Primary directory
Secondary directory
Tertiary directory
1, Installation
1. Remove Docker from the system
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
2. Configure yum source
sudo yum install -y yum-utils sudo yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
3. Install docker
sudo yum install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # Docker CE is a docker server # Docker CE cli is a docker command tool # containerd.io is a Docker environment # Install other versions yum install -y docker-ce-20.10.7 docker-ce-cli-20.10.7 containerd.io-1.4.6
4. Start and start
systemctl enable docker --now
5. Configure accelerated mirroring
# Create path
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://82m9ar63.mirror.aliyuncs.com"],
"exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"],
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "100m"
},
"storage-driver": "overlay2"
}
EOF
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# restart
sudo systemctl restart docker
2, Docker use command
1. Mirror operation command
(1) , search: Docker Hub official website
(2) . Download: docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG|@DIGEST]
Note: use the command plus -- help to view the detailed description of the command, for example: docker pull --help
# For example, download the latest version of nginx docker pull nginx # For example, download the specified version of nginx docker pull nginx:1.20.1
(3) . view the downloaded image: docker images [OPTIONS] [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
# View all downloaded images docker images
(4) . delete image: docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
# Delete nginx image docker rmi nginx
2. Container operation command
(1) , create and start container: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
docker run --name=nginx -d --restart=always -p 88:80 nginx # --Name: the name of the startup container # -d: Background operation # -P 88:80 map the container internal port 80 to the server 88 port # --restart=always: start automatically
| Description of common OPTIONS | effect |
|---|---|
| –name | The name of the startup container |
| -d | Background operation |
| –restart=always | Start and start automatically |
| -p 88:80 | Map container internal port 80 to server port 88 |
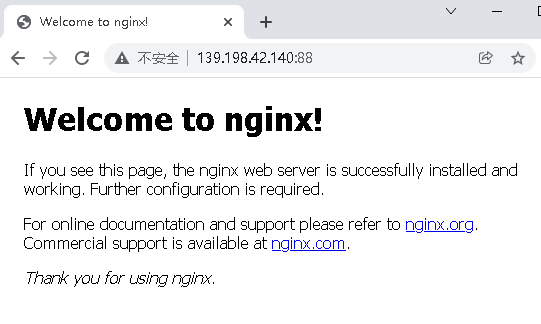
Access after startup http://139.198.42.140:88/ , if it is an ECS, you need to open port 88 in the security group
(2) . viewing container: docker ps [OPTIONS]
# View running containers docker ps
| Description of common OPTIONS | effect |
|---|---|
| -a | View all containers (non running containers are not displayed by default) |
| -n | View the last n containers started |
| -l | View the last container started |
(3) . stop container: docker stop [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
# First check the container name or container ID with docker ps docker stop Container name or container ID #Restart docker start Container name or container ID
(4) . delete container: docker rm [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
# Delete stopped containers docker rm Container name or container ID # Force deletion of running docker rm -f Container name or container ID
(5) Modify the parameters of the created container: docker update [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...], Some parameters cannot be modified: for example, - p and - v
#Modify -- restart docker update Container name or container ID --restart=no
3. Enter the container to modify the file
docker exec -it Container name or container ID /bin/bash
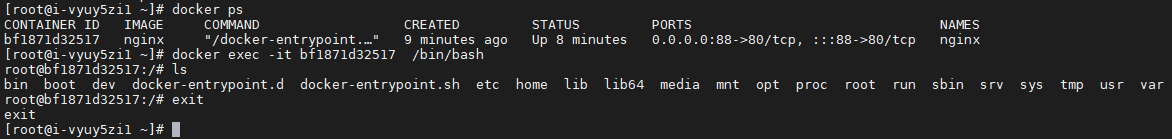
Take nginx as an example. You can see the page path of nginx in Docker Hub: / usr/share/nginx/html. Enter the container and modify / usr/share/nginx/html / index HTML, you can see the changes after you brush the page.
4. Create a new image from the container
docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
| Description of common OPTIONS | effect |
|---|---|
| -a | Submitted by |
| -m | Submission instructions |
| -p | Pause container on commit |
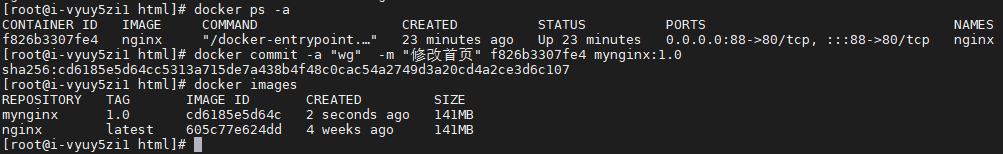
docker commit -a "wg" -m "Modify home page" f826b3307fe4 mynginx:1.0
5. Share mirror to another host
(1) Package, transfer, decompress and package the image: docker save - O mynginx Tar mynginx: 1.0, transfer the compressed package to other hosts and decompress the image: docker load - I mynginx tar.
(2) Upload the local image to the image warehouse (log in to the image warehouse first):
a. in Docker Hub official website Register an account with the user name studydocker88 and create a warehouse named mynginx;
b. docker login enter the user name and password to log in;
c. docker tag mynginx:1.0 studydocker88/mynginx:1.0 mark the local image mynginx:1.0 and put it into the myimages warehouse;
d. docker push studydocker88/mynginx:1.0, push the image to the remote warehouse;
e. other hosts can pull images: docker pull studydocker88/mynginx:1.0;
g. then create the container and start: docker run -d -p 99:80 studydocker88/mynginx:1.0. Open port 99.
6. Container and host file mount
Note: the command is too long. You can wrap with "\"
docker run --name=nginx -d --restart=always \ -p 88:80 -v /data/html:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
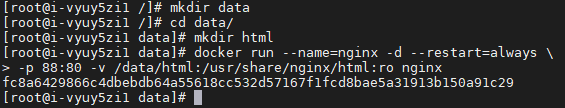
Visit now http://139.198.42.140:88/
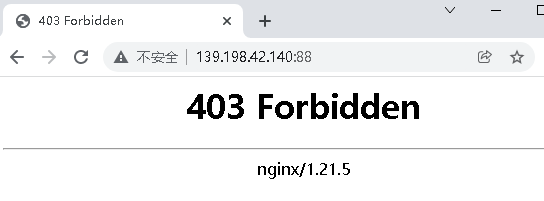
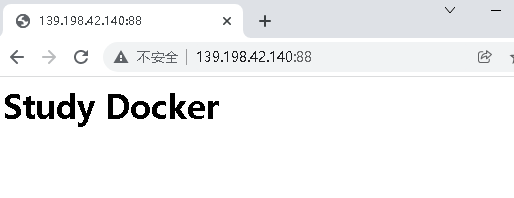
The reason is that there is no page under the mounting path. Create an index.html under the host path / data/html HTML, as follows:
<h1>Study Docker</h1>
Then visit again
7. Get metadata of container or image
docker inspect [OPTIONS] NAME|ID [NAME|ID...]
8. View container log
docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
| Description of common OPTIONS | effect |
|---|---|
| -f | Trace log output |
| –since | Show all logs for a start time |
| -t | presentation time stamp |
| –tail | Only the latest N container logs are listed |
9. Data copy between container and host
nginx copy container data to host
docker cp 5eff66eec7e1:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf /data/conf/nginx.conf # 5eff66eec7e1 is the container ID
nginx copy host data to container
ocker cp /data/conf/nginx.conf 5eff66eec7e1:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf # 5eff66eec7e1 is the container ID