1, LVS-DR packet flow analysis
In order to facilitate the principle analysis, the Client and the cluster machine are placed in the same network, and the route of data packets is 1-2-3-4
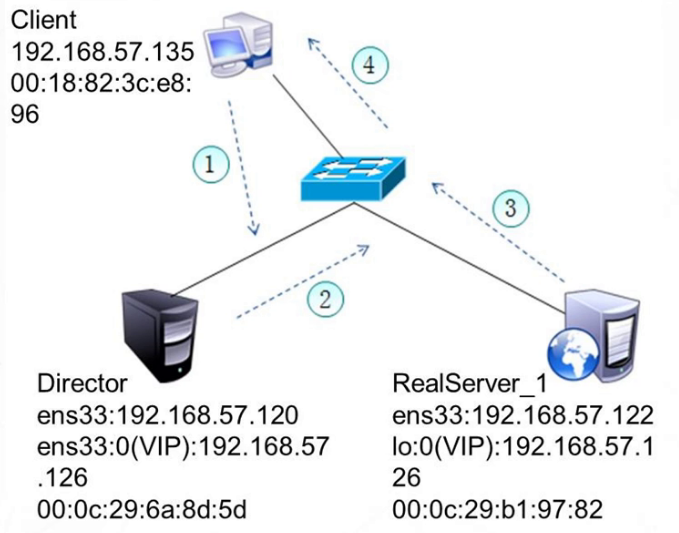
1. The Client sends a request to the target VIP and the Director receives it. At this time, the source MAC address is the Client MAC address, and the target MAC address is the MAC address of the scheduler Director.
2. The Director selects RealServer according to the load balancing algorithm_ 1. The IP message is not modified or encapsulated, but the MAC address of the data frame is changed to RealServer_1, and then send it on the LAN. At this time, the source MAC address is the MAC address of Director and the destination MAC address is RealServer_ MAC address of 1.
3,RealServer_1 after receiving this frame, it is found that the target IP matches the local machine after unpacking (RealServer has bound VIP in advance), so the message is processed. Then re encapsulate the message, transmit the response message to the physical network card through the lo interface, and then send it out. At this time, the source MAC address is RealServer_1. The destination MAC address is the MAC address of the Client.
4. The Client will receive the reply message. The Client thinks it can get the normal service, but it doesn't know which server handles it.
Note: if it crosses the network segment, the message will be returned to the user via the Internet through the router.
2, ARP problem in LVS-DR
1. In LVS-DR load balancing cluster, both load balancing and node server should be configured with the same VIP address.
2. Having the same IP address in the LAN is bound to cause the disorder of ARP communication among servers.
——When ARP broadcast is sent to LVS-DR cluster, both load balancer and node server will receive ARP broadcast because they are connected to the same network.
——Only the front-end load balancer responds, and other node servers should not respond to ARP broadcast.
3. Process the node server so that it does not respond to the ARP request for VIP.
——Use virtual interface lo:0 to host VIP address
——Set kernel parameter arp_ignore=1: the system only responds to ARP requests whose destination IP is local IP
4. The message returned by RealServer (the source IP is VIP) is forwarded by the router. When repackaging the message, you need to obtain the MAC address of the router first.
5. When sending an ARP request, Linux uses the source IP address of the IP packet (VIP s) as the source IP address in the ARP request packet by default instead of the IP address of the sending interface
For example: 33
6. After receiving the ARP request, the router will update the ARP table entry
7. The MAC address of the Director corresponding to the original VIP will be updated to the MAC address of the RealServer corresponding to the VIP
8. According to the ARP table entry, the router will forward the new request message to RealServer, resulting in the failure of the Director's VIP
resolvent:
——Process the node server and set the kernel parameter ARP_ Announcement = 2: the system does not use the source address of the IP packet to set the source address of the ARP request, but selects the IP address of the sending interface.
9. Setting methods to solve two problems of ARP
Modify / etc / sysctl Conf file
net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore=1 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce=2 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore=1 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce=2
3, DR mode, LVS load balancing cluster
(1) Packet flow analysis
(1) The client sends a request to the Director Server (load balancer), and the requested data message (the source IP is CIP and the target IP is VIP) reaches the kernel space.
(2) , Director Server and Real Server are in the same network, and the data is transmitted through the two-layer data link layer.
(3) . the kernel space judges that the target IP of the packet is the local VIP. At this time, IPVS (IP virtual server) compares whether the service requested by the packet is a cluster service. If it is a cluster service, the packet will be re encapsulated. Modify the source MAC address to the MAC address of Director Server and the target MAC address to the MAC address of Real Server. The source IP address and the target IP address have not changed, and then send the packet to Real Server.
(4) . if the MAC address of the request message arriving at the Real Server is its own MAC address, this message will be received. The data packet re encapsulates the message (the source IP address is VIP and the target IP is CIP), transmits the response message to the physical network card through the lo interface, and then sends it out.
(5) . the Real Server directly transmits the response message to the client.
(2) Characteristics of DR mode
(1) , Director Server and Real Server must be in the same - physical network.
(2) . Real Server can use private address or public address. If the public network address is used, RIP can be accessed directly through the Internet.
(3) . Director Server is used as the access portal of the cluster, but not as the gateway.
(4) All request messages pass through the Director Server, but the reply response message cannot pass through the Director Server.
(5) . the gateway of Real Server is not allowed to point to the Director Server IP, that is, the packets sent by Real Server are not allowed to pass through the Director Server.
(6) The lo interface on the Real Server configures the IP address of the VIP.
4, LVS-DR load balancing cluster deployment steps
Construction environment:
DR server (load scheduler) (centos7-5): 192.168.200.50
Web server 1 (CentOS 7-6): 192.168.200.60
Web server 2 (CentOS 7-7): 192.168.200.70
Server for NFS (centos7-8): 192.168.200.80
VIP: 192.168.200.188
Windows10 client: 192.168.200.200
(1) Configure load scheduler (192.168.200.50)
systemctl stop firewalld.service systemctl disable firewalld.service setenforce 0 modprobe ip_vs #Load ip_vs module cat /proc/net/ip_vs #View ip_vs version information yum install -y ipvsadm (1),Configure virtual IP Address( VIP: 192.168.200.188) cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens33:0 vim ifcfg-ens33:0 DEVICE=ens33:0 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.200.188 NETMASK=255.255.255.255 ifup ens33:0 ifconfig ens33:0 (2),adjustment proc Response parameters #Since the LVS load scheduler and all nodes need to share VIP addresses, the redirection parameter response of the Linux kernel should be turned off instead of acting as a router, vim /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.ens33.send_redirects = 0 sysctl -p (3),Configure load distribution policy ipvsadm-save > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm perhaps ipvsadm --save > /etc/sysconfig/ipvsadm systemctl start ipvsadm.service ipvsadm -C #Clear original policy ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.200.188:80 -s rr ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.200.188:80 -r 192.168.200.60:80 -g #In case of tunnel mode, - g is replaced by - i ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.200.188:80 -r 192.168.200.70:80 -g ipvsadm -ln #Check the node status. Route represents DR mode
(2) Deploy shared storage (NFS server: 192.168.200.80)
systemctl stop firewalld.service systemctl disable firewalld.service setenforce 0 yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind systemctl start nfs.service systemctl start rpcbind.service systemctl enable nfs.service systemctl enable rpcbind.service mkdir /opt/gcc /opt/benet chmod 777 /opt/gcc/ /opt/benet/ vim /etc/exports /usr/share *(ro,sync) /opt/gcc 192.168.200.0/24(rw,sync) #/There must be no spaces between 24 and () /opt/benet 192.168.200.0/24(rw,sync) exportfs -rv showmount -e
(3) Configure node servers (192.168.200.60, 192.168.200.70)
systemctl stop firewalld.service systemctl disable firewalld.service setenforce 0 #Comment out the gateway and DNS of the two node servers and restart the network card. If there is a gateway server, point to the gateway server (1),Configure virtual IP Address( VIP: 192.168.200.188) #This address is only used as the source address for sending Web response packets, and does not need to listen to the client's access requests (instead, it is monitored and distributed by the scheduler). Therefore, the virtual interface lo:0 is used to host the VIP address, and a path is added for the local machine with records, so as to limit the data accessing the VIP locally to avoid communication disorder. cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ cp ifcfg-lo ifcfg-lo:0 vim ifcfg-lo:0 DEVICE=lo:0 IPADDR=192.168.200.188 NETMASK=255.255.255.255 #Note that the subnet mask must be all 1 #NETWORK=127.0.0.0 # If you're having problems with gated making 127.0.0.0/8 a martian, # you can change this to something else (255.255.255.255, for example) #BROADCAST=127.255.255.255 ONBOOT=yes #NAME=loopback ifup lo:0 ifconfig lo:0 route add -host 192.168.200.188 dev lo:0 #Confinement routing route -n #View route vim /etc/rc.local /sbin/route add -host 192.168.200.188 dev lo:0 chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local (2),Adjust kernel ARP Response parameters to prevent updates VIP of MAC Address to avoid conflicts vim /etc/sysctl.conf ...... net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1 #The system only responds to ARP requests whose destination IP is local IP net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2 #The system does not use the source address of the IP packet to set the source address of the ARP request, but selects the IP address of the sending interface net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2 sysctl -p perhaps echo "1" >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_ignore echo "2" >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/lo/arp_announce echo "1" >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_ignore echo "2" >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/all/arp_announce yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind httpd systemctl start rpcbind systemctl start httpd ----------192.168.200.60----------------- mount.nfs 192.168.200.80:/opt/gcc /var/www/html/ echo 'this is gcc web!' > /var/www/html/index.html #Set to auto mount vim /etc/fstab 192.168.200.80:/opt/gcc /var/www/html nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0 mount -a ----------192.168.200.70----------------- mount.nfs 192.168.200.80:/opt/benet /var/www/html/ echo 'this is benet web!' > /var/www/html/index.html #Set to auto mount vim /etc/fstab 192.168.200.80:/opt/benet /var/www/html nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0 mount -a