Docker Compose
1. Introduction
Official introduction
Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you use a YAML file to configure your application's services. Then, with a single command, you create and start all the services from your configuration. To learn more about all the features of Compose, see the list of features.
- How to define and run multiple containers
- YAML file configuration file
- What are the advantages of single common
Compose works in all environments: production, staging, development, testing, as well as CI workflows. You can learn more about each case in Common Use Cases.
- Docker Compose can be used in all environments
Using Compose is basically a three-step process:
-
Define your app's environment with a Dockerfile so it can be reproduced anywhere.
Dockerfile ensures that our project (app) can run anywhere
-
Define the services that make up your app in docker-compose.yml so they can be run together in an isolated environment.
Configure the service in the YAML configuration file
-
Run docker compose up and the Docker compose command starts and runs your entire app. You can alternatively run docker-compose up using the docker-compose binary.
Launch our project (app)
Summary: batch container orchestration can manage multiple services (containers)
Compose is an official open source project of Docker, so it needs to be installed!
Configuration file: docker-compose.yml
version: "3.9" # optional since v1.27.0
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
volumes:
- .:/code
- logvolume01:/var/log
links:
- redis
redis:
image: redis
volumes:
logvolume01: {}
Our task is to write such a configuration file to manage our multiple services (containers)
It can start multiple services at the same time through docker compose up
2. Install Compose
Address: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
1. Download docker compose
#Installed in Linux system csudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose #If the installation is too slow, change the github source to get.daocloud.io curl -L https://get.daocloud.io/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Go to the installation directory and check: Download succeeded!

2. Set file executable permissions
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
3. View version information
docker-compose -version

4. Uninstall docker compose
sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
3. Experience Docker Compose quickly
Reference documents: https://docs.docker.com/compose/gettingstarted/
1. Create a directory under which all operations are performed
mkdir composetest cd composetest
2. Create a py application (similar to counting browsing times and counters)
import time
import redis #Imported our redis
from flask import Flask #Imported our Flask (a framework dependency of python)
app = Flask(__name__)
cache = redis.Redis(host='redis', port=6379)
def get_hit_count():
retries = 5
while True:
try:
return cache.incr('hits')
except redis.exceptions.ConnectionError as exc:
if retries == 0:
raise exc
retries -= 1
time.sleep(0.5)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
count = get_hit_count()
return 'Hello World! I have been seen {} times.\n'.format(count)
3. Create a configuration text, requirements.txt
flask redis
4. Create Dockerfile
# syntax=docker/dockerfile:1 FROM python:3.7-alpine WORKDIR /code ENV FLASK_APP=app.py ENV FLASK_RUN_HOST=0.0.0.0 RUN apk add --no-cache gcc musl-dev linux-headers COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt RUN pip install -r requirements.txt EXPOSE 5000 COPY . . CMD ["flask", "run"]
5. Create docker-compose.yml
version: "3.9"
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"
6. Start
docker-compose up
Start successfully!
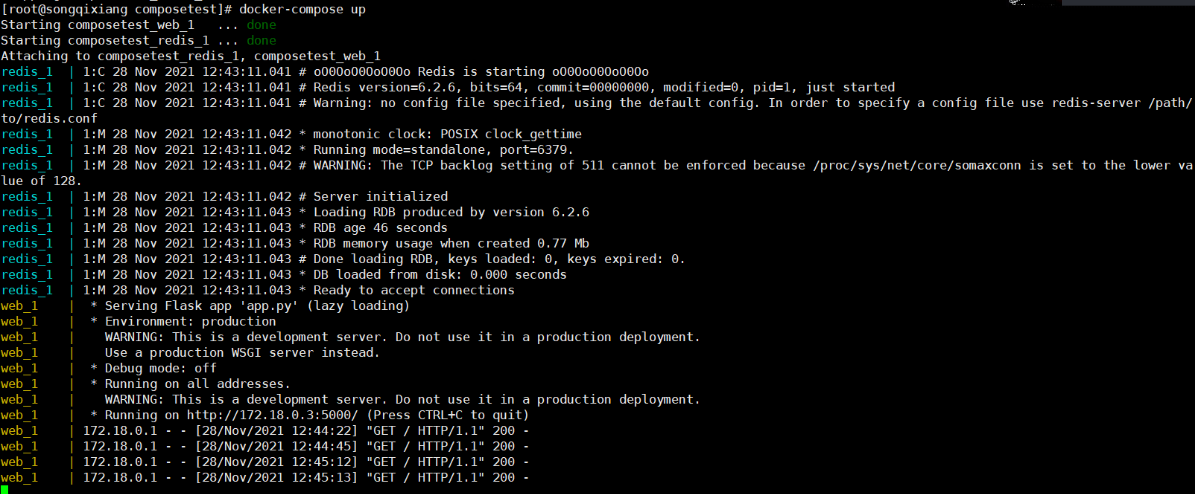
test result
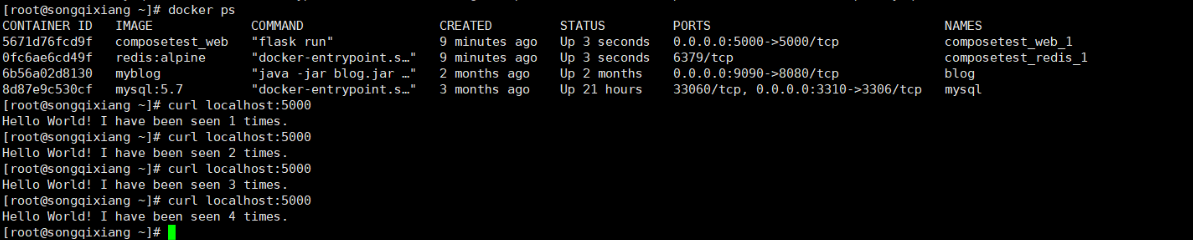
hh, it's really comfortable to start two applications with one click!
4. Docker Compose default configuration
1. Automatically download the image in the configuration file docker-compose.yml
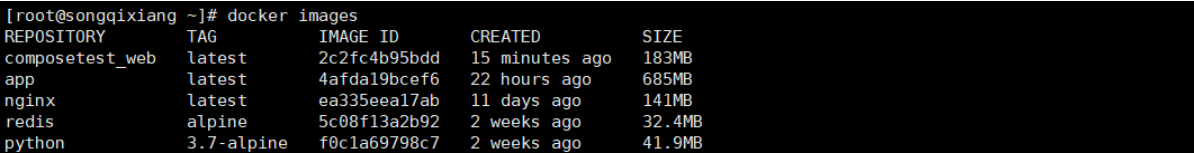
2. Automatically generate service name and file name_ Service name_ num
Starting composetest_web_1 ... done #web Services Starting composetest_redis_1 ... done #redis service
3. Network rules
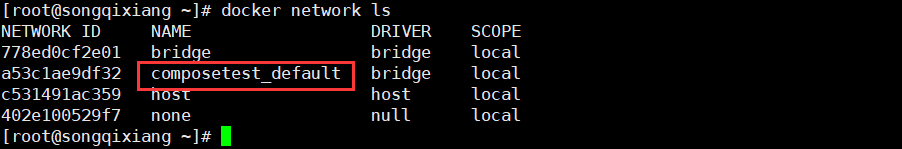
By default, a network will be generated, with 10 services = > networks (the contents of the project are all under the same network and can be accessed by container name)
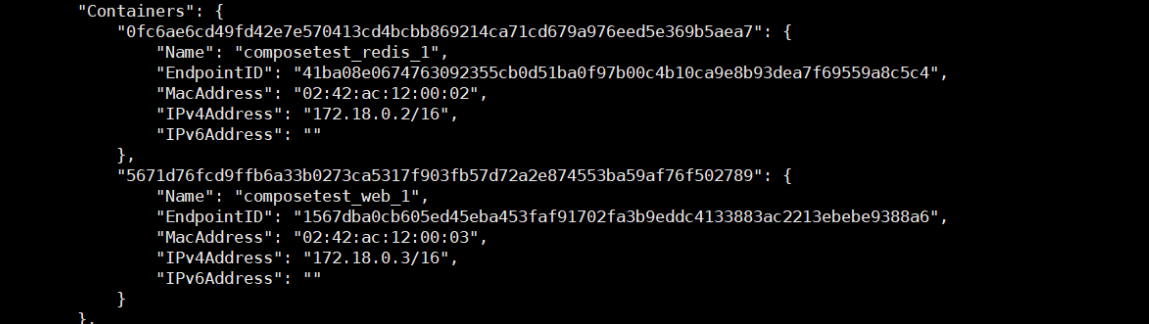
In the same network, it can be accessed directly through the container name (domain name)
4. Stop
- Docker compose down: it needs to be executed in the yaml configuration file directory of compose, otherwise it cannot be found!
- ctrl + c
Section
1. Docker image, run = = > container
2. Dockerfile build image (service packaging)
3. Docker compose startup project (orchestration, multiple microservices / environments)
4. Docker network!
5. The project needs to be updated. docker compose up --build is enough
5. Compose write configuration rules
Reference documents: https://docs.docker.com/compose/compose-file/compose-file-v3/
Core: write docker-compose.yaml
#3rd floor version: '' #edition services: #service Service 1: web #Configuration of service docker container images: build: network: depends_on: #depents_on: web services depend on redis and mysql. Let them start first! (this is the reason for the arrangement) -redis -mysql Service 2: redis ... Service 2: mysql ... #Other configuration network / volume, global rules volumes: network: configs:
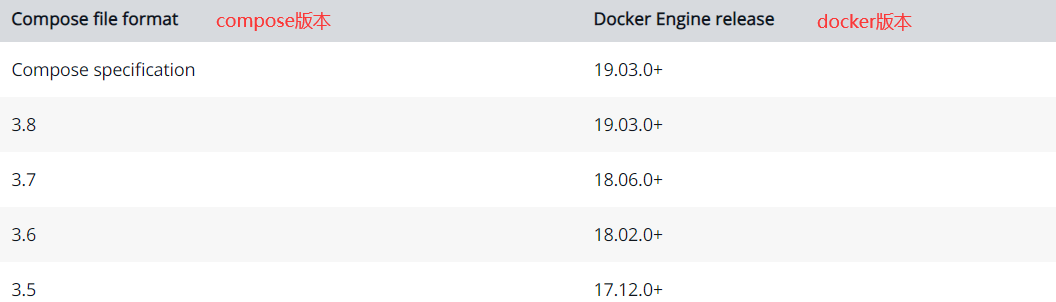
1. Version selection
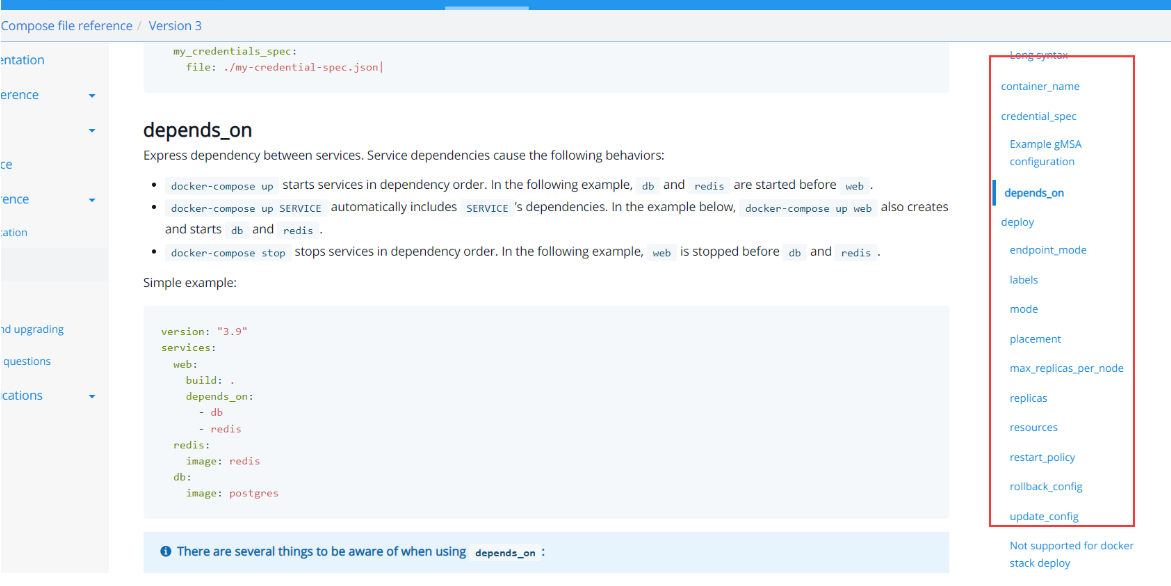
2. Service related configuration
6. Compose one click deployment WP blog
Reference documents: https://docs.docker.com/samples/wordpress/
1. Create directory and enter directory
mkdir my_wordpress/ cd my_wordpress/
2. Write docker-compose.yml
version: "3.9"
services:
db:
image: mysql:5.7
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: somewordpress
MYSQL_DATABASE: wordpress
MYSQL_USER: wordpress
MYSQL_PASSWORD: wordpress
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
image: wordpress:latest
volumes:
- wordpress_data:/var/www/html
ports:
- "8000:80"
restart: always
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: wordpress
volumes:
db_data: {}
wordpress_data: {}
3. Port 8000 of our server is released
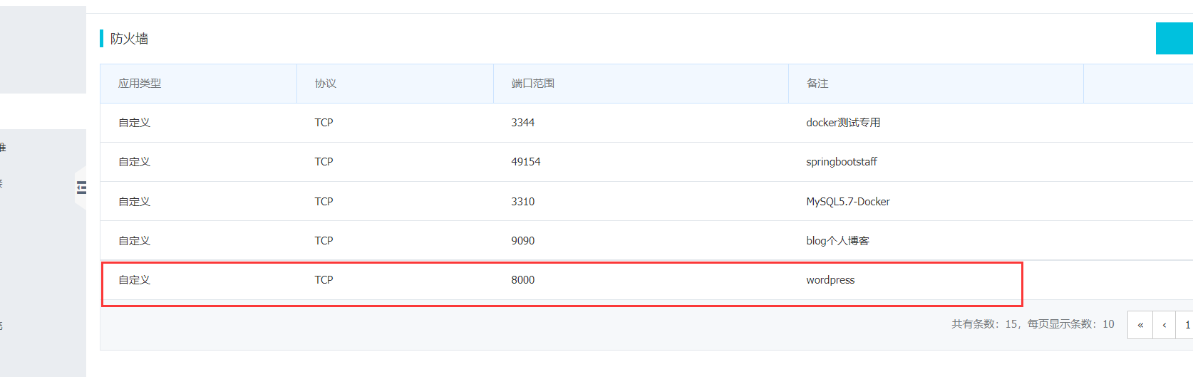
4. Start Compose
docker-compose up -d

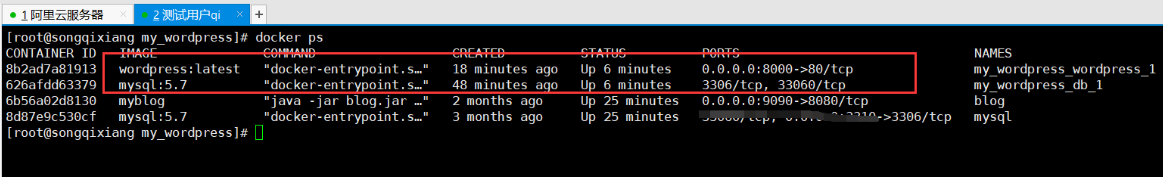
5. Detect whether the container is started
docker ps
6. Access test: http://qxsong.top:8000/ (own ip+8000 port)
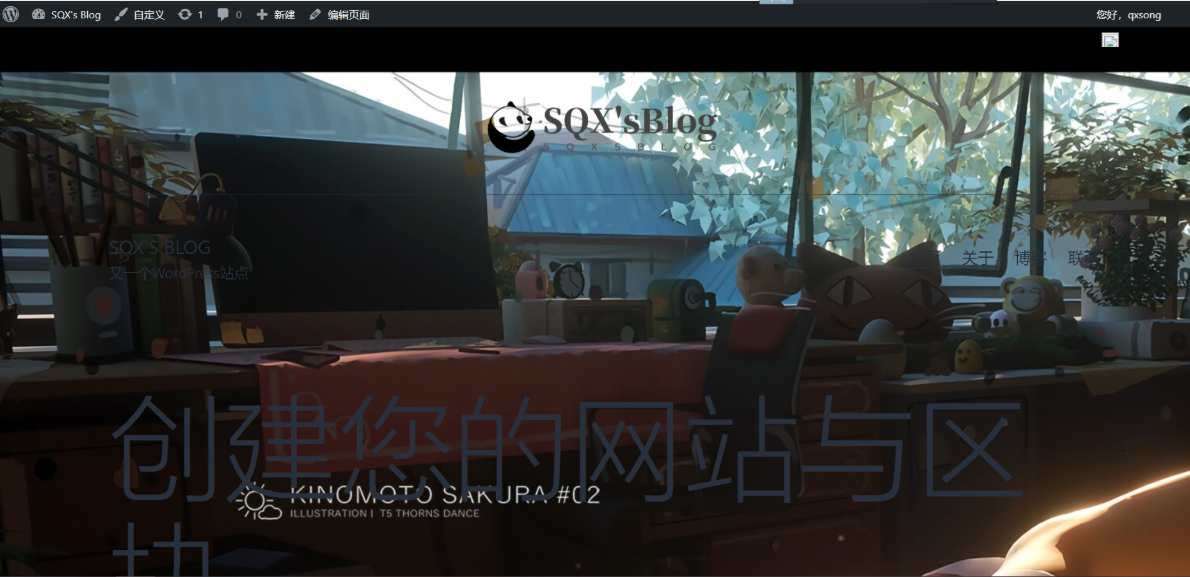
End of work!!!