9, Service gateway: Gateway
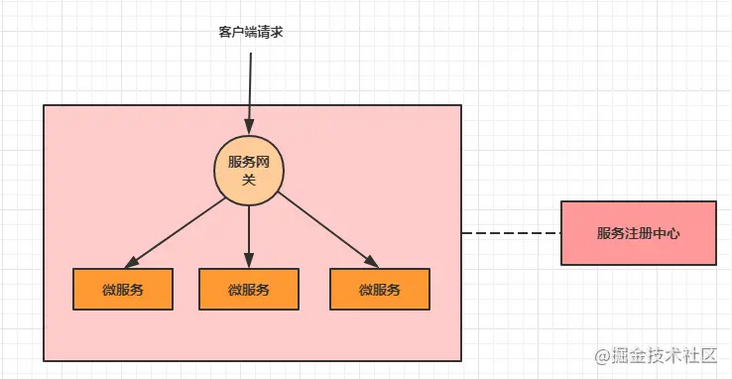
9.1 introduction to gateway
As we all know, in the microservice architecture, a system will be divided into many microservices. So how can a client call so many microservices? If there is no gateway, we can only record the address of each microservice on the client and call it separately.
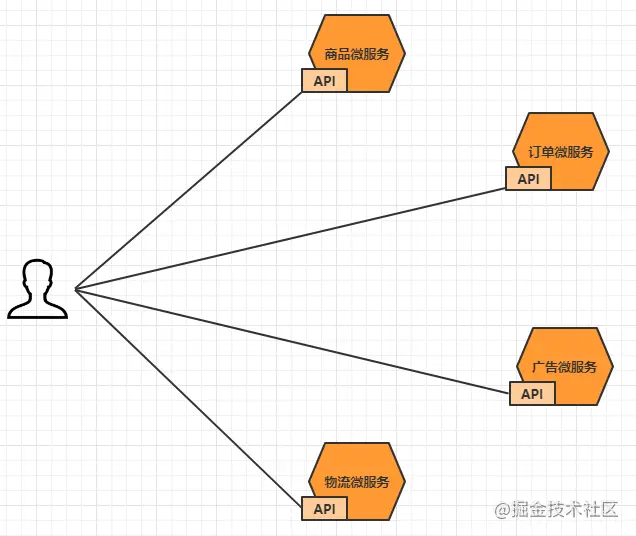
Such an architecture will have many problems:
- The client requests different microservices many times, which increases the complexity of client code or configuration writing.
- Authentication is complex, and each service needs independent authentication.
- There are cross domain requests, which are relatively complex to process in certain scenarios.
Gateway is designed to solve these problems. The so-called API gateway refers to the unified entrance of the system. It encapsulates the internal structure of the application and provides unified services for the client. Some public logic independent of the function of the business itself can be realized here, such as authentication, authentication, monitoring, routing and forwarding, etc.
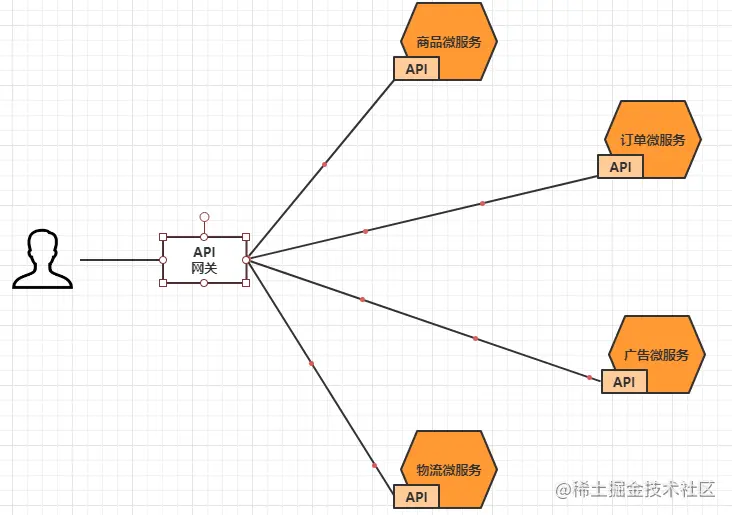
9.2. Common gateways
9.2.1,Ngnix+lua
Using nginx's reverse proxy and load balancing can realize load balancing and high availability of api servers.
lua is a scripting language that can write some simple logic. nginx supports lua scripts
9.2.2,Kong
Developed based on Nginx+Lua, it has high performance and stability. There are multiple available plug-ins (current limiting, authentication, etc.) that can be used out of the box.
His shortcomings:
- Only Http protocol is supported.
- Secondary development and free expansion are difficult.
- The Management API is provided, and there is a lack of more easy-to-use control and configuration methods.
9.2.3,Zuul
Netflix is an open source gateway with rich functions. It is developed in JAVA and easy for secondary development.
His shortcomings:
- Lack of control and dynamic configuration.
- There are many dependent components.
- Processing Http requests depends on the Web container, and its performance is not as good as Nginx.
9.2.4,Spring Cloud Gateway
The gateway service developed by Spring company to replace Zuul does not provide its own gateway in the Spring cloud Alibaba technology stack. We can use Spring Cloud Gateway as the gateway
9.3 introduction to Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway is a gateway developed by spring company based on Spring 5.0, Spring Boot 2.0 and Project Reactor. It aims to provide a simple and effective unified API routing management method for microservice architecture. Its goal is to replace Netflix Zuul, which not only provides a unified routing method, but also provides the basic functions of the gateway based on the Filter chain, such as security, monitoring and current limiting.
Its main functions are:
- Forward and redirect.
- At the beginning, all classes need to be initialized.
- Network isolation.
9.4. Quick start
Requirements: access the api gateway through the browser, and then forward the request to the commodity micro service through the gateway.
9.4.1 basic version
Create an API gateway module and import the following dependencies.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
Shop-parent
<groupId>cn.linstudy</groupId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
api-gateway
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--gateway gateway-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
spring-cloud-starter-gateway
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
lombok
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Copy codeWrite configuration file
server:
port: 9000 # Specified gateway service port
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes: # Routing array [routing is to specify which micro service to go to when the request meets what conditions]
- id: product_route # The identifier of the current route. It must be unique
uri: http://localhost:8081 # request address to forward
order: 1 # The lower the number, the higher the priority of the route
predicates: # Assertion (that is, the condition to be met by route forwarding)
- Path=/product-serv/** # When the request Path meets the rules specified by Path, route forwarding is carried out
filters: # Filter. The request can be modified through the filter during transmission
- StripPrefix=1 # Remove layer 1 path before forwarding
Copy codetest
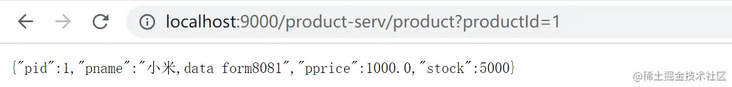
9.4.2. Upgraded version
We found a big problem with the upgraded version, that is, the address of the forwarding path is written in the configuration file. We need to get the address in the registry.
Join nacos dependency
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
Shop-parent
<groupId>cn.linstudy</groupId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
api-gateway
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--gateway gateway-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
spring-cloud-starter-gateway
</dependency>
<!--nacos client-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
lombok
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Copy codeAdd annotation on main class
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class GateWayServerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GateWayServerApp.class,args);
}
}
Copy codeModify profile
server:
port: 9000
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true # Let gateway discover microservices in nacos
routes:
- id: product_route # Name of route
uri: lb://Product service # LB refers to obtaining microservices by name from nacos and following load balancing policies
predicates:
- Path=/product-serv/** # Only those who meet this requirement will be 1 forwarded
filters:
- StripPrefix=1 # Remove the first layer
Copy codeWe can also customize multiple routing rules.
spring:
application:
gateway:
routes:
- id: product_route
uri: lb://product-service
predicates:
- Path=/product-serv/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: order_route
uri: lb://order-service
predicates:
- Path=/order-serv/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
Copy code9.4.3 simplified version
Our configuration file does not need to be written as complex as 1 to realize functions. There is a simplified version.
server:
port: 9000
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true # Let gateway discover microservices in nacos
Copy code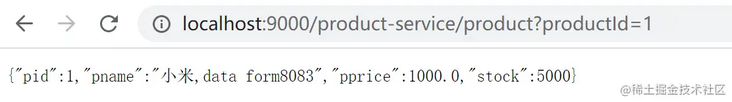
We found that as long as we access in the format of gateway address / microservice name / interface, we can get a successful response.
9.5 Gateway core architecture
9.5.1 basic concepts
Route is one of the most basic components in gateway, which represents a specific route information carrier. The following information is mainly defined:
- Route id: route id, which is different from other route identifiers.
- uri: the destination uri pointed by the route, that is, the micro service to which the client request is finally forwarded.
- order: used for sorting among multiple routes. The smaller the value, the higher the ranking and the higher the matching priority.
- predicate: the function of assertion is to judge conditions. Only when the assertions return true can the route be truly executed.
- Filter: filter is used to modify request and response information.
- predicate: assertion, which is used to judge conditions. Only when the assertions return true can the route be truly executed.
9.5.2 execution principle
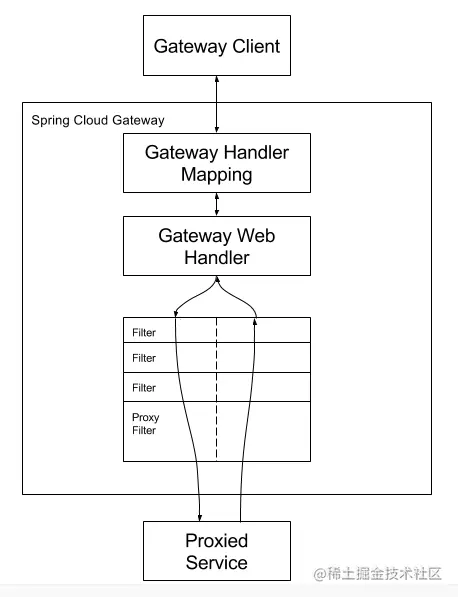
- After receiving the user's request, the request processor gives it to the processor mapper and returns to the execution chain.
- The request processor calls the web processor and processes our path 1 in the web processor. Suppose 1 our path 1 is: http://localhost:9000/product-serv/get?id=1 , according to the configured routing rules, find the corresponding service information locally: the host ip corresponding to product service is 192.168.10.130.
- Select a node according to 1ribbon's load balancing strategy, then splice it, and replace the product serv in the path with 192.168.10.130:8081. If you configure filter, it will go through the filter.
- If you don't have a custom route, the default Gateway will help you remove the first layer. The Gateway port starts from one / to the second / and counts as the first layer.

9.6 filter
The function of Gateway filter is to do some tricks on the request and response in the process of request transmission.
Life cycle of Gateway filter:
- PRE: this filter is called before the request is routed. We can use this filter to realize authentication, select the requested micro service in the cluster, record debugging information, etc.
- POST: this filter is executed after routing to the microservice. This filter can be used to add standard HTTP headers for responses, collect statistics and indicators, send responses from microservices to clients, and so on.
There are two types of Gateway filters in terms of scope: Gateway Filter and GlobalFilter:
- Gateway filter: applied to a single route or a packet route.
- GlobalFilter: applies to all routes.
9.6.1 local filter
A local filter is a filter for a single route. It is divided into built-in filter and custom filter.
9.6.1.1 built in filter
Many different types of gateway routing filters are built in the spring cloud gateway.
9.6.1.1.1 local filter content
| Filter factory | effect | parameter |
|---|---|---|
| AddRequestHeader | Add Header for original request | Name and value of Header |
| AddRequestParameter | Add request parameters to the original request | Parameter name and value |
| AddResponseHeader | Add Header for original response | Name and value of Header |
| DedupeResponseHeader | Eliminate duplicate values in response headers | De duplicate the name of the Header |
| Hystrix | Introduce circuit breaker protection of Hystrix for routing | The name of the HystrixCommand |
| FallbackHeaders | Add specific exception information to the request header of fallbackUri | The name of the Header |
| PrefixPath | Prefix the original request path | prefix path |
| PreserveHostHeader | Add a property of preserveHostHeader=true to the request, and the routing filter will check this property to decide whether to send the original Host | nothing |
| RequestRateLimiter | It is used to limit the current of requests. The current limiting algorithm is token bucket | keyResolver,rateLimiter,statusCode,denyEmptyKey,emptyKeyStatus |
| RedirectTo | Redirect the original request to the specified URL | http status code and redirected url |
| RemoveHopByHopHeadersFilter | Delete a series of headers specified by IETF organization for the original request | It will be enabled by default. You can specify which headers to delete only through configuration |
| RemoveRequestHeader | Delete a Header for the original request | Header name |
| RemoveResponseHeader | Delete a Header for the original response | Header name |
| RewritePath | Rewrite the original request path | Regular expressions of original path and rewritten path |
| RewriteResponseHeader | Override a Header in the original response | Header name, regular expression of value, rewritten value |
| SaveSession | Force the WebSession::save operation before forwarding the request | nothing |
| secureHeaders | Add a series of security response headers to the original response | None. It supports modifying the values of these security response headers |
| SetPath | Modify the original request path | Modified path |
| SetResponseHeader | Modify the value of a Header in the original response | Header name, modified value |
| SetStatus | Modify the status code of the original response | HTTP status code, which can be a number or a string |
| StripPrefix | The path used to truncate the original request | Use a number to indicate the number of paths to truncate |
| Retry | Retry for different responses | retries,statuses,methods,series |
| RequestSize | Sets the size of the maximum request packet allowed to be received. If the requested packet size exceeds the set value, 413 Payload Too Large is returned | The size of the request packet, in bytes. The default value is 5M |
| ModifyRequestBody | Modify the content of the original request body before forwarding the request | Modified request body content |
| ModifyResponseBody | Modify the content of the original response body | Modified response body content |
9.6.1.1.2 use of local filter
server:
port: 9000
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true # Let gateway discover microservices in nacos
routes:
- id: product_route # Name of route
uri: lb://Product service # LB refers to obtaining microservices by name from nacos and following load balancing policies
predicates:
- Path=/product-serv/** # Only those who meet this requirement will be 1 forwarded
filters:
- StripPrefix=1 # Remove the first layer
- SetStatus=2000 # The built-in filter is used here to modify the return status
Copy code9.6.1.2. User defined local filter
Many times, the built-in filter cannot meet our needs. At this time, we must customize the local filter. We assume that a requirement is to count the time-consuming of order service invocation.
Write a class for implementing logic
The name is a fixed format xxxGatewayFilterFactory
@Component
public class TimeGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<TimeGatewayFilterFactory.Config> {
private static final String BEGIN_TIME = "beginTime";
//Constructor
public TimeGatewayFilterFactory() {
super(TimeGatewayFilterFactory.Config.class);
}
//Read the parameter assignment in the configuration file and assign it to the configuration class
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() {
return Arrays.asList("show");
}
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config) {
return new GatewayFilter() {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
if (!config.show){
// If show in the configuration class is false, it means release
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
exchange.getAttributes().put(BEGIN_TIME, System.currentTimeMillis());
/**
* pre Logic of
* chain.filter().then(Mono.fromRunable(()->{
* post Logic of
* }))
*/
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(()->{
Long startTime = exchange.getAttribute(BEGIN_TIME);
if (startTime != null) {
System.out.println(exchange.getRequest().getURI() + "Request time: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms");
}
}));
}
};
}
@Setter
@Getter
static class Config{
private boolean show;
}
}
Copy codeWrite application xml
server:
port: 9000
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true # Let gateway discover microservices in nacos
routes:
- id: product_route # Name of route
uri: lb://Product service # LB refers to obtaining microservices by name from nacos and following load balancing policies
predicates:
- Path=/product-serv/** # Only those who meet this requirement will be 1 forwarded
filters:
- StripPrefix=1 # Remove the first layer
- id: order_route
uri: lb://order-service
predicates:
- Path=/order-serv/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- Time=true
Copy codeAccess path: http://localhost:9000/order-serv/getById?o=1&pid=1

9.6.2 global filter
The global filter works on all routes without configuration. Through the global filter, the functions of unified verification of permissions and security verification can be realized. Spring cloud gateway also processes the whole route forwarding through a series of built-in global filters.
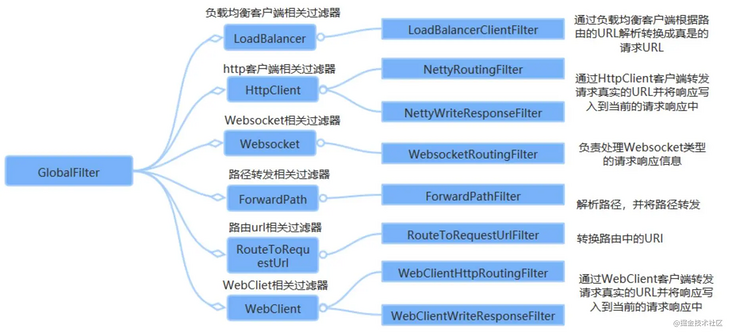
Authentication logic in development:
- When the client requests the service for the first time, the server authenticates (logs in) the user.
- After passing the authentication, the user information is encrypted to form a token, which is returned to the client as the login credential.
- After each request, the client will carry the authentication token.
- The server decrypts the token to determine whether it is valid.
Let's simulate a requirement: to realize the function of unified authentication, we need to judge whether the request contains a token in the gateway, and if not, we will not forward the route, and if yes, we will execute the normal logic.
Write global filter
@Component
public class AuthGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter {
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
String token = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("token");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(token)) {
System.out.println("Authentication failed");
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete();
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
}
Copy code9.6.3 gateway current limiting
The gateway is the common entrance for all requests, so the current can be limited in the gateway, and there are many ways to limit the current. This time, we use the sentinel component learned earlier to realize the current limit of the gateway. Sentinel supports current limiting for spring cloud gateway, Zuul and other mainstream gateways.
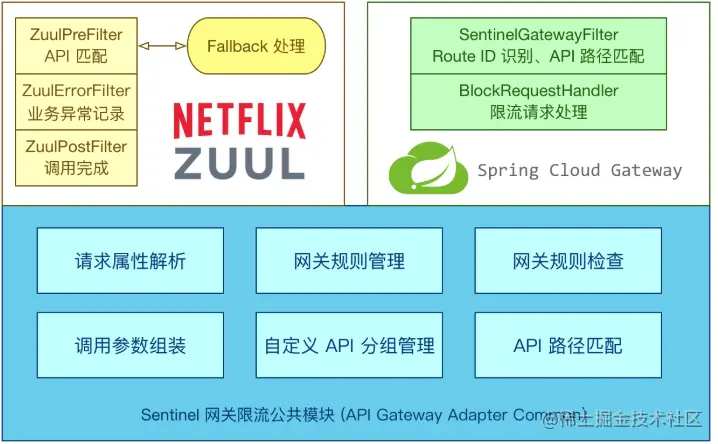
Starting from version 1.6.0, Sentinel provides the adaptation module of spring cloud gateway, which can provide flow restriction of two resource dimensions:
- Route dimension: the route entry configured in the Spring configuration file. The resource name is the corresponding routeId
- Custom API dimension: users can use the API provided by Sentinel to customize some API groups
9.6.3.1 gateway integration Sentinel
Add dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
sentinel-spring-cloud-gateway-adapter
</dependency>
Copy codeWrite configuration class for current limiting
The essence of configuration class is to replace the current limiting of nacos graphical interface with code.
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfiguration {
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public GatewayConfiguration(ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer) {
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
// Configure current limiting exception handler
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler sentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler() {
// Register the block exception handler for Spring Cloud Gateway.
return new SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler(viewResolvers, serverCodecConfigurer);
}
// Initialize a current limiting filter
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public GlobalFilter sentinelGatewayFilter() {
return new SentinelGatewayFilter();
}
//Increase the flow restriction of goods and micro services
@PostConstruct
private void initGatewayRules() {
Set<GatewayFlowRule> rules = new HashSet<>();
rules.add(new GatewayFlowRule("product_route")
.setCount(3) // Three times
.setIntervalSec(1) // One second means that the current will be limited after one second 1 exceeds three times
);
GatewayRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
}
Copy codeModify the default return format of current limiting
If we don't want to return the default error when limiting the current, we need to customize the error and specify the custom return format. We just need to add a configuration to the class.
@PostConstruct
public void initBlockHandlers() {
BlockRequestHandler blockRequestHandler = new BlockRequestHandler() {
public Mono<ServerResponse> handleRequest(ServerWebExchange serverWebExchange, Throwable throwable) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", 0);
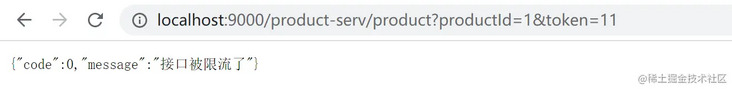
map.put("message", "The interface is current limited");
return ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.OK).
contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).
body(BodyInserters.fromValue(map));
}
};
GatewayCallbackManager.setBlockHandler(blockRequestHandler);
}
Copy codetest
9.6.3.2. User defined API grouping
We can find that the above definition limits the flow of the whole service, and the granularity is not fine enough. Custom API grouping is a more fine-grained flow restriction rule definition, which can realize the fine-grained flow restriction of a method.
Add ApiController to the shop order server project
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String api1(){
return "api";
}
}
Copy codeAdd configuration in gateway configuration
@PostConstruct
private void initCustomizedApis() {
Set<ApiDefinition> definitions = new HashSet<>();
ApiDefinition api1 = new ApiDefinition("order_api")
.setPredicateItems(new HashSet<ApiPredicateItem>() {{
add(new ApiPathPredicateItem().setPattern("/order-serv/api/**"). setMatchStrategy(SentinelGatewayConstants.URL_MATCH_STRATEGY_PREFIX));
}});
definitions.add(api1);
GatewayApiDefinitionManager.loadApiDefinitions(definitions);
}
@PostConstruct
private void initGatewayRules() {
Set<GatewayFlowRule> rules = new HashSet<>();
rules.add(new GatewayFlowRule("product_route")
.setCount(3)
.setIntervalSec(1)
);
rules.add(new GatewayFlowRule("order_api").
setCount(1).
setIntervalSec(1));
GatewayRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
Copy codetest
Direct access http://localhost:8082/api/hello Current limiting will not occur, and access http://localhost:9000/order-serv/api/hello There will be current limiting.
Author: XiaoLin_Java
Link: https://juejin.cn/post/700181...
Source: rare earth Nuggets
The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprint, please contact the author for authorization. For non-commercial reprint, please indicate the source.
WeChat public number [programmer Huang Xiaoxie] is the former engineer of ant Java, who focuses on sharing Java technology dry cargo and job search experience. It is not limited to BAT interview, algorithm, computer basis, database, distributed official account, spring family bucket, micro service, high concurrency, JVM, Docker container, ELK, big data, etc. After paying attention, reply to [book] to receive 20 selected high-quality e-books necessary for Java interview.