1, docker network
1.1 understanding docker0
- Empty all containers in docker
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
- Clear all images in docker
docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq)
- ctrl+l is the shortcut key to clear the screen, which is equivalent to clear
- ip addr view the IP address information of the server, and you can see the information of three network cards
Run a tom1.2 container
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat
- -P. Randomly map the port number between the native and the container
[root@zhouhao ~]# docker ps -l CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 27deb683e957 tomcat "catalina.sh run" 16 minutes ago Up 16 minutes 0.0.0.0:49155->8080/tcp, :::49155->8080/tcp tomcat01
Check the internal network card information of the container. There is no ip addr command in the new version of tomcat. You need to install this command first
- Enter container installation
apt update && apt install -y iproute2
apt command
apt (Advanced Packaging Tool) is a Shell front-end package manager in Debian and Ubuntu.
apt command provides commands for finding, installing, upgrading and deleting one or a group of software packages, and the commands are simple and easy to remember.
apt command execution requires super administrator privileges (root).
View container internal network card information
root@27deb683e957:/usr/local/tomcat# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
70: eth0@if71: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:12:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.18.0.2/16 brd 172.18.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
1.3 can the Linux server ping through the docker container?
[root@zhouhao ~]# ping 172.18.0.2 PING 172.18.0.2 (172.18.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.049 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.060 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.059 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.067 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.061 ms
- The conclusion is that ping can pass
- The IP address in the dockers container is 172.18.0.2, and the IP address of the Linux server docker0 is 172.18.0.1, which is the same network end
[root@zhouhao ~]# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:16:3e:0e:ac:db brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.17.139.29/20 brd 172.17.143.255 scope global dynamic eth0
valid_lft 314555882sec preferred_lft 314555882sec
inet6 fe80::216:3eff:fe0e:acdb/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:4c:c9:62:7c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.18.0.1/16 brd 172.18.255.255 scope global docker0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::42:4cff:fec9:627c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
71: veth721544e@if70: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue master docker0 state UP group default
link/ether aa:e7:6a:71:ee:4e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet6 fe80::a8e7:6aff:fe71:ee4e/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
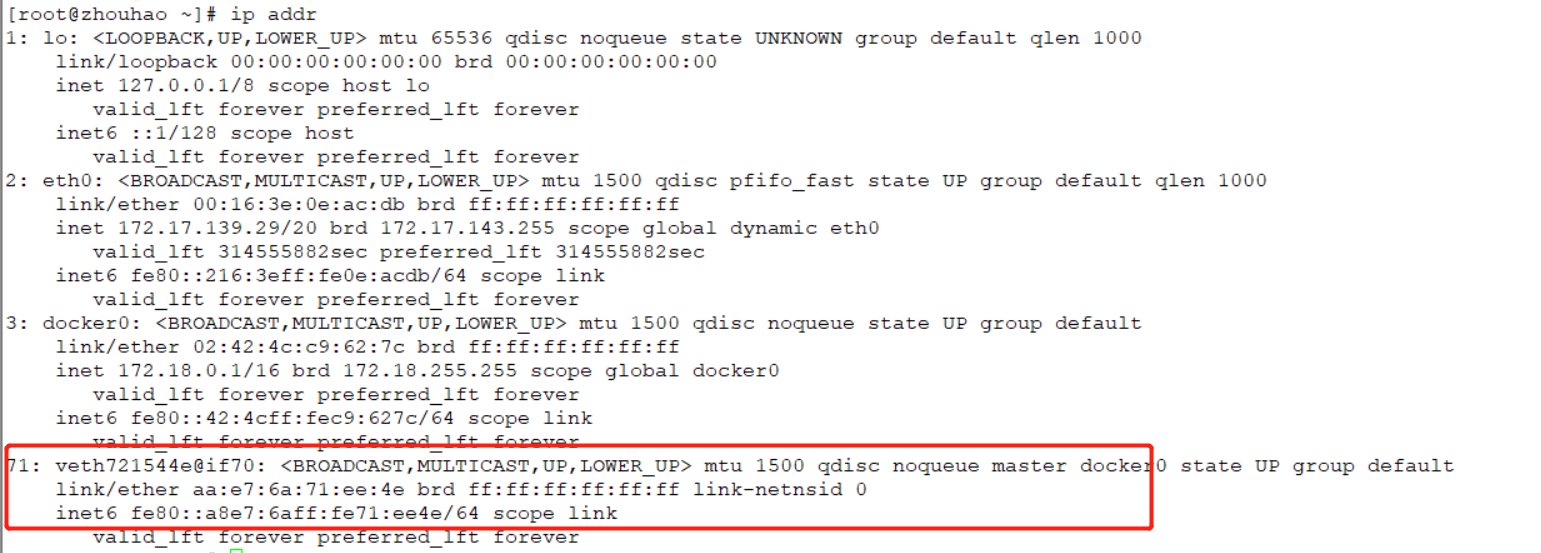 The network card numbered 71 is automatically generated after the docker container is started
The network card numbered 71 is automatically generated after the docker container is started
1.4 network principle
As long as docker is installed on the Linux server, there will be a docker0 network card, which is a bridge mode and uses evth pair technology. Start a docker container, and docker will assign an IP address to the docker container.
Veth pair Technology
It is found that the network card information in the Linux server corresponds to the network card information in the docker container and appears in pairs.
Veth pair technology is a virtual device interface, one is connected to the protocol, and the other is connected to each other. Veth pair acts as a bridge to connect virtual network devices.
1.5 start tomcat02 container
docker run -d -P --name tomcat02 tomcat
View started containers
[root@zhouhao ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6e124d494351 tomcat "catalina.sh run" 21 seconds ago Up 19 seconds 0.0.0.0:49156->8080/tcp, :::49156->8080/tcp tomcat02 27deb683e957 tomcat "catalina.sh run" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:49155->8080/tcp, :::49155->8080/tcp tomcat01
Enter the tomcat02 container and install the ip addr command
docker exec -it tomcat02 /bin/bash
apt update && apt install -y iproute2
View the network card information of tomcat02 container
root@6e124d494351:/usr/local/tomcat# ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
72: eth0@if73: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:12:00:03 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.18.0.3/16 brd 172.18.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Install ping command in container
apt install iputils-ping
pingtomcat01 container in tomcat02 container
root@6e124d494351:/usr/local/tomcat# ping 172.18.0.2 PING 172.18.0.2 (172.18.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.102 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.078 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.072 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.072 ms 64 bytes from 172.18.0.2: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.071 ms
- Containers are isolated, but can be ping ed
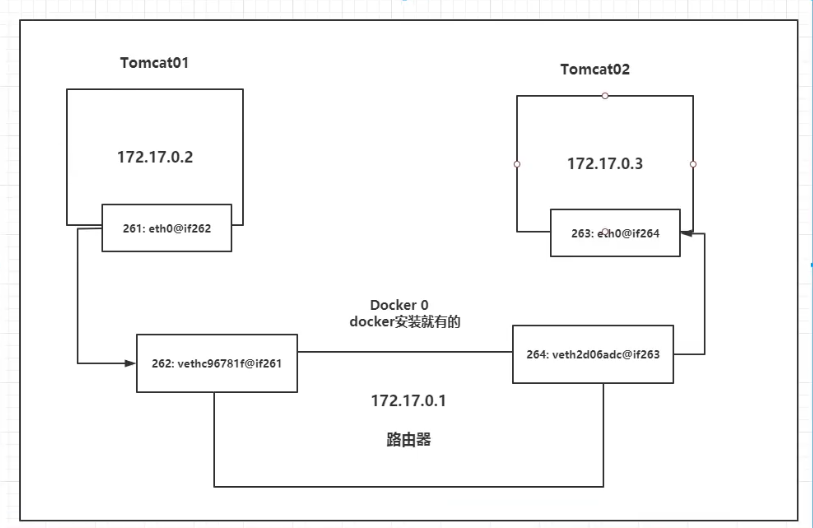
conclusion
tomcat01 and tomcat02 share one route, that is, docker0 route.
When all containers do not specify a network, they are routed by docker0, and docker assigns an available IP to the container.
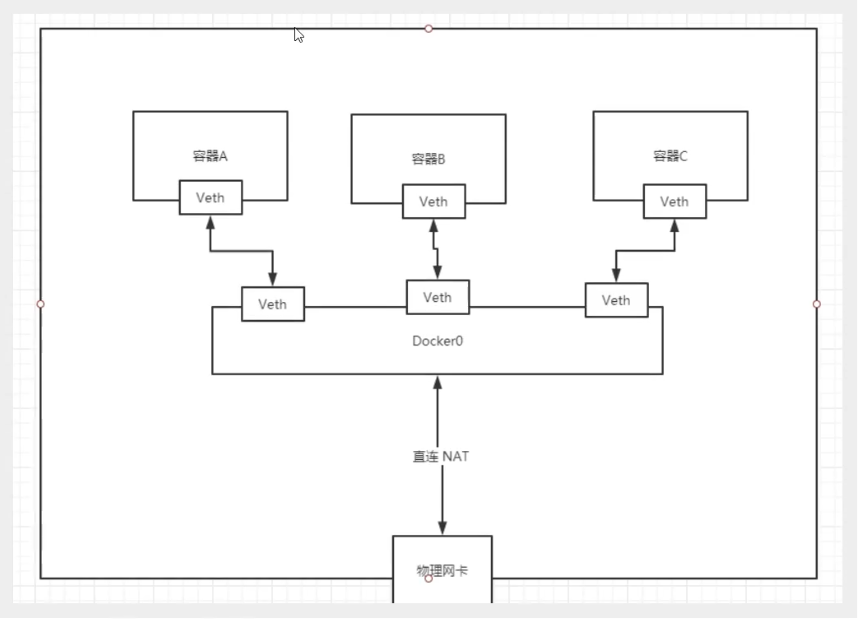
- Docker uses the bridging technology of Linux system. The host is a bridge of docker container, docker0. The core is the virtualization network technology of Linux system.
- In the docker container, all network interfaces are virtual and the forwarding efficiency is high
- As long as the container is deleted, the corresponding bridge pair is deleted
2, Container interconnection – link
2.1 start tomcat01 container
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat
Problem: the tomcat01 container cannot be ping ed in the tomcat02 container
docker exec -it tomcat02 ping tomcat01 ping: tomcat01: Name or service not known
Start tomcat03 container and connect with tomcat02 container
docker run -d -P --name tomcat03 --link tomcat02 tomcat
There is no ping command in tomcat03 container, which needs to be installed
apt update && apt install iputils-ping
ping the tomcat02 container in the tomcat03 container to ping the
root@94c7a93d3a2f:/usr/local/tomcat# ping tomcat02 PING tomcat02 (172.18.0.3) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from tomcat02 (172.18.0.3): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.090 ms 64 bytes from tomcat02 (172.18.0.3): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.080 ms 64 bytes from tomcat02 (172.18.0.3): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.069 ms
Can reverse ping pass? tomcat02 container pingtomcat03 container
[root@zhouhao ~]# docker exec -it tomcat02 ping tomcat03 ping: tomcat03: Name or service not known
- The conclusion is that reverse ping does not work
View the network information of the container
docker network ls NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE 8332af64f234 bridge bridge local 7abdac590e2b host host local f0c3788f5cda none null local
View the detailed network information of the specified container
docker network inspect 8332af64f234
[
{
"Name": "bridge",
"Id": "8332af64f2342b019f5b0c007159cebf7ee99b8c5be0a8701fe3de99890940ff",
"Created": "2022-02-04T14:05:43.401697636+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": null,
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "172.18.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "172.18.0.1"
}
]
},
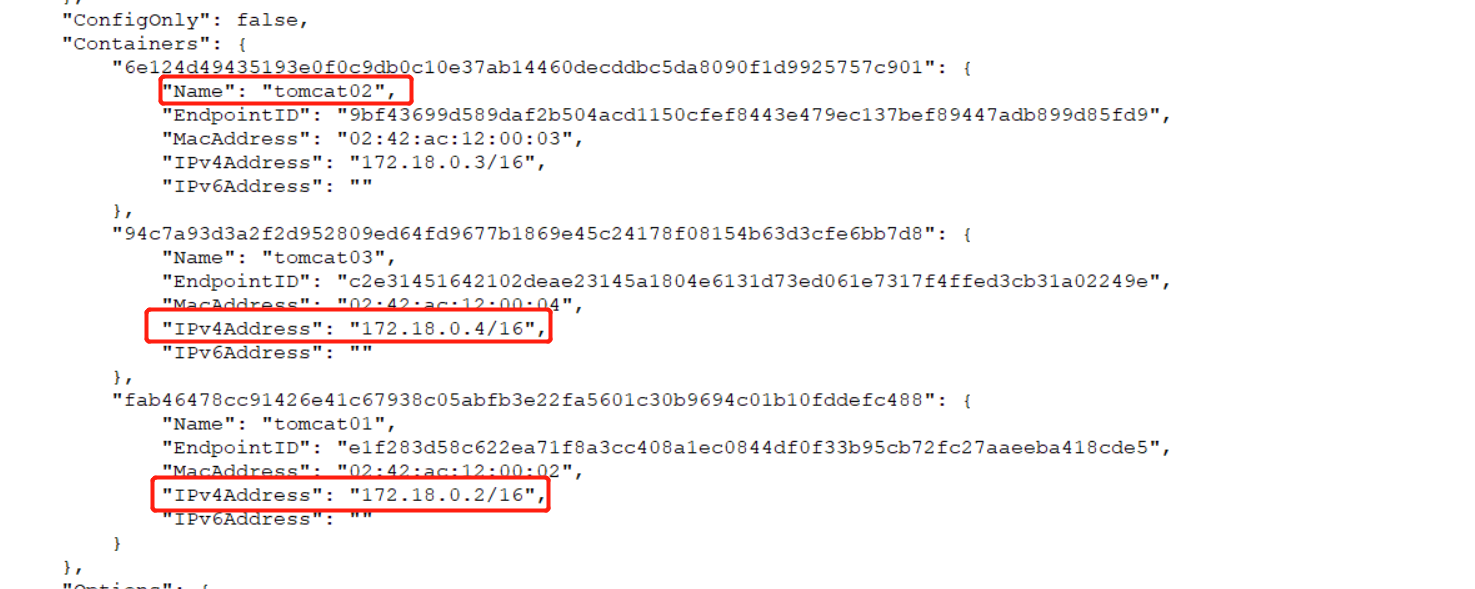
2.2 view details of specified containers
docker inspect 6e124d494351
Check the / etc/hosts file of tomcat03 container
cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.18.0.3 tomcat02 6e124d494351 172.18.0.4 94c7a93d3a2f
- In tomcat03 container, write the IP address of tomcat02 container in / etc/hosts file
- – link, the essence of which is to add the mapping of tomcat02 in the hosts file, 172.18.0.3 tomcat02 6e124d494351
2.3 view / etc/hosts file information
View the / etc/hosts file information of tomcat02 container
docker exec -it tomcat02 cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopback fe00::0 ip6-localnet ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix ff02::1 ip6-allnodes ff02::2 ip6-allrouters 172.18.0.3 6e124d494351
- It is no longer recommended to use – link when playing docker. We usually use custom networks, but not for docker0.
- docker0 has its own problem. It does not support container name connection access.
3, Custom network
3.1 view all docker networks
docker network ls NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE 8332af64f234 bridge bridge local 7abdac590e2b host host local f0c3788f5cda none null local
3.2 network mode
- Bridge, bridge mode, docker, default
- none, no network configuration
- Host to share the network with the host
- Container, the network in the container is connected, which has great limitations and uses less
Clear all containers
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
3.3 testing
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 --net bridge tomcat And docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat Same effect
- When the docker container is started, it has a default parameter - net bridge, which uses the network of docker0 by default,
- The docker0 network domain name cannot be accessed, and the – link can be connected
3.4 custom network
docker network command
docker network --help Usage: docker network COMMAND Manage networks Commands: connect Connect a container to a network create Create a network disconnect Disconnect a container from a network inspect Display detailed information on one or more networks ls List networks prune Remove all unused networks rm Remove one or more networks Run 'docker network COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
docker network create command
docker network create --help
Usage: docker network create [OPTIONS] NETWORK
Create a network
Options:
--attachable Enable manual container attachment
--aux-address map Auxiliary IPv4 or IPv6 addresses used by Network driver (default map[])
--config-from string The network from which to copy the configuration
--config-only Create a configuration only network
-d, --driver string Driver to manage the Network (default "bridge")
--gateway strings IPv4 or IPv6 Gateway for the master subnet
--ingress Create swarm routing-mesh network
--internal Restrict external access to the network
--ip-range strings Allocate container ip from a sub-range
--ipam-driver string IP Address Management Driver (default "default")
--ipam-opt map Set IPAM driver specific options (default map[])
--ipv6 Enable IPv6 networking
--label list Set metadata on a network
-o, --opt map Set driver specific options (default map[])
--scope string Control the network's scope
--subnet strings Subnet in CIDR format that represents a network segment
Create mynet network
docker network create --driver bridge --subnet 192.168.0.0/16 --gateway 192.168.0.1 mynet
- – subnet 192.168.0.0/16, IP address range 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.255.255.
- –gateway 192.168.0.1
View the created mynet network
docker network ls NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE 8332af64f234 bridge bridge local 7abdac590e2b host host local e7525fc2fc6a mynet bridge local f0c3788f5cda none null local
View the created mynet network. For details, see inspect
docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "e7525fc2fc6ab9a3d500b2f4c6e7670b8b532016b9d5048054777953f5bd9926",
"Created": "2022-02-15T11:45:41.854137623+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
Start tomcat01 and tomcat02 containers using custom network
docker run -d -P --name tomcat-net-01 --net mynet tomcat
docker run -d -P --name tomcat-net-02 --net mynet tomcat
View details of custom network mynet
[root@zhouhao ~]# docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "e7525fc2fc6ab9a3d500b2f4c6e7670b8b532016b9d5048054777953f5bd9926",
"Created": "2022-02-15T11:45:41.854137623+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {
"742a0507cc599c268052459f1ba48dc13f5da0f820e512aa9da7a34cba482761": {
"Name": "tomcat-net-01",
"EndpointID": "33983a1c49a1befa8000e5f9eb703d4b1a41a326881e44a13530b27f2149e2e9",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:02",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.2/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
},
"ea41c7650e0c5df3faf10832d6ef2994e85885f2673e3aa1555585f724bf8994": {
"Name": "tomcat-net-02",
"EndpointID": "0a53a95aa04f6317509674bd286bb6d753df215deafc983a19b1fdfd05b831ae",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:03",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.3/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
}
},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
You can see the detailed network information of tomcat01 and tomcat02 containers.
Tomcat-net-01 container ping tomcat-net-02 container name, tomcat-net-01 container pingtomcat-net-02 container IP address can be pinged.
docker exec -it tomcat-net-01 ping tomcat-net-02
docker exec -it tomcat-net-01 ping 192.168.0.3
- Now you can ping the container without going through – link
3.5 summary
- The user-defined network has helped us maintain the corresponding relationship. It is recommended to use the user-defined network
- For example, redis cluster and MySQL Cluster. Different clusters use different networks to ensure that the cluster is safe and healthy
4, Network connectivity
4.1 start tomcat01 and tomcat02 containers and use docker0 network by default
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat
docker run -d -P --name tomcat02 tomcat
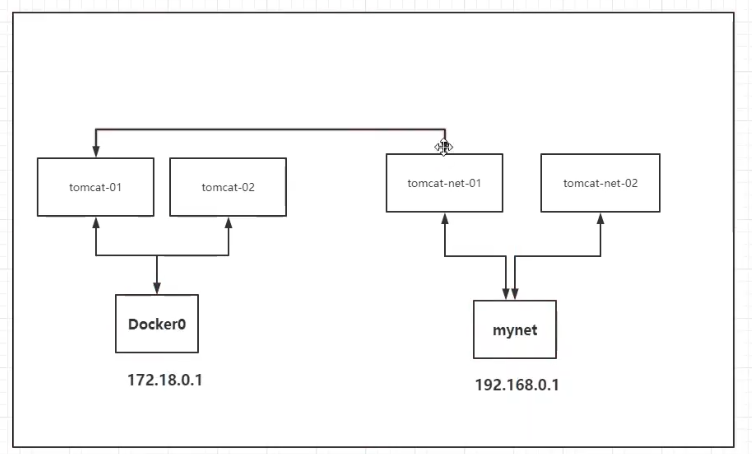
ping the tomcat-net-01 container in the tomcat01 container, but the ping fails. The two containers depend on different network cards and different IP network segments.
root@3d049ffd705b:/usr/local/tomcat# ping tomcat-net-01 ping: tomcat-net-01: Name or service not known
docker network connect command
Usage: docker network connect [OPTIONS] NETWORK CONTAINER
Connect a container to a network
Options:
--alias strings Add network-scoped alias for the container
--driver-opt strings driver options for the network
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip strings Add a link-local address for the container
4.2 connect tomcat01 container with mynet network card
docker network connect mynet tomcat01
View the details of mynet network card after connection
docker network inspect mynet
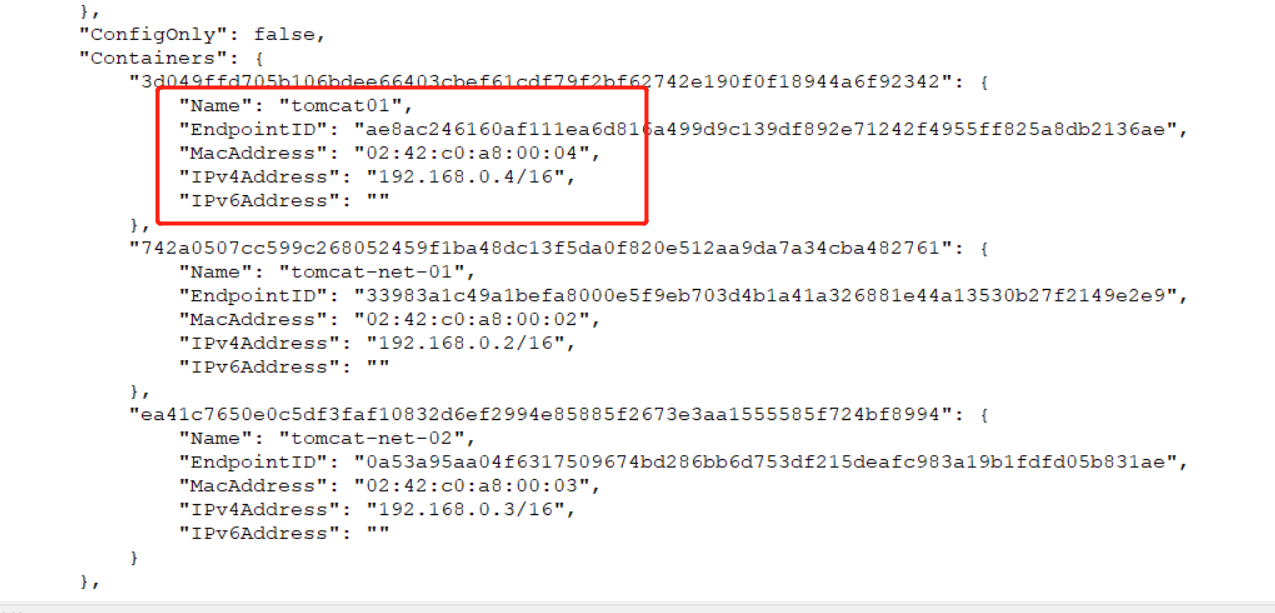 Tomcat01 container network is found and has been added to mynet network card. The network segment of tomcat01 container is the same as that of mynet network card. Here, virtual IP technology is used, that is, IP mapping.
Tomcat01 container network is found and has been added to mynet network card. The network segment of tomcat01 container is the same as that of mynet network card. Here, virtual IP technology is used, that is, IP mapping.
- tomcat01 container is a container with two IP addresses
- The container and network card can be connected
Tom-cat-01-tom3 container
[root@zhouhao ~]# docker exec -it tomcat01 ping tomcat-net-01 PING tomcat-net-01 (192.168.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.091 ms 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.068 ms 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.070 ms 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.072 ms 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.068 ms 64 bytes from tomcat-net-01.mynet (192.168.0.2): icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.077 ms
- Can ping through
5, redis cluster deployment
5.1 create redis network card
docker network create redis --subnet 172.38.0.0/16
View the created redis network card
docker network ls NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE 8332af64f234 bridge bridge local 7abdac590e2b host host local e7525fc2fc6a mynet bridge local f0c3788f5cda none null local 7cd2081215f8 redis bridge local
docker network inspect redis
[
{
"Name": "redis",
"Id": "7cd2081215f86d013cc78e19ad2bfe134e8ad78d6cf81407fd9223f242f9eebf",
"Created": "2022-02-15T16:16:24.942200934+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "172.38.0.0/16"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
seq command
Used to generate all integers from one number to another
[root@zhouhao ~]# seq 1 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Cat > file < < EOF command
Cat > file name < < EOF: used to create a file. Anything entered after that is in the file. After the input is completed, it ends with EOF.
Cat > > file name < < EOF: the same as above, but it is appended to the file, which is overwritten.
[root@zhouhao ~]# cat << EOF > 1.txt > a > b > c > d > e > EOF [root@zhouhao ~]# cat 1.txt a b c d e
cat command
cat --help
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output.
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Examples:
cat f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat Copy standard input to standard output.
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'cat invocation'
Cat is not only used to view files. Use the man cat command to view the official description of cat: output [file] or standard input (i.e. keyboard input) to standard output.
Using cat directly without option parameters is to directly output standard input (i.e. keyboard input) to standard output.
a b b d d d^H d e e dd dd jj jj ^C
5.2 writing automated scripts for creating configuration files
for port in $(seq 1 6);
do
mkdir -p /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf
touch /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
cat << EOF > /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
port 6379
bind 0.0.0.0
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
cluster-announce-ip 172.38.0.1${port}
cluster-announce-port 6379
cluster-announce-bus-port 16379
appendonly yes
EOF
done
docker run command
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
Command to start redis-1 container
docker run -p 6371:6379 -p 16371:16379 --name redis-1 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-1/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-1/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.11 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Command to start redis-2 container
docker run -p 6372:6379 -p 16372:16379 --name redis-2 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-2/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-2/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.12 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Command to start redis-3 container
docker run -p 6373:6379 -p 16373:16379 --name redis-3 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-3/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-3/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.13 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Command to start redis-4 container
docker run -p 6374:6379 -p 16374:16379 --name redis-4 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-4/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-4/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.14 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Command to start redis-5 container
docker run -p 6375:6379 -p 16375:16379 --name redis-5 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-5/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-5/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.15 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Command to start redis-5 container
docker run -p 6376:6379 -p 16376:16379 --name redis-6 \ -v /mydata/redis/node-6/data:/data \ -v /mydata/redis/node-6/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.16 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
View the started redis container
docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES a545cf1e7ad0 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 5 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:6376->6379/tcp, :::6376->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16376->16379/tcp, :::16376->16379/tcp redis-6 8036afc6e674 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:6375->6379/tcp, :::6375->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16375->16379/tcp, :::16375->16379/tcp redis-5 5ce3258cb6c2 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes 0.0.0.0:6374->6379/tcp, :::6374->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16374->16379/tcp, :::16374->16379/tcp redis-4 dea3eecff780 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:6373->6379/tcp, :::6373->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16373->16379/tcp, :::16373->16379/tcp redis-3 122fca28023e redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 7 minutes ago Up 7 minutes 0.0.0.0:6372->6379/tcp, :::6372->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16372->16379/tcp, :::16372->16379/tcp redis-2 7e88c95b2a84 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 "docker-entrypoint.s..." 14 minutes ago Up 14 minutes 0.0.0.0:6371->6379/tcp, :::6371->6379/tcp, 0.0.0.0:16371->16379/tcp, :::16371->16379/tcp redis-1
5.3 start redis cluster
Enter redis-1 container
docker exec -it redis-1 /bin/sh
- There is no / bin/bash command in redis container, but there is / bin/sh command
Start redis cluster
redis-cli --cluster create 172.38.0.11:6379 172.38.0.12:6379 172.38.0.13:6379 172.38.0.14:6379 172.38.0.15:6379 172.38.0.16:6379 --cluster-repl icas 1
Enter redis cluster
redis-cli -c
View redis cluster nodes
cluster nodes e70fc91669d2e19929d7058c6f3cbd1227b66fe2 172.38.0.13:6379@16379 master - 0 1644933783590 3 connected 10923-16383 3c1ce8913d0285a5ac709445f0674227196272ad 172.38.0.14:6379@16379 slave e70fc91669d2e19929d7058c6f3cbd1227b66fe2 0 1644933784000 4 connected 2452bc8374d17a92a9609dff068fe22df2df5477 172.38.0.11:6379@16379 myself,master - 0 1644933782000 1 connected 0-5460 b8337f97893ee1ece43e1420c2064f6db55ea20e 172.38.0.15:6379@16379 slave 2452bc8374d17a92a9609dff068fe22df2df5477 0 1644933782189 5 connected c5f3cb140fcc78d5754651fcb270ea17563155f2 172.38.0.16:6379@16379 slave e917bdffad645b7a4df55513252396e4e71a2cb6 0 1644933784191 6 connected e917bdffad645b7a4df55513252396e4e71a2cb6 172.38.0.12:6379@16379 master - 0 1644933784191 2 connected 5461-10922