Docker
1, About Docker
Docker official website: https://www.docker.com
Github Docker source code: https://github.com/docker/docker-ce
Install Docker
1. View version
Before installing, check whether it is installed and the version number
$ docker --version Docker version 20.10.6, build 370c289 $ docker-compose --version docker-compose version 1.29.1, build c34c88b2 $ docker version # More comprehensive information Client: Cloud integration: 1.0.14 Version: 20.10.6 API version: 1.41 Go version: go1.16.3 Git commit: 370c289 Built: Fri Apr 9 22:46:57 2021 OS/Arch: darwin/amd64 Context: default Experimental: true Server: Docker Engine - Community Engine: Version: 20.10.6 API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12) Go version: go1.13.15 Git commit: 8728dd2 Built: Fri Apr 9 22:44:56 2021 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false containerd: Version: 1.4.4 GitCommit: 05f951a3781f4f2c1911b05e61c160e9c30eaa8e runc: Version: 1.0.0-rc93 GitCommit: 12644e614e25b05da6fd08a38ffa0cfe1903fdec docker-init: Version: 0.19.0 GitCommit: de40ad0
2. Installation
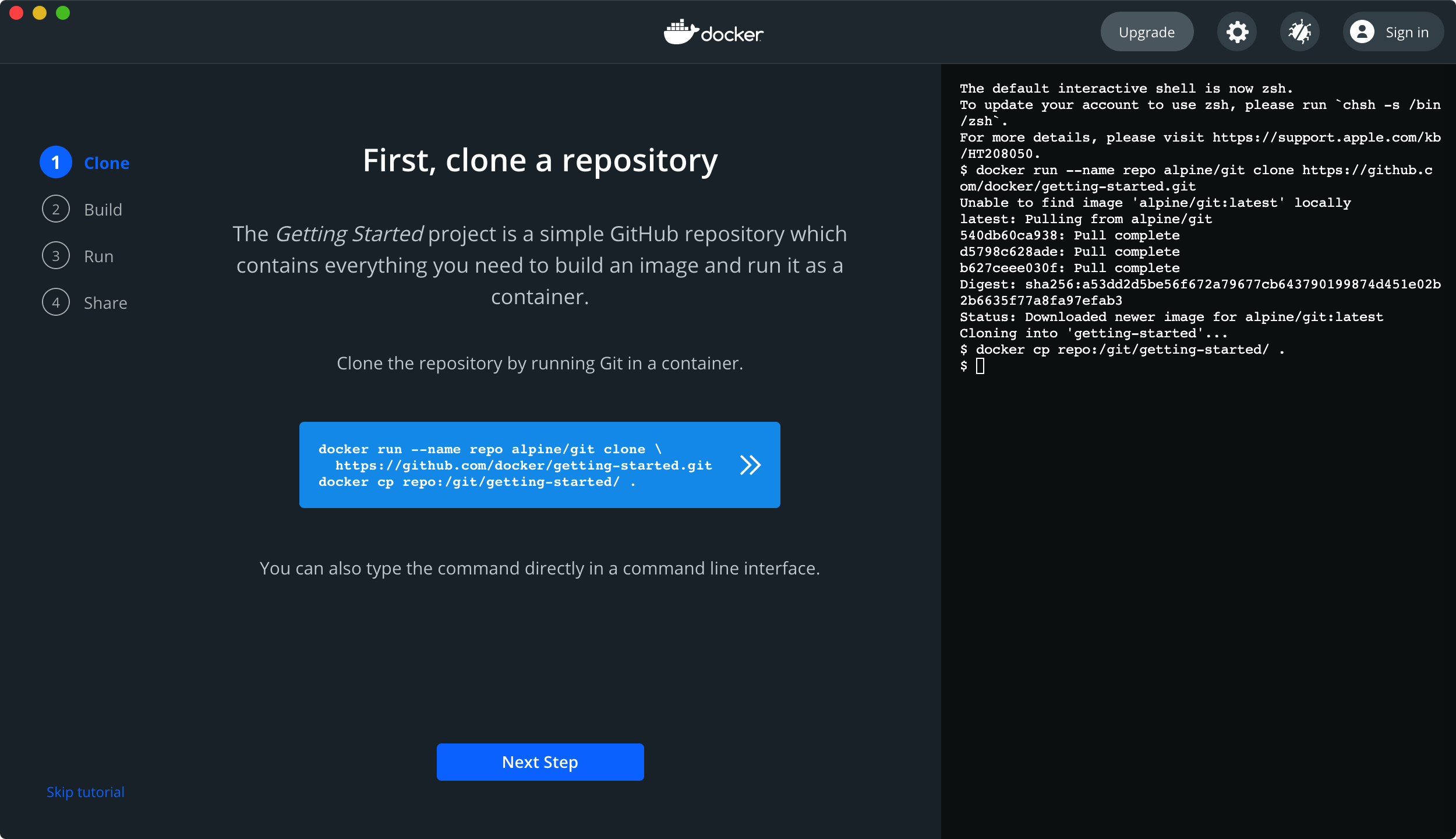
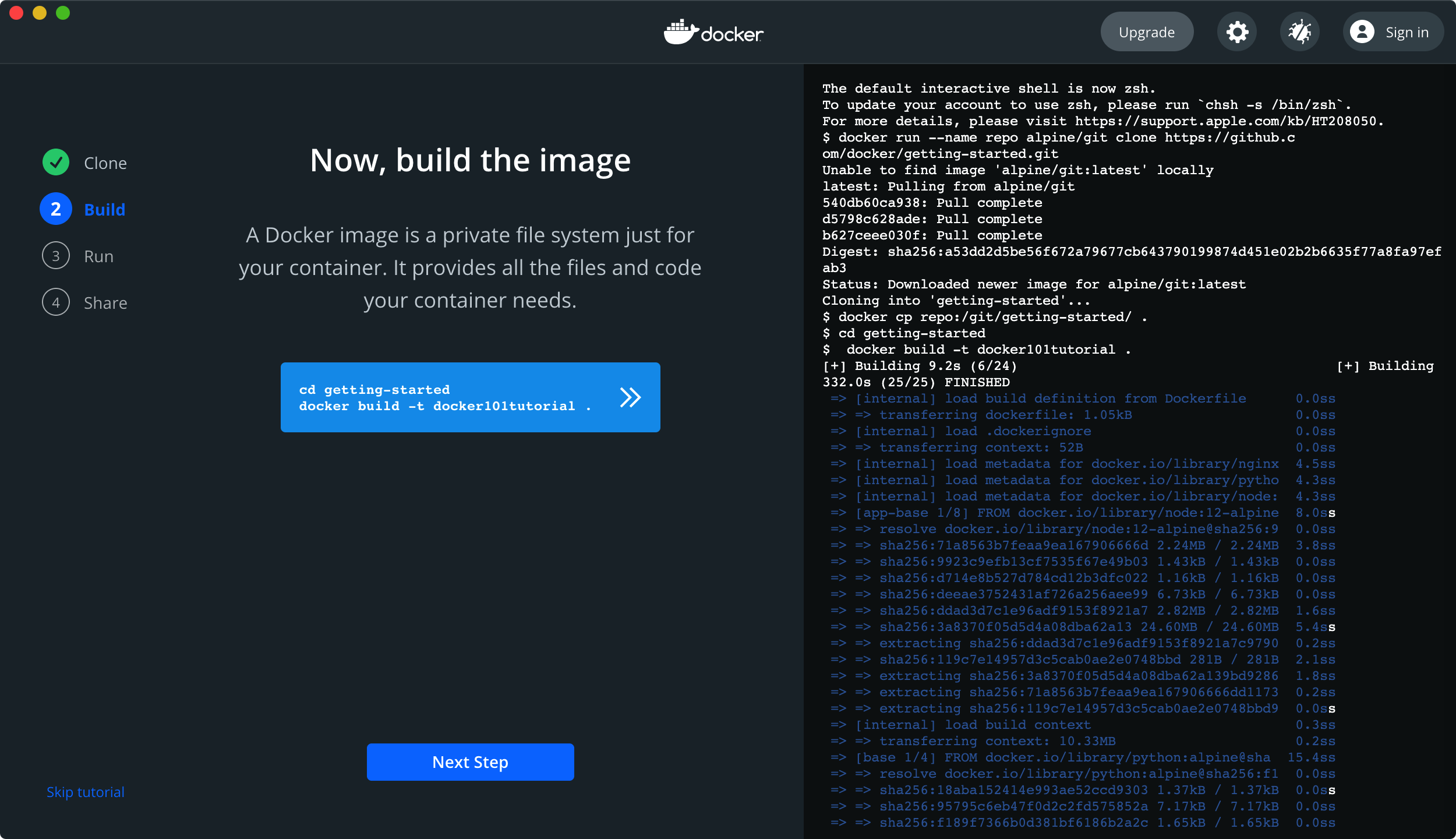
$ docker cp repo:/git/getting-started/ . $ cd getting-started $ docker build -t docker101tutorial . [+] Building 9.2s (6/24) [+] Building 332.0s (25/25) FINISHED Use 'docker scan' to run Snyk tests against images to find vulnerabilities and learn how to fix them $ docker run -d -p 80:80 --name docker-tutorial docker101tutorial 8b17f9ba92e67e2d475db56345c23873129cf15f31688ba0ce2d860fe0d58a98 docker: Error response from daemon: Ports are not available: listen tcp 0.0.0.0:80: bind: address already in use.
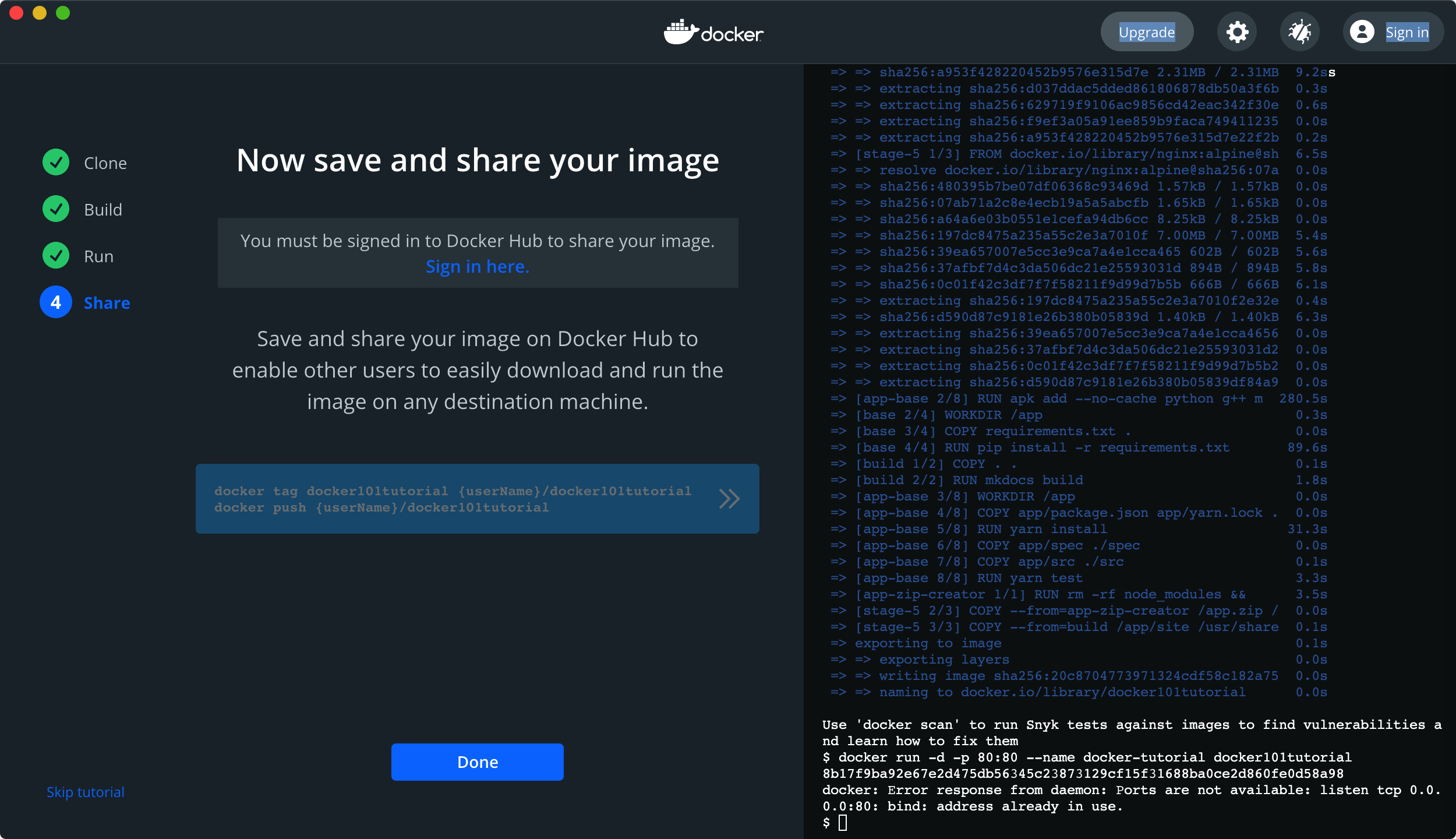
3. Uninstall Docker
Common commands
attach Attach to a running container # The attach connection under the current shell specifies the running image build Build an image from a Dockerfile # Customized image through Dockerfile commit Create a new image from a container changes # Commit the current container as a new image cp Copy files/folders from the containers filesystem to the host path #Copy the specified file or directory from the container to the host create Create a new container # Create a new container, the same as run, but do not start the container diff Inspect changes on a container's filesystem # View docker container changes events Get real time events from the server # Get container real-time events from docker service exec Run a command in an existing container # Run the command on an existing container export Stream the contents of a container as a tar archive # Export the content stream of the container as a tar archive [corresponding to import] history Show the history of an image # Show a mirror formation history images List images # Lists the current image of the system import Create a new filesystem image from the contents of a tarball # Create a new file system image from the contents of the tar package [corresponding to export] info Display system-wide information # Display system related information inspect Return low-level information on a container # View container details kill Kill a running container # kill specifies the docker container load Load an image from a tar archive # Load an image from a tar package [corresponding to save] login Register or Login to the docker registry server # Register or log in to a docker source server logout Log out from a Docker registry server # Exit from the current Docker registry logs Fetch the logs of a container # Output current container log information port Lookup the public-facing port which is NAT-ed to PRIVATE_PORT # View the internal source port of the container corresponding to the mapped port pause Pause all processes within a container # Pause container ps List containers # List containers pull Pull an image or a repository from the docker registry server # Pull the specified image or library image from the docker image source server push Push an image or a repository to the docker registry server # Push the specified image or library image to the docker source server restart Restart a running container # Restart the running container rm Remove one or more containers # Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images # Remove one or more images [no container can be deleted without using the image, otherwise the relevant container needs to be deleted before continuing or -f forced deletion] run Run a command in a new container # Create a new container and run a command save Save an image to a tar archive # Save an image as a tar package [corresponding to load] search Search for an image on the Docker Hub # Search for images in docker hub start Start a stopped containers # Start container stop Stop a running containers # Stop container tag Tag an image into a repository # Label the image in the source top Lookup the running processes of a container # View the process information running in the container unpause Unpause a paused container # Unsuspend container version Show the docker version information # View docker version number wait Block until a container stops, then print its exit code # Intercept the exit status value when the container stops
View Docker disk usage
$ docker system df
Clean disk
$ docker system prune
Delete closed containers, useless data volumes and network images without TAG - a parameter useless images will also be deleted (use with caution)
Stop Docker service
$ systemctl stop docker
2, Mirror image
View installed images
# Currently installed image $ docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE docker101tutorial latest 20c870477397 21 hours ago 28MB alpine/git latest 7660bb3edeb5 4 days ago 25.1MB ubuntu latest 7e0aa2d69a15 4 weeks ago 72.7MB
- -a: List all local mirrors
- -q: Display only image id
- -digests: displays the summary information of the image
- --No TRUNC: displays the complete image information
Pull image
Take ubuntu as an example
# First pull $ docker pull ubuntu Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/ubuntu 345e3491a907: Pull complete 57671312ef6f: Pull complete 5e9250ddb7d0: Pull complete Digest: sha256:cf31af331f38d1d7158470e095b132acd126a7180a54f263d386da88eb681d93 Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:latest docker.io/library/ubuntu:latest # Second pull $ docker pull ubuntu Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/ubuntu Digest: sha256:adf73ca014822ad8237623d388cedf4d5346aa72c270c5acc01431cc93e18e2d Status: Image is up to date for ubuntu:latest docker.io/library/ubuntu:latest
Pull the image of the specified tag
delete mirror
# delete mirror $ docker rmi ubuntu Error response from daemon: conflict: unable to remove repository reference "ubuntu" (must force) - container 5235a49aea61 is using its referenced image 7e0aa2d69a15 # If a container depends on this image (whether it is running or not), the image cannot be deleted # Delete multiple $ docker rmi Image name 1:TAG Image name 2:TAG # Delete all $ docker rmi -f $(docker images -qa)
Find mirror
Method 1: through Docker Hub
Search for images from Docker Hub website. Docker Hub website is: https://hub.docker.com/

Method 2: docker search command
$ docker search ubuntu NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED ubuntu Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating sys... 12302 [OK] dorowu/ubuntu-desktop-lxde-vnc Docker image to provide HTML5 VNC interface ... 535 [OK] websphere-liberty WebSphere Liberty multi-architecture images ... 273 [OK] rastasheep/ubuntu-sshd Dockerized SSH service, built on top of offi... 251 [OK]
OPTIONS:
- -s: Lists the images with the number of collections not less than the specified value
- --Automated: only images of type automated build are listed
Label description
- REPOSITORY: indicates the warehouse source of the image
- TAG: the label of the image
- IMAGE ID: IMAGE ID
- CREATED: image creation time
- SIZE: mirror SIZE
The same warehouse source can have multiple tags, representing different versions of the warehouse source.
For example, there are 15.10, 14.04 and other different versions in the ubuntu warehouse source. We use REPOSITORY:TAG to define different images.
Acceleration service (daocloud)
There are many acceleration service providers in the market, such as DaoCloud, Alibaba cloud, etc.
It is slow to access docker hub directly. adopt daocloud Come and visit a little faster.
Open in virtual machine browser< http://www.daocloud.io/ >Then register the user or log in directly with wechat scanning QR code. After logging in, click "image warehouse".
Click DockerHub image, here you can open the official image warehouse of docker, and then search the image you want in it.
3, Container
Creating containers is described separately
View container
The rightmost NAMES column corresponds to the name of the container
# View all containers (including not running) $ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES dd05dd4f0b3d docker101tutorial "/docker-entrypoint...." 2 minutes ago Exited (0) About a minute ago vibrant_franklin 8b17f9ba92e6 docker101tutorial "/docker-entrypoint...." 16 hours ago Created docker-tutorial f0ecd71a3a90 alpine/git "git clone https://g..." 21 hours ago Exited (0) 21 hours ago repo # View currently running containers $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
-
-a: list all currently running containers + those that have been run in history
-
-l: displays recently created containers.
-
-n: Displays the last n containers created.
-
-q: silent mode, only the container number is displayed.
-
--No TRUNC: do not truncate the output.
Start / stop container
$ docker start c001 # Start container c001 $ docker restart <container ID> # Restart container c001 $ docker ps # View containers in operation CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES ab16bcb55850 ubuntu "bash" 8 minutes ago Up 17 seconds c001 $ docker stop c001 # Close the container c001 $ docker start -i c001 # -i enter bash after startup root@ab16bcb55850:/# exit exit # Force stop container $ docker kill <container ID>/<container NAME>
When using the ubuntu system image with version 15.10 to run the container, the command is as follows:
$ docker run -t -i ubuntu:15.10 /bin/bash root@d77ccb2e5cca:/#
Exit container
Method 1: exit
Container stop exit
Method 2: ctrl + P + Q
The container does not stop exiting
Delete container
# Delete (stopped) container $ docker rm b83c32b59c67 docker rm -f tomcat1/containerid #Delete container # delete mirror $ docker rmi 7e0aa2d69a15 # List all and then delete $ docker rm -f $(docker ps -a)
Check the status information of the container
View container interior details
$ docker inspect Container name
View the processes running in the container
$ docker top Container name
For example:
$ docker top con4 Error response from daemon: Container bd9177d4ec977dcc5cb1920fd23a3e0c4 is not running
Start container run
# Start daemon container $ docker run -d con4 # View container log $ docker logs -f -t --tail con4
Enter the container and command interaction
Method 1: exec
# $ docker exec -it c001 bashShell $ docker exec -it c001 /bin/bash
Open the terminal in the container and start a new process.
Method 2: attach
reenter
$ docker attach c001
Directly enter the container and start the terminal of the command without starting a new process
Copy files from container to host
$ docker cp container ID:In container path destination host path
Port mapping
$ docker run -d -p 80:5000 training/webapp python app.py
- -p 80:5000 bind port 80 of this machine to port 5000 in the container for local direct access http://127.0.0.1 that will do
$ docker run-p80--name web-i-t centos/bin/bash
- -The i option tells the Docker container to keep the standard input stream open to the container, even if the container has no terminal connection
- -The t option tells Docker to assign a virtual terminal to the container so that we can install the Nginx server next. (author's note: Docker also supports entering the - d option to tell Docker to run the daemon of the container in the background)
- --The name web option tells Docker to create a container named web;
Docker will automatically generate a random name for each container we create. In fact, although this method is convenient, its readability is poor, and the cost of understanding our later maintenance will be relatively large. - -p80 tells Docker to open port 80 so that Nginx can access and serve the outside world.
Export container export
$ docker export con4 > sp.tar
Import container
Method 1: import local tar
Method 2: import from url
$ docker import http://example.com/exampleimage.tgz example/imagerepo
Relevant information
- Zhihumu.com: it may be the most clear article on the concept of Docker
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38552635 - Legend of swordsman: detailed analysis of Docker application
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ddcea0e29a31 - Zhihushili: using Docker to build ubuntu environment under macOS
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/59548929 - Three squirrels in blog Garden: Docker practice: container of python application
https://www.cnblogs.com/shenh/p/9518343.html - Compose command description
https://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/docker-technology-and-combat/commands.html - Liang Guizhao: 30 minute quick start Docker tutorial
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/DY3pLat1ehudP624Io73Hg