Deployment steps
1. Installing docker
yum install -y docker systemctl enable docker systemctl start docker
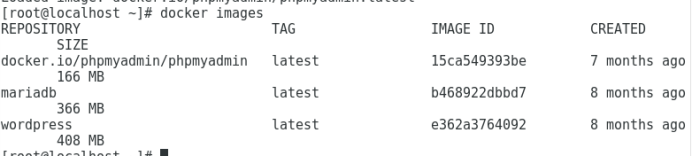
2. Look at the docker image. There is nothing in the container at this time.
docker images

3. Download docker image
docker pull mariadb docker pull wordpress docker pull phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
If it fails, copy it from the U disk, download the compressed package and import it into the docker container.
docker load -i mariadb.tar docker load -i wordpress.tar docker load -i phpmyadmin.tar docker images
4. Running mariadb
docker run --name mariadb-test -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mariadb #Set the password to 123456 on the command line.
5. Run wordpress
docker run --name wordpress-test --link mariadb-test:mysql -p 8081:80 -d wordpress

6. Run phpmyadmin
docker run --name phpmyadmin --link mariadb-test:db -p 8080:80 -d phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin

7. View the status of the container
docker container inspect 9b6b

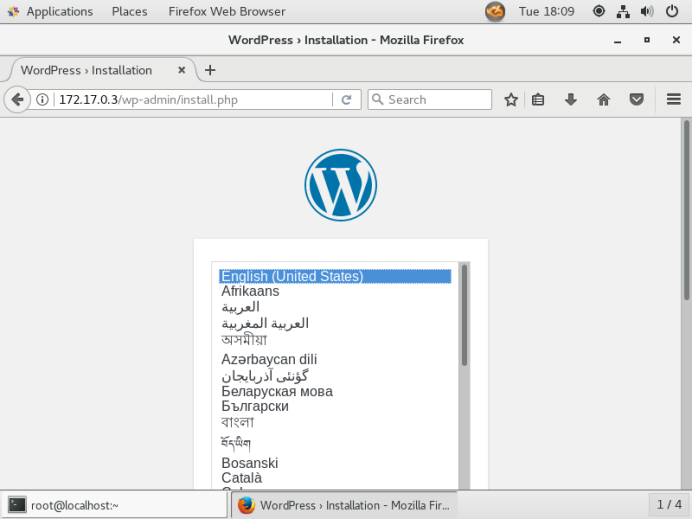
- firefox http://172.17.0.3 Use Firefox Browser to open web pages and access them locally
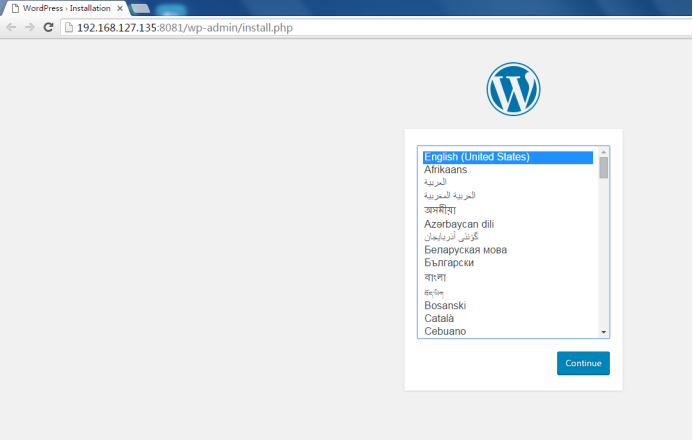
- It can also be accessed through ip extranet. http://192.168.127.135:8081 Because I mapped the port to 8081 when I added it, I need to add the port, or I can set the port to 80.
Introduction to other orders
1. Running Container Commands
docker run --name Parameters, followed by mariadb-test Is the name of the container you named yourself -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456Abc,this is mariadb Of root Set the password to 123456 Abc,This is Wordpress Requirements, 8 digits, capital letters and numbers -d mariadb,This is mariadb stay docker Mirror Name of the Official Registry --name Parameters, followed by wordpress-test Is the name of the container you named yourself --link Is the container name and standard service name associated with your dependency -p 80,Open port 80 on the firewall -d wordpress,This is wordpress stay docker Mirror Name of the Official Registry
2. Look at the log file and find the ip address, which may be 172.17.0.3
docker logs dec3
firefox http://172.17.0.3 &
Setting Background Administrator Password
3. Query all containers, whether they are running or not.
docker ps -a
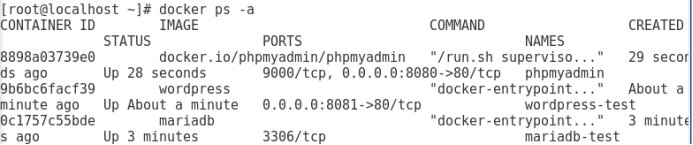
Container ID is the number of the container, just write the first four bits.
01) View the processes in the container
docker top ContainerID
02) Stop the process in the container
docker stop ContainerID
03) View a container process
docker stats ContainerID
Information similar to the following will be displayed, and in constant updates, press ctrl + c to terminate
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS
ddff 0.13% 101.1 MiB / 3.685 GiB 2.68% 4.93 kB / 2.53 kB 11 MB / 4.4 MB 30
ddff: The top four IDs of the container. You will display different information.
CPU%: CPU utilization
MEM USAGE/LIMIT: Memory usage/limit
MEM%: Memory utilization
Network card entry/exit:
Block equipment in/out:
PIDS (number of processes): 30
04) Enter the container and run commands interactively
docker exec -it ContainerID /bin/bash
05) Check the operation of docker
docker ps -a
06) To suspend one item and cancel the suspension
docker pause ContainerID docker unpause ContainerID
07) Eliminate one item
docker kill ContainerID docker rm ContainerID