Dockerfile builds nginx and combines php
1. Build base image
First, build a basic image, add a repo environment and a compilation environment, and the centos image is the initial official image. Later, build php, nginx and mysql, and use the image as base image:
[root@server myCentos]# cat Dockerfile #View Dockerfile file
# base image
FROM centos:centos7.3.1611
# MAINTAINER
MAINTAINER 2331233079@qq.com
# add epel and 163 yum
RUN yum install wget epel-release -y \
&& mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.back \
&& wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo \
&& wget -P /etc/yum.repos.d/ http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo \
&& yum clean all && yum makecache
# Necessary packages
RUN yum install -y wget gcc gcc-c++ glibc make autoconf openssl openssl-devel ntpdata crontabs
# change timzone to Asia/Shanghai
RUN cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
[root@server myCentos]# docker build -t centos:v1 . #The build image is named centos:v1
[root@server myCentos]# docker images #View the image after the build is complete REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE centos v1 cca50f986518 About a minute ago 665MB
View the directory structure of nginx and php:
[root@server ~]# tree nginx nginx ├── Dockerfile ├── fastcgi_params ├── nginx-1.8.1.tar.gz ├── nginx.conf └── www.conf
[root@server ~]# tree php php ├── Dockerfile ├── libmcrypt-2.5.8.tar.gz ├── php-5.6.35.tar.gz ├── php-fpm.conf.default └── php.ini-production
The construction process of nginx and php is described in detail here. All toolkits and configuration files used in the construction process have been described
2. Building nginx images
First, build the nginx image and view the Dockerfile of nginx:
[root@server nginx]# cat Dockerfile # base image FROM centos:v1 MAINTAINER 2331233079@qq.com RUN useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin www ADD nginx-1.8.1.tar.gz /usr/local/src # install Dependency package RUN yum install libxslt-devel -y gd gd-devel GeoIP GeoIP-devel pcre pcre-devel libxml2 libxml2-dev libxslt-devel WORKDIR /usr/local/src/nginx-1.8.1 # make && make install RUN ./configure --user=www --group=www --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-file-aio --with-ipv6 --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_spdy_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_stub_status_module && make && make install # configure COPY nginx.conf /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf COPY fastcgi_params /usr/local/nginx/conf/fastcgi_params RUN mkdir /usr/local/nginx/conf/conf.d COPY www.conf /usr/local/nginx/conf/conf.d/www.conf EXPOSE 80 CMD ["/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx","-g","daemon off;"]
Here, nginx adopts compilation and installation, creates the user www and installs some dependent packages of nginx, and copies some configuration files into the image. Detailed configuration file reference:
Build nginx image through Dockerfile:
[root@server nginx]# docker build -t nginx:v1 . #Build nginx image with tag v1 [root@server nginx]# docker images #View the built image REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE nginx v1 c1c90aaefa1e 33 seconds ago 752MBcentos v1 cca50f986518 2 hours ago 665MB
Specify the following configuration files:
[root@server nginx]# cat www.conf
server {
listen 80;
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
index index.htm index.html index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass php:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Fastcgi can be found_ pass php:9000;
This is because php is also a container, which is isolated from nginx. When the container is started later, nginx will be interconnected with the image through - link
3. Build php image
View the Dockerfile of php:
[root@server php]# cat Dockerfile # base image FROM centos:v1 MAINTAINER 2331233079@qq.com ADD libmcrypt-2.5.8.tar.gz /usr/local/src WORKDIR /usr/local/src/libmcrypt-2.5.8 RUN ./configure && make && make install ADD php-5.6.35.tar.gz /usr/local/src RUN yum -y install libxml2 libxml2-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel libjpeg-turbo libjpeg-turbo-devel libpng libpng-devel freetype freetype-devel zlib zlib-devel libcurl libcurl-devel WORKDIR /usr/local/src/php-5.6.35 RUN ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php --with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --with-mysql=mysqlnd --with-openssl --enable-mbstring --with-freetype-dir --with-jpeg-dir --with-png-dir --with-mcrypt --with-zlib --with-libxml-dir=/usr --enable-xml --enable-sockets --enable-fpm --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/php/etc --with-bz2 --with-gd && make && make install COPY php.ini-production /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini COPY php-fpm.conf.default /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf RUN useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin php RUN sed -i -e 's@;pid = run/php-fpm.pid@pid = run/php-fpm.pid@g' -e 's@nobody@php@g' -e 's@listen = 127.0.0.1:9000@listen = 0.0.0.0:9000@g' /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf RUN sed -i 's@;daemonize = yes@daemonize = no@g' /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf EXPOSE 9000 CMD ["/usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm"]
The built service must run in the foreground. For nginx, daemon off means that the background operation is turned off, so it runs in the foreground
For PHP: sed -i's@;daemonize = yes@daemonize = no@g ’ /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf
The daemon mode is also turned off here, so / usr / local / PHP / SBIN / PHP FPM runs in the foreground
Build php image through Dockerfile:
[root@server php]# docker build -t php:v1 . #Build php image with tag v1 [root@server php]# docker images #View the built image REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE php v1 2019612cc0a4 35 seconds ago 1.19GBnginx v1 c1c90aaefa1e About an hour ago 752MBcentos v1 cca50f986518 2 hours ago 665M
4. Start the nginx container and php container
Start php and nginx services with the built image:
[root@server php]# docker run -d --name php -v /www:/usr/local/nginx/html php:v1 #Start a php container and map it with - v cf77c85e7c2f63a7ac2db2edaa37d22418503e8cfa35d87b9cfad541d03e004a [root@server php]# docker run -d --name nginx -p 80:80 -v /www:/usr/local/nginx/html --link=php:php nginx:v1 #Start an nginx container, map it through - v and associate it with a php container through -- link 3bbc12db8e9cc118a7824c5a314d13c4e37f3a6397f32bbfe939f9e424b306e0
When starting the php container above, use - v for mapping. If there is no mapping here, the php program will start, but the file at the end of php will not be parsed, resulting in a file not found error
Supplement: the production environment generally stores the configuration files, log files and web site directories on the host machine, which is convenient for management. If the nginx configuration changes, you can directly dock stop the nginx container name and then start it. Start the nginx container as follows
# docker run -d --name nginx -p 80:80 -v /opt/docker/www:/usr/local/nginx/html -v /docker/NginxConf/:/usr/local/nginx/conf/conf.d -v /docker/log:/usr/local/nginx/logs --link=php:php nginx:v1
To view container status:
[root@server php]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3bbc12db8e9c nginx:v1 "/usr/local/nginx/sb..." 26 seconds ago Up 25 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp nginx cf77c85e7c2f php:v1 "/usr/local/php/sbin..." 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 9000/tcp php
Create a test file on the host to the site directory:
[root@server www]# tree . #View the structure of the site directory . ├── index.php └── test.html [root@server www]# cat index.php #View index PHP file <?php phpinfo() ?> [root@server www]# cat test.html #View test HTML file <h1>Hello Docker nginx-php</h1>
Access test:
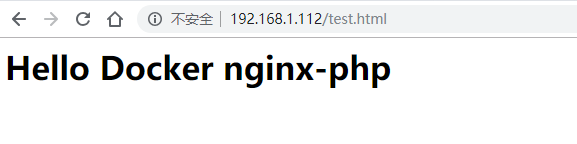
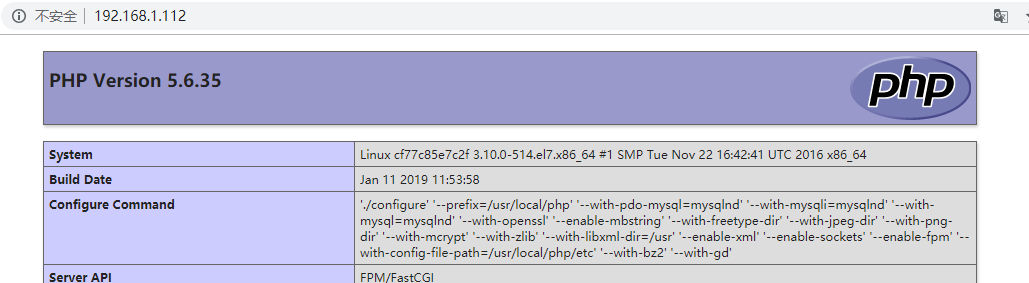 Enter the php container to view the hosts file:
Enter the php container to view the hosts file:
[root@server ~]# docker exec -it php /bin/bash #Use exec to enter php container [root@cf77c85e7c2f php-5.6.35]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.2 cf77c85e7c2f
Enter the nginx container to view the hosts file:
[root@server ~]# docker exec -it nginx /bin/bash #Use exec to enter the nginx container [root@3bbc12db8e9c nginx-1.8.1]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.2 php cf77c85e7c2f 172.17.0.3 3bbc12db8e9c
Copy code
You can see that there is a php parsing in the hosts file of nginx, which is why nginx can communicate with php (specified through – link)
Based on the above steps, the connection between nginx and php is ok. Next, add a mysql and test the deployment of wordpress
5. Build mysql image
View the directory structure of mysql:
[root@server mysql]# tree . . ├── business.sql ├── Dockerfile ├── MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-client.rpm ├── MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-common.rpm ├── MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-compat.rpm ├── MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-server.rpm ├── server.cnf └── setup.sh
View the Dockerfile of mysql:
[root@server mysql]# cat Dockerfile FROM centos MAINTAINER 381347268@qq.com COPY MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-client.rpm /root/MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-client.rpm COPY MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-common.rpm /root/MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-common.rpm COPY MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-compat.rpm /root/MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-compat.rpm COPY MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-server.rpm /root/MariaDB-10.0.33-centos7-x86_64-server.rpm WORKDIR /root RUN yum remove mysql-libs -y RUN yum -y install *.rpm ADD business.sql /root/business.sql ADD server.cnf /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf ADD setup.sh /root/setup.sh RUN yum clean all RUN chmod +x /root/setup.sh EXPOSE 3306 CMD ["/root/setup.sh"]
(1) The basic image used here is centos (official image, latest); (2) The configuration file is mounted during startup (if there are changes later, you only need to create the configuration file in a directory and then mount it); (3)business.sql is about executing sql (giving root password, creating database, etc.); (4)setup.sh is to reinitialize mysql (mariadb) and finally restart the service (use -- user=mysql to avoid starting mariadb with the root user)
setup.sh script principle: Dockerfile is used to install the database service. After the installation is completed, use setup After the SH script reinitializes my sql, start the MySQL service and execute setup SH, close the MySQL database and restart the MySQL database service from the previous server
[root@server mysql]# cat setup.sh
#!/bin/sh
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
mysql_install_db --user=mysql > /dev/null
mysqld_safe --user=mysql &
sleep 5
mysql < /root/business.sql
sleep 5
ps -wef | grep mysql | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
mysqld_safe --user=mysql
setup.sh
[root@server mysql]# cat business.sql
create database wordpress DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8;
USE mysql;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD("root") WHERE user='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
business.sql
[root@server mysql]# cat server.cnf [mysqld] bind-address=0.0.0.0 console=1 general_log=1 general_log_file=/dev/stdout collation-server=utf8_unicode_ci character-set-server=utf8 server.cnf
Build mysql image through Dockerfile:
[root@server mysql]# docker build -t mysql:v1 . #Build mysql image
To view the built image:
[root@server mysql]# docker images #View three mirrors REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE mysql v1 4a3e428817c1 2 hours ago 813MB php v1 2019612cc0a4 3 hours ago 1.19GB nginx v1 c1c90aaefa1e 4 hours ago 752MB
6. Deploy lnmp environment and wordpress
Build the lnmp environment based on the above three images nginx, mysql and php. We first delete the container started above because it is useless
Start three containers first
[root@server mysql]# docker run -d --name mysql -v /root/mysql/server.cnf:/etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf -v /data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql -p 3306:3306 mysql:v1 #Start a mysql container df28bcb97289676654ea7b573b0e3e52f910a599ff03b2dbf2dfe6345726127d [root@server mysql]# docker run -d --name php -v /www:/usr/local/nginx/html --link=mysql:mysql php:v1 #Start a php container 2f7fd098f0069deeaef4eb5b067e981c6be01a16d0769c3bc4203eab03a45c40 [root@server mysql]# docker run -d --name nginx -p 80:80 -v /www:/usr/local/nginx/html --link=php:php nginx:v1 #Start an nginx container b68688cd6f2d324e58c469cfb49fa7a14257ef2bb0c301a40a36ef244201c159 [root@server mysql]# docker ps #View the status of the three containers started CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES b68688cd6f2d nginx:v1 "/usr/local/nginx/sb..." 11 seconds ago Up 10 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp nginx 2f7fd098f006 php:v1 "/usr/local/php/sbin..." About a minute ago Up About a minute 9000/tcp php df28bcb97289 mysql:v1 "/root/setup.sh" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp mysql
Here are the three containers to be started: (1) start a mysql container and connect the above server CNF configuration files and data directories are mounted inside the container to prevent data loss; (2) Then start a php container and use - v for mapping. If there is no mapping here, the php program will start, but the file at the end of php will not be parsed, resulting in the error of file not found, and -- link is used to associate with mysql, so that the php container can connect to the mysql database; (3) Finally, start an nginx container, also use - v for mapping, map the website directory to the host, and associate it with php through -- link.
To begin installing wordpress:
[root@server ~]# cd /www/ [root@server www]# wget https://cn.wordpress.org/wordpress-4.7.4-zh_CN.tar.gz [root@server www]# tar xf wordpress-4.7.4-zh_CN.tar.gz [root@server www]# ll Total consumption 8324 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19 1 November 12:27 index.php -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 32 1 November 12:04 test.html drwxr-xr-x 5 nobody nfsnobody 4096 4 March 23, 2017 wordpress -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8507412 4 March 23, 2017 wordpress-4.7.4-zh_CN.tar.gz
Access the host through the browser for installation: http://IP/wordpress
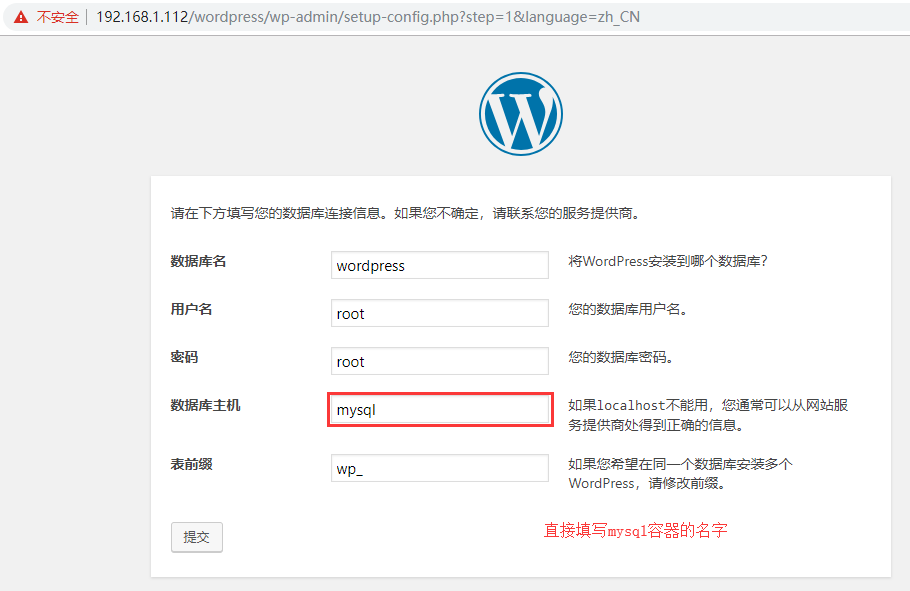
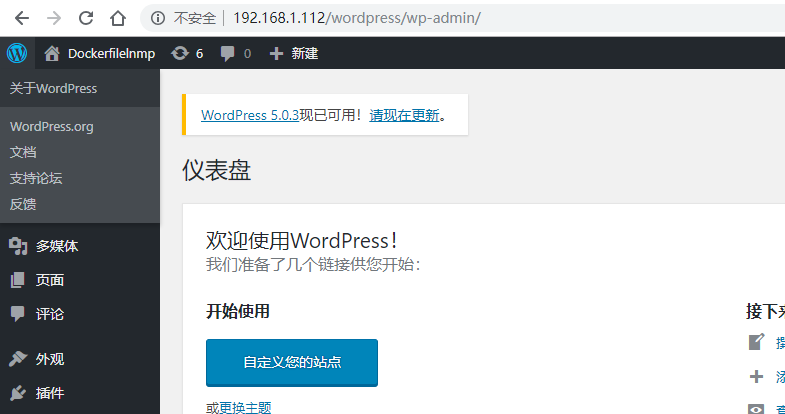
Enter the mysql container to view the hosts:
[root@server ~]# docker exec -it mysql /bin/bash #Use exec to enter mysql container [root@df28bcb97289 ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.2 df28bcb97289
Enter the php container to view the hosts:
[root@server ~]# docker exec -it php /bin/bash #Use exec to enter the php container [root@2f7fd098f006 php-5.6.35]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.2 mysql df28bcb97289 172.17.0.3 2f7fd098f006
Enter the nginx container to view the hosts:
[root@server ~]# docker exec -it nginx /bin/bash #Use exec to enter the nginx container [root@b68688cd6f2d nginx-1.8.1]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.17.0.3 php 2f7fd098f006 172.17.0.4 b68688cd6f2d
Through observation, we can see that there is a mysql record in the hosts of the php container, which is why when wordpress is installed, we can directly fill in the name of the mysql container to connect. Similarly, there is also a php record in nginx.
See GitHub for relevant software packages and configuration files: https://github.com/buji595/docker_project/tree/master/Dockerfile_Project/lnmp