Environmental Science:
- centos8.2 minimize installation
- docker
1, docker concept
Official website: https://www.docker.com/
Github Docker source code: https://github.com/docker/docker-ce
Docker is an open source application container engine, which is based on Go language and complies with Apache 2.0 0 protocol is open source.
Docker allows developers to package their applications and dependency packages into a lightweight and portable container, and then publish them to any popular Linux machine. It can also realize virtualization.
The container uses the sandbox mechanism completely, and there will be no interface between them (similar to iPhone app). More importantly, the performance overhead of the container is very low.
After version 17.0 three, Docker is divided into CE (Community Edition) and EE (Enterprise Edition). We can use the Community Edition.
reference: Docker tutorial
2, docker installation
2.1 installation dependency
First, install GCC and gcc-c + +:
yum -y install gcc yum -y install gcc-c++
Then, install other dependencies:
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
2.2 installing docker
First, configure the docker warehouse address:
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Then, before installing, we can search the docker package:
[root@bogon ~]# yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates | sort -r docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.6-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.5-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.4-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.3-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.2-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.1-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:20.10.0-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:19.03.15-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:19.03.14-3.el8 docker-ce-stable docker-ce.x86_64 3:19.03.13-3.el8 docker-ce-stable Docker CE Stable - x86_64 2.8 kB/s | 12 kB 00:04 Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:02 Before, it was implemented at 08:38:18 on Wednesday, May 12, 2021. Installable packages [root@bogon ~]#
Finally, install the latest docker CE directly: Yum - y install docker CE
[root@bogon ~]# yum -y install docker-ce Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:08 Before, it was implemented at 08:38:18 on Wednesday, May 12, 2021. Dependency resolution. ============================================================================================================================================================================================= software package framework edition Warehouse size ============================================================================================================================================================================================= install: docker-ce x86_64 3:20.10.6-3.el8 docker-ce-stable 27 M upgrade: libsemanage x86_64 2.9-3.el8 BaseOS 165 k Install dependencies: checkpolicy x86_64 2.9-1.el8 BaseOS 348 k ... tar x86_64 2:1.30-5.el8 BaseOS 838 k Enable module flow: container-tools rhel8 Transaction summary ============================================================================================================================================================================================= Install 20 packages Upgrade 1 package Total Download: 112 M Download package: (1/21): container-selinux-2.155.0-1.module_el8.3.0+699+d61d9c41.noarch.rpm 208 kB/s | 51 kB 00:00 ... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- total 3.1 MB/s | 112 MB 00:36 Warning:/var/cache/dnf/docker-ce-stable-fa9dc42ab4cec2f4/packages/containerd.io-1.4.4-3.1.el8.x86_64.rpm: head V4 RSA/SHA512 Signature, secret key ID 621e9f35: NOKEY Docker CE Stable - x86_64 2.6 kB/s | 1.6 kB 00:00 Import GPG Public key 0 x621E9F35: Userid: "Docker Release (CE rpm) <docker@docker.com>" fingerprint: 060A 61C5 1B55 8A7F 742B 77AA C52F EB6B 621E 9F35 come from: https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/gpg Import public key succeeded Run transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Run transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Run transaction In preparation : 1/1 install : docker-scan-plugin-0.7.0-3.el8.x86_64 ... Upgraded: libsemanage-2.9-3.el8.x86_64 already installed: checkpolicy-2.9-1.el8.x86_64 container-selinux-2:2.155.0-1.module_el8.3.0+699+d61d9c41.noarch containerd.io-1.4.4-3.1.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-3:20.10.6-3.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-cli-1:20.10.6-3.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-rootless-extras-20.10.6-3.el8.x86_64 docker-scan-plugin-0.7.0-3.el8.x86_64 fuse-common-3.2.1-12.el8.x86_64 fuse-overlayfs-1.3.0-2.module_el8.3.0+699+d61d9c41.x86_64 fuse3-3.2.1-12.el8.x86_64 fuse3-libs-3.2.1-12.el8.x86_64 libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 libslirp-4.3.1-1.module_el8.3.0+475+c50ce30b.x86_64 policycoreutils-python-utils-2.9-9.el8.noarch python3-audit-3.0-0.17.20191104git1c2f876.el8.x86_64 python3-libsemanage-2.9-3.el8.x86_64 python3-policycoreutils-2.9-9.el8.noarch python3-setools-4.3.0-2.el8.x86_64 slirp4netns-1.1.8-1.module_el8.3.0+699+d61d9c41.x86_64 tar-2:1.30-5.el8.x86_64 complete! [root@bogon ~]#
2.3 start docker
systemctl start docker
Note: if you run the docker command without starting docker, you may be prompted: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
2.4 check the installed version of docker:
[root@bogon ~]# clear [root@bogon ~]# docker --version Docker version 20.10.6, build 370c289 [root@bogon ~]# docker version Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 20.10.6 API version: 1.41 Go version: go1.13.15 Git commit: 370c289 Built: Fri Apr 9 22:44:36 2021 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Context: default Experimental: true Server: Docker Engine - Community Engine: Version: 20.10.6 API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12) Go version: go1.13.15 Git commit: 8728dd2 Built: Fri Apr 9 22:43:02 2021 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false containerd: Version: 1.4.4 GitCommit: 05f951a3781f4f2c1911b05e61c160e9c30eaa8e runc: Version: 1.0.0-rc93 GitCommit: 12644e614e25b05da6fd08a38ffa0cfe1903fdec docker-init: Version: 0.19.0 GitCommit: de40ad0 [root@bogon ~]#
3, Docker image, container and warehouse
DockerHub address: https://hub.docker.com/
-
Image: similar to the software installed in the operating system (existing in the hard disk and not running).
-
Container: similar to the process in the operating system (running from the installed software).
Note: it is a virtual sandbox. If a redis is running in the container, we need to manually expose the external interface of redis so that it can be accessed from the outside. Also, for each container, it has its own localhost and 127.0.0.1, so be careful when it comes to ip addresses.
-
Warehouse: docker has created a hub for sharing packaged images, which is similar to maven in java and npm in js net.
We can not only pull the packaged images of others from it, but also register our own account and upload them.
Of course, we can only package the image locally for our own use without uploading it to the hub, and the image pulled from the hub will be cached locally.
Version control of image:
Each image has a tag to identify the version of the image, so that we can specify a special version of the image during installation. Unfortunately, however, the tag is not displayed in the search results of docker (I will write my own script later).
Take redis as an example to illustrate the use of docker command:
3.1 search available Redis images from DockerHub: docker search redis
[root@bogon ~]# docker search redis NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED redis Redis is an open source key-value store that... 9417 [OK] bitnami/redis Bitnami Redis Docker Image 178 [OK] sameersbn/redis 83 [OK] grokzen/redis-cluster Redis cluster 3.0, 3.2, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 6.2 78 rediscommander/redis-commander Alpine image for redis-commander - Redis man... 58 [OK] redislabs/redisearch Redis With the RedisSearch module pre-loaded... 34 redislabs/redisinsight RedisInsight - The GUI for Redis 30 redislabs/redis Clustered in-memory database engine compatib... 29 oliver006/redis_exporter Prometheus Exporter for Redis Metrics. Supp... 25 redislabs/rejson RedisJSON - Enhanced JSON data type processi... 23 arm32v7/redis Redis is an open source key-value store that... 23 bitnami/redis-sentinel Bitnami Docker Image for Redis Sentinel 21 [OK] redislabs/redisgraph A graph database module for Redis 15 [OK] redislabs/redismod An automated build of redismod - latest Redi... 12 [OK] arm64v8/redis Redis is an open source key-value store that... 12 webhippie/redis Docker images for Redis 11 [OK] insready/redis-stat Docker image for the real-time Redis monitor... 10 [OK] s7anley/redis-sentinel-docker Redis Sentinel 10 [OK] circleci/redis CircleCI images for Redis 7 [OK] centos/redis-32-centos7 Redis in-memory data structure store, used a... 5 clearlinux/redis Redis key-value data structure server with t... 3 tiredofit/redis Redis Server w/ Zabbix monitoring and S6 Ove... 1 [OK] wodby/redis Redis container image with orchestration 1 [OK] runnable/redis-stunnel stunnel to redis provided by linking contain... 1 [OK] xetamus/redis-resource forked redis-resource 0 [OK] [root@bogon ~]#
3.2 view the version of the official redis image
There is an official image in the above search results: "redis", but the tag list is not displayed. We will make our own script to realize it:
- Create the file docker search show tag in the directory / bin SH, as follows:
#!/bin/sh # # Simple script that will display docker repository tags. # # Usage: # $ docker-show-repo-tags.sh ubuntu centos for Repo in $* ; do curl -s -S "https://registry.hub.docker.com/v2/repositories/library/$Repo/tags/" | \ sed -e 's/,/,\n/g' -e 's/\[/\[\n/g' | \ grep '"name"' | \ awk -F\" '{print $4;}' | \ sort -fu | \ sed -e "s/^/${Repo}:/" done - Give the script executable permission: Chmod 744 / bin / docker search show tag sh
[root@bogon ~]# chmod 744 /bin/docker-search-show-tag.sh
Use the above script to show all versions of image redis:
[root@bogon ~]# docker-search-show-tag.sh redis redis:6.0 redis:6.0-buster redis:6.0.13 redis:6.0.13-buster redis:6.2 redis:6.2-buster redis:6.2.3 redis:6.2.3-buster redis:buster redis:latest [root@bogon ~]#
Many tags (versions) are listed above. Note: there is a latest in it. Literally, this version should represent the latest. In fact, this tag is also an ordinary tag, but the name is a little special (Note: once downloaded locally, it belongs to the local and will not be automatically updated from the remote every time it runs...).
In addition, we all agree that the image of this version should always be kept up-to-date, so we can pull and manually update this version to keep our program up-to-date;
3.3 install redis image & view the existing local image
Install the latest redis image: docker pull redis
Install the image of the specified version: docker pull redis:6.0
When installing the latest redis image:
[root@bogon ~]# docker pull redis Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/redis f7ec5a41d630: Pull complete a36224ca8bbd: Pull complete 7630ad34dcb2: Pull complete e74b2f747260: Pull complete ebc61c7bf222: Pull complete 1aafd9c07208: Pull complete Digest: sha256:6cddb3822e19f09a6a369c35680562ddd2e44bd3bfd6fe25ec6456c42f45728b Status: Downloaded newer image for redis:latest docker.io/library/redis:latest [root@bogon ~]#
You can see that since there is no tag specified for installation, docker cli will have a confirmation process and just enter.
After installation, run docker images to view the local image list:
[root@bogon ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE redis latest ccee4cdf984f 8 days ago 105MB [root@bogon ~]#
The above shows that we have installed the latest version of redis, but which version of redis is this version? We can use the following command:
[root@bogon ~]# docker image inspect redis:latest | grep -i version
"GOSU_VERSION=1.12",
"REDIS_VERSION=6.2.3",
"DockerVersion": "19.03.12",
"GOSU_VERSION=1.12",
"REDIS_VERSION=6.2.3",
[root@bogon ~]#
We can know that the latest version of redis downloaded at present is actually version 6.2.3.
Of course, we can manually specify the image version when downloading:
[root@bogon ~]# docker pull redis:6.0 6.0: Pulling from library/redis f7ec5a41d630: Already exists a36224ca8bbd: Already exists 7630ad34dcb2: Already exists b794377c17d4: Pull complete a134ee7a12b3: Pull complete ab302c2d25fc: Pull complete Digest: sha256:dee031783fcbe8b5d9056303091043f1023853d73dfd3a83c7802c5038ad6f84 Status: Downloaded newer image for redis:6.0 docker.io/library/redis:6.0 [root@bogon ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE redis 6.0 3038fc9615f1 8 days ago 104MB redis latest ccee4cdf984f 8 days ago 105MB [root@bogon ~]#
3.4 running redis container
Execute the following command to run redis: docker run -it --name="redis6.0" -p 6379:6379 redis:6.0
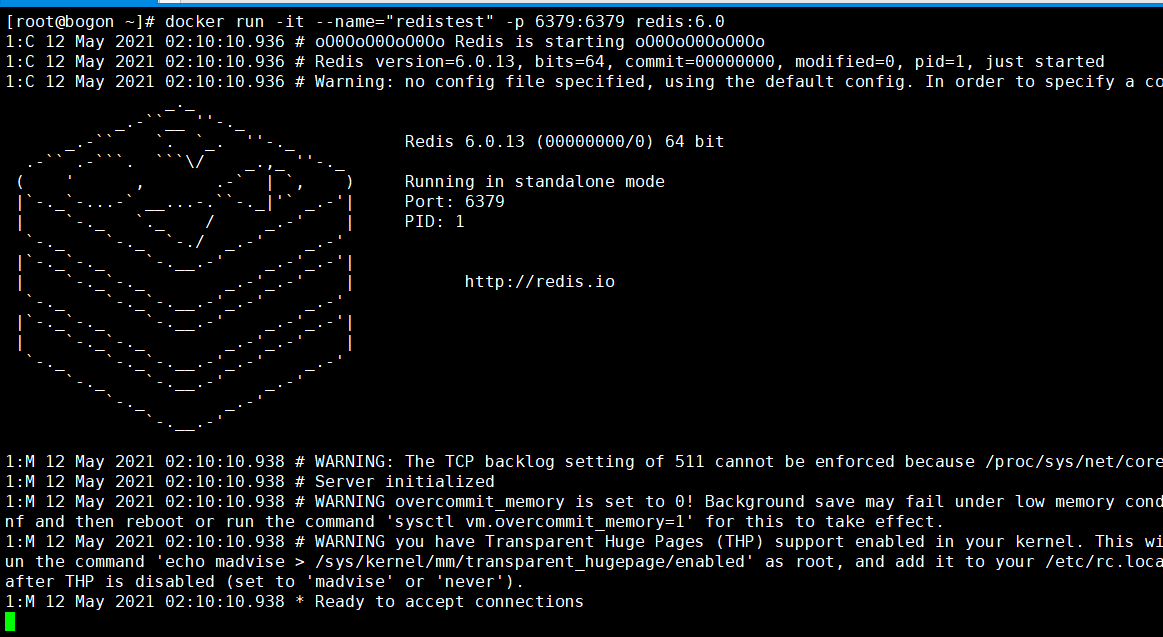
After running, we can access it from the outside (linux is the virtual machine, and the local physical machine is windows10):
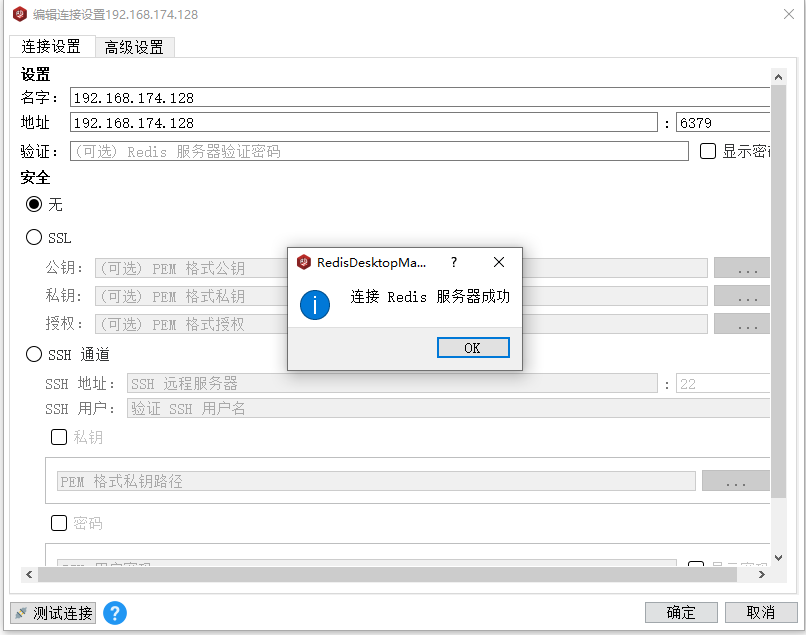
The above command allows us to run redis in blocking mode, but more often we want to run redis in background mode and re run the following command:
[root@bogon ~]# docker run -d --name="redistest2" -p 16379:6379 redis:6.0 2420c44f4576cd9d66980b2eb7a3cdba39a0413353e07a0e9c09299145a498d5 [root@bogon ~]#
After the above command is executed, the redis container id is returned.
We use redis client to connect:
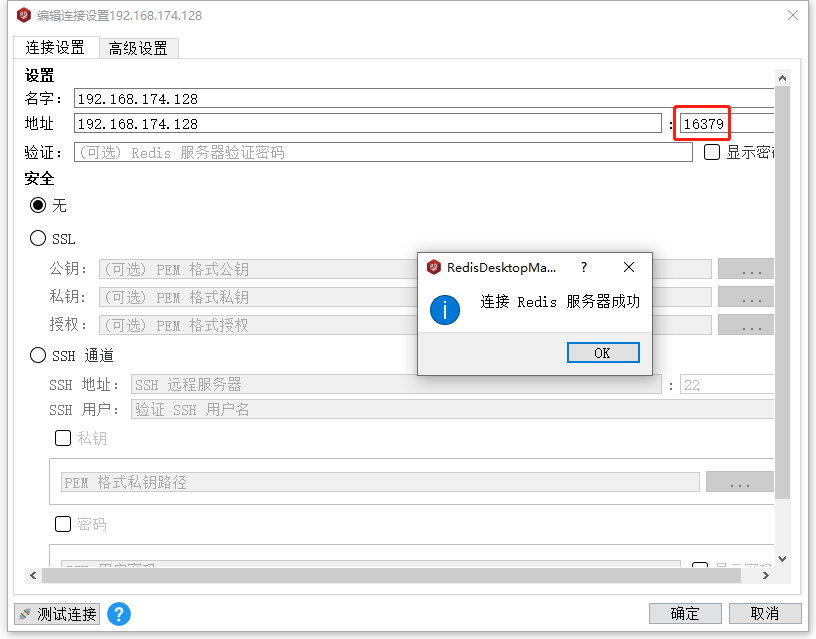
3.5 start and stop of redis container & view redis container
View the running container command: docker ps
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2420c44f4576 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes 0.0.0.0:16379->6379/tcp, :::16379->6379/tcp redistest2 d7fa06746181 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 9 minutes ago Up 9 minutes 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp, :::6379->6379/tcp redistest [root@bogon ~]#
If you want to pause a container (redistest), you can use the following command:
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2420c44f4576 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes 0.0.0.0:16379->6379/tcp, :::16379->6379/tcp redistest2 d7fa06746181 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 9 minutes ago Up 9 minutes 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp, :::6379->6379/tcp redistest [root@bogon ~]# docker stop redistest redistest [root@bogon ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2420c44f4576 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:16379->6379/tcp, :::16379->6379/tcp redistest2 [root@bogon ~]#
If we want to stop all the containers (including the ones below):
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2420c44f4576 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 6 minutes ago Up 6 minutes 0.0.0.0:16379->6379/tcp, :::16379->6379/tcp redistest2 d7fa06746181 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 12 minutes ago Exited (0) About a minute ago redistest [root@bogon ~]#
The existing (0) about a minute ago shown above indicates that the redistest container has stopped running 1 minute ago.
We can rerun it with the following command:
[root@bogon ~]# docker start redistest redistest [root@bogon ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2420c44f4576 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 8 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:16379->6379/tcp, :::16379->6379/tcp redistest2 d7fa06746181 redis:6.0 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 14 minutes ago Up 2 seconds 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp, :::6379->6379/tcp redistest [root@bogon ~]#
About docker run command:
Common parameters of the docker run command above
-it: means to run the container interactively (temporarily, generally in the background);
-d: Indicates that the container has been run in background mode;
--Name: name of the running container,
For example: docker run -it --name="redistest" -p 6379:6379 redis indicates that the container name after running is redistest.
-p: Indicates the exposed interface,
For example: docker run -it --name="redistest" -p 16379:6379 redis means that after the container runs, the 6379 port of the internal program is provided externally as 16379.
If there are more than one port, it is as follows: - p 16379:6379 -p 80:80.
If you want to expose continuous ports, as follows: -p 9600-9700:9600-9700, refer to: https://www.cnblogs.com/zhzhlong/p/12581934.html
-e: Represents the environment variable of the container,
For example, run ASP Net core program, if we want to specify the running environment as Development, we can use the following command:
docker -e "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=FatA" -d --name="coreweb" -p 5000:5000 coreweb
If there are multiple environment variables, see the following:
docker -e "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=FatA" -e "env_test=tag" -d --name="coreweb" -p 5000:5000 coreweb
-v: Mount the storage volume to the container and mount it to a directory of the container,
For example, we can use this parameter to manually specify the time zone in the docker container, as follows:
docker -e "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=FatA" -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime -d --name="coreweb" -p 5000:5000 coreweb
In the above command, we specify that the time zone in the docker container uses the time zone setting of the linux machine.
3.6 removing mirrors and containers
-
Remove image: docker rmi redis:6.0
First of all, we must remove all the containers that are running (including all the ones that have been removed).
-
Remove container: docker rmi redistest
We must stop this container before removing it.
-
Remove containers that have been stopped: docker container prune