Xiaobai anti forgetting
Recently, I learned the basic usage of k8s and wanted to practice with an actual springCloud project. As a result, I was directly stopped in the first level registration center. Fortunately, there are official configuration documents, but there are still some holes in the configuration process, so I record it here.
Deployment environment:
- ubuntu20.04
- docker version 20.10.12
- k8s version 1.23.1
- Kubedm one master and two slaves
This article is mainly for reference Official k8s configuration document of nacos Configuration order, configuration file.
No more nonsense, just open the liver.
nfs needs to be installed on the virtual machine
#All commands executed in this article are operated under the root user #Install the command. Both the master node and the node node need to be installed apt-get install nfs-kernel-server -y #Restart command service nfs-kerenl-server restart
The first step is to configure NFS client provisioner. The purpose is to automatically apply for pvc and pv when expanding and shrinking nacos later, which saves the time of manually creating pvc and pv when expanding and shrinking nacos.
Create a role and execute RBAC yaml
kind: ClusterRole apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["persistentvolumes"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["endpoints"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"] - apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"] resources: ["storageclasses"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["events"] verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"] --- kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: run-nfs-client-provisioner subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: nfs-client-provisioner namespace: default roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io --- kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["endpoints"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"] --- kind: RoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: nfs-client-provisioner # replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed namespace: default roleRef: kind: Role name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
When executing deployment Before yaml files, you need to create pv and pvc. They are not given in the official documents, so you need to create them yourself.
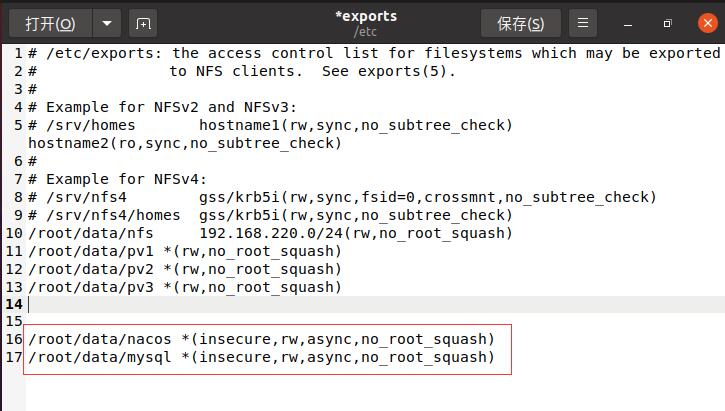
Before creating pv and pvc, you need to expose the file on nfs and the read-write permission of the file
#You only need to operate on the master node once. #Create a file. The file address is arbitrary. Just find it yourself mkdir /root/data/nacos #Grant authority chmod 777 /root/data/nacos #Add files to be exposed and their read-write permissions in nfs gedit /etc/exports perhaps vi /etc/exports #Add the file location to be exposed and its read-write permissions to the open file /root/data/nacos *(insecure,rw,async,no_root_squash) #Restart the nfs service after saving. Remember to restart service nfs-kernel-server restart
mysql is prepared when deploying mysql later
 After restarting nfs, you can directly execute PV Yaml and PVC Yaml (executed in sequence).
After restarting nfs, you can directly execute PV Yaml and PVC Yaml (executed in sequence).
pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nacos-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 2Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nfs:
path: /root/data/nacos #The location of the exposed file is the same as the actual storage volume, nfs
server: 192.168.220.131 #ip address of nfs server
pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: nfs-client-root #The name of pvc needs to be and deployment Same name in yaml
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
pv.yaml and PVC After the execution of deployment.yaml Yaml, you need to modify the configuration in the yaml file before execution, which has been indicated in the code block.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
---
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccount: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
#The reasons for not using officially prepared images are explained below.
#image: quay.io/external_storage/nfs-client-provisioner:latest
image: easzlab/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner:v4.0.1
#Look at your network speed according to the image pull strategy
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: fuseim.pri/ifs #The name is the same as that in storageClass
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 192.168.220.131 #nfs server address
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /root/data/nacos #File address exposed on nfs server
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root #pvc has the same name
nfs:
server: 192.168.220.131 #nfs server address
path: /root/data/nacos #File address exposed on nfs server
The reason why the official prepared image is not needed is because of the version problem of k8s. selfLink is disabled in the version above k8s 1.20. If nothing is modified, the nacos pod created later will always be in the pending state.
There are two modification methods:
The first is to modify Kube apiserver Yaml, add a line -- - feature gates = removeselflink = false
#Open file gedit /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml #perhaps vi /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
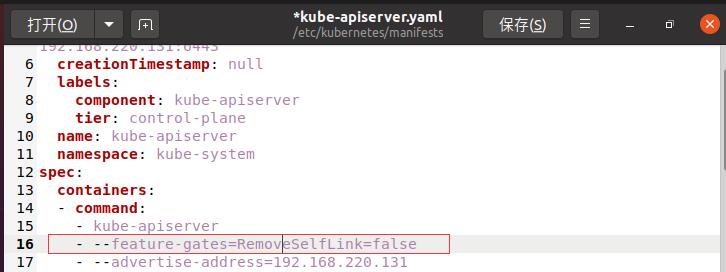 After saving, execute Kube apiserver again Yaml is enough
After saving, execute Kube apiserver again Yaml is enough
kubectl apply -f /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
The second is to directly specify that the image of the provider is more than 4.0.
Reference article: Article 1,Article 2
Then check the status of the pod. If it is running, the deployment is successful.
Finally, StorageClass is deployed to automatically apply for pv and pvc and execute clss Yaml file
class.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: managed-nfs-storage provisioner: fuseim.pri/ifs #And deployment Provisioner in yaml_ Same name parameters: archiveOnDelete: "false"
The second step is to deploy mysql. Before deploying mysql, you also need to configure pv and pvc. The configuration steps are the same as above (remember to expose the file first). I put the yaml configuration file directly.
pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nacos-mysql-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 2Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nfs:
path: /root/data/mysql #Before executing yaml, remember to expose the file address in the exports file and restart the nfs service
server: 192.168.220.131
pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-data #The name here needs to be the same as mysql Same name in yaml
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 2Gi
After creating pv and pvc (execute in order), execute MySQL NFS Yaml file. Some configurations need to be modified before execution, which has been indicated.
mysql-nfs.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: mysql
labels:
name: mysql
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
name: mysql
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: mysql
spec:
containers:
- name: mysql
#The image pull policy of the specified version number defaults to IfNotPresent
image: nacos/nacos-mysql:5.7
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-data #It should be the same as the name in the following volumes
mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD #root user password
value: "123123" #value can be customized
- name: MYSQL_DATABASE #database name
value: "nacos_devtest"
- name: MYSQL_USER #user name
value: "nacos"
- name: MYSQL_PASSWORD #User password
value: "123123"
volumes:
- name: mysql-data #Naming and PVC The name in yaml is the same
nfs:
server: 192.168.220.131 #nfs server address
path: /root/data/mysql #nfs exposed files
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mysql
labels:
name: mysql
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306
targetPort: 3306
selector:
name: mysql
Similarly, if the created pod is in running status, the configuration is successful.
The third step is to configure nacos and execute nacos PVC NFS Yaml, some configurations need to be modified before execution, which has been indicated.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nacos-headless
labels:
app: nacos
annotations:
service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints: "true"
spec:
ports:
- port: 8848
name: server
targetPort: 8848
- port: 9848
name: client-rpc
targetPort: 9848
- port: 9849
name: raft-rpc
targetPort: 9849
## Compatible with 1.4 X version of the election port
- port: 7848
name: old-raft-rpc
targetPort: 7848
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nacos
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nacos-cm
data:
#According to MySQL Modify the information configured in yaml
mysql.db.name: "nacos_devtest"
mysql.port: "3306"
mysql.user: "root"
mysql.password: "123123"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: nacos
spec:
serviceName: nacos-headless
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nacos
annotations:
pod.alpha.kubernetes.io/initialized: "true"
spec:
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: "app"
operator: In
values:
- nacos
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
initContainers:
- name: peer-finder-plugin-install
image: nacos/nacos-peer-finder-plugin:1.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/nacos/plugins/peer-finder
name: nacos-data
subPath: peer-finder
containers:
- name: nacos
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: nacos/nacos-server:latest
resources:
requests:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 8848
name: client-port
- containerPort: 9848
name: client-rpc
- containerPort: 9849
name: raft-rpc
- containerPort: 7848
name: old-raft-rpc
env:
- name: NACOS_REPLICAS
value: "2"
- name: SERVICE_NAME
value: "nacos-headless"
- name: DOMAIN_NAME
value: "cluster.local"
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_DB_NAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.db.name
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_PORT
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.port
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_USER
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.user
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.password
- name: NACOS_SERVER_PORT
value: "8848"
- name: NACOS_APPLICATION_PORT
value: "8848"
- name: PREFER_HOST_MODE
value: "hostname"
volumeMounts:
- name: nacos-data #The name here should be the same as that in volumeClaimTemplates
mountPath: /home/nacos/plugins/peer-finder
subPath: peer-finder
- name: nacos-data
mountPath: /home/nacos/data
subPath: data
- name: nacos-data
mountPath: /home/nacos/logs
subPath: logs
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: nacos-data
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "managed-nfs-storage" #Fill in class name in yaml
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteMany" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nacos
Finally, check the status of the pod. If it is in the running status, it means success.
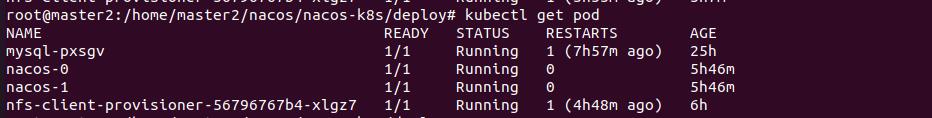 I have the number of restarts here because my nacos cluster is not deployed at one time. I shut down the virtual machine halfway. Under normal circumstances, the number of restarts should be 0.
I have the number of restarts here because my nacos cluster is not deployed at one time. I shut down the virtual machine halfway. Under normal circumstances, the number of restarts should be 0.
Finally, deploy ingress and execute Nacos ingress yaml
nacos-ingress.yaml
#In particular, different versions of k8s have different details about the configuration of inress. For details, please refer to the official website,
#The configuration information I show can only guarantee that version 1.23.1 of k8s can be used.
#There is also the configuration of ingress in nacos-k8s. You can refer to it
#./nacos-k8s/deploy/nacos/nacos-no-pvc-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nacos-ingress-http
labels:
nacos: ingress-http
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
spec:
rules:
- host: nacos.yufang.com #custom
http:
paths:
- path: /nacos #custom
pathType: Prefix #Matching policy must be configured
backend:
service:
name: nacos-headless
port:
number: 8848
After execution, you can directly access nacos.com through the browser yufang. COM: 32508 / Nacos. The port number can be viewed through the kubectl get SVC - N ingress nginx command.
It should be emphasized that the ingress controller needs to be deployed in advance instead of being used directly.
The deployment method is relatively simple.
 Browser access, account and password are nacos.
Browser access, account and password are nacos.
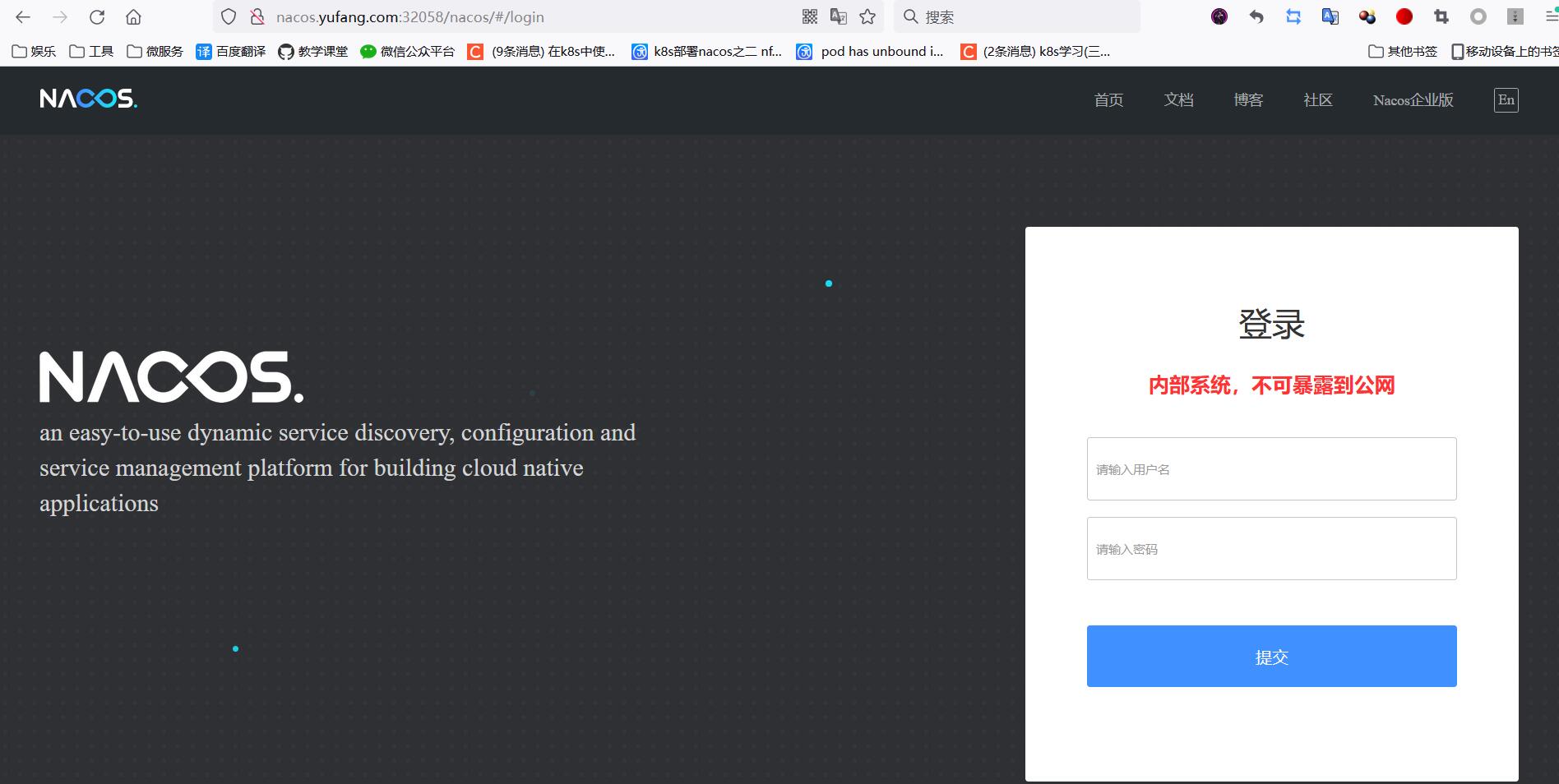
Seeing the hanging heart of the login page can also land safely.