1. Disk Foundation
1. Data structure
Sectors: The disk is divided into sectors, each containing 5 12 bytes of data
Track: Concentric circles of the same disc with different radii
Cylindrical surface: Cylindrical surface with the same radius of different discs
2. Physical Structure
Disk: Hard disk has multiple disks, two sides each
Head: one head on each side
3. Storage capacity (Understanding)
Hard Disk Storage Capacity = Number of Heads × Track (Cylindrical) Number × Sectors Per Trark × Bytes per sector
Each region on the disk can be uniquely located using a cylindrical surface/head/sector
4. Disk interface type
IDE, SATA, SCSI, SAS, Fiber Channel
2. Disk Partition Representation
1.MBR
MBR is Master Boot Record
Located in the first physical sector of the hard disk.
MBR contains the hard disk bootstrapper and hard disk partition table.
The partition table has four partition record areas, each of which accounts for 16 bytes.
/dev/sda5 /dev/hda2
Explain:
/dev is the directory where the files of the hardware device are located
sd means SCSI device, hd means IDE device
A denotes the serial number of the hard disk, in order a,b,c
5 represents the order number of the partition, sorted by 1,2,3
2. Structure of disk partitions
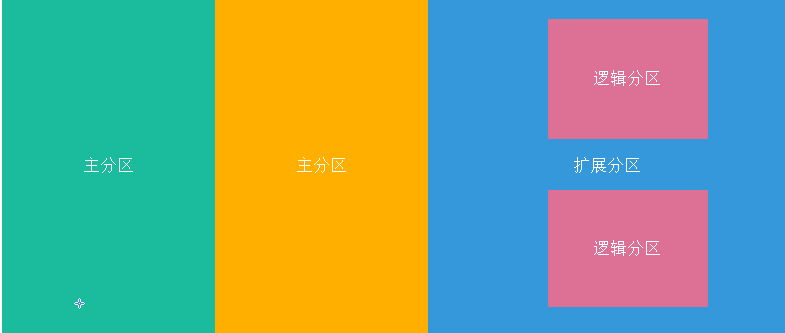
Common hard disks can be divided into primary partitions, extended partitions, and logical partitions.
A hard disk may all be a primary partition, up to four.
The maximum number of primary plus extended partitions is 4.
Extended partitions are divided into logical partitions. Extended partitions are shells that do not have data, and the data is mainly stored in logical partitions.
Logical partitions always start with a sequence number of 5.
3. File system type
(1) XFS file system
Partitions holding file and directory data
High Performance Logged File System
File system used by default in CentOS7 system
(2) SWAP, Exchange File System
Setting up a swap partition for Linux systems
(3) Other file system types supported by Linux
FAT16,FAT32,NTFS
EXT4,JFS...
4. Manage disks and partitions
(1) Add and detect new hard disks to confirm
The virtual machine emulates the addition of a hard drive, which needs to be restarted.
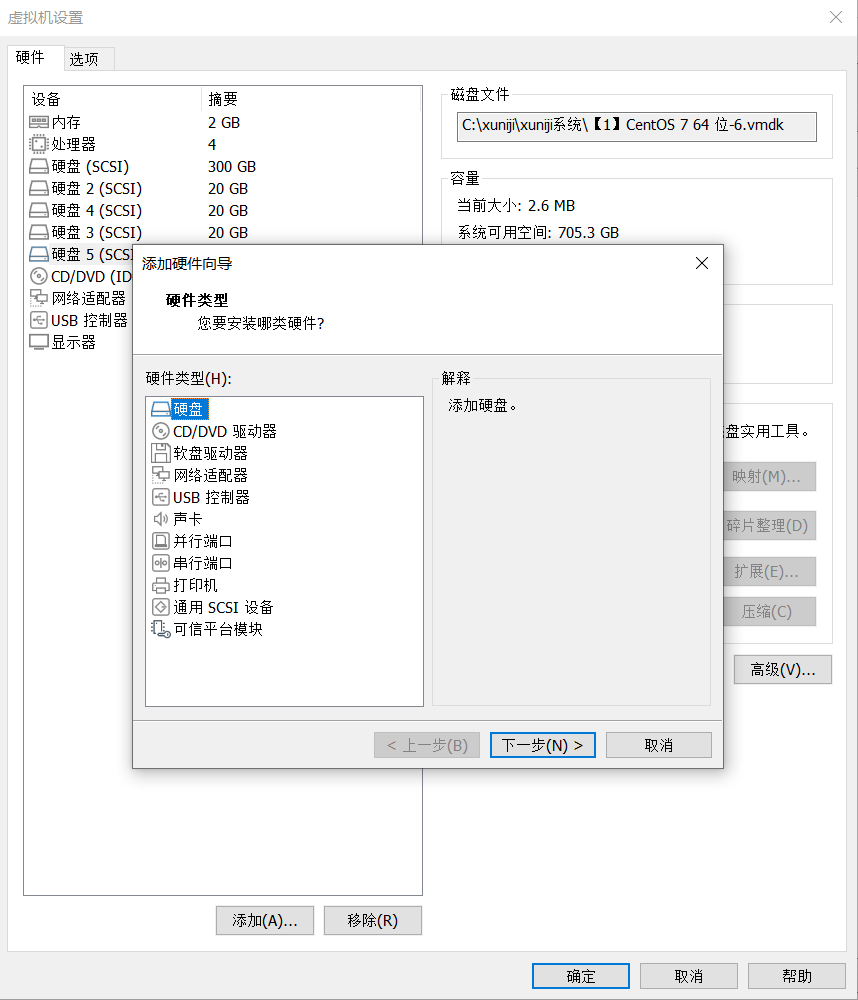
View all hard disk devices and their partitions in the current system after restart
fdisk -l
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l disk /dev/sda: 322.1 GB, 322122547200 Bytes, 629145600 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0 x0009b660 equipment Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 2048 41 1647 204800 83 Linux /dev/sda2 411648 6703103 3145728 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda3 6703104 629145599 311221 24 8 83 Linux disk /dev/sdc: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte disk /dev/sde: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte disk /dev/sdd: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte
(2) Planning partitions on your hard disk
Create Delete Change Partition on Hard Disk Use fdisk command to enter interactive setup page
Take the hard disk/dev/sdd partition as an example
fidsk /dev/sdd
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /etc/sdd fdisk: Cannot be opened /etc/sdd: No file or directory [root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdd Welcome fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory until you decide to write them to disk. Think twice before using the Write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table Use disk identifier 0 xbb987682 Create a new DOS Disk label. command(input m get help):
Enter m for help
command(input m get help): m Command Action a toggle a bootable flag b edit bsd disklabel c toggle the dos compatibility flag d delete a partition g create a new empty GPT partition table G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table l list known partition types m print this menu n add a new partition o create a new empty DOS partition table p print the partition table q quit without saving changes s create a new empty Sun disklabel t change a partition's system id u change display/entry units v verify the partition table w write table to disk and exit x extra functionality (experts only)
1) p Directive - List partitions on your hard drive and view partition tables
Empty list without partition
command(input m get help): p disk /dev/sdd: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0 xbb987682 equipment Boot Start End Blocks Id System
2) n Directive - New Partition
New partition includes primary partition and extended partition, p new primary partition, e new extended partition
command(input m get help): n Partition type: p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended Select (default p):
Create 2 new primary partitions
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition Number (1-4,Default 1): 1
Starting Sector (2048-41943039,Default is 2048): 2048
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039,Default is 444339): 2G
Value is out of range.
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039,Default is 444339): +2G
Partition 1 is set to Linux Type, size set to 2 GiB
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition Number (2-4,Default 2): 2
Starting Sector (4196352-41943039,Default is 4196352):
Default value 4196352 will be used
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (4196352-41943039,Default is 444339): +2g
Unsupported suffix: g".
Support:10^N: KB (Kilobytes), MB (Megabytes), GB (Gigabytes)
2^N: K (About kilobytes), M (About megabytes), G (Yogi bytes)
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (4196352-41943039,Default is 444339): +2G
Partition 2 is set to Linux Type, size set to 2 GiB
command(input m get help):
Create one extended partition and two logical partitions
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended
Select (default p): e
Partition Number (3,4,Default 3): 4
Starting Sector (8390 65 6-41943039,Default is 8390656):
Default value 8390656 will be used
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (8390656-41943039,Default is 444339): +2G
Partition 4 is set to Extended Type, size set to 2 GiB
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 1 extended, 1 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l
Add Logical Partition 5
Starting Sector (8392704-12584959,Default is 8392704):
Default value 8392704 will be used
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (8392704-12584959,Default is 12584959): +2G
Value is out of range.
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (8392704-12584959,Default is 12584959): +1G
Partition 5 is set to Linux Type, size set to 1 GiB
command(input m get help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 1 extended, 1 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l
Add Logical Partition 6
Starting Sector (10491904-12584959,Default is 10491904):
Default value 10491904 will be used
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (10491904-12584959,Default is 12584959):
The default value of 12584959 will be used
Partition 6 is set to Linux Type, size set to 1022 MiB
command(input m get help):
You can check the partition again after completing the p command
command(input m get help): p disk /dev/sdd: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = A sector of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0 xbb987682 equipment Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdd1 2048 4196351 2097152 83 Linux /dev/sdd2 4196352 6293503 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdd4 8390656 12584959 2097152 5 Extended /dev/sdd5 8392704 10489855 1048576 83 Linux /dev/sdd6 10491904 12584959 1046528 83 Linux command(input m get help):
3) d Directive - Delete Partition
Delete Partition Enter Partition Sequence Number
command(input m get help): d Partition Number (1,2,4-6,Default 4): 6 Partition 6 deleted command(input m get help):
4) t Directive - Change Partition Type
The t command changes the ID number of the partition, and different types of file systems correspond to different ID numbers. The swap file system ID number is 82.
Change primary partition 2 to swap partition
command(input m get help): t Partition Number (1,2,4,5,Default 5): 2 Hex Code(input L List all codes): L 0 empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / used Linu bf Solaris 1 FAT12 27 Hidden NTFS Win 82 Linux exchange / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 2 XENIX root 39 Plan 9 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 3 XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic 84 OS/2 Hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT- 4 FAT16 <32M 40 Venix 80286 85 Linux extend c7 Syrinx 5 extend 41 PPC PReP Boot 86 NTFS Volume Set da Non-file system data 6 FAT16 42 SFS 87 NTFS Volume Set db CP/M / CTOS / . 7 HPFS/NTFS/exFAT 4d QNX4.x 88 Linux Pure text de Dell tool 8 AIX 4e QNX4.x Part 2 8 e Linux LVM df BootIt 9 AIX Startable 4f QNX4.x Part 3 93 Amoeba e1 DOS Visit a OS/2 Startup Manager 50 OnTrack DM 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O b W95 FAT32 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 52 CP/M a0 IBM Thinkpad Rest eb BeOS fs e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a5 FreeBSD ee GPT f W95 extend (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/ 10 OPUS 55 EZ-Drive a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC 11 Hidden FAT12 56 Golden Bow a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor 12 Compaq Diagnosis 5c Priam Edisk a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor 14 Hidden FAT16 <3 61 SpeedStor ab Darwin start-up f2 DOS secondary 16 Hidden FAT16 63 GNU HURD or Sys af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS 17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 64 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE 18 AST Smart Sleep 65 Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid automatic 1b Hidden W95 FAT3 70 DiskSecure Multiple Enables bb Boot Wizard latent fe LANstep 1c Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX be Solaris start-up ff BBT 1e Hidden W95 FAT1 80 used Minix Hex Code(input L List all codes): 82 Partitioned" Linux"Change the type of Linux swap / Solaris" command(input m get help):
p Directive View After Changes Complete
command(input m get help): p disk /dev/sdd: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 Bytes, 41943040 sectors Units = cylinder of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Sector Size(logic/Physics): 512 byte / 512 byte I/O Size(Minimum/optimum): 512 byte / 512 byte Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0 xbb987682 equipment Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdd1 1 262 2097152 83 Linux /dev/sdd2 262 524 2103296 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sdd4 524 786 2104320 5 Extended /dev/sdd5 524 785 2102272 83 Linux command(input m get help):
5) w and q directives - Exit fdisk partition tool
The w directive is a save partition operation
q directive exits without saving partition operation
command(input m get help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Synchronizing disks.
3. Manage File System
1. Create a file system
The mkfs command tool formats partitions, and the mkswap command formats swap exchange partitions.
(1) mkfs command
View all partitions and partition types in the system
blkid
[root@localhost ~]# blkid /dev/sr0: UUID="2018-11-25-23-54-16-00" LABEL="CentOS 7 x86_64" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="dos" /dev/sda1: UUID="193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sda2: UUID="7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769" TYPE="swap" /dev/sda3: UUID="0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81" TYPE="xfs"
Lsblk-f more detailed
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk -f NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 xfs 193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813 /boot ├─sda2 swap 7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769 [SWAP] └─sda3 xfs 0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81 / sdb sdc sdd ├─sdd1 ├─sdd2 ├─sdd4 └─sdd5 sde sr0 iso9660 CentOS 7 x86_64 2018-11-25-23-54-16-00 /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
1) Create xfs file system
xfs file system is used by default in centos7 system
Mkfs-t XFS partition device
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdd1
meta-data=/dev/sdd1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
2) Create ext4 file system
Mkfs-t ext4 partition device
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdd2 mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013) File System Label= OS type: Linux Block size=4096 (log=2) Block size=4096 (log=2) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 131648 inodes, 525824 blocks 26291 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=538968064 17 block groups 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group 7744 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912 Allocating group tables: complete Writing inode surface: complete Creating journal (16384 blocks): complete Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: complete
View after creation
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk -f NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 xfs 193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813 /boot ├─sda2 swap 7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769 [SWAP] └─sda3 xfs 0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81 / sdb sdc sdd ├─sdd1 xfs be9f4ade-f3a9-41c1-8acd-83ce58271edd ├─sdd2 ext4 b431d684-f210-4f4a-abf9-8f9698a353dd ├─sdd4 └─sdd5 sde sr0 iso9660 CentOS 7 x86_64 2018-11-25-23-54-16-00 /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
(2) mkswap command
Create Exchange File System
mkswap partition device
If the target partition ID number is 82, fdisk is required to swap partitions first if it is not 82.
[root@localhost ~]# blkid /dev/sr0: UUID="2018-11-25-23-54-16-00" LABEL="CentOS 7 x86_64" TYPE="iso9660" PTTYPE="dos" /dev/sda1: UUID="193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sda2: UUID="7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769" TYPE="swap" /dev/sda3: UUID="0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sdd1: UUID="be9f4ade-f3a9-41c1-8acd-83ce58271edd" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sdd2: UUID="b91ec746-8bbf-4258-8d03-a2d1f081a897" TYPE="swap" [root@localhost ~]# mkswap /dev/sdd2 mkswap: /dev/sdd2: warning: wiping old swap signature. Setting swap space version 1, size = 2103292 KiB No label, UUID=ed114f9a-cd02-4c4d-a67e-489b9218bd60 [root@localhost ~]# lsblk -f NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 xfs 193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813 /boot ├─sda2 swap 7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769 [SWAP] └─sda3 xfs 0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81 / sdb sdc sdd ├─sdd1 xfs be9f4ade-f3a9-41c1-8acd-83ce58271edd ├─sdd2 swap ed114f9a-cd02-4c4d-a67e-489b9218bd60 ├─sdd4 └─sdd5 sde sr0 iso9660 CentOS 7 x86_64 2018-11-25-23-54-16-00 /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
swapon enables swap partitions, swapoff disables swap partitions
Swapon-s See what swap partitions your current system is using
[root@localhost ~]# swapon /dev/sdd2 [root@localhost ~]# swapon -s file name type Size Used Jurisdiction /dev/sda2 partition 3145724 0 -2 /dev/sdd2 partition 2103292 0 -3
view memory
[root@localhost ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 792 155 28 870 763
Swap: 5125 0 5125
[root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/meminfo | grep -i "swaptotal"
SwapTotal: 3145724 kB
[root@localhost ~]# swapon /dev/sdd2
[root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/meminfo | grep -i "swaptotal"
SwapTotal: 5249016 kB
2. Mount and uninstall the file system
When mounting a partition, you must specify a directory as the mount point through which users can access file directory data in the device.
(1) Mount the file system mount command
Create a new directory Tom and mount device/dev/sdd1 under root/tom
mkdir tom
mount /dev/sdd1 /root/tom
[root@localhost ~]# lsblk -f NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 xfs 193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813 /boot ├─sda2 swap 7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769 [SWAP] └─sda3 xfs 0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81 / sdb sdc sdd ├─sdd1 xfs be9f4ade-f3a9-41c1-8acd-83ce58271edd ├─sdd2 swap ed114f9a-cd02-4c4d-a67e-489b9218bd60 [SWAP] ├─sdd4 └─sdd5 sde sr0 iso9660 CentOS 7 x86_64 2018-11-25-23-54-16-00 /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64 [root@localhost ~]# mkdir tom [root@localhost ~]# ls 11 123 145 195 22 33 a aa anaconda-ks.cfg b bb initial-setup-ks.cfg qq tom Public Template Video Picture Document Download Music Desktop [root@localhost ~]# cd tom [root@localhost tom]# pwd /root/tom [root@localhost tom]# cd [root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sdd1 /root/tom [root@localhost ~]# lsblk -f NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 xfs 193b25aa-faee-4342-a79b-4eb3e023d813 /boot ├─sda2 swap 7f11b069-c75e-453e-a192-62c8dc883769 [SWAP] └─sda3 xfs 0ce0ca4e-ddf3-474f-8a4e-a7ee517b5b81 / sdb sdc sdd ├─sdd1 xfs be9f4ade-f3a9-41c1-8acd-83ce58271edd /root/tom ├─sdd2 swap ed114f9a-cd02-4c4d-a67e-489b9218bd60 [SWAP] ├─sdd4 └─sdd5 sde sr0 iso9660 CentOS 7 x86_64 2018-11-25-23-54-16-00 /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64
Explain:
Mount mounts are temporary and will not occur after the device is restarted. To take effect permanently, you need to write the mount configuration to / etc/fstab and save it
vim /etc/fstab

Write in
/dev/sdd1 /root/tom xfs defaults 0 0
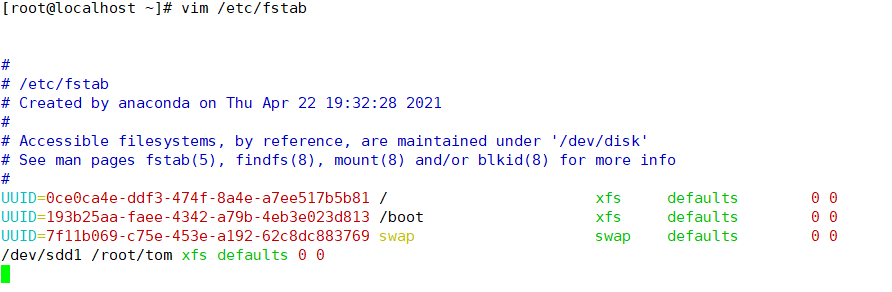
How to mount the tray permanently
mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
vim /etc/fstab
/dev/sr0 /mnt iso9660 defaults 0 0
wq save
Mount-a mount takes effect immediately
(2) Uninstall the file system umount command
umount device name or mount mount point
Umount/dev/sdd1 or umount/root/tom
(3) View disk usage
df -Th
[root@localhost ~]# df -Th file system type Capacity used Available Used% mount point /dev/sda3 xfs 297G 5.4G 292G 2% / devtmpfs devtmpfs 895M 0 895M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 910M 11M 900M 2% /run tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 xfs 197M 152M 45M 78% /boot tmpfs tmpfs 182M 8.0K 182M 1% /run/user/42 tmpfs tmpfs 182M 36K 182M 1% /run/user/0 /dev/sr0 iso9660 4.3G 4.3G 0 100% /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64 /dev/sdd1 xfs 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /root/tom