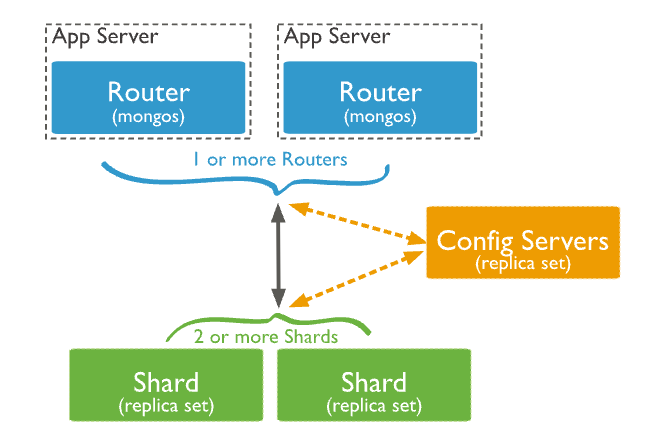
Mongodb shared cluster consists of:
Shards: each shard needs to be deployed as a replica set, which is responsible for storing data. Multiple shards can be deployed
mongos: equivalent to routing
config servers: the configuration server of the entire cluster, which is also a replica set
The development environment can be simpler:
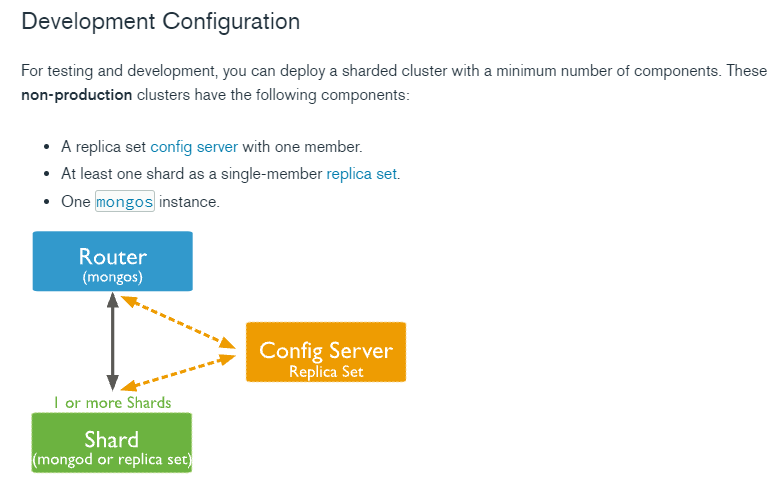
docker builds a simple fragment cluster
One mongos node, two shard s (each replica set has two nodes, and one node can also be used), and one configuration server (replica set has only one node)
Create network
Create a network for the whole cluster to facilitate interworking between nodes
docker network create mongo_shard_net
Start configuration server
docker run --name rs_config --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongod --configsvr --replSet rs_config_server \ --bind_ip_all
Connect to the configuration database, execute rs.initiate, and configure the replica set. Note that the port number is 27019
docker exec -it rs_config mongosh --port 27019
Note here that the configsvr attribute is true
rs.initiate(
{
_id : "rs_config_server",
configsvr: true,
members: [
{ _id : 0, host : "rs_config:27019" }
]
}
);
Create shard
Start a shard with replica set name rs_shard_g1, containing two nodes
docker run --name rs_shard_11 --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongod --shardsvr --replSet rs_shard_g1 \ --bind_ip_all docker run --name rs_shard_12 --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongod --shardsvr --replSet rs_shard_g1 \ --bind_ip_all
Connect to any of these nodes and perform configuration
docker exec -it rs_shard_11 mongosh --port 27018
rs.initiate(
{
_id : "rs_shard_g1",
members: [
{ _id : 0, host : "rs_shard_11:27018" },
{ _id : 1, host : "rs_shard_12:27018" }
]
}
);
Start the second shard, replica set name rs_shard_g2
docker run --name rs_shard_21 --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongod --shardsvr --replSet rs_shard_g2 \ --bind_ip_all docker run --name rs_shard_22 --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongod --shardsvr --replSet rs_shard_g2 \ --bind_ip_all
docker exec -it rs_shard_21 mongosh --port 27018
Configure second replica set
rs.initiate(
{
_id : "rs_shard_g2",
members: [
{ _id : 0, host : "rs_shard_21:27018" },
{ _id : 1, host : "rs_shard_22:27018" }
]
}
);
Start mongos
To start mongos, you need to specify the replica set of the configuration database
docker run --name shard_mongos --network mongo_shard_net \ -d mongo mongos --configdb rs_config_server/rs_config:27019 \ --bind_ip_all
Connect mongos nodes on mongosh and add Shards
docker exec -it shard_mongos mongosh --port 27017
sh.addShard( "rs_shard_g1/rs_shard_11:27018,rs_shard_12:27018"); sh.addShard( "rs_shard_g2/rs_shard_21:27018,rs_shard_22:27018");
Enable sharding for the specified database and specify the collection to be fragmented
sh.enableSharding("somedb");
sh.shardCollection("somedb.helloDoc", { "name" : "hashed" } )
Verify slicing effect
Connect to mongos, switch to somedb and insert 1000 pieces of data
[direct: mongos] test> use somedb
switched to db somedb
[direct: mongos] somedb> for(var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) db.helloDoc.insert({age:i, name:"ly"+i})
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedIds: { '0': ObjectId("6198bd3eea75ef2ba111591a") }
}
Connect to two shard s respectively, and you can see that some data is stored respectively
rs_shard_g1 [direct: primary] somedb> db.helloDoc.count() 508
rs_shard_g2 [direct: primary] somedb> db.helloDoc.count() 492 rs_shard_g2 [direct: primary] somedb>
be careful
- There can also be only one replica set of the local test shard, and the slave node of the default replica set cannot directly connect to read data, so it is necessary to
- If the host machine wants to access the database, it should at least configure mongos port mapping; The default port of the configuration node is 27019, the default port of the shard node is 27018, and the default port of mongos is 27017
-p 27017:27017
- You can also mount local folders to place database files as needed
-v /my/own/datadir:/data/db
- For more usage of mongo image, please refer to dockerhub official document