Master-slave database
Install docker
Please refer to my other article:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46435741/article/details/121502952
Create a new instance of the main mysql container
Create a container with mysql version 5.7.
Mount data volume:
Mount the configuration file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL master / conf
Mount the log file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL master / log
Mount the data file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL master / data
External port 3307 is mapped to container port 3306
docker run -p 3307:3306 --name mysql-master \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/log:/var/log/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/data:/var/lib/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-master/conf:/etc/mysql \ -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \ -d mysql:5.7
Modify the main mysql configuration file
Enter the configuration directory
cd /mydata/mysql-master/conf
Create and edit a profile
vim my.cnf
Copy the following code into the configuration file
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, which needs to be unique in the same LAN server_id=101 ## Specify the name of the database that does not need to be synchronized binlog-ignore-db=mysql ## Enable binary log function log-bin=mall-mysql-bin ## Set the memory size used by binary log (transaction) binlog_cache_size=1M ## Set the binary log format used (mixed,statement,row) binlog_format=mixed ## Binary log expiration cleanup time. The default value is 0, which means no automatic cleaning. expire_logs_days=7 ## Skip all errors encountered in master-slave replication or specified types of errors to avoid the interruption of slave side replication. ## For example, the 1062 error refers to the duplication of some primary keys, and the 1032 error is due to the inconsistency of data between the master and slave databases slave_skip_errors=1062
After esc, type: wq save
Restart container instance
docker restart mysql-master
Enter the container instance operation main mysql
docker exec -it mysql-master /bin/bash
Enter MySQL operation interface
mysql -uroot -proot
Create a data synchronization user in the main container
create user 'slave'@'%' identified by '123456'
grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to 'slave'@'%'
Create a new instance from mysql container
Create a container with mysql version 5.7.
Mount data volume:
Mount the configuration file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL slave / conf
Mount the log file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL slave / log
Mount the data file to the host Directory: / mydata / MySQL slave / data
External port 3308 is mapped to container port 3306
docker run -p 3308:3306 --name mysql-slave \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/log:/var/log/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/data:/var/lib/mysql \ -v /mydata/mysql-slave/conf:/etc/mysql \ -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root \ -d mysql:5.7
Modify from mysql configuration file
Enter the configuration directory
cd /mydata/mysql-slave/conf
Create and edit a profile
vim my.cnf
Copy the following code into the configuration file
[mysqld] ## Set up server_id, which needs to be unique in the same LAN server_id=102 ## Specify the name of the database that does not need to be synchronized binlog-ignore-db=mysql ## Enable the binary log function for use when Slave is the Master of other database instances log-bin=mall-mysql-slave1-bin ## Set the memory size used by binary log (transaction) binlog_cache_size=1M ## Set the binary log format used (mixed,statement,row) binlog_format=mixed ## Binary log expiration cleanup time. The default value is 0, which means no automatic cleaning. expire_logs_days=7 ## Skip all errors encountered in master-slave replication or specified types of errors to avoid the interruption of slave side replication. ## For example, the 1062 error refers to the duplication of some primary keys, and the 1032 error is due to the inconsistency of data between the master and slave databases slave_skip_errors=1062 ## relay_log configure relay log relay_log=mall-mysql-relay-bin ## log_slave_updates indicates that the slave writes the replication event to its binary log log_slave_updates=1 ## slave is set to read-only (except for users with super permission) read_only=1
After esc, type: wq save
Restart the instance from mysql container
docker restart mysql-slave
Enter from container instance
docker exec -it mysql-slave /bin/bash
Enter MySQL console
mysql -uroot -proot
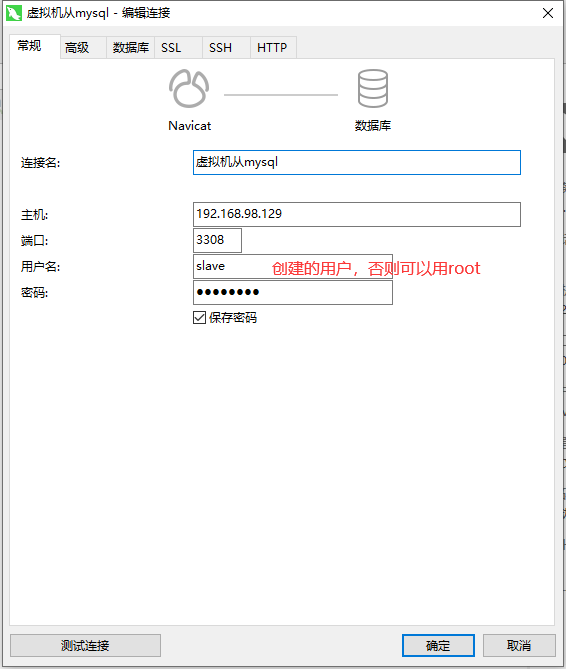
View master-slave synchronization status
show slave status \G;
Synchronization did not start
Detailed parameter description
master_host: the IP address of the main database;
master_port: the running port of the master database;
master_user: the user account created in the master database for data synchronization;
master_password: the user password created in the master database for synchronizing data;
master_log_file: Specifies the log file to copy data from the database, and obtains the file parameter by viewing the status of the master data;
master_log_pos: specify where to copy data from the database, and obtain the Position parameter by viewing the status of the master data;
master_connect_retry: the time interval between connection failures and retries, in seconds.
Configure master-slave replication basic information
change master to master_host='Host computer ip', master_user='slave', master_password='123456', master_port=3307, master_log_file='mall-mysql-bin.000001', master_log_pos=617, master_connect_retry=30;
(if it is a virtual machine, you can fill in the ip of the virtual machine. Mine is 192.168.98.129. If it is a virtual machine, it is the ip of the virtual machine)
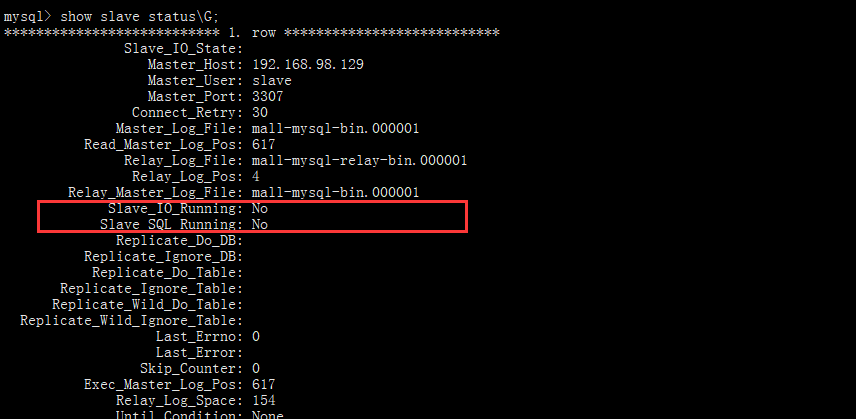
Enable master-slave synchronization
show slave status \G;
Check the master-slave synchronization status again
show slave status \G;
Synchronization has started
Master-slave test
Create a new database in the master database - > use a database - > create a new table - > insert data
To and from the database
Enter container - > call out from database console - > use library - > view records
If data synchronization is found, the master-slave configuration is successful!!
Create a new read-only role for the slave database (can be saved)
According to the project requirements, there may be two master-slave databases, one is responsible for reading and the other is responsible for writing. Of course, the master database must perform writing operations and reading can also be performed, while the slave database can only perform reading operations and cannot write. Once the write operation is performed by root, the data consistency of the master-slave database will be damaged
So we create a new user from the database
Enter from database
docker exec -it mysql-slave /bin/bash
Open mysql console
mysql -uroot -proot
Create a user slave with a password of 123456 (change according to actual needs):
create user 'slave'@'%' identified by '123456';
Only grant the slave user select permission:
grant select on *.* to 'slave'@'%';
Refresh database:
flush privileges;
Check whether the user is created successfully:
select host,user from mysql.user;
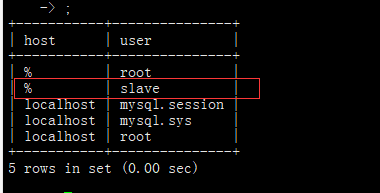
Connecting master-slave database with navicat
Master database:
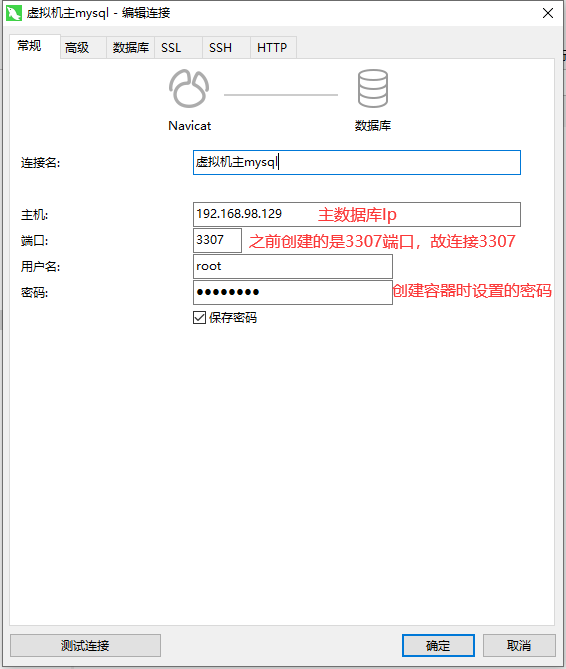
From database:
If you have created a read-only user, I suggest you connect directly with this user to avoid inconsistency between master and slave.
If you are only used for testing and viewing, you can also log in as root user. Please be careful not to modify the data from the database