1. Mysql (master)
1, Create a new master server container instance 3307
docker run --restart=always -p 3307:3306 --name mysql-master \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/log:/var/log/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/data:/var/lib/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/conf:/etc/mysql \ -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \ -d mysql:5.7
Command details
--restart=always Startup container self start -p Port mapping, inside the host 3307 port mapping container 3306 --name Container name -v Data volume mapping directory generally maps log data configuration files -e Runtime environment -d Run the container in the background and return to the container ID
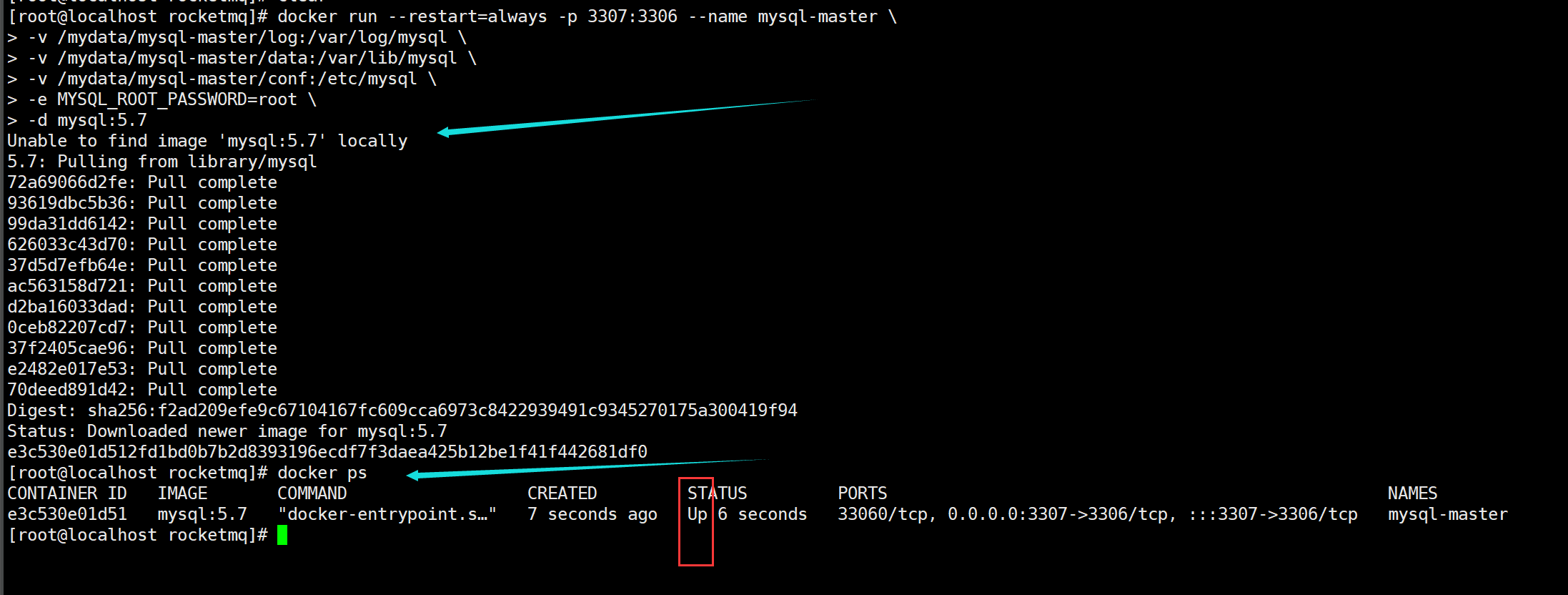
If you have not pulled it before, you will pull it first and then run the container # docker ps # if you see the STATUS # STATUS # is Up, the operation is successful
2, Enter / mydata / MySQL master / conf directory to create a new my cnf
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, which needs to be unique in the same LAN server_id=101 ## Specify the name of the database that does not need to be synchronized binlog-ignore-db=mysql ## Enable binary log function log-bin=mall-mysql-bin ## Set the memory size used by binary log (transaction) binlog_cache_size=1M ## Set the binary log format used (mixed,statement,row) binlog_format=mixed ## Binary log expiration cleanup time. The default value is 0, which means no automatic cleaning. expire_logs_days=7 ## Skip all errors encountered in master-slave replication or specified types of errors to avoid the interruption of slave side replication. ## For example, the 1062 error refers to the duplication of some primary keys, and the 1032 error is due to the inconsistency between the primary and secondary database data slave_skip_errors=1062
Enter the / mydata / MySQL master / conf directory
vi my.cnf
Just stick it in
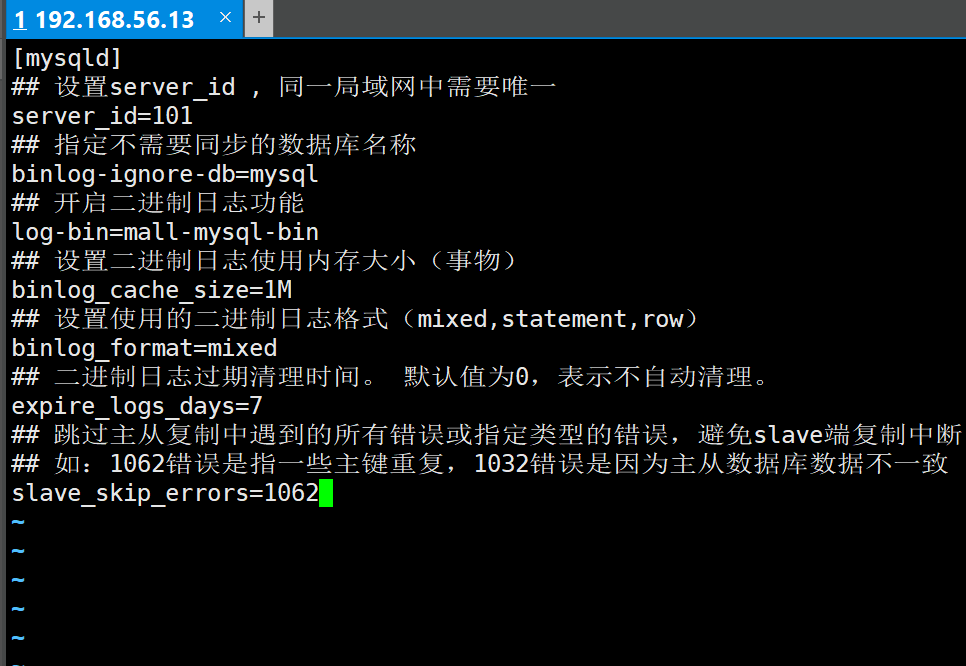
3, Restart the master instance after modifying the configuration
docker restart mysql-master
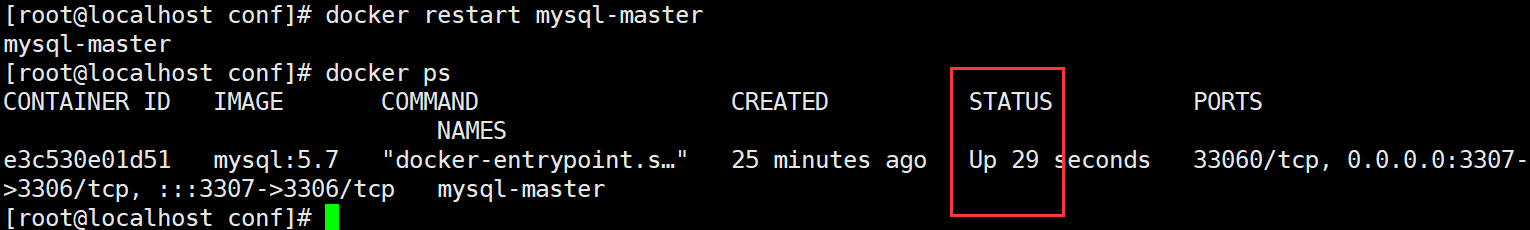
4, Enter MySQL master container
1. Pass the container name
docker exec -it mysql-master /bin/bash
2. Pass the container id
docker exec -it e3c bash

Both commands can be entered
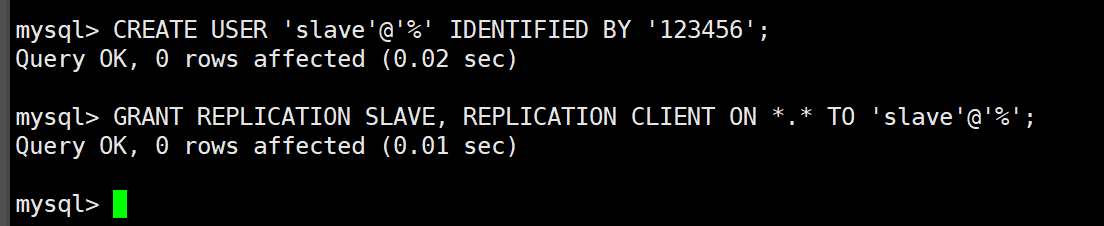
5, Create a data synchronization user in the master container instance
Let the slave server use this user for data synchronization.
1. Create user
CREATE USER 'slave'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
2. Grant permissions
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'slave'@'%';
Enter mysql
mysql -uroot -p
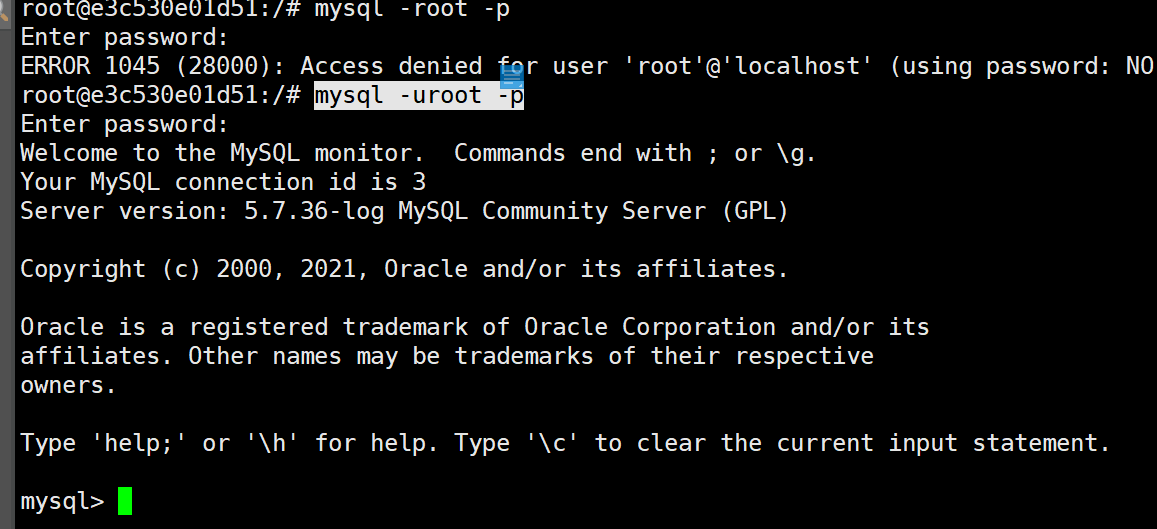
2. From Mysql (slave)
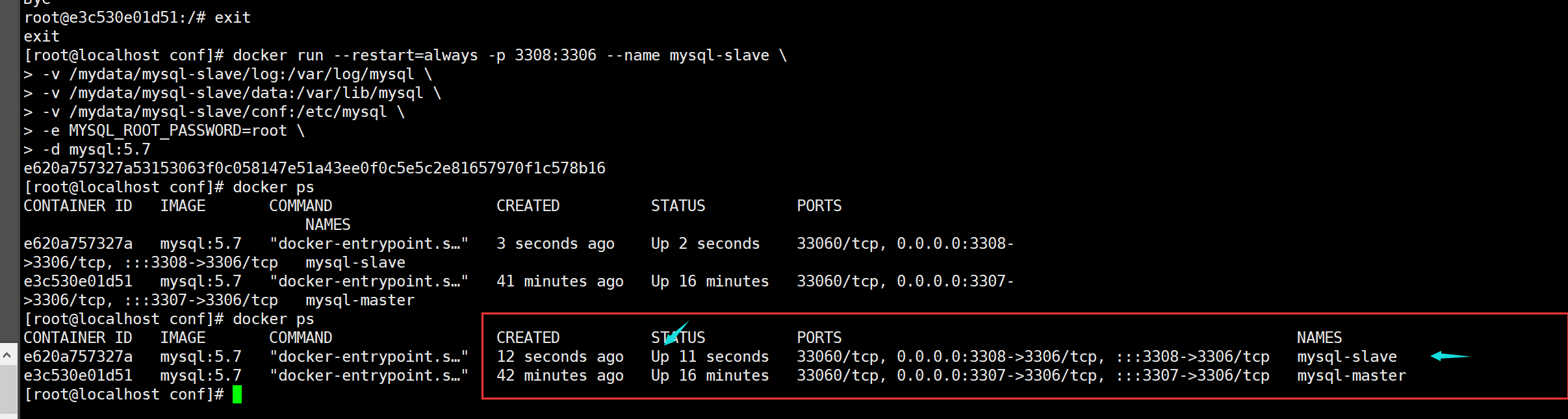
1, New slave server container instance 3308
docker run --restart=always -p 3308:3306 --name mysql-slave \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/log:/var/log/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/data:/var/lib/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/conf:/etc/mysql \ -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \ -d mysql:5.7
2, Enter the / mydata / MySQL slave / conf directory to create a new my cnf
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, which needs to be unique in the same LAN server_id=102 ## Specify the name of the database that does not need to be synchronized binlog-ignore-db=mysql ## Enable binary log function log-bin=mall-mysql-slave1-bin ## Set the memory size used by binary log (transaction) binlog_cache_size=1M ## Set the binary log format used (mixed,statement,row) binlog_format=mixed ## Binary log expiration cleanup time. The default value is 0, which means no automatic cleaning. expire_logs_days=7 ## Skip all errors encountered in master-slave replication or specified types of errors to avoid the interruption of slave side replication. ## For example, the 1062 error refers to the duplication of some primary keys, and the 1032 error is due to the inconsistency between the primary and secondary database data slave_skip_errors=1062 ## relay_log configure relay log relay_log=mall-mysql-relay-bin ## log_slave_updates means that the slave writes the replication event to its binary log log_slave_updates=1 ## slave is set to read-only (except for users with super permission) read_only=1
Enter the / mydata / MySQL slave / conf directory
vi my.cnf

3, Restart the slave instance after modifying the configuration
docker restart mysql-slave
4, View master-slave synchronization status in master database
show master status;

5, Enter MySQL slave container
Enter the docker container first, and then enter mysql
e62 is the container id
docker exec -it e62 bash
mysql -uroot -proot

Vi. configure master-slave replication in the slave database
change master to master_host='Host computer ip',master_user='slave',master_password='123456',master_port=3307,master_log_file='mall-mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=617,master_connect_retry=30;
master_host: IP address of the main database;
master_port: the running port of the master database;
master_user: the user account created in the master database for data synchronization;
master_password: the user password created in the master data to synchronize data;
master_log_file: Specifies the day file to copy data from the database, and obtains the file parameter by viewing the status of the master data;
master_log_file: specify where to copy data from the database, and obtain the position parameter by viewing the status of the master data;
master_connect_retry: the time interval between connection failures and retries, in seconds.
Note that this is from the database

Corresponding to the related configuration of the host
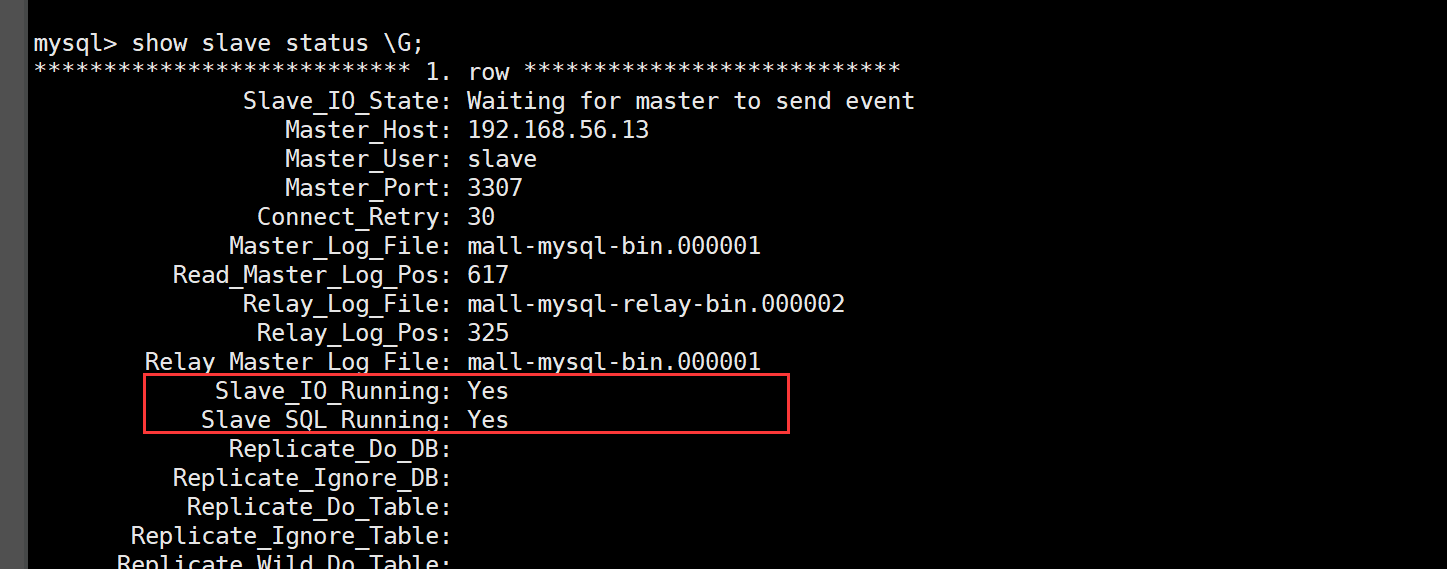
VII. View the master-slave synchronization status in the slave database
show slave status \G;

Key value = key value pair
VIII. Start master-slave synchronization in the slave database
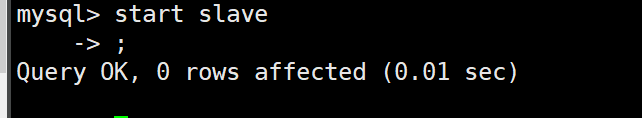
start slave
IX. check the database status and find that it has been synchronized
show slave status \G;
3. Test read-write separation
1, Host write data
Enter the host

create database db01; use db01; create table t1( id int, name varchar(20) ); insert into t1 values(1,'zs');
2, Read data from machine
Enter slave

Data synchronization succeeded} and the work was finished