Docker introduction
What is Docker?
When people say "Docker", they usually refer to Docker Engine, which is a client server application, which is controlled by Docker
A daemon, a REST API that specifies the interface to interact with the daemon, and a command line interface (CLI) to communicate with the daemon (by encapsulating the REST API). The Docker Engine receives docker commands from the CLI, such as docker run, docker ps to list running containers, docker images to list images, and so on.
- docker is a software that can run on window s, linux, mac and other operating systems.
- docker is an open source application container engine. It is developed based on Go language and complies with Apache 2.0 protocol. The project code is entrusted to
Tube maintenance on github - docker allows developers to package their applications and dependent packages into a lightweight and portable container, and then publish them to anyone
On popular Linux machines. - Containers completely use sandbox mechanism, and there will be no interface between them. More importantly, the performance overhead of containers is very low.
Basic composition of Docker
- Docker host: the machine on which the docker program is installed (docker is directly installed on the operating system);
- docker repository (Registry): used to store various packaged software images; Warehouses are divided into public warehouses and private warehouses. (very similar)
maven) - Docker images: images packaged by software; placed in docker warehouse;
- docker container: the instance after the image is started is called a container; a container is an application or group of applications running independently
Comparison between Docker and operating system
Docker is a lightweight virtualization method. The characteristics of docker compared with traditional operating system technology are as follows:
| characteristic | container | virtual machine |
|---|---|---|
| Starting speed | Second order | Minute level |
| performance | Near primary | Weaker |
| Memory cost | Very small | More |
| Hard disk usage | Typically MB | Generally GB |
| Operating density | A single machine supports thousands of containers | Generally dozens |
| Isolation | Safety isolation | Complete isolation |
| Mobility | excellent | commonly |
The traditional virtual machine provides relatively closed isolation. Docker uses a variety of protection technologies on Linux system to achieve strict isolation
Since version 1.3.0, docker has focused on improving the security control and mirroring of containers
The security mechanism greatly improves the security of using docker.
Docker version
After version 17.03, docker is divided into CE (Community Edition) and EE (Enterprise Edition)
This tutorial uses the Community Edition (CE).
Advantages of Docker
One product: development – launch two sets of environments! Application environment, application configuration! Development – operation and maintenance. Problem: I can allow it on my computer! Version update makes the service unavailable! It is a great test for operation and maintenance!!! Environment configuration is very troublesome, and each machine needs to deploy the environment (cluster Redis, ES, Hadoop...) ! it's a lot of trouble. If you publish a project (jar + (Redis MySQL JDK ES)), can the project be installed and packaged with the environment! It's too troublesome to configure an application environment Redis MySQL JDK ES Hadoop on the server before
And can't cross platform.
-
Development environment Windows, finally released to Linux!
Tradition: development jar, operation and maintenance to do!
Now: development, packaging, deployment and launch, and a set of processes are completed! -
Faster delivery and deployment of applications
Traditional: help documentation, setup.
Docker: the packaged image publishing test runs with one click. -
More convenient upgrade and capacity expansion
After using Docker, we deploy applications just like building blocks
The project is packaged as an image to expand server A and server B -
Simpler system operation and maintenance
After containerization, our development and test environments are highly consistent -
More efficient utilization of computing resources
Docker is kernel level virtualization, which can run many container instances on a physical machine! The performance of the server can be squeezed to the extreme
Docker installation
Docker official website
docker official website address:
https://www.docker.com
docker official document address:
https://docs.docker.com/
Alibaba cloud Developer Platform official website address:
(you can refer to the docker installation tutorial provided on Alibaba cloud's official website for installation.)
https://developer.aliyun.com/article/110806
Hardware requirements for installation
When we install Docker, two main components will be involved:
- Docker CLI: client
- Docker daemon: sometimes called "server" or "engine"
docker hardware installation should meet the following conditions:
| Serial number | Hardware | requirement |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CPU | More than 2 cores are recommended |
| 2 | Memory | At least 2G |
| 3 | Hard disk | At least 50G |
| 4 | system | docker and K8S clusters recommend that you use CentOS 7.8 |
System configuration of centos virtual machine
- View centos system version command:
cat /etc/centos-release
- Configure Alibaba cloud yum source
#Download and install wget yum install -y wget #Backup default yum mv /etc/yum.repos.d /etc/yum.repos.d.backup #Set new yum directory mkdir -p /etc/yum.repos.d #Download Alibaba yum configuration to this directory and select the corresponding version wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo #Update the epel source to Alibaba cloud epel source mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo.backup mv /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-testing.repo.backup wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo #Rebuild cache yum clean all yum makecache #Let's see how many bags there are in the warehouse yum repolist
- Upgrade system kernel
rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-3.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install -y kernel-lt grep initrd16 /boot/grub2/grub.cfg grub2-set-default 0 reboot
- View system kernel commands
uname -r uname -a
- View CPU commands
lscpu
- View memory commands
free free -h
- View hard disk information
fdisk -l
- Turn off firewall
systemctl stop firewalld systemctl disable firewalld
- Close selinux
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux setenforce 0
- Bridge filtering
vi /etc/sysctl.conf net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 net.ipv4.ip_forward_use_pmtu = 0 #Effective order sysctl --system
- Open command completion
#Installing bash completion yum -y install bash-completion bash-completion-extras #Using bash completion source /etc/profile.d/bash_completion.sh
- Upload file function
yum -y install lrzsz
#1. Drag the mouse to upload the file
#2. Download files
#2.1 download a file
sz filename
#2.2 downloading multiple files
sz filename1 filename2
#2.3 download all files in dir directory, excluding folders in dir
sz dir/*
Installation of Docker
# step 1: install some necessary system tools sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 # Step 2: add software source information sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo # Step 3: update and install docker CE sudo yum makecache fast sudo yum -y install docker-ce # Step 4: start Docker service sudo service docker start Note: other considerations are in the notes below # The official software source enables the latest software by default. You can obtain the software packages of various versions by editing the software source. For example, the official does not make the software source of the test version available, you can open it in the following ways. Similarly, you can open various test versions, etc. # vim /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo # Change enabled=0 under [docker CE test] to enabled=1 # # Install the specified version of docker Ce: # Step 1: find docker CE version: # yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates | sort -r # Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile # Loaded plugins: branch, fastestmirror, langpacks # docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.1.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable # docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.1.ce-1.el7.centos @docker-ce-stable # docker-ce.x86_64 17.03.0.ce-1.el7.centos docker-ce-stable # Available Packages # Step 2: install the specified version of docker Ce: (version, for example, 17.03.0.ce.1-1. EL7. CentOS above) # sudo yum -y install docker-ce-[VERSION] # Note: after some versions, other dependent packages appear in docker CE installation. If the installation fails, please pay attention to the error information. For example, after docker CE 17.03, you need to install docker CE SELinux first. # yum list docker-ce-selinux- --showduplicates | sort -r # sudo yum -y install docker-ce-selinux-[VERSION] # When installing through classic network and VPC network intranet, replace the command in Step 2 with the following command # Classic network: # sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.aliyuncs.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo # VPC network: # sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo http://mirrors.could.aliyuncs.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Install alicloud image accelerator
The image accelerator can speed up the download of docker image. Whether it is installed or not depends on your mood
mkdir -p /etc/docker
tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://Copy your accelerator address. mirror.aliyuncs.com "]
}
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
docker command
docker command classification
This chapter records the use of docker commands in most situations. If you want to know the details of each option, please refer to the official documents according to the case on docker's official website.
docker official website address: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/
Generally speaking, it can be divided into the following categories:
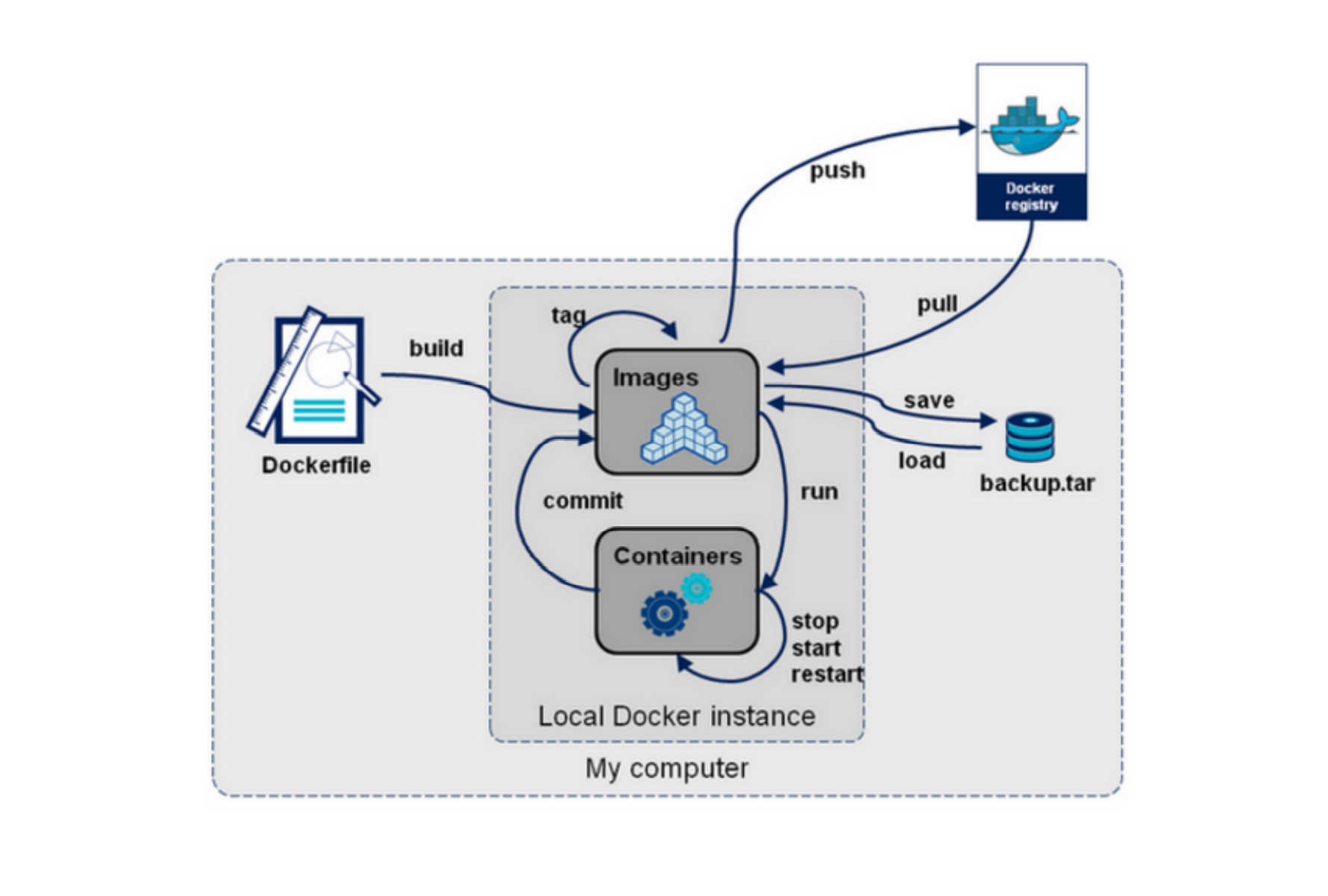
#docker environment information docker -v docker info docker version #Container lifecycle management docker [create|exec|run|start|stop|restart|kill|rm|pause|unpause] #Container operation management docker [ps|inspect|top|attach|wait|export|port|rename|stat] #Container rootfs command docker [commit|cp|diff] #Mirror warehouse docker [login|pull|push|search] #Local image management docker [build|images|rmi|tag|save|import|load] #Container resource management docker [volume|network] #System log information docker [events|history|logs]
Starting from the docker command, sort out the following structure diagram: