Install Docker
Uninstall older Docker
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Installation dependency
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
Set docker warehouse
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Install Docker engine
sudo yum install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Start Docker
sudo systemctl start docker
Test whether Docker is installed successfully
Run docker run Hello word and the installation is successful when you see the following output
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker run hello-world
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
Basic use
Docker workflow
Execute some DockerClient commands locally, such as docker run nginx. Docker will enable the Images side of sever side
If there is a corresponding nginx in Images, it will be placed in the Container for execution
If not, pull the image from the Registry and then put it into the Container to pull the image. By default, it is in the hub docker. com
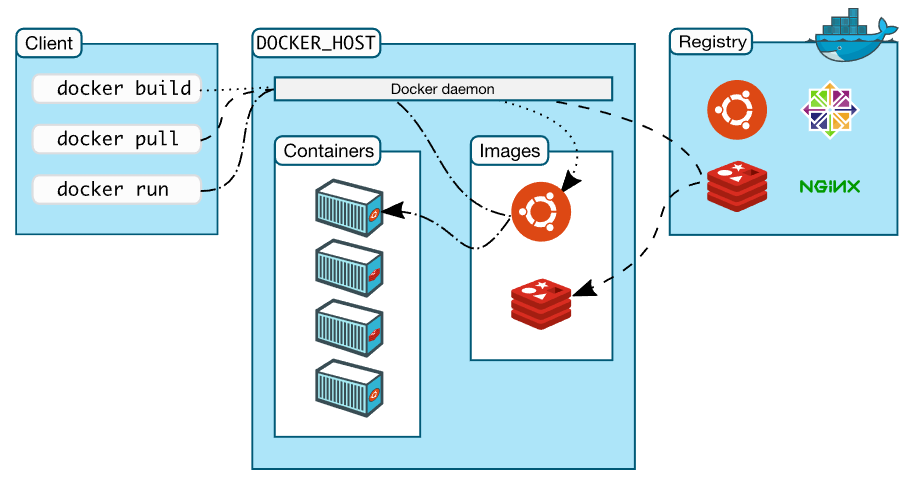
Docker command basic experience
docker images view images
View the images in the current images
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z bin]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 3 months ago 13.3kB
docker pull pulls the image to the local
For example, to pull the nginx image: docker pull nginx (the latest version is pulled by default)
Take a look at docker images before pulling. There are no docker images now
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z bin]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 3 months ago 13.3kB
Then pull to pull the image
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker pull nginx Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/nginx b4d181a07f80: Pull complete edb81c9bc1f5: Pull complete b21fed559b9f: Pull complete 03e6a2452751: Pull complete b82f7f888feb: Pull complete 5430e98eba64: Pull complete Digest: sha256:47ae43cdfc7064d28800bc42e79a429540c7c80168e8c8952778c0d5af1c09db Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest docker.io/library/nginx:latest
Then take a look at docker images
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE nginx latest 4f380adfc10f 11 days ago 133MB hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 months ago 13.3kB
docker run creates a container based on an image
Parameters:
- d let the container run in the background, which is actually a process
- -- name specifies a name for the Container container
- - p map the port of the container to the port of the host
Start nginx in the background and specify the Container name as my_nginx specifies the default 80 port of nginx as the 80 port of the current machine
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker run -d --name my_nginx -p 80:80 nginx 085e8e8df9ccf14d8bffd742250cb3254ba9e0f5a3be81e92d6d8a12eebc208c
Return Container id after startup
Enter ip:port in the browser to access
docker exec enters the Container
Parameters:
- -d: separation mode: running in the background
- -i: keep STDIN open even if there is no attachment
- -t: assign a pseudo terminal
After entering the Container, you can ls view the directory structure
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker exec -it my_nginx /bin/bash root@7ceadf2fa7f6:/# ls bin boot dev docker-entrypoint.d docker-entrypoint.sh etc home lib lib64 media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
The directory structure is basically the same as that on the host
You can also use the id returned after run
docker exec -it 085e8e8df9cc /bin/bash
docker ps
View containers that docker is running
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 085e8e8df9cc nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9090->80/tcp my_nginx
Add - a to view non running
[root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 24f04186d5ef python:3.8.8 "python3" 4 minutes ago Exited (2) 3 minutes ago optimistic_napier b36394f55dab python:3.8.8 "python3" 4 minutes ago Created blissful_chebyshev 2347a4ec1933 python:3.8.8 "python3" 5 minutes ago Exited (0) 4 minutes ago fervent_merkle 75dbf77a96be python:3.8.8 "python3" 8 minutes ago Exited (0) 8 minutes ago my_python 2241ddd2cb6b nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 3 hours ago Up 3 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp my_nginx
Stop stop container
After termination, the container will be in a non running state, which can be viewed using ps -a
First ps look at the current status
[root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES f0edc5be6346 nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 7 minutes ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp my_nginx
Then terminate the container and ps -a view the container that is not running
[root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker stop f0edc5be6346 f0edc5be6346 [root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES f0edc5be6346 nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 8 minutes ago Exited (0) 8 seconds ago my_nginx
docker start to restart
If you terminated the nginx container with stop, you can now restart it with start
[root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker start f0edc5be6346 f0edc5be6346 [root@iZ2zednq312875fg7oxr3bZ ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES f0edc5be6346 nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 11 minutes ago Up 12 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp my_nginx
Delete images Image
Take a look at images first
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE nginx latest 4f380adfc10f 12 days ago 133MB hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 months ago 13.3kB
Then delete Hello word
docker rmi -f hello-word
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker rmi -f hello-world Untagged: hello-world:latest Untagged: hello-world@sha256:9f6ad537c5132bcce57f7a0a20e317228d382c3cd61edae14650eec68b2b345c Deleted: sha256:d1165f2212346b2bab48cb01c1e39ee8ad1be46b87873d9ca7a4e434980a7726 Deleted: sha256:f22b99068db93900abe17f7f5e09ec775c2826ecfe9db961fea68293744144bd
Delete and then look at images
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE nginx latest 4f380adfc10f 12 days ago 133MB
Delete Container
docker rn -f delete container by container id
First, use ps to see the id running in the container
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 085e8e8df9cc nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9090->80/tcp my_nginx
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker rm -f 085e8e8df9cc 085e8e8df9cc
After deletion, take a look at the container
[root@iZj6ceofz5f9y3zvpwrig1Z ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
Delete all through container
docker rm -f $(docker container ls -qa)