1, Introduction
shardingsphere is a product of Apache, mainly including Sharding JDBC and Sharding Proxy. The former can be regarded as an enhanced version of JDBC, and the latter is an independent proxy system without coupling in the code. In this regard, it is very similar to Mycat
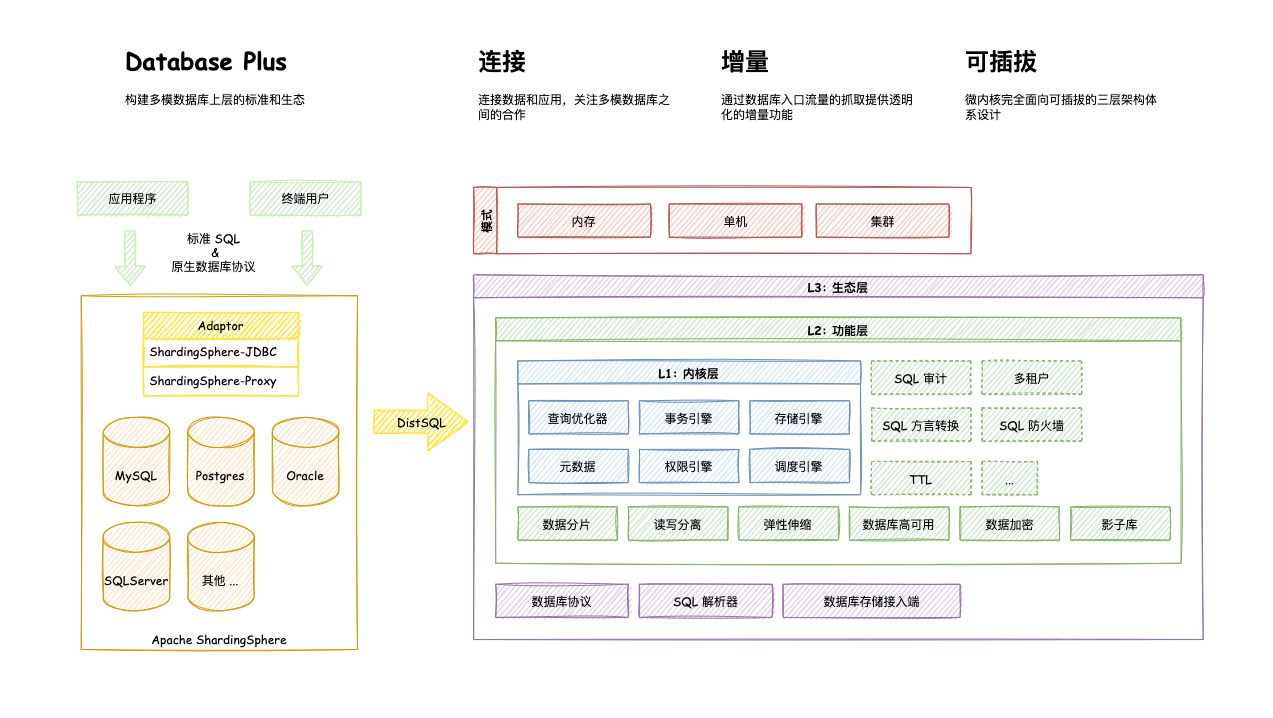
2, What did ShardingJDBC do for me?
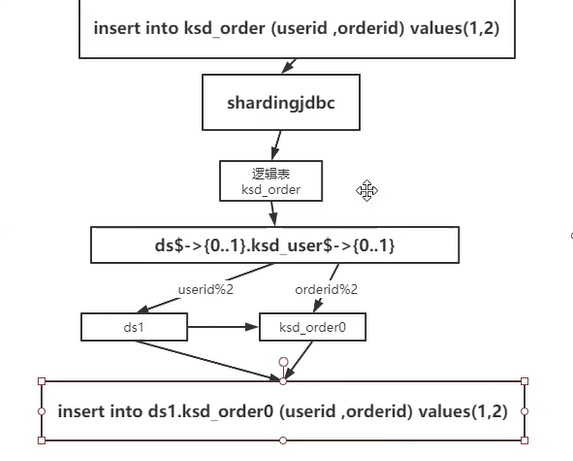
When using Sharding JDBC, we need to configure rules in the configuration file. This rule is used to tell it how to parse an SQL we send, such as the following figure, logical table ksd_order does not exist at all. It will judge the data source and the table of the corresponding data source according to the configured rules, and finally send the SQL conversion to the corresponding data source for execution.
How does distributed Sharding JDBC ensure distributed transaction management?
1. Local non cross database
In this case, local transactions can be used, for example, the @ Transactional annotation can be used directly
2. Distributed cross database
In this case, there is good support for two-phase XA transactions. Dependency is introduced and implemented with the annotation @ ShardingTransactionType
Rigid - XA transactions
XA transaction provides an implementation mechanism based on two-phase commit protocol. The so-called two-stage submission, as the name suggests, is divided into two stages, one is the preparation stage and the other is the implementation stage. In the preparation phase, the coordinator initiates a proposal and asks each participant whether they accept it. In the execution phase, the coordinator commits or terminates the transaction according to the feedback of the participants. If all participants agree, submit, and terminate as long as one participant disagrees.
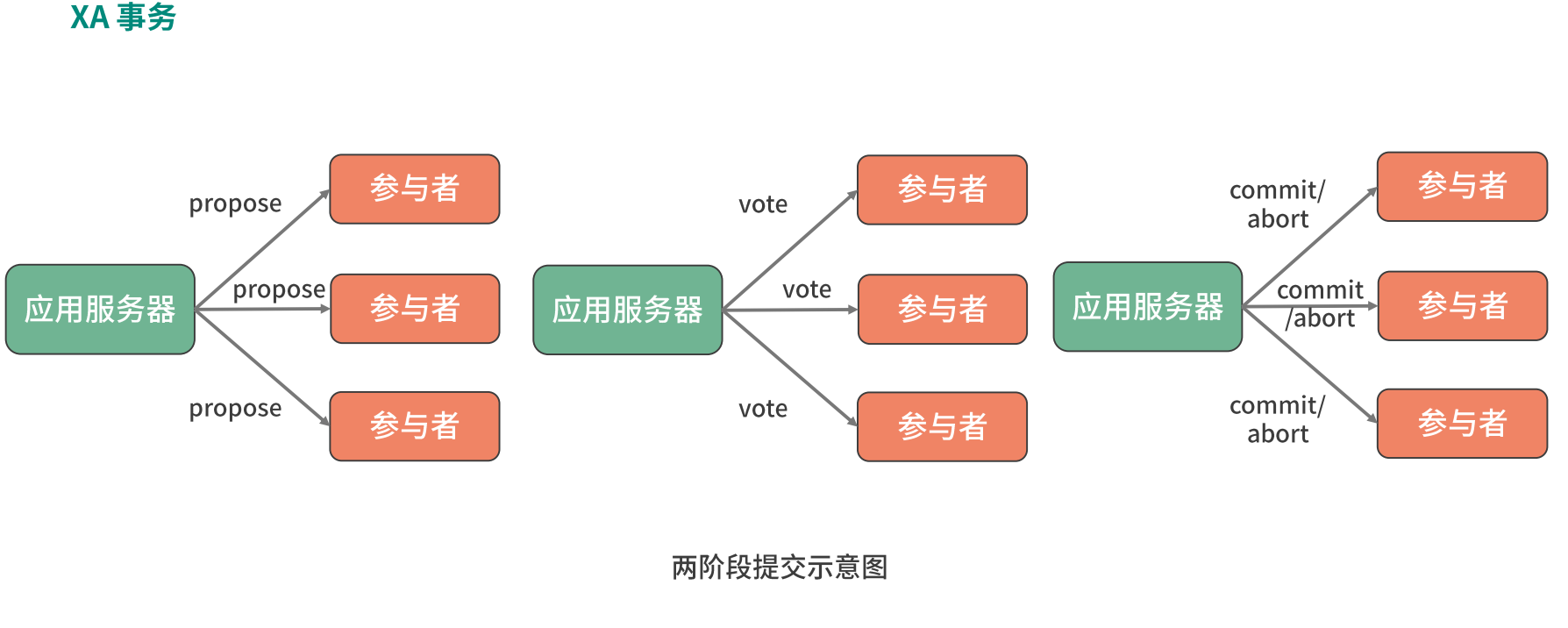
At present, there are also some mainstream tool libraries in the industry when implementing XA transactions, including Atomikos, Narayana and Bitronix. ShardingSphere integrates these three tool libraries and uses Atomikos by default to complete the two-phase submission.
Flexible - use BASE transactions
Compared with XA transactions, the process of integrating BASE transactions in business code is relatively complex, because we need to do this with the help of an external framework. Here, we will demonstrate how to use BASE transactions based on the Seata framework provided by Alibaba.
The only thing to do when switching from XA transaction to BASE transaction is to reset the TransactionType, that is, modify a line of code:
@Override
public void processWithBASE() throws SQLException {
TransactionTypeHolder.set(TransactionType.BASE);
insertHealthRecords();
}
Configuration item of Sharding JDBC data fragmentation
dataSources: # Omit the data source configuration, please refer to the user manual
rules:
- !SHARDING
tables: # Data fragmentation rule configuration
<logic-table-name> (+): # Logical table name
actualDataNodes (?): # It consists of data source name + table name (refer to Inline syntax rules)
databaseStrategy (?): # Sub database policy: default indicates that the default sub database policy is used. Only one of the following sub database policies can be selected
standard: # Standard slicing scenario for single slicing key
shardingColumn: # Partition column name
shardingAlgorithmName: # Partition algorithm name
complex: # Composite sharding scene for multi sharding key
shardingColumns: #Fragmented column names, multiple columns separated by commas
shardingAlgorithmName: # Partition algorithm name
hint: # Hint fragmentation strategy
shardingAlgorithmName: # Partition algorithm name
none: # Undivided
tableStrategy: # Sub table strategy is the same as sub database strategy
keyGenerateStrategy: # Distributed sequence strategy
column: # Auto increment column name. By default, auto increment primary key generator is not used
keyGeneratorName: # Name of distributed sequence algorithm
autoTables: # Automatic partition table rule configuration
t_order_auto: # Logical table name
actualDataSources (?): # Data source name
shardingStrategy: # Segmentation strategy
standard: # Standard slicing scenario for single slicing key
shardingColumn: # Partition column name
shardingAlgorithmName: # Name of automatic slicing algorithm
bindingTables (+): # Binding table rule list
- <logic_table_name_1, logic_table_name_2, ...>
- <logic_table_name_1, logic_table_name_2, ...>
broadcastTables (+): # Broadcast table rule list
- <table-name>
- <table-name>
defaultDatabaseStrategy: # Default database fragmentation policy
defaultTableStrategy: # Default table fragmentation policy
defaultKeyGenerateStrategy: # Default distributed sequence policy
defaultShardingColumn: # Default tile column name
# Partition algorithm configuration
shardingAlgorithms:
<sharding-algorithm-name> (+): # Partition algorithm name
type: # Partition algorithm type
props: # Partition algorithm attribute configuration
# ...
# Distributed sequence algorithm configuration
keyGenerators:
<key-generate-algorithm-name> (+): # Name of distributed sequence algorithm
type: # Distributed sequence algorithm type
props: # Attribute configuration of distributed sequence algorithm
# ...
props:
# ...