This article records the usage information of common components of Kubernetes. Please correct any errors.
Pod
Pod is a container running environment that contains a group of containers and enables each container to share namespace, network, cgroups, data volumes and other resources with each other. Pod is just a container running environment, not a thread. It will always exist unless it is deleted. Two forms of pod.
- A pod with only one container: This pod can be considered as a wrapper of the container
- pod of a group of containers: it aggregates a group of tightly coupled containers that need to share resources
pod controller
Manage pod components
- Deployment
- ReplicaSet
- ReplicationController
- StatefulSet
- DaemonSet
Pod templates
The description of creating a pod tells the controller how to create a pod and what state you want the pod to run in k8s.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: hello
spec:
template:
# This is the pod template
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo "Hello, Kubernetes!" && sleep 3600']
restartPolicy: OnFailure
# The pod template ends here
Pod life cycle
Start - > pending
If at least one master node is started successfully - > running
If any container fails to start - > failed, otherwise it is successful - > succeeded
The pod will only be called once and will remain in the storage node unless the pod is stopped or removed. If the node hangs up, it will be deleted after exceeding the time limit. Pod creates a new one every time. With the same lifecycle is volume.
Init container
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/init-containers/
pod cluster distribution constraints (topology constraints)
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-topology-spread-constraints/
ReplicaSet
A ReplicaSet's purpose is to maintain a stable set of replica Pods running at any given time. As such, it is often used to guarantee the availability of a specified number of identical Pods.
This means that a certain number of replica sets of pods are always running to achieve high availability of pods. y generally, ReplicaSet is rarely used directly.
- Replicas: number of replicas expected by pod
- selector: Label used to filter the target Pod
- Template: the Pod template used to create a new Pod when the number of copies of the Pod is less than the expected number
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: frontend
labels:
app: guestbook
tier: frontend
spec:
# modify replicas according to your case
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
tier: frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
tier: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: php-redis
image: gcr.io/google_samples/gb-frontend:v3
Deployments
A Deployment provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
You describe a desired state in a Deployment, and the Deployment Controller changes the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate. You can define Deployments to create new ReplicaSets, or to remove existing Deployments and adopt all their resources with new Deployments.
Create a deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Compared with ReplicaSet, the biggest upgrade is that you can not only create replicas, but also view the status of deployment.
kubectl get deployments kubectl rollout status deployment/nginx-deployment
update deployment
kubectl set image deployment/nginx-deployment nginx=nginx:1.16.1 --record
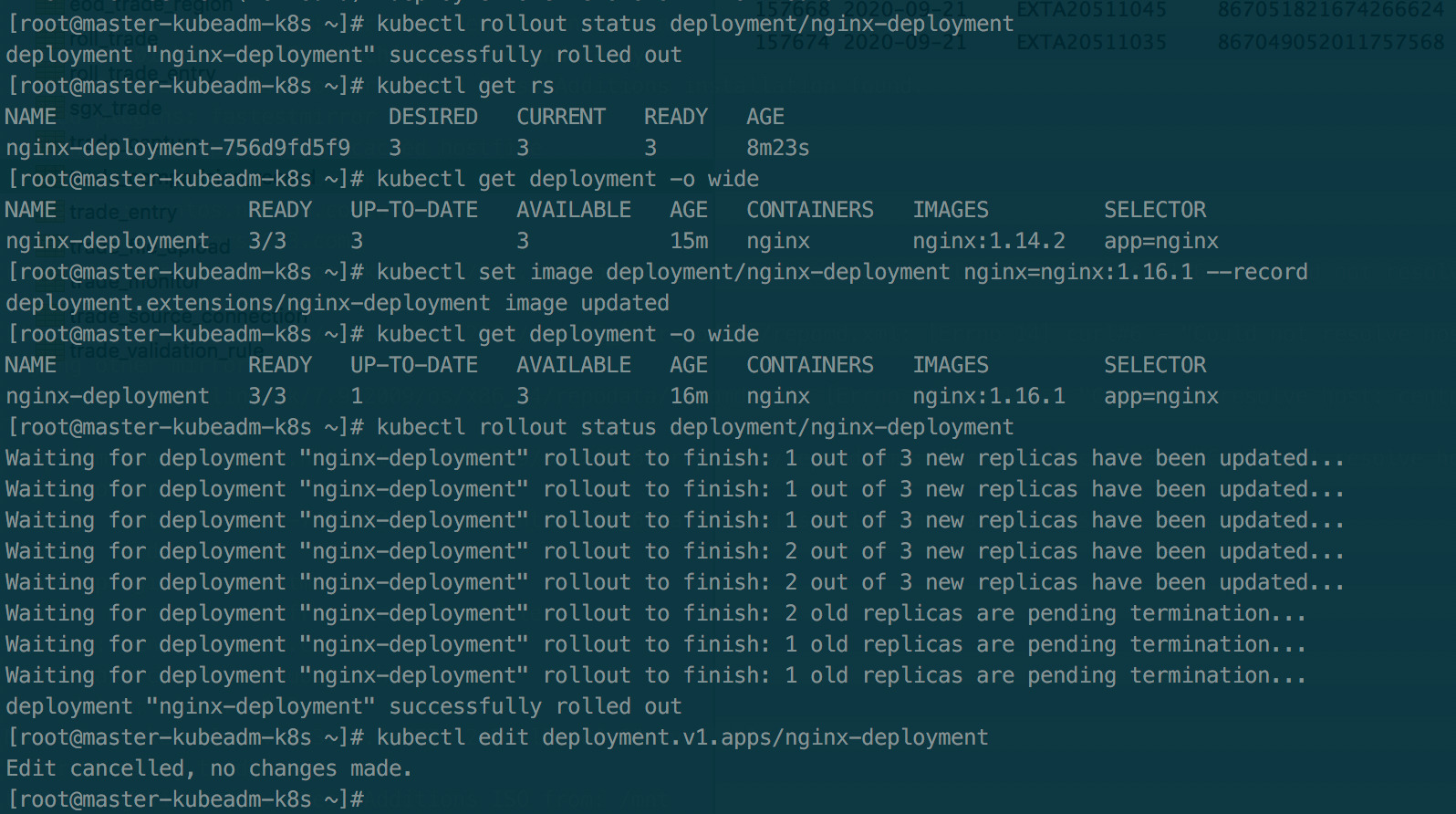
Rolling Back a Deployment
Sometimes there may be a problem with the deployed pod. At this time, you need to roll back to the previous version.
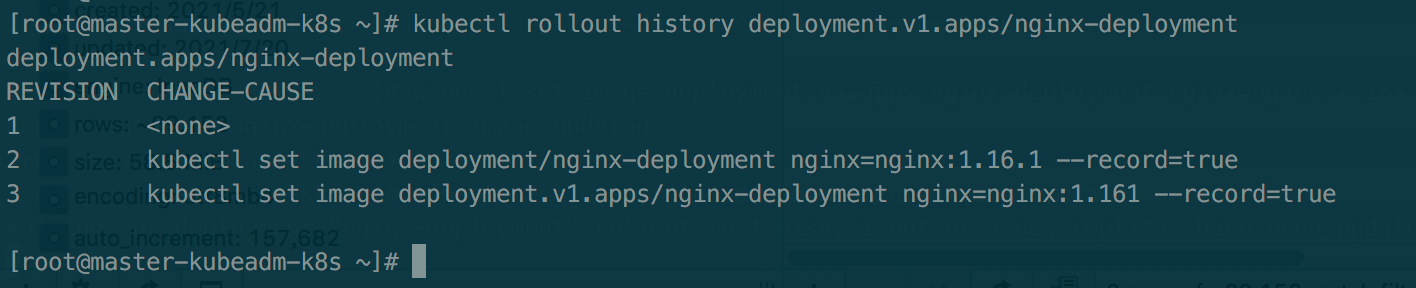
View version information
kubectl rollout history deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment #View version information kubectl describe deployment # View current deployment information kubectl rollout history deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment --revision=2 #View version details kubectl rollout undo deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment #Fallback to previous version kubectl rollout undo deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment --to-revision=2 #Fallback to the specified version
 ! [insert picture description here]( https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/51ff93353c7c893ac8baccf91b536753.png
! [insert picture description here]( https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/51ff93353c7c893ac8baccf91b536753.png

scale
kubectl scale deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment --replicas=10 kubectl autoscale deployment.v1.apps/nginx-deployment --min=10 --max=15 --cpu-percent=80
Labels and Selectors
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels/
Namespace
kubectl get pods -n kube-system kubectl get ns kubectl get pods --all-namespaces #Find pod s under all namespaces
Create namespace myns namespace yaml
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: myns