catalogue
1, Concepts of sets, lists, and arrays
(2) Advantages and disadvantages
(2) The difference between array and list
1. One dimensional array concept
4. Subscript of one-dimensional array
5. Application of one-dimensional array
1. Find the maximum and minimum value in the array
2. Sort the array a[10]={10,4,3,7,9,18,14,12,17,15}
1. Concept of two-dimensional array
2. Definition of two-dimensional array
3. Initialization of two-dimensional array
1. Find the central index of the array

1, Concepts of sets, lists, and arrays
1. Assemble
(1) Set concept
A set is generally a collective composed of one or more definite elements.
Example a: all the fruits in the store
Example b: there are many heroes in the glory of the king
(2) Three elements of set
Curly braces, commas, and elements
Example a: {1,2,3,4,5}
Example b: {apple, banana, watermelon}
(3) Properties of sets
a: Disorder: the order of elements in the set is irregular and disordered.
b: Certainty: the elements in the set are deterministic
c: Dissimilarity: the elements in the collection must be different from each other
2. List
(1) List concept
List: a list is a finite sequence of data items, that is, a set of data items arranged in a certain linear order.
(2) List features
a: Orderly
b: Variable length
(3) Main performance
Array and linked list, stack and queue are two special types of linked list.
Note: the specific implementation methods of adding and deleting elements in the list are different from different programming languages.
3. Index
(1) Index concept
Index is a decentralized storage structure established for a table to accelerate the retrieval of data rows in the table.
(2) Advantages and disadvantages
advantage:
a: Fast data retrieval speed
b: Uniqueness is created to ensure the uniqueness of data records in each row;
c: It speeds up the connection between tables and reduces the time of grouping and sorting in query
Disadvantages:
a: Indexes need to occupy physical space.
b: When the data in the table is added, deleted and modified, the index should also be maintained dynamically, which reduces the speed of data maintenance.
4. Array
(1) Array concept
Arrays use numbers called indexes to identify the position of each item of data in the array, and in most programming languages, the index is calculated from 0.
(2) The difference between array and list
There is no index in the list and there is an index in the array, which is the biggest difference between the array and the list. At the same time, the elements in the array are continuously stored in memory, and each element occupies the same size of memory; The elements in the list may or may not be adjacent to each other in memory.
2, One dimensional array
1. One dimensional array concept
Collections of the same type are called arrays.
2. Definition method
Data type array name [constant expression]
int a[10] //Integer array, array name is a, 10 is a constant expression, [] array length
3. Array initialization
/*
int a[3];
a[0]=1;
a[1]=2;
a[3]=4;
//Due to the complexity of this method, its ellipsis is generally used
*/
int a[0]={1,2,4}; //Ellipsis
float b[10]={3,2,4,5,1}; //All unassigned values are 0
char s[]="study" //Character type array s [], with a length of 6 and characters ending with "\ 0", so the length is 6;4. Subscript of one-dimensional array
The subscript of a one-dimensional array is actually the offset of the first element of the array.
The subscript of the last element of one-dimensional array is (length - 1)
Example 1:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10]={1,4,3,7,9,18,14,12,17,15};
for(int i=0;i<10;++i)
{
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}Result demonstration:

5. Application of one-dimensional array
1. Find the maximum and minimum value in the array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10]={10,4,3,7,9,18,14,12,17,15};
int max=a[0],min=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<10;++i)
{
if(a[i]>=max)
{
max=max;
}
if(a[i]<min)
{
min=a[i];
}
}
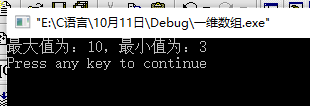
printf("The maximum value is:%d,The minimum value is:%d",max,min);
printf("\n");
}Result demonstration:
2. Sort the array a[10]={10,4,3,7,9,18,14,12,17,15}
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10]={10,4,3,7,9,18,14,12,17,15};
int tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;++i)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<10;++j)
{
if(a[i]>=a[j])
{
tmp=a[j];
a[j]=a[i];
a[i]=tmp;
}
}
}
for(int k=0;k<10;++k)
{
printf("%d ",a[k]);
}
printf("\n");
}Result demonstration:

III. two dimensional array
1. Concept of two-dimensional array
An array that stores arrays is called a two-dimensional array
Example 2: a[3][4]
| a[0][0] | a[0][1] | a[0][2] | a[0][3] |
| a[1][0] | a[1][1] | a[1][2] | a[1][3] |
| a[2][0] | a[2][1] | a[2][2] | a[2][3] |
2. Definition of two-dimensional array
Data type array name [constant expression] [constant expression]
3. Initialization of two-dimensional array
//Piecewise assignment
int a[3][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6},{7,8,9}};
//continuous assignment
int b[3][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};Example 3:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[3][3]={80,89,85,90,98,88,87,86,99};
for(int i=0;i<3;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<3;++j)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
Result demonstration:

4, Examples
1. Find the central index of the array
To give you an integer array {nums, please calculate the central subscript of the array.
The central subscript of the array is a subscript of the array. The sum of all elements on the left is equal to the sum of all elements on the right.
If the central subscript is at the leftmost end of the array, the sum of the numbers on the left is regarded as 0 because there is no element to the left of the subscript. The same applies when the central subscript is at the rightmost end of the array.
If the array has multiple central subscripts, the one closest to the left should be returned. Returns - 1 if the array does not have a central subscript
(author: LeetCode)
Link: https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/array-and-string/yf47s/
Source: LeetCode

Code details:
int pivotIndex(int* nums, int numsSize){
int sum=0,a=0;
for(int i=0;i<numsSize;++i){
sum+=nums[i]; //Sum
}
for(int i=0;i<numsSize;++i){
if(2*a+nums[i]==sum){
return i;
}else a+=nums[i];
}
return -1;
}2. Search insertion location
Given a sort array and a target value, find the target value in the array and return its index. If the target value does not exist in the array, return the position where it will be inserted in order.
You must use an algorithm with a time complexity of O(log n).
Author: leetcode
Link: https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/array-and-string/cxqdh/
Source: LeetCode
The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprint, please contact the author for authorization. For non-commercial reprint, please indicate the source.
Author: leetcode
Link: https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/array-and-string/cxqdh/
Source: LeetCode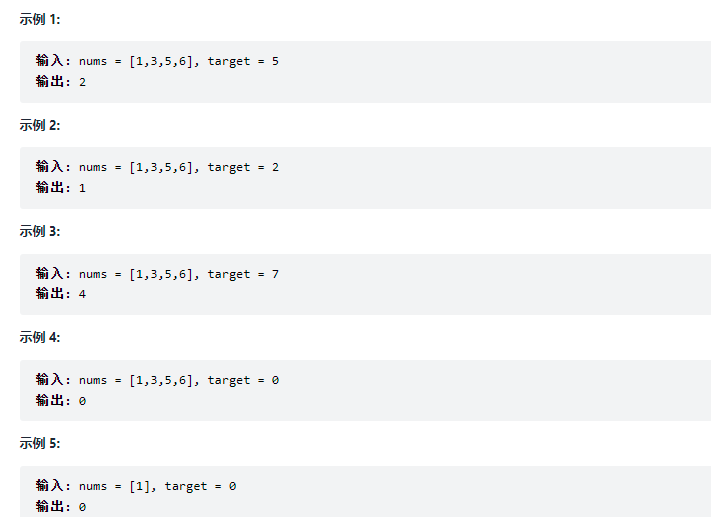
//Since the nums [] array is ordered, the binary search method can be used
int searchInsert(int* nums, int numsSize, int target){
int left=0,right=numsSize-1; //Define left and right boundaries
int mid;
while(left<=right){
mid=left+(right-left)/2; //Find intermediate subscript
if(nums[mid]==target){ //Judge whether the intermediate value is equal to the target value
return mid;
}
if(nums[mid]>target){ //When the intermediate value is greater than the target value
right=mid-1; //Narrow the judgment range,
}else {
left=mid+1;
}
}
return left;
}5, Summary
Array is very important in C language. It is a common data structure in programming and belongs to construction type. Array should be used flexibly in design.