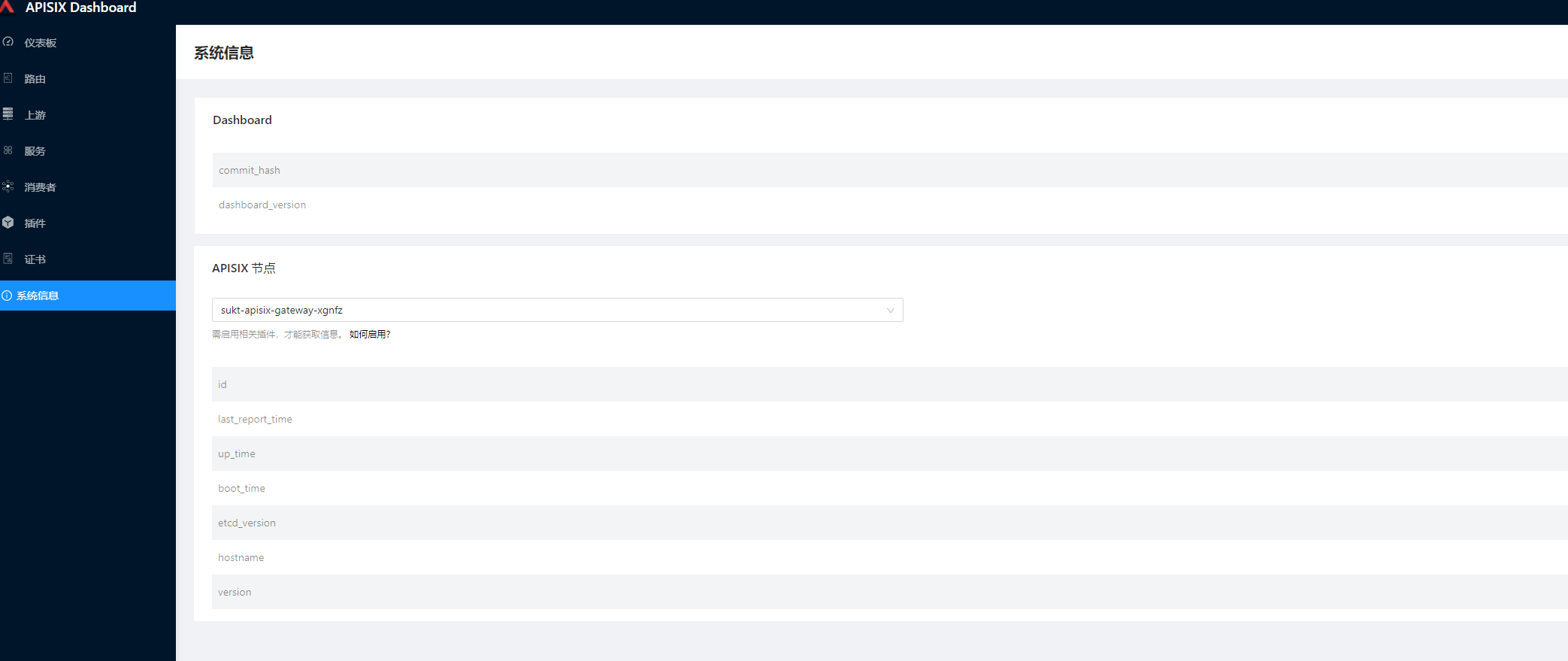
epilogue
The apifix gateway article is divided into a special topic. This article only explains how to install and start in k8s. Later, it will explain how to forward and other functions.