Docker's Learning Notes
1. Overview of Docker
Virtual Machine Data Model:
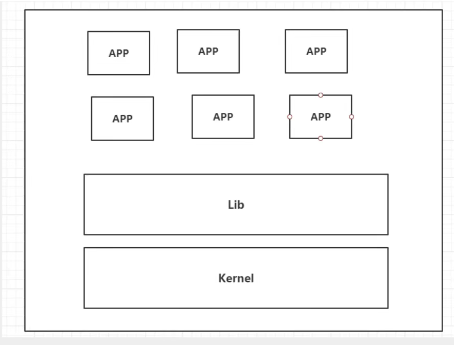
VM Data Disadvantages:
- High resource usage
- Too many redundant steps
- Start very slowly
Containerized technology model:
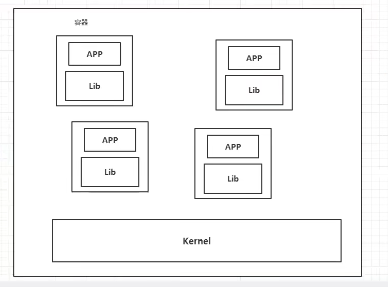
Compare Docker with virtual machine technology:
- Traditional virtual machines virtualize a piece of hardware, run a complete operating system, and then install and run software on this system.
- Applications inside containers run directly on the host's content. Containers are lightweight without their own cores or virtual hardware.
- Each container is isolated from each other, and each container has its own file system, which does not affect each other.
Docker's advantages:
- Apply faster delivery and deployment
- Tradition: a bunch of help documents, Installers
- Docker: Package the mirror publish test, run at one click
- Easier upgrade and expansion
- After using Docker, our deployment applications are just like building blocks, system upgrades require only one click to upgrade the image and the project is packaged into one image, and server extensions can be accomplished directly by running the image on new servers (larger, better-performing new servers).
- Simpler System Operations
- After containerization, our system development and test environments are highly consistent.
- More efficient use of computing resources
- Docker is kernel-level virtualization that can run many container instances on a single physical machine, and server performance can be squeezed to the extreme
Docker's schematic diagram:
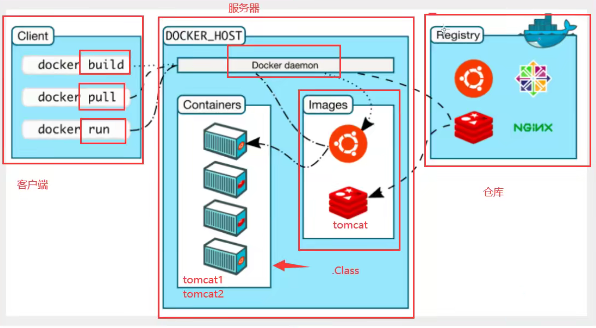
Docker related terms introduction:
- Image: A Docker image is like a template through which a container service can be created, a Tomcat image --> run --> tomcat01 container (which provides services), through which multiple containers can be created (where the final service runs or the project runs).
- Container: Docker uses container technology to run one or more application groups independently, created by mirroring. At present, this container can be understood as a simple Linux system.
- repository: Warehouses are places where mirrors are stored. They are divided into public warehouses and private warehouses. Our Docker warehouses are foreign by default and need to be changed to Ali Cloud's (with mirroring acceleration) or the download of mirrors will be particularly slow.
2. Docker Installation
1. Environmental preparation
- Need a little bit of Linux Basics
- CentOS 7
- We use Xshell to connect to remote servers for operation
2. Environment Viewing
# The system core is more than 3.10 [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# uname -r 3.10.0-514.26.2.el7.x86_64 # Version of the system [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
3. Uninstall the old Docker version
Install Docker Official Documentation on Linux
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# yum remove docker \ > docker-client \ > docker-client-latest \ > docker-common \ > docker-latest \ > docker-latest-logrotate \ > docker-logrotate \ > docker-engine Loaded plugins: fastestmirror No Match for argument: docker No Match for argument: docker-client No Match for argument: docker-client-latest No Match for argument: docker-common No Match for argument: docker-latest No Match for argument: docker-latest-logrotate No Match for argument: docker-logrotate No Match for argument: docker-engine No Packages marked for removal
4. Installation packages required (online installation)
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# yum install -y yum-utils Loaded plugins: fastestmirror base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00 epel | 4.7 kB 00:00:00 extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 (1/4): epel/x86_64/updateinfo | 1.0 MB 00:00:00 (2/4): updates/7/x86_64/primary_db | 13 MB 00:00:00 (3/4): docker-ce-stable/7/x86_64/primary_db | 70 kB 00:00:00 (4/4): epel/x86_64/primary_db | 7.0 MB 00:00:00 Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Package yum-utils-1.1.31-54.el7_8.noarch already installed and latest version Nothing to do
5. Set up mirror warehouse (default is foreign, change to domestic Aliyun)
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# yum-config-manager \ > --add-repo \ > http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo Loaded plugins: fastestmirror adding repo from: http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo grabbing file http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo to /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo repo saved to /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo
6. Update package index
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# yum makecache fast Loaded plugins: fastestmirror base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 docker-ce-stable | 3.5 kB 00:00:00 epel | 4.7 kB 00:00:00 extras | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 updates | 2.9 kB 00:00:00 Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Metadata Cache Created
7. Install the latest Docker engine
# docker-ce community ee Enterprise Edition yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
8. Start Docker and see if the installation was successful
# Start Docker [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# systemctl start docker # Check to see if the installation was successful [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker version Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 20.10.12 API version: 1.41 Go version: go1.16.12 Git commit: e91ed57 Built: Mon Dec 13 11:45:41 2021 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Context: default Experimental: true Server: Docker Engine - Community Engine: Version: 20.10.12 API version: 1.41 (minimum version 1.12) Go version: go1.16.12 Git commit: 459d0df Built: Mon Dec 13 11:44:05 2021 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false containerd: Version: 1.4.12 GitCommit: 7b11cfaabd73bb80907dd23182b9347b4245eb5d runc: Version: 1.0.2 GitCommit: v1.0.2-0-g52b36a2 docker-init: Version: 0.19.0 GitCommit: de40ad0
9. Test Run hello-world Mirror
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run hello-world
10. View the hello-world mirror
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB
Understanding: Uninstall docker
# 1. Uninstall dependency yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # 2. Delete resources (/var/lib/docker docker's default working path) rm -rf /var/lib/docker
Configure Ali Cloud Mirror Acceleration
- Log on to Aliyun account and click on Container Mirror Service
2. Find and configure mirroring acceleration addresses
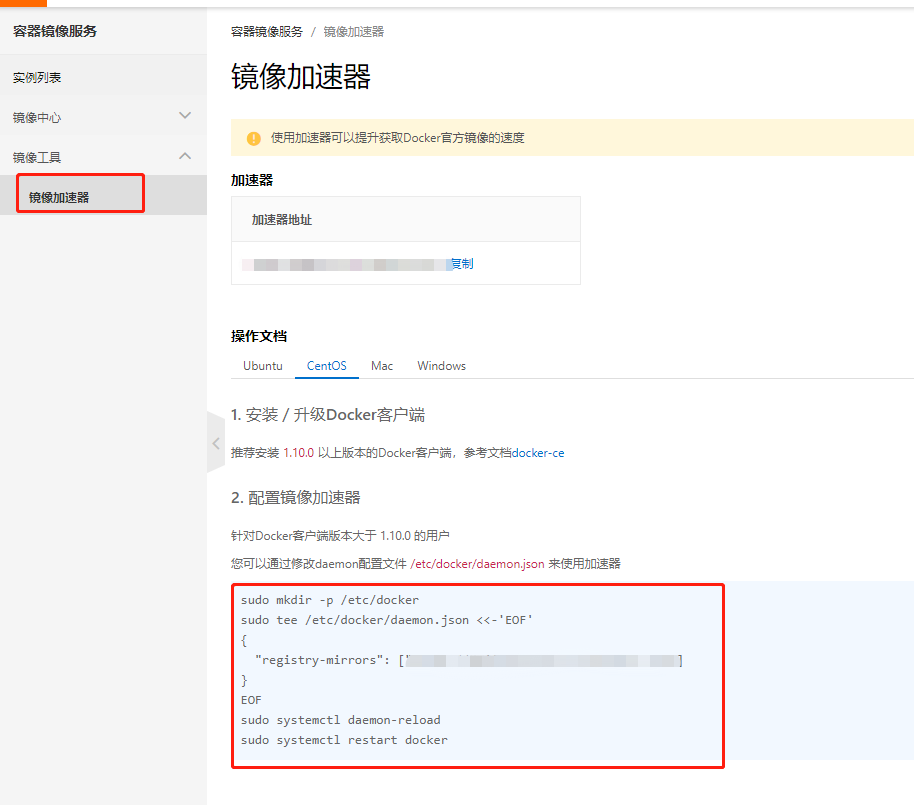
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
> {
> "registry-mirrors": ["Your own address"]
> }
> EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["Your own address"]
}
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# sudo systemctl daemon-reload
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# sudo systemctl restart docker
Flow diagram for running hello-world mirror
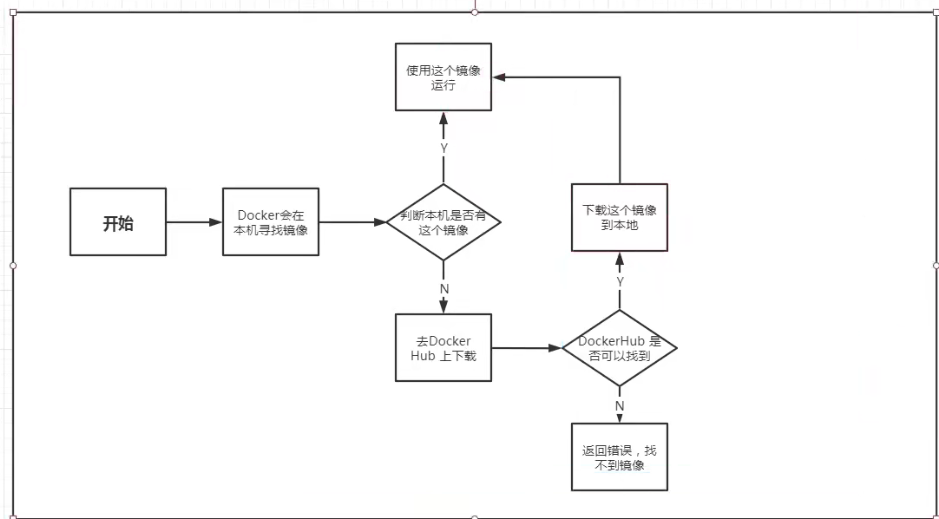
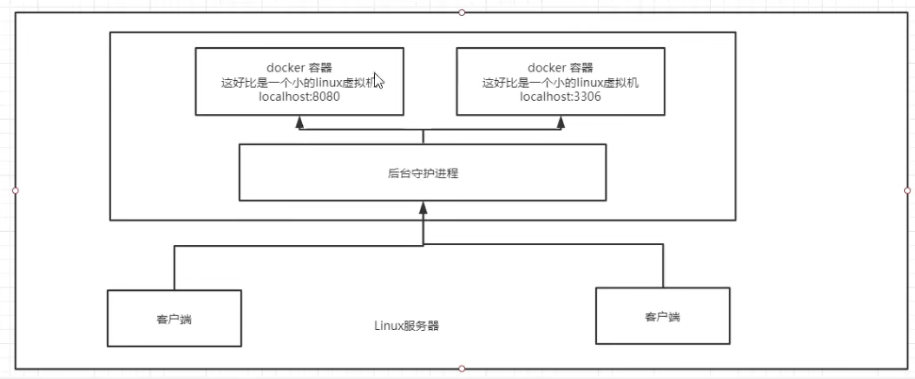
How does Docker work?
- Docker is a Client-Server structured system whose daemon runs on the host and is accessed from the client through a Socket.
- DockerServer receives instructions from Docker-Client and executes them.
Why is Docker faster than a virtual machine? - Docker has fewer abstraction layers than virtual machines.
- Docker takes advantage of the host's kernel, and virtual machines require Guest OS.
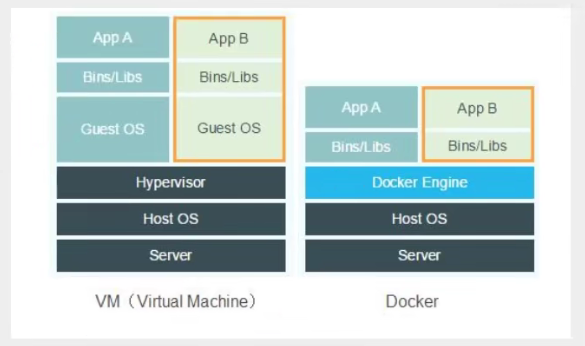
So when you create a new container, Docker doesn't need to reload an operating system kernel like a virtual machine to avoid booting. A virtual machine loads Guest OS at the minute level, while a Docker uses the host's operating system to omit this complex process, in seconds!
3. Docker Order
1. Help commands
docker version # Display docker version information docker info # Displays docker system information, including mirror and container information docker --help # Help Command
Docker Command Official Document
2. Mirror commands
docker images view mirrors on all local hosts
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB # explain REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source TAG Mirror Label IMAGE ID mirrored id CREATED Creation time of mirror SIZE The size of the mirror # Optional --all , -a # List all mirrors --quiet , -q # Show only the id of the mirror [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images -a REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images -q feb5d9fea6a5 5d0da3dc9764
docker search Search Search mirror
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker search mysql NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11803 [OK] mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4492 [OK] mysql/mysql-server Optimized MySQL Server Docker images. Create... 885 [OK] # Optional, filter by search --filter=STARS=3000 # Searched mirror is STARS greater than 3000 [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker search mysql --filter=STARS=3000 NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11803 [OK] mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4492 [OK]
docker pull download mirror
# Download Mirror (Download the latest by default) [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest # If no tag is written, the default is latest latest: Pulling from library/mysql ffbb094f4f9e: Pull complete # Hierarchical download, core of docker image, federated file system df186527fc46: Pull complete fa362a6aa7bd: Pull complete 5af7cb1a200e: Pull complete 949da226cc6d: Pull complete bce007079ee9: Pull complete eab9f076e5a3: Pull complete 8a57a7529e8d: Pull complete b1ccc6ed6fc7: Pull complete b4af75e64169: Pull complete 3aed6a9cd681: Pull complete 23390142f76f: Pull complete Digest: sha256:ff9a288d1ecf4397967989b5d1ec269f7d9042a46fc8bc2c3ae35458c1a26727 # autograph Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest # Real Address docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Equivalent to it docker pull mysql docker pull docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Specified version download [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker pull mysql:5.7 5.7: Pulling from library/mysql ffbb094f4f9e: Already exists df186527fc46: Already exists fa362a6aa7bd: Already exists 5af7cb1a200e: Already exists 949da226cc6d: Already exists bce007079ee9: Already exists eab9f076e5a3: Already exists c7b24c3f27af: Pull complete 6fc26ff6705a: Pull complete bec5cdb5e7f7: Pull complete 6c1cb25f7525: Pull complete Digest: sha256:d1cc87a3bd5dc07defc837bc9084f748a130606ff41923f46dec1986e0dc828d Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.7 docker.io/library/mysql:5.7
docker rmi delete mirror
docker rmi -f container id # Delete the specified image [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE mysql 5.7 738e7101490b 12 days ago 448MB mysql latest bbf6571db497 12 days ago 516MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker rmi -f 738e7101490b Untagged: mysql:5.7 Untagged: mysql@sha256:d1cc87a3bd5dc07defc837bc9084f748a130606ff41923f46dec1986e0dc828d Deleted: sha256:738e7101490b45decf606211a5437ed87aa6a82f1ff03c354564bf9375ce20f9 Deleted: sha256:addad8cfeac97b96eb6652a576269346ac96def9a6709ed2388e24fff4345837 Deleted: sha256:e288c3439a7e2f423f50bf22979a759371c51a70bbbaa450993c336978460b1a Deleted: sha256:33ece15accaa3bb20e3dee84e2e4501469b917c3abba3d5475cd1fec8bb3e82c Deleted: sha256:6b15390bceeca8424d82e75f5c9aca5eb4693f96849d6382168a99747877693d [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE mysql latest bbf6571db497 12 days ago 516MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB docker rmi -f container id container id container id # Delete Multiple Mirrors docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) # Remove all mirrors
3. Container commands
Note: We have mirrors to create containers, Linux, download a centos image to test learning
docker pull centos
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker pull centos Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/centos Digest: sha256:a27fd8080b517143cbbbab9dfb7c8571c40d67d534bbdee55bd6c473f432b177 Status: Image is up to date for centos:latest docker.io/library/centos:latest
New Container and Start
docker run [Optional parameters] image # Parameter Description --name="Name" Container name tomcat01 tomcat02 Used to distinguish containers -d Background operation mode -it Run interactively for container viewing -P Specify the port of the container -P 8080:8080 -P ip:Host Port: Container Port -P Host Port: Container Port (Common) -P Container Port -p Randomly specified port # Test, start and enter container [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@7873af79c113 /]# ls # Looking at centos inside the container, the base version, many commands are imperfect bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var # Exit from container to host [root@cd742af46c77 /]# exit exit [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# ls bin boot data dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
List all running containers
# docker ps command # List all running containers -a # List currently running containers + bring out historically run containers -n=? # Show recently created containers -q # Display container number only [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES cd742af46c77 centos "/bin/bash" 49 minutes ago Exited (0) 49 minutes ago zealous_murdock 7873af79c113 centos "/bin/bash" 53 minutes ago Exited (130) 49 minutes ago stoic_hellman 0448aa7b6032 hello-world "/hello" 6 hours ago Exited (0) 6 hours ago amazing_hellman cf34bafc4f4b centos "/bin/bash" 20 hours ago Exited (0) 20 hours ago vigilant_moser b233ad3d909d centos "/bin/bash" 43 hours ago Exited (0) 43 hours ago quizzical_ishizaka 9abf86b62b40 hello-world "/hello" 2 days ago Exited (0) 2 days ago ecstatic_jackson [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps -a -n=1 CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES cd742af46c77 centos "/bin/bash" 49 minutes ago Exited (0) 49 minutes ago zealous_murdock [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps -aq cd742af46c77 7873af79c113 0448aa7b6032 cf34bafc4f4b b233ad3d909d 9abf86b62b40
Exit Container
exit # Direct container stops and exits Ctrl + P + Q # Container does not stop exiting [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@907a070a9091 /]# # Ctrl + P + Q [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 907a070a9091 centos "/bin/bash" 41 seconds ago Up 40 seconds adoring_cerf
Delete Container
docker rm container id # Delete the specified container, not the running container, if you want to force the deletion of rm-f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) # Delete all containers docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm # Delete all containers
Start and stop container operations
docker start container id # Start Container docker restart container id # Restart Container docker stop container id # Stop the currently running container docker kill container id # Force stop of current container
Background startup container
# Command docker run-d mirror name [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker run -d centos 304a9798adeb9f85e9856063fd3b87179f57e4ef7eaf75a86d8592671d9cbc3a [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES # Problem docker ps found centos stopped # Common pits, docker containers run in the background, there must be a foreground process, docker found no application, will automatically stop # nginx, when the container starts up and finds itself not servicing, it stops immediately, or there is no program
view log
docker logs -f -t --tail Container, no log # Write a shell script yourself [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo UZI;sleep 1;done" [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 7c7180a2de02 centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds angry_lewin # Show Log -tf #Show Log --tail number #To display the number of log entries [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 7c7180a2de02 centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds angry_lewin [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 7c7180a2de02 2021-12-15T11:46:29.318643184Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:30.320057098Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:31.321457226Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:32.322890799Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:33.324313728Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:34.325861478Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:35.327300274Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:36.328808505Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:37.330254542Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:38.331815325Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:39.333342324Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:40.334873853Z UZI 2021-12-15T11:46:41.336293624Z UZI
View process information in container
# Command docker top container id [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 7c7180a2de02 centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 7 minutes ago Up 7 minutes angry_lewin [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker top 7c7180a2de02 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY root 2651 2613 0 19:42 ? root 3889 2651 0 19:50 ?
View mirrored metadata
# command
docker inspect container id
# test
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker inspect 7c7180a2de02
[
{
"Id": "7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb",
"Created": "2021-12-15T11:42:24.764104676Z",
"Path": "/bin/sh",
"Args": [
"-c",
"while true;do echo UZI;sleep 1;done"
],
"State": {
"Status": "running",
"Running": true,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 2651,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2021-12-15T11:42:24.957721927Z",
"FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
},
"Image": "sha256:5d0da3dc976460b72c77d94c8a1ad043720b0416bfc16c52c45d4847e53fadb6",
"ResolvConfPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb/resolv.conf",
"HostnamePath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb/hostname",
"HostsPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb/hosts",
"LogPath": "/var/lib/docker/containers/7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb/7c7180a2de024dce9acda6708d1187a0075ebb838fbfa65e7693385758a83dbb-json.log",
"Name": "/angry_lewin",
"RestartCount": 0,
"Driver": "overlay2",
"Platform": "linux",
"MountLabel": "",
"ProcessLabel": "",
"AppArmorProfile": "",
"ExecIDs": null,
"HostConfig": {
"Binds": null,
"ContainerIDFile": "",
"LogConfig": {
"Type": "json-file",
"Config": {}
},
"NetworkMode": "default",
"PortBindings": {},
"RestartPolicy": {
"Name": "no",
"MaximumRetryCount": 0
},
"AutoRemove": false,
"VolumeDriver": "",
"VolumesFrom": null,
"CapAdd": null,
"CapDrop": null,
"CgroupnsMode": "host",
"Dns": [],
"DnsOptions": [],
"DnsSearch": [],
"ExtraHosts": null,
"GroupAdd": null,
"IpcMode": "private",
"Cgroup": "",
"Links": null,
"OomScoreAdj": 0,
"PidMode": "",
"Privileged": false,
"PublishAllPorts": false,
"ReadonlyRootfs": false,
"SecurityOpt": null,
"UTSMode": "",
"UsernsMode": "",
"ShmSize": 67108864,
"Runtime": "runc",
"ConsoleSize": [
0,
0
],
"Isolation": "",
"CpuShares": 0,
"Memory": 0,
"NanoCpus": 0,
"CgroupParent": "",
"BlkioWeight": 0,
"BlkioWeightDevice": [],
"BlkioDeviceReadBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteBps": null,
"BlkioDeviceReadIOps": null,
"BlkioDeviceWriteIOps": null,
"CpuPeriod": 0,
"CpuQuota": 0,
"CpuRealtimePeriod": 0,
"CpuRealtimeRuntime": 0,
"CpusetCpus": "",
"CpusetMems": "",
"Devices": [],
"DeviceCgroupRules": null,
"DeviceRequests": null,
"KernelMemory": 0,
"KernelMemoryTCP": 0,
"MemoryReservation": 0,
"MemorySwap": 0,
"MemorySwappiness": null,
"OomKillDisable": false,
"PidsLimit": null,
"Ulimits": null,
"CpuCount": 0,
"CpuPercent": 0,
"IOMaximumIOps": 0,
"IOMaximumBandwidth": 0,
"MaskedPaths": [
"/proc/asound",
"/proc/acpi",
"/proc/kcore",
"/proc/keys",
"/proc/latency_stats",
"/proc/timer_list",
"/proc/timer_stats",
"/proc/sched_debug",
"/proc/scsi",
"/sys/firmware"
],
"ReadonlyPaths": [
"/proc/bus",
"/proc/fs",
"/proc/irq",
"/proc/sys",
"/proc/sysrq-trigger"
]
},
"GraphDriver": {
"Data": {
"LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/508aaa276b048c3a0fb4dd8a2d022ba19c6a19dc8a680b5e0a84d6d5139fd6df-init/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/6bb58fdacfa3f03bd88b1169e1f421f7df2e22c8171994f474c17b3f4556cc48/diff",
"MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/508aaa276b048c3a0fb4dd8a2d022ba19c6a19dc8a680b5e0a84d6d5139fd6df/merged",
"UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/508aaa276b048c3a0fb4dd8a2d022ba19c6a19dc8a680b5e0a84d6d5139fd6df/diff",
"WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/508aaa276b048c3a0fb4dd8a2d022ba19c6a19dc8a680b5e0a84d6d5139fd6df/work"
},
"Name": "overlay2"
},
"Mounts": [],
"Config": {
"Hostname": "7c7180a2de02",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": false,
"AttachStderr": false,
"Tty": false,
"OpenStdin": false,
"StdinOnce": false,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin"
],
"Cmd": [
"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"while true;do echo UZI;sleep 1;done"
],
"Image": "centos",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": null,
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": {
"org.label-schema.build-date": "20210915",
"org.label-schema.license": "GPLv2",
"org.label-schema.name": "CentOS Base Image",
"org.label-schema.schema-version": "1.0",
"org.label-schema.vendor": "CentOS"
}
},
"NetworkSettings": {
"Bridge": "",
"SandboxID": "fbfa2f75182781284716c31d52d8fff0bb735d138716974ea281aaf3f2d27e75",
"HairpinMode": false,
"LinkLocalIPv6Address": "",
"LinkLocalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"Ports": {},
"SandboxKey": "/var/run/docker/netns/fbfa2f751827",
"SecondaryIPAddresses": null,
"SecondaryIPv6Addresses": null,
"EndpointID": "f6ee96c8e9055a747198d3907263c98aa8681496cfc933e9a261caf47cc63c61",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "f43965cd248966c0dee0abdfc2595284feb0f522cd2df0c0245c45f34a17bc09",
"EndpointID": "f6ee96c8e9055a747198d3907263c98aa8681496cfc933e9a261caf47cc63c61",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
}
]
Enter the currently running container
# Usually we have containers running in the background and need to go into them and modify some configuration # command docker exec -it # test [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker exec -it 7c7180a2de02 /bin/bash [root@7c7180a2de02 /]# ls bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var [root@7c7180a2de02 /]# ps -ef UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 1 0 0 11:42 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c while true;do echo UZI;sleep 1;done root 1153 0 0 12:01 pts/0 00:00:00 /bin/bash root 1195 1 0 12:01 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/coreutils --coreutils-prog-shebang=sleep /usr/bin/sleep 1 root 1196 1153 0 12:01 pts/0 00:00:00 ps -ef # Mode 2 docker attach container id # test [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker attach 7c7180a2de02 Executing current code (non-stop printing) UZI) # docker exec # Open a new terminal after entering the container to operate inside (commonly used) # docker attach # Enter the terminal that the container is executing and will not start a new process
Copy files from container to host
docker cp container id: Host path for in-container path purpose [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 0bf351fa76f2 centos "/bin/bash" About a minute ago Up About a minute elated_sammet f1b9afbe52ee centos "/bin/bash" 7 minutes ago Up 7 minutes dreamy_hermann [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker attach 0bf351fa76f2 [root@0bf351fa76f2 /]# cd /home [root@0bf351fa76f2 home]# ls [root@0bf351fa76f2 home]# touch test.java [root@0bf351fa76f2 home]# ls test.java [root@0bf351fa76f2 home]# exit exit [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker cp 0bf351fa76f2:/home/test.java /home [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# ls admin staragent test.java UZI.java www # Copying is a manual process. In the future, we will use the technology of -v volume to achieve automatic synchronization.
IV. Deployment of Nginx
- Search Mirror Search recommends you go to docker to search for help documents
Docker Search Nginx
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker search nginx NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED nginx Official build of Nginx. 15928 [OK] jwilder/nginx-proxy Automated Nginx reverse proxy for docker con... 2101 [OK] richarvey/nginx-php-fpm Container running Nginx + PHP-FPM capable of... 820 [OK] jc21/nginx-proxy-manager Docker container for managing Nginx proxy ho... 288 linuxserver/nginx An Nginx container, brought to you by LinuxS... 160 tiangolo/nginx-rtmp Docker image with Nginx using the nginx-rtmp... 147 [OK] jlesage/nginx-proxy-manager Docker container for Nginx Proxy Manager 145 [OK] alfg/nginx-rtmp NGINX, nginx-rtmp-module and FFmpeg from sou... 111 [OK] nginxdemos/hello NGINX webserver that serves a simple page co... 79 [OK] privatebin/nginx-fpm-alpine PrivateBin running on an Nginx, php-fpm & Al... 61 [OK] nginx/nginx-ingress NGINX and NGINX Plus Ingress Controllers fo... 57 nginxinc/nginx-unprivileged Unprivileged NGINX Dockerfiles 55 nginxproxy/nginx-proxy Automated Nginx reverse proxy for docker con... 29 staticfloat/nginx-certbot Opinionated setup for automatic TLS certs lo... 25 [OK] nginx/nginx-prometheus-exporter NGINX Prometheus Exporter for NGINX and NGIN... 22 schmunk42/nginx-redirect A very simple container to redirect HTTP tra... 19 [OK] centos/nginx-112-centos7 Platform for running nginx 1.12 or building ... 16 centos/nginx-18-centos7 Platform for running nginx 1.8 or building n... 13 bitwarden/nginx The Bitwarden nginx web server acting as a r... 11 flashspys/nginx-static Super Lightweight Nginx Image 11 [OK] mailu/nginx Mailu nginx frontend 9 [OK] sophos/nginx-vts-exporter Simple server that scrapes Nginx vts stats a... 7 [OK] ansibleplaybookbundle/nginx-apb An APB to deploy NGINX 3 [OK] wodby/nginx Generic nginx 1 [OK] arnau/nginx-gate Docker image with Nginx with Lua enabled on ... 1 [OK]
- Download mirror pull
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker pull nginx Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/nginx e5ae68f74026: Pull complete 21e0df283cd6: Pull complete ed835de16acd: Pull complete 881ff011f1c9: Pull complete 77700c52c969: Pull complete 44be98c0fab6: Pull complete Digest: sha256:9522864dd661dcadfd9958f9e0de192a1fdda2c162a35668ab6ac42b465f0603 Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest docker.io/library/nginx:latest [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE mysql latest bbf6571db497 13 days ago 516MB nginx latest f652ca386ed1 13 days ago 141MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB
- Run tests
# -d Background Run
# --name Name the container
# -p host port, container internal port
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker run -d --name nginx01 -p 3344:80 nginx
b1f9ba923daab45bed2beee6f4ae59611aa006e14b19ff20dabaadc12c5816e4
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b1f9ba923daa nginx "/docker-entrypoint...." 5 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:3344->80/tcp nginx01
f1b9afbe52ee centos "/bin/bash" 27 minutes ago Up 27 minutes dreamy_hermann
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# curl localhost:3344
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
# Enter Container
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker exec -it nginx01 /bin/bash
root@b1f9ba923daa:/# whereis nginx
nginx: /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/lib/nginx /etc/nginx /usr/share/nginx
root@b1f9ba923daa:/# cd /etc/nginx
root@b1f9ba923daa:/etc/nginx# ls
conf.d fastcgi_params mime.types modules nginx.conf scgi_params uwsgi_params
The concept of port exposure
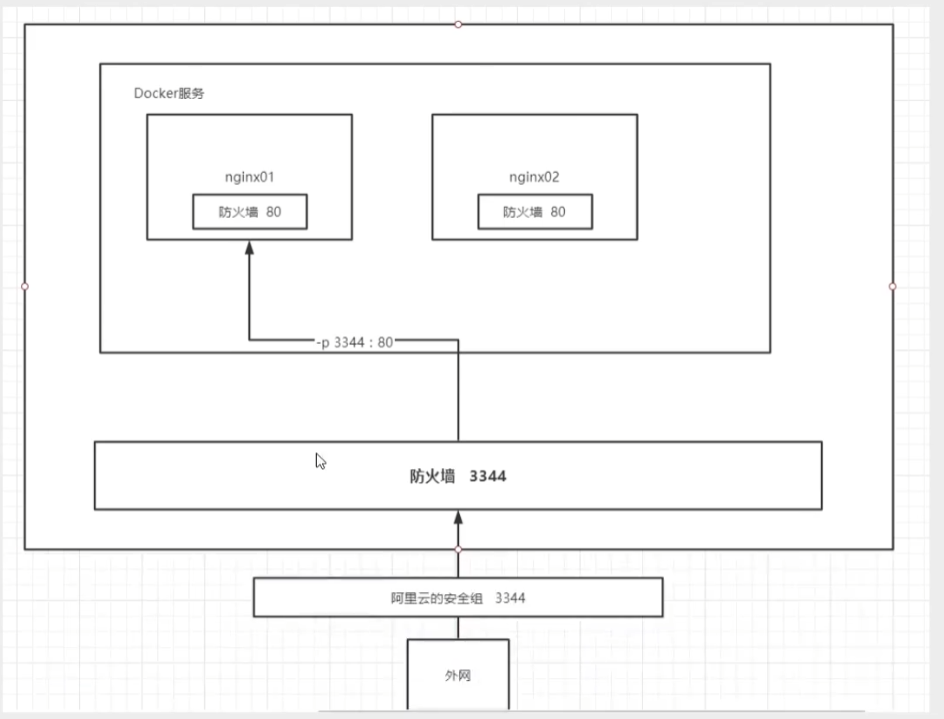
Think about it: Do we need to go inside the container every time we change the nginx configuration file? Very cumbersome, if I can provide a mapping path outside the container so that the file name can be modified inside the container automatically? - v Data Volume!
5. Deploying Tomcat
Official use:
docker run -it --rm tomcat:9.0
Our previous startups were all background, after stopping the container, the container can also be found, docker run-t-rm, commonly used for testing, delete when used up.
-
Download Mirror
- docker pull tomcat
-
Start Run
- docker run -d -p 3355:8080 --name tomcat01 tomcat
-
Access tests are OK
-
Enter Container
- d[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker exec -it tomcat01 /bin/bash
Problem found: 1. The Linux command is 2 less. There are no webapps.
For Ali cloud mirroring reasons, the default is the smallest mirror, all unnecessary are removed to ensure the smallest runnable environment
Think about it: Would it be a hassle for us to deploy the project in the future if we had to enter the container every time? I wish I could provide a mapping path outside the container, webapps, and we could project externally and synchronize internally automatically!
Docker container tomcat + website docker + mysql
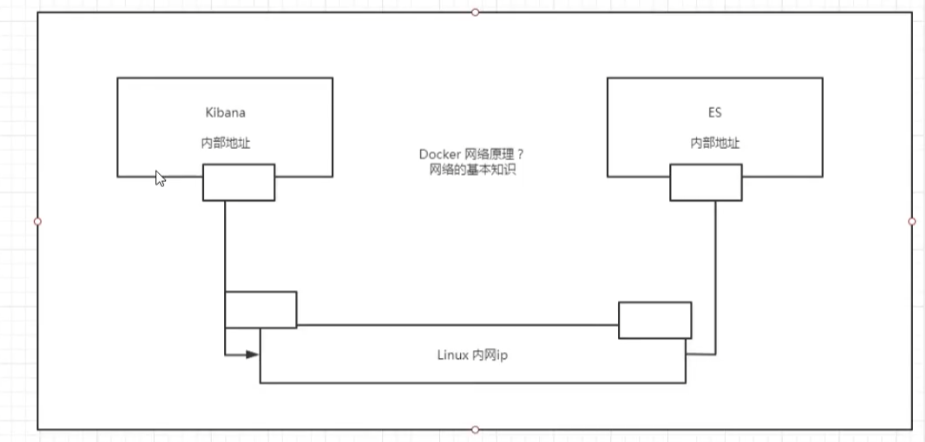
V. Deployment of ES + Kibana
# es exposes many ports
# es10 consumes memory
# es data generally needs to be placed in a secure directory! mount
# Start elasticsearch
docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:7.6.2
# Start the elasticaserch linux card owner, because the elasticaserch takes up a lot of memory (1.xG)
# Doker stats checked the status of cup and found that 1.25G was used to boot light es, accounting for 35.53 memory!
CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS
7f8f3d2f4177 elasticsearch 0.13% 1.25GiB / 3.519GiB 35.53% 0B / 0B 32MB / 729kB 43
eb22f4cb0852 tomcat01 0.07% 143.5MiB / 3.519GiB 3.98% 1.64kB / 13.9kB 65.5kB / 0B 31
f1b9afbe52ee dreamy_hermann 0.00% 520KiB / 3.519GiB 0.01% 306B / 0B 0B / 0B 1
# Test if es succeeds
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# curl localhost:9200
{
"name" : "7f8f3d2f4177",
"cluster_name" : "docker-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "s9ncNoy1QtS_Wz3YilFKOA",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.6.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "ef48eb35cf30adf4db14086e8aabd07ef6fb113f",
"build_date" : "2020-03-26T06:34:37.794943Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.4.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
# Close now, increase memory limit, modify profile-e environment configuration modification
docker run -d --name elasticsearch02 -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms64m -Xmx512m" elasticsearch:7.6.2
# Looking at all the es memory docker stats here, we found that they are much smaller!
CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS
69edec2b1847 elasticsearch02 183.49% 365.3MiB / 3.519GiB 10.14% 0B / 0B 9.39MB / 471kB 43
eb22f4cb0852 tomcat01 0.06% 143.5MiB / 3.519GiB 3.98% 1.68kB / 13.9kB 65.5kB / 0B 31
f1b9afbe52ee dreamy_hermann 0.00% 520KiB / 3.519GiB 0.01% 348B / 0B 0B / 0B 1
Job: Connect es using kibana? Think about how the network can connect to the past!
6. Portainer Visualization Panel Installation
What is portainer?
Docker GUI management tool! Provide a background panel for us to operate!
docker run -d -p 8088:9000 \--restart=always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --privileged=true portainer/portainer
The interface after starting the access is shown below
Visualization panel we do not normally use, you can test and play!
7. Docker Mirror Explanation
1. What is the mirror
Mirroring is a lightweight, executable, stand-alone package that packages software developed for both the software runtime and the basic runtime environments. It contains everything you need to run a software, including code, runtime, libraries, environment variables, and configuration files.
All applications, just pack a docker image and run!
How to get a mirror:
- Download from remote repository
- Friend's copy for you
- Make your own mirror DockerFile
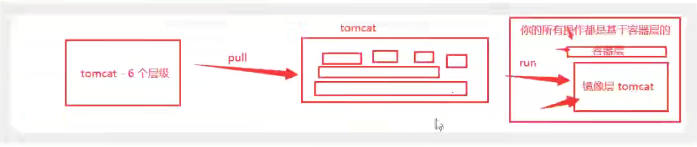
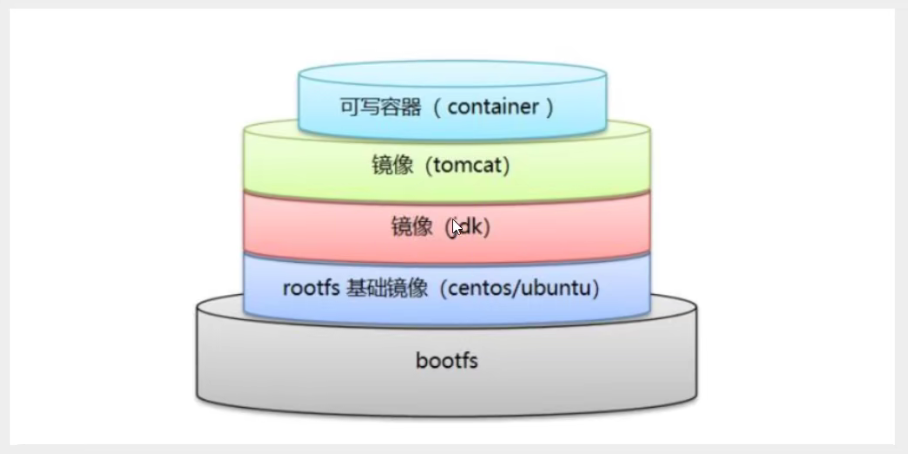
2. Docker mirror loading principle


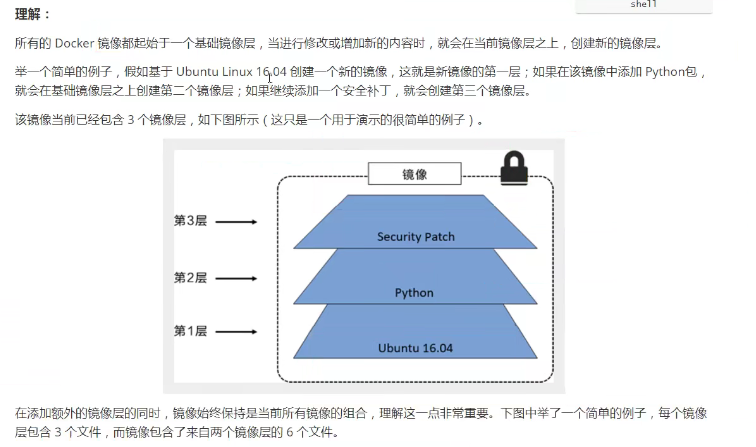
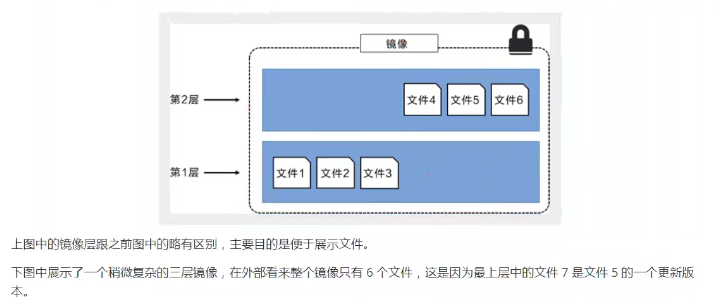
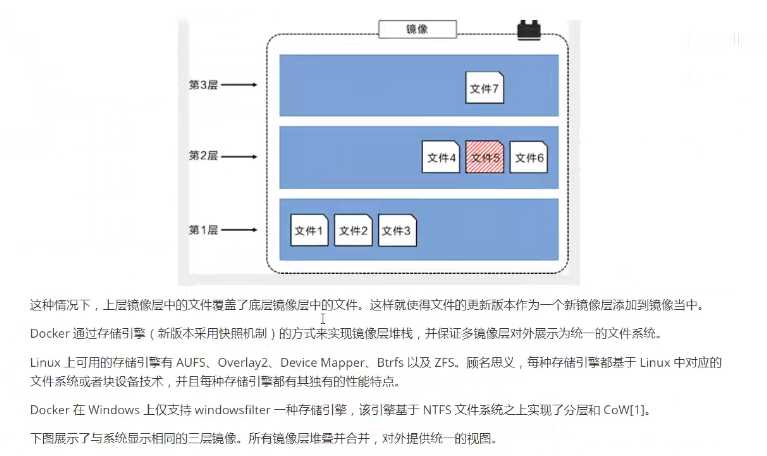
3. Hierarchical Understanding
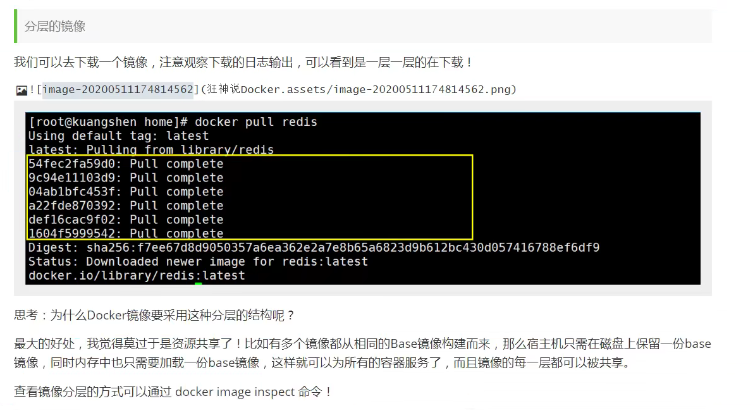
[root@iZwz99sm8v95sckz8bd2c4Z ~]# docker image inspect nginx:latest
[
{
"Id": "sha256:ae2feff98a0cc5095d97c6c283dcd33090770c76d63877caa99aefbbe4343bdd",
"RepoTags": [
"nginx:latest"
],
"RepoDigests": [
"nginx@sha256:4cf620a5c81390ee209398ecc18e5fb9dd0f5155cd82adcbae532fec94006fb9"
],
"Parent": "",
"Comment": "",
"Created": "2020-12-15T20:21:00.007674532Z",
"Container": "4cc5da85f27ca0d200407f0593422676a3bab482227daee044d797d1798c96c9",
"ContainerConfig": {
"Hostname": "4cc5da85f27c",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": false,
"AttachStderr": false,
"ExposedPorts": {
"80/tcp": {}
},
"Tty": false,
"OpenStdin": false,
"StdinOnce": false,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin",
"NGINX_VERSION=1.19.6",
"NJS_VERSION=0.5.0",
"PKG_RELEASE=1~buster"
],
"Cmd": [
"/bin/sh",
"-c",
"#(nop) ",
"CMD [\"nginx\" \"-g\" \"daemon off;\"]"
],
"Image": "sha256:13bffe371b56f4aeed88218ec17d0c6f653a83b49bd3e211fc8cfa2ca5d7a3d3",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": [
"/docker-entrypoint.sh"
],
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": {
"maintainer": "NGINX Docker Maintainers <docker-maint@nginx.com>"
},
"StopSignal": "SIGQUIT"
},
"DockerVersion": "19.03.12",
"Author": "",
"Config": {
"Hostname": "",
"Domainname": "",
"User": "",
"AttachStdin": false,
"AttachStdout": false,
"AttachStderr": false,
"ExposedPorts": {
"80/tcp": {}
},
"Tty": false,
"OpenStdin": false,
"StdinOnce": false,
"Env": [
"PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin",
"NGINX_VERSION=1.19.6",
"NJS_VERSION=0.5.0",
"PKG_RELEASE=1~buster"
],
"Cmd": [
"nginx",
"-g",
"daemon off;"
],
"Image": "sha256:13bffe371b56f4aeed88218ec17d0c6f653a83b49bd3e211fc8cfa2ca5d7a3d3",
"Volumes": null,
"WorkingDir": "",
"Entrypoint": [
"/docker-entrypoint.sh"
],
"OnBuild": null,
"Labels": {
"maintainer": "NGINX Docker Maintainers <docker-maint@nginx.com>"
},
"StopSignal": "SIGQUIT"
},
"Architecture": "amd64",
"Os": "linux",
"Size": 132935043,
"VirtualSize": 132935043,
"GraphDriver": {
"Data": {
"LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/cb791e78a08db7091bf2ce1d78603f1758f52199e57f1805156fe30e39067aae/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/1e73a72b25af68ee9abf4eb443f778d31226e12e9af428fcc14c7b044c83b258/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/88c9c01762f2af8327db65d0b0d4a64785e87c9c2ab76c62e7d03619db03a985/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/7304ab112ac4a9cb91fc6f74730be28fecbe19f042e92d321aa9181424cc4b2e/diff",
"MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/48b288740bbb2b07b41ed43a4d17a005c46b08d3357d2960b5ef7db4b2de6618/merged",
"UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/48b288740bbb2b07b41ed43a4d17a005c46b08d3357d2960b5ef7db4b2de6618/diff",
"WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/48b288740bbb2b07b41ed43a4d17a005c46b08d3357d2960b5ef7db4b2de6618/work"
},
"Name": "overlay2"
},
"RootFS": {
"Type": "layers",
"Layers": [
"sha256:87c8a1d8f54f3aa4e05569e8919397b65056aa71cdf48b7f061432c98475eee9",
"sha256:5c4e5adc71a82a96f02632433de31c998c5a9e2fccdcbaee780ae83158fac4fa",
"sha256:7d2b207c26790f693ab1942bbe26af8e2b6a14248969e542416155a912fec30d",
"sha256:2c7498eef94aef8c40d106f3e42f7da62b3eee8fd36012bf7379becc4cd639a2",
"sha256:4eaf0ea085df254fd5d2beba4e2c11db70a620dfa411a8ad44149e26428caee4"
]
},
"Metadata": {
"LastTagTime": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
}
}
]
Here is the hierarchical information:
"RootFS": {
"Type": "layers",
"Layers": [
"sha256:87c8a1d8f54f3aa4e05569e8919397b65056aa71cdf48b7f061432c98475eee9",
"sha256:5c4e5adc71a82a96f02632433de31c998c5a9e2fccdcbaee780ae83158fac4fa",
"sha256:7d2b207c26790f693ab1942bbe26af8e2b6a14248969e542416155a912fec30d",
"sha256:2c7498eef94aef8c40d106f3e42f7da62b3eee8fd36012bf7379becc4cd639a2",
"sha256:4eaf0ea085df254fd5d2beba4e2c11db70a620dfa411a8ad44149e26428caee4"
]
},
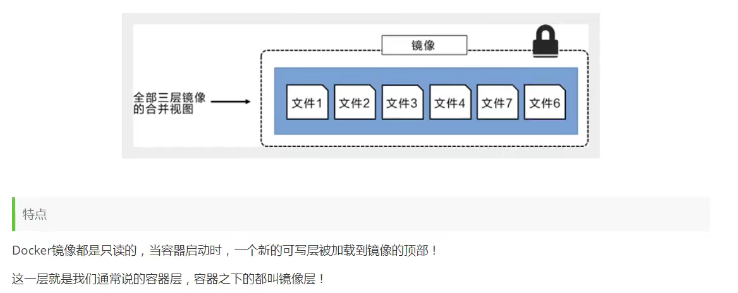
3. commit mirror
docker commit Price increase container becomes a new copy # Commands work like GITS docker commit -m="Descriptive information submitted" -a="author" container id Target Mirror Name:[TAG]
Field Test
# 1. Start a default tomcat # 2. Discover that this default tomcat is not used by webapps. The reason for mirroring is that there are no files underneath the official mirror default webapps! # 3. I copied in the basic files myself # 4. Submit containers that we've worked with to a mirror via commit, and we'll use the mirror we've modified in the future, which is one of our own modified images [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE tomcat 9.0 3f3cadde9a68 8 days ago 680MB tomcat latest 24207ccc9cce 8 days ago 680MB mysql latest bbf6571db497 2 weeks ago 516MB nginx latest f652ca386ed1 2 weeks ago 141MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB portainer/portainer latest 580c0e4e98b0 9 months ago 79.1MB elasticsearch 7.6.2 f29a1ee41030 21 months ago 791MB [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker commit -a="xiaowang" -m="add webapps app" eb22f4cb0852 tomcat02:1.0 sha256:f6500329aeb683d003f709e9a63d9da2b51cf476faf73ed3dbf6de79d72c8539 [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker iamges docker: 'iamges' is not a docker command. See 'docker --help' [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE tomcat02 1.0 f6500329aeb6 9 seconds ago 684MB tomcat 9.0 3f3cadde9a68 8 days ago 680MB tomcat latest 24207ccc9cce 8 days ago 680MB mysql latest bbf6571db497 2 weeks ago 516MB nginx latest f652ca386ed1 2 weeks ago 141MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 2 months ago 13.3kB centos latest 5d0da3dc9764 3 months ago 231MB portainer/portainer latest 580c0e4e98b0 9 months ago 79.1MB elasticsearch 7.6.2 f29a1ee41030 21 months ago 791MB
8. Container Data Volume
1. What is a container data volume
docker's concept review
Package applications and environments into a single image!
Data? If the data is all in containers, our containers will delete and the data will be lost! Requirement: Data can be persisted
MySql, container deleted, library deleted run! Requirement: MySQL data can be stored locally!
There can be a data sharing technology between containers! Data generated in Docker container, sync to local!
This is volume technology! Mount directories, mount directories inside our containers onto Linux!
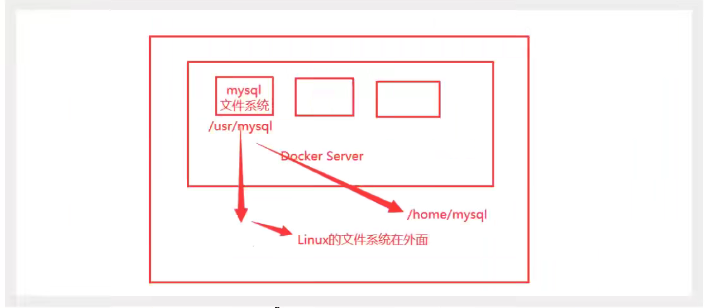
In a word: container persistence and synchronization! Containers can also share data!
2. Use data volumes
Mode 1: mount -v directly by command
docker run -it -v Host Directory: Container Directory
# test
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz home]# docker run -it -v /home/ceshi:/home centos /bin/bash
# We started by docker inspect container id
"Mounts": [ # Mount-v Volume
{
"Type": "bind",
"Source": "/home/ceshi", # Address inside host
"Destination": "/home", # Address inside docker container
"Mode": "",
"RW": true,
"Propagation": "rprivate"
}
],
Synchronization of test files (two-way synchronization)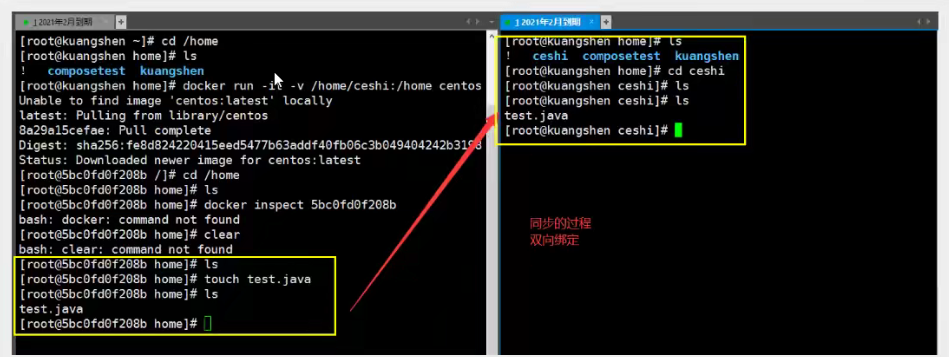
Test again!
- Stop Container
- Modify Files on Host
- Start Container
- The data in the container is still synchronized!
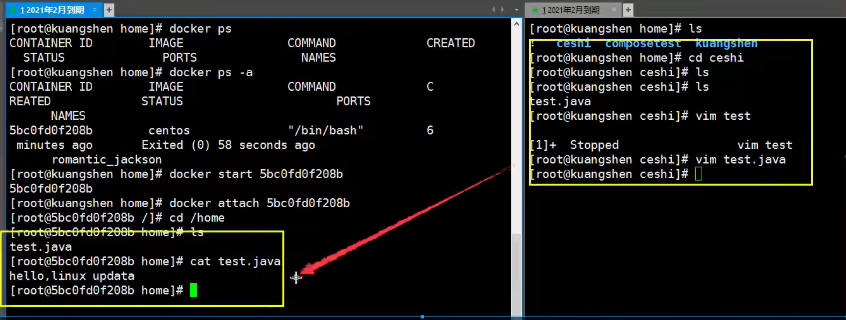
** Benefits: ** In the future, we only need to make local changes, which will synchronize automatically in the container!
3. Actual: Mysql synchronizes data
Think: MySql's data persistence problem!
# Get Mirror [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ceshi]# docker pull mysql:5.7 # Run the container, need to do data mount installation to start mysql, need to configure the password, just pay attention! Official test: docker run-name some-mysql-e MYSQL_ ROOT_ PASSWORD=my-secret-pw-d mysql:tag # Start our mysql -d Background running -p Port Mapping -v Volume mount -e Environment Configuration --name Container name [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ceshi]# docker run -d -p 3310:3306 -v /home/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /home/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name mysql101 mysql:5.7 # After successful startup, we used Navicat locally to connect to the test # Navicat -- 3310 - 3310 connected to the server and 3306 mapping inside the container, then we can connect! As follows # Create a database in a local test to see if our mapped path is ok!
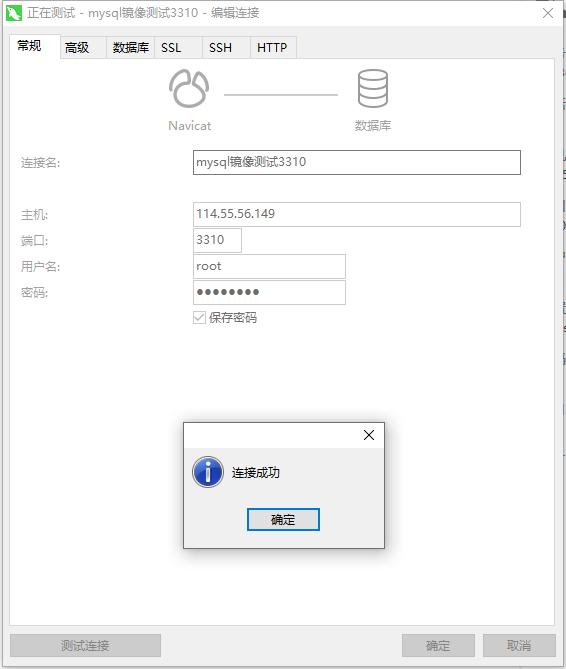
When we delete the container, we find that the volume we mounted locally is still not lost, which makes the container data persistent.
4. Named and anonymous mounts
# Anonymous mount
-v Path inside container!
docker run -d --name nginx -v /etc/nginx nginx
# View all volume s
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local d5f431ccd26ebe8ca0f27051419ac7ff4ec60eec176ee7f96e2d49d0cbe85017
local e977864fb9b5123ab7dc675c61e51031417d9c83ec38826b400a3e6215b681e6
#We found here that this is an anonymous mount. We only wrote paths inside the container at -v, not outside!
# Named Mount
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -d -P --name nginx03 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx nginx
cd0d95d4e296fe0bbccd4050f9cf7553ec3bb538216a82fbfebed45f90d62b9b
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker volume ls
DRIVER VOLUME NAME
local d5f431ccd26ebe8ca0f27051419ac7ff4ec60eec176ee7f96e2d49d0cbe85017
local e977864fb9b5123ab7dc675c61e51031417d9c83ec38826b400a3e6215b681e6
local juming-nginx
# Pass-v Volume Name: Path in Container
# Check out this volume
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker volume inspect juming-nginx
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2021-12-18T12:48:59+08:00",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": null,
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/juming- nginx/_data", # !!
"Name": "juming-nginx",
"Options": null,
"Scope": "local"
}
]
# Volumes in all docker containers, without a specified directory, are in/var/lib/docker/volumes/xxx/_data
We can easily find one of our volumes by using named mounts, most of the time using named mounts.
# How to determine whether to mount anonymously or with a named path -v Path inside container # Hang Anonymously -v Volume Name:Path inside container # Named Mount -v /Host Path::Path inside container # Specify the path to mount!
Expand:
# Change Read and Write Permissions by Path in-v Container: ro rw ro readonly #read-only rw readwrite # Read-write # Once this has set container permissions, containers have limits on what we can mount! docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:ro nginx docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:rw nginx. # When ro sees ro, it means that this path can only be operated on by the host machine. It cannot be operated on inside the container!
9. DockerFile
1. Initial DockerFile
DockerFile is the build file used to build the docker image! Command script, try it first! Through this script, mirrors can be produced one layer at a time, scripts command by command, and each command is a layer!
# Create a dockerfile with a name that randomly suggests a Dockerfile # Content directive (uppercase) parameters in file FROM centos VOLUME ["volume01","volume02"] CMD echo "----end-----" CMD /bin/bash # Every command here is the mirror floor! As follows
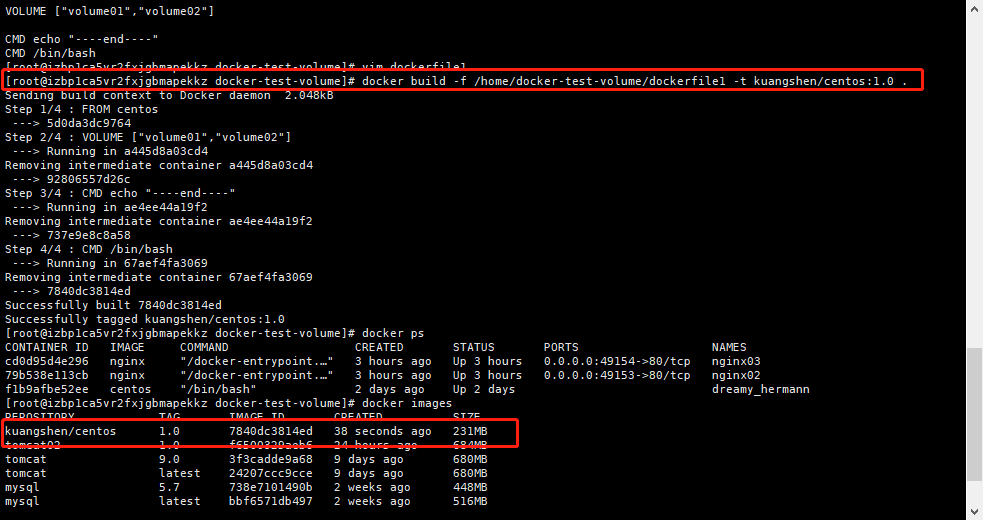
Start your own write container:
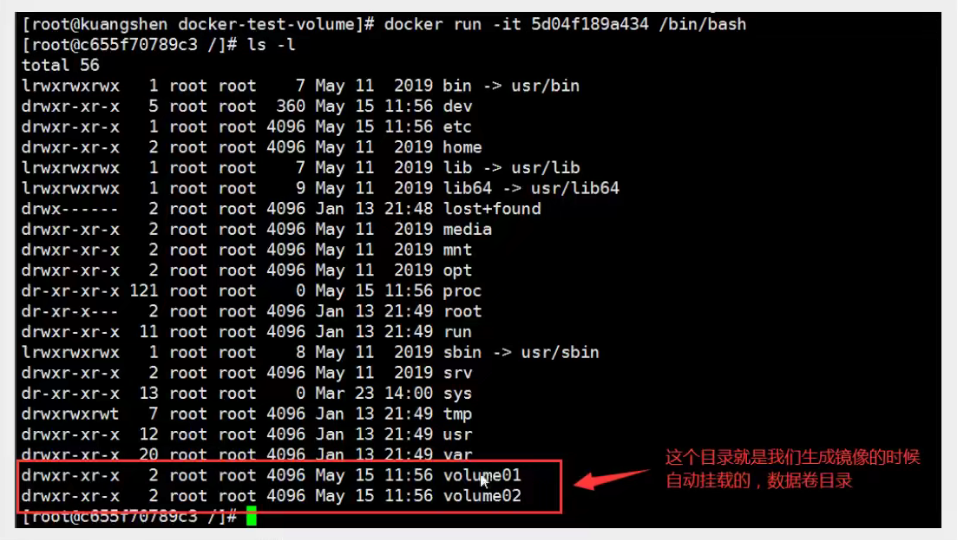
There must be a synchronized directory outside this volume!
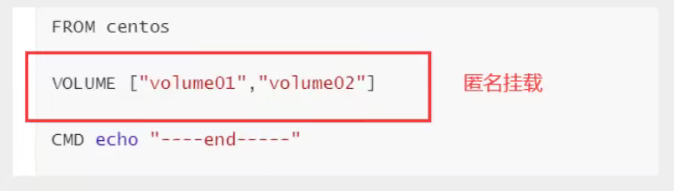
Check the path of the volume mount:
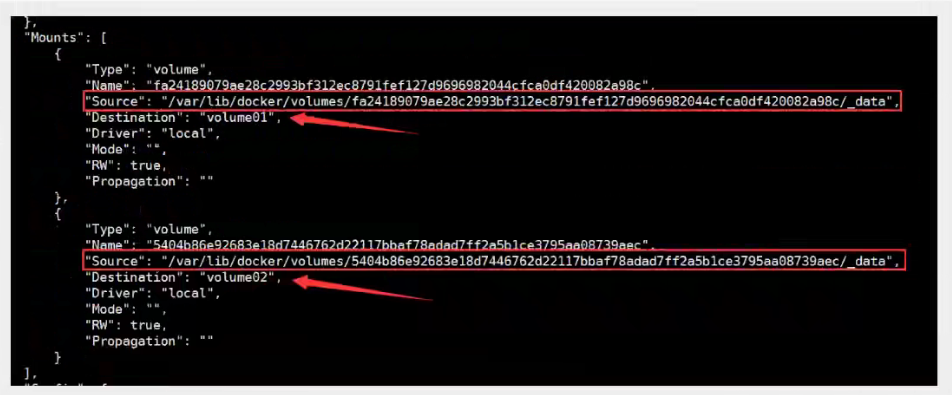
This way we will use a lot in the future, because we usually build our own mirrors! Assuming the volume was not mounted when the mirror was built, mount the-v volume name manually: path inside the container
2. Data Volume Container
Synchronize data with multiple mysql s!

Start three containers, starting with the mirror we just wrote
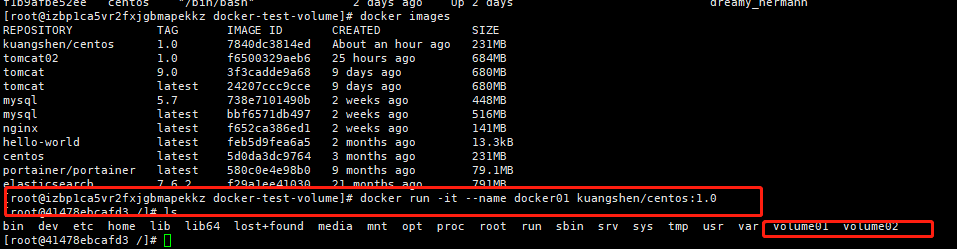
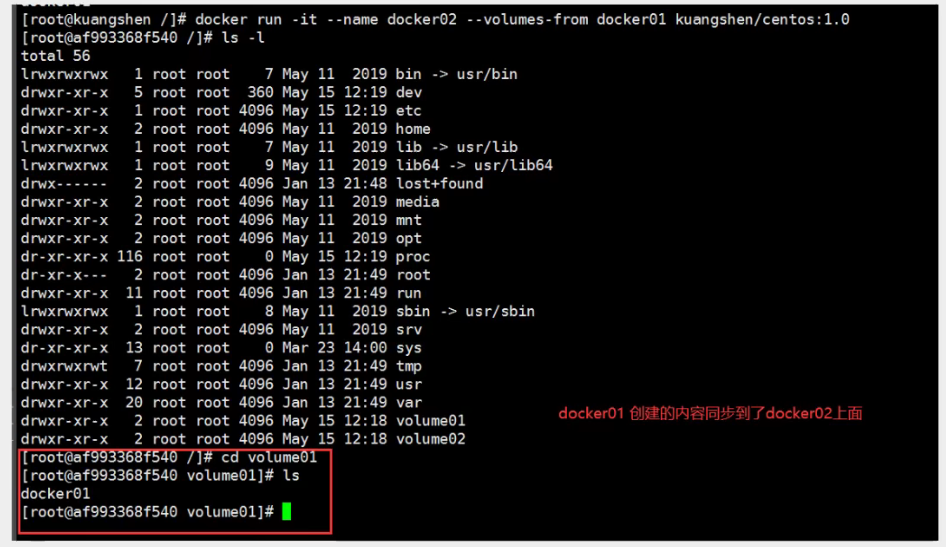
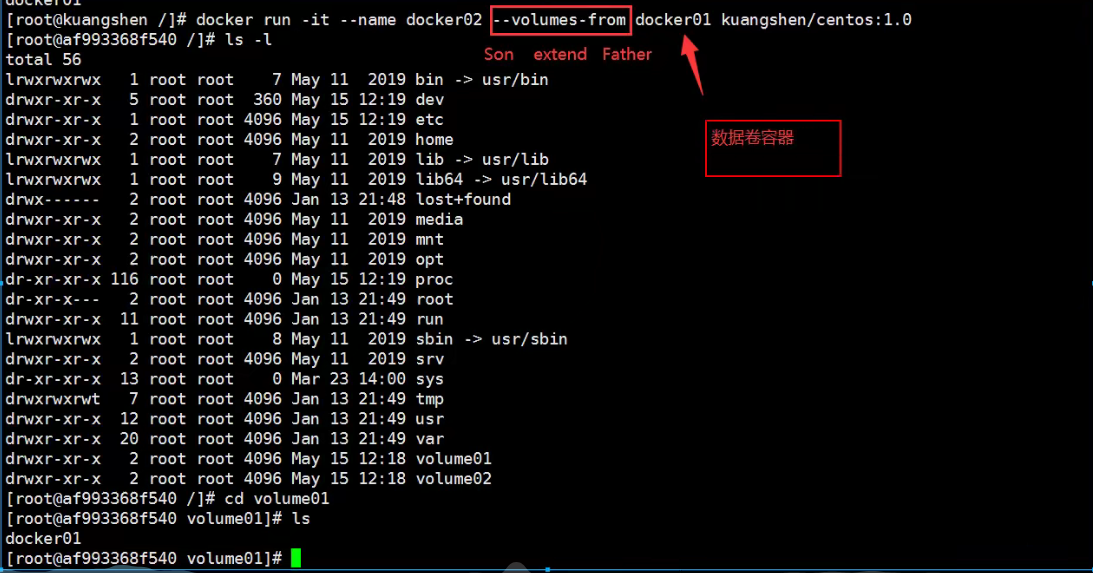
Test to see if docker02 and docker01 can access this file by deleting docker01
Tested, still accessible
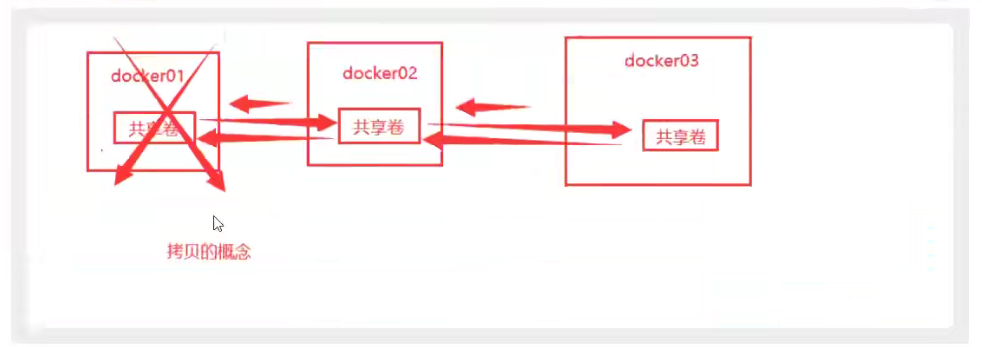
Multiple mysql s for data sharing
docker run -d -p 3310:3306 -v /etc/mysql/conf.d -v /var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name mysql01 mysql:5.7
docker run -d -p 3310:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 --name mysql02 --volumes-from mysql01 mysql:5.7
Conclusion:
Configuration information is passed between containers, and the life cycle of a data volume container lasts until no containers are used.
But once you persist locally, the local data will not be deleted at this time.
3. Introduction to DockerFile
The dockerfile is the file used to build the docker image! Command parameter script name!
Construction steps:
- Write a dockerfile
- Docker builds into a mirror
- docker run run mirror
- docker push Release Mirror (DockerHub, Ali Cloud Mirror Warehouse!)
Check what the authorities are doing?
Many official mirrors are basic packages, many functions are not, we usually build our own mirrors! Now that the authorities can make mirrors, so can we!
Fundamentals:
- Each reserved keyword (instruction) must be an uppercase letter
- Execute from top to bottom
- #indicates a comment
- Each instruction creates a new mirror layer for the price increase and submits it!
The dockerfile is for development. To publish projects for mirroring in the future, we need to write a dockerfile, which is very simple!
Docker mirroring is becoming the standard for enterprise delivery and must be mastered!
DockerFile: Build the file, define all the steps, source code.
DockerImages: Build a generated image through DockerFile and ultimately publish and run the product, originally the jar, war package.
Docker container: A container is one that runs as a mirror to provide services.
4. DockerFile directives
We used to use someone else, but now that we know these instructions, let's practice writing a mirror for ourselves!
FROM # Basic Mirror, everything built from here MAINTAINER # Who wrote the mirror, name + mailbox RUN # Commands to run when building a mirror ADD # Step, tomcat image, this tomcat compressed package adds content WORKDIR # Mirrored Working Directory VOLUME # Mounted Directory EXPOST # Keep Port Configuration CMD # Specifies the command to run when this container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT # Specifies that commands to run when this container starts can be appended ONBUILD # When an inherited DockerFile is built, the ONBUILD directive is run, triggering the directive COPY # Like ADD, copy our files into a mirror ENV # Set environment variables when building
5. Field Test
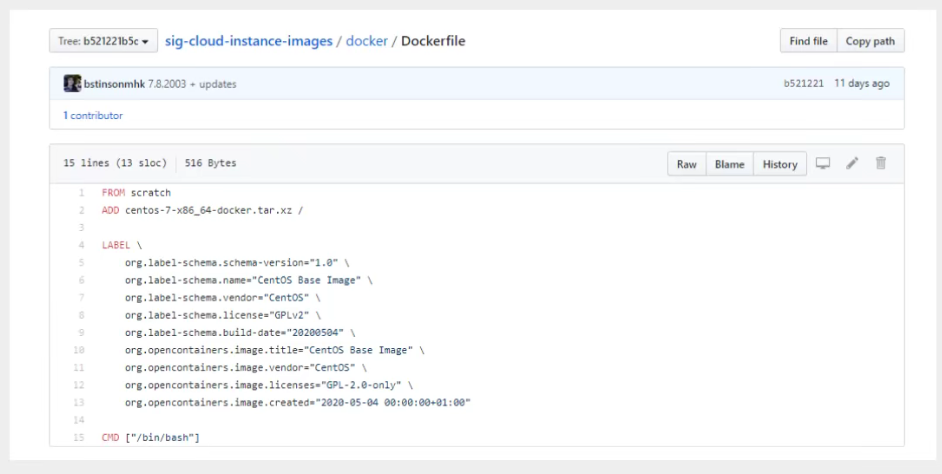
99% of the mirrors in Docker Hub are FROM scratch es mirrored from this base, then configured with the software and configuration needed to build them.
Create your own centos
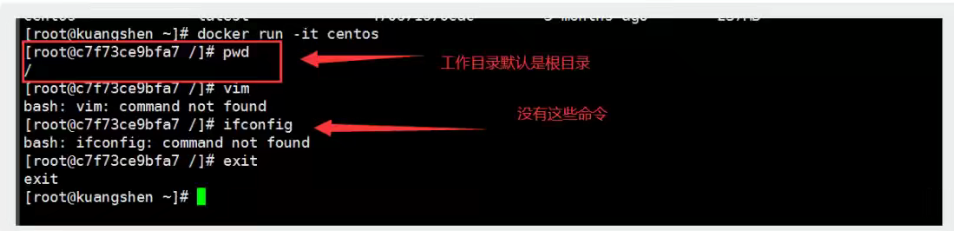
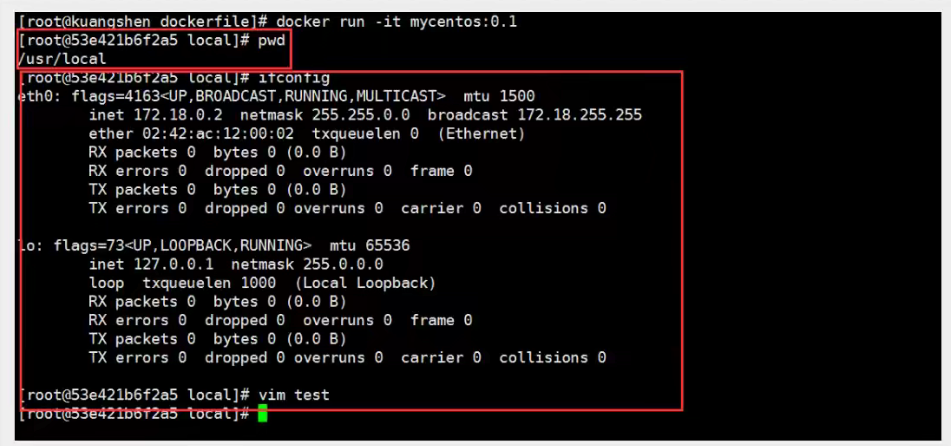
# 1. Write DockerFile files FROM centos MAINTAINER wangjian<571376264@qq.com> ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install net-tools EXPOSE 80 CMD echo $MYPATH CMD echo "-----end-----" CMD /bin/bash # 2. Build a mirror from this file # Command docker build-f dockerfile file file path-t mirror name: [tag] Successfully built a33e391002e6 Successfully tagged mycentos:0.1 # 3. Under Test Run
Contrast: Previous native centos
Our added mirror
We can list the history of local mirroring changes
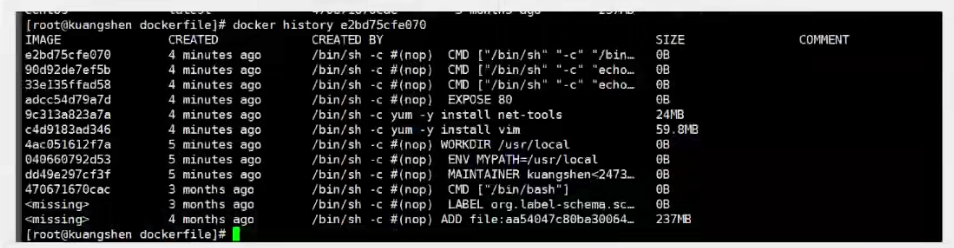
We usually get a mirror, you can study how it does the following?
6. Differences between CMD and ENTRYPOINT
CMD # Specifies the command to run when this container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT # Specifies that commands to run when this container starts can be appended
Test cmd
# Write dockerfile file [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# vim dockefile-cmd-test FROM centos CMD ["ls","-a"] # Build Mirror [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# docker build -f dockefile-cmd-test -t cmdtest . # run runs and finds our ls-a command in effect [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# docker run 24bf9aa5c445 . .. .dockerenv bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var # To append a command, -l Ls-al [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz /]# docker run 24bf9aa5c445 -l docker: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime create failed: container_linux.go:380: starting container process caused: exec: "-l": executable file not found in $PATH: unknown. ERRO[0000] error waiting for container: context canceled # Clean-up of cmd-l replaces the CMD ['ls', -a'] command, -l is not a command and therefore errors
Test ENTRYPOINT
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# vim dockerfile-cmd-entrypoint FROM centos CMD ["ls","-a"] [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# docker build -f dockerfile-cmd-entrypoint -t entrypoint-test . Sending build context to Docker daemon 18.43kB [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# docker build -f dockerfile-cmd-entrypoint -t entrypoint-test . Sending build context to Docker daemon 18.43kB Step 1/2 : FROM centos ---> 5d0da3dc9764 Step 2/2 : ENTRYPOINT ["ls","-a"] ---> Running in 020e6f08f0e1 Removing intermediate container 020e6f08f0e1 ---> 968a3b950425 Successfully built 968a3b950425 Successfully tagged entrypoint-test:latest # Our appended command is directly cleaned after our ENTRYPOINT command! [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz dockerfile]# docker run 968a3b950425 -l total 56 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Dec 19 11:59 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Dec 19 11:59 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Dec 19 11:59 .dockerenv lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 2020 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 340 Dec 19 11:59 dev drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Dec 19 11:59 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 2020 home lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Nov 3 2020 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Nov 3 2020 lib64 -> usr/lib64 drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 lost+found drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 2020 media drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 2020 mnt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 2020 opt dr-xr-xr-x 104 root root 0 Dec 19 11:59 proc dr-xr-x--- 2 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 root drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 run lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 Nov 3 2020 sbin -> usr/sbin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Nov 3 2020 srv dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Dec 19 11:59 sys drwxrwxrwt 7 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 tmp drwxr-xr-x 12 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 usr drwxr-xr-x 20 root root 4096 Sep 15 14:17 var
Many of the commands in Dockerfile are very similar. We need to understand their differences. Our best way to learn is to compare them and test the results!
7. Actual Warfare: Tomcat Mirror
-
Prepare a tomcat zip package for the mirror file, a jdk zip package!

-
Write a dockerfile, officially name the Dockerfile, build will automatically find this file, do not need to specify -f!
FROM centos
MAINTAINER wangjian<571376264@qq.com>
COPY readme.txt /usr/local/readme.txt
ADD jdk-8u301-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/
ADD apache-tomcat-9.0.56.tar.gz /usr/local/
RUN yum -y install vim
ENV MYPATH /usr/local
WORKDIR $MYPATH
ENV JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_301
ENV CLASSPATH $JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
ENV CATALINA_HOME /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56
ENV CATALINA_BASH /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56
ENV PATH $PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$CATALINA_HOME/lib:$CATALINA_HOME/bin
EXPOSE 8080
CMD /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56/bin/startup.sh && tail -F /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56/bin/logs/catalina.out
- Build Mirror
# docker build -t diytomcat .
- Boot Mirror
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz tomcat]# docker run -d -p 9090:8080 --name kuangshentomcat -v /home/kuangshen/build/tomaca/test:/usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56/webapps/test -v /home/kuangshen/build/tomcat/tomcatlogs/:/usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.56/logs diytomcat 8289664b6082b079faa98aecc3b0483d6318decb1d165ad29f51d8354667a934
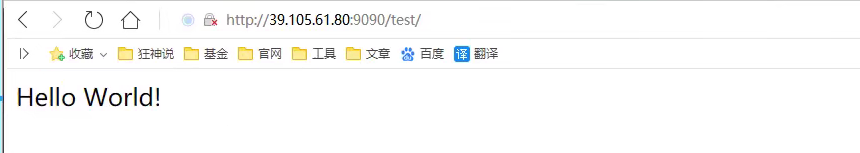
- Access Test
- No items to post (we can publish directly by writing projects locally because of volume mounting!)

Discovery: Project deployment is successful, you can access ok directly!
Steps for future development: Dockerfile writing is required! After that, all of us use the docker image to publish and run!
8. Publish your own image
- address https://hub.docker.com/ Register your own account
- Make sure this account is logged in
- Submit our own mirror on our server
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker login --help
Usage: docker login [OPTIONS] [SERVER]
Log in to a Docker registry.
If no server is specified, the default is defined by the daemon.
Options:
-p, --password string Password
--password-stdin Take the password from stdin
-u, --username string Username
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker login -u 571376264 Password: WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /root/.docker/config.json. Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store Login Succeeded
- Once you've logged in, you can raise the price mirror, which is a docker push
# push's own mirror on the server! [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker push diytomcat Using default tag: latest The push refers to repository [docker.io/library/diytomcat] fd740bc0e32a: Preparing ea73d22b8ff1: Preparing 4e549b25c75d: Preparing 8e974a7551e0: Preparing 74ddd0ec08fa: Preparing denied: requested access to the resource is denied # push mirror problem? [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker push kuangshen/diytomcat:1.0 The push refers to repository [docker.io/kuangshen/diytomcat] An image does not exist locally with the tag: kuangshen/diytomcat # Resolve, add a tag 571376264-digit account name, and it must be the account name otherwise error will occur [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker tag 9db79fb71c38 571376264/diytomcat:1.0 # docker push up! Publish your own images with version numbers whenever possible [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker push 571376264/diytomcat:1.0 The push refers to repository [docker.io/571376264/diytomcat] fd740bc0e32a: Pushed ea73d22b8ff1: Pushed 4e549b25c75d: Pushed 8e974a7551e0: Pushed 74ddd0ec08fa: Pushed 1.0: digest: sha256:6e67022eb83001e991ae70e18dd73226b506813d2c4715d01795c97a6482d726 size: 1373 # Submitted at the same level as the mirror
9. Publish on Ali Cloud Mirror
-
Landing in Ali Yun
-
Find Container Mirror Service
-
Create Namespace
-
Create Container Mirror
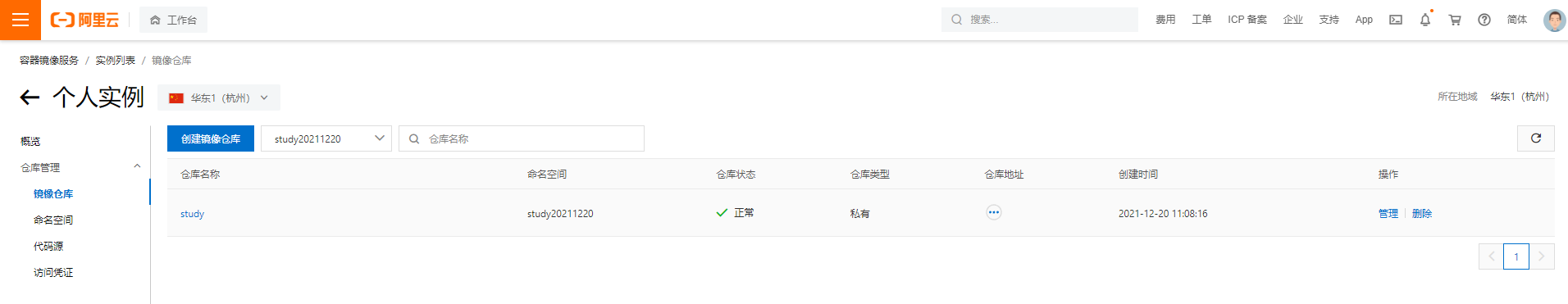
-
Browse Ali Cloud
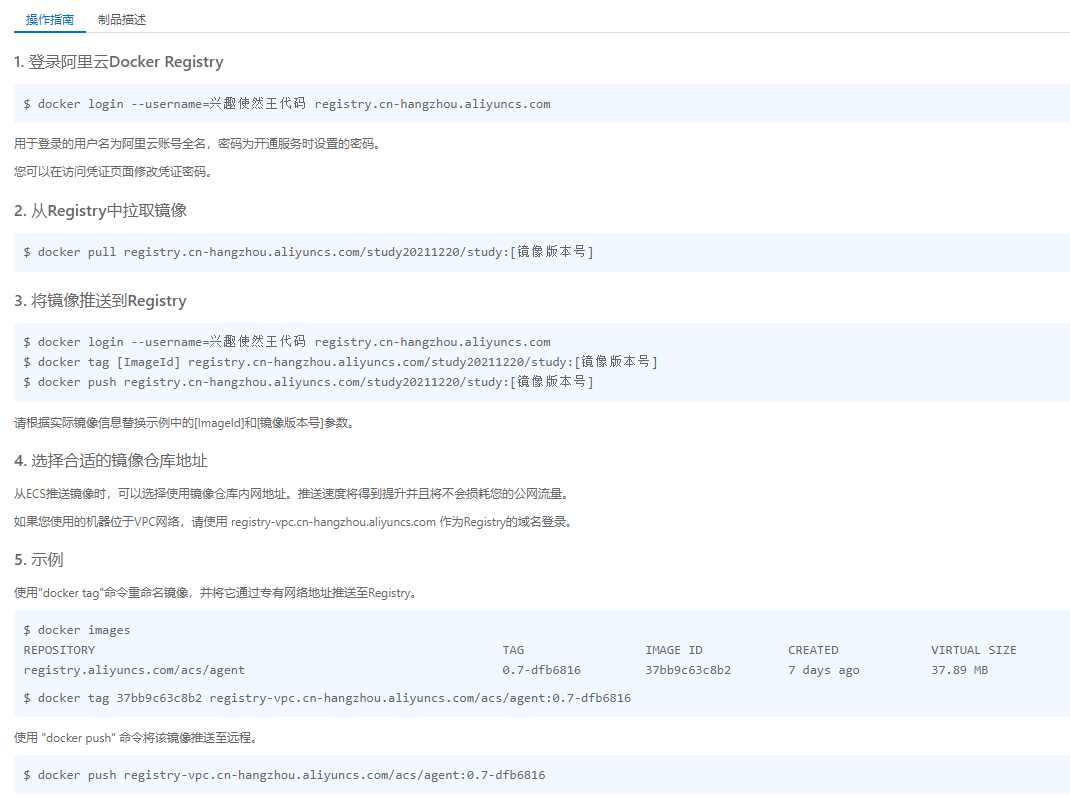
Ali cloud container mirror refers to the official address!
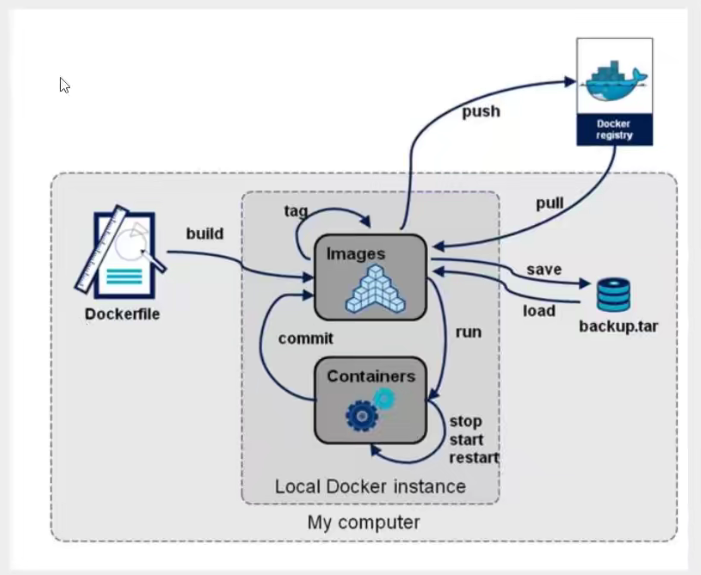
10. Summary
10. Docker Network
1. Understand Docker0
test
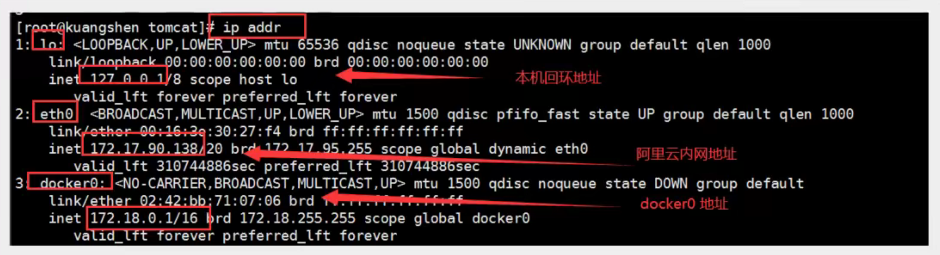
Three networks, how does docker handle container network access?

# [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat
# Look at the internal network address ip addr of the container, where there is no command for ip addr. Just execute apt update && apt install -y iproute2 to install it.
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker exec -it tomcat01 ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
134: eth0@if135: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:02 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 172.17.0.2/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
# There eth0@if135 ip address is docker assigned
# Think: can linux ping through the inside of the container?
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# ping 172.17.0.2
PING 172.17.0.2 (172.17.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 172.17.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.034 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.043 ms
64 bytes from 172.17.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.036 ms
^C
--- 172.17.0.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2000ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.034/0.037/0.043/0.008 ms
# linux can ping through the docker container interior
Principle:
-
Each time we start a docker container, the docker will assign an ip to the docker container. As long as the docker is installed, there will be a docker 0 bridge mode for the network card. The technology used is evth-pair technology!
Test ip addr again on the host
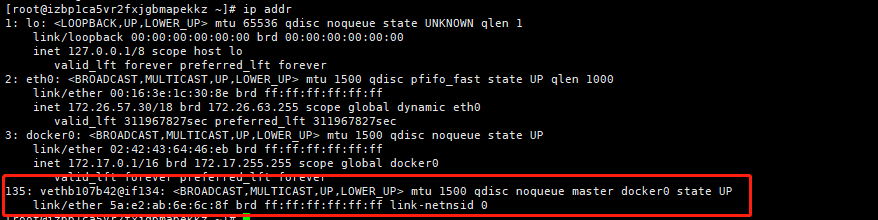
-
Starting a container test, I found another network card~!

We find that this container brings network cards in pairs, evth-pair is a pair of virtual device interfaces. They appear in pairs, one-to-one connectivity protocol, one-to-one connectivity. Because of this feature, evth-pari acts as a bridge to connect various virtual network devices. OpenStac, connections between Docker containers, and OVS connections all use evth-pair technology. -
Let's test if tomcat01 and tomcat02 can ping!

Draw a network model diagram:
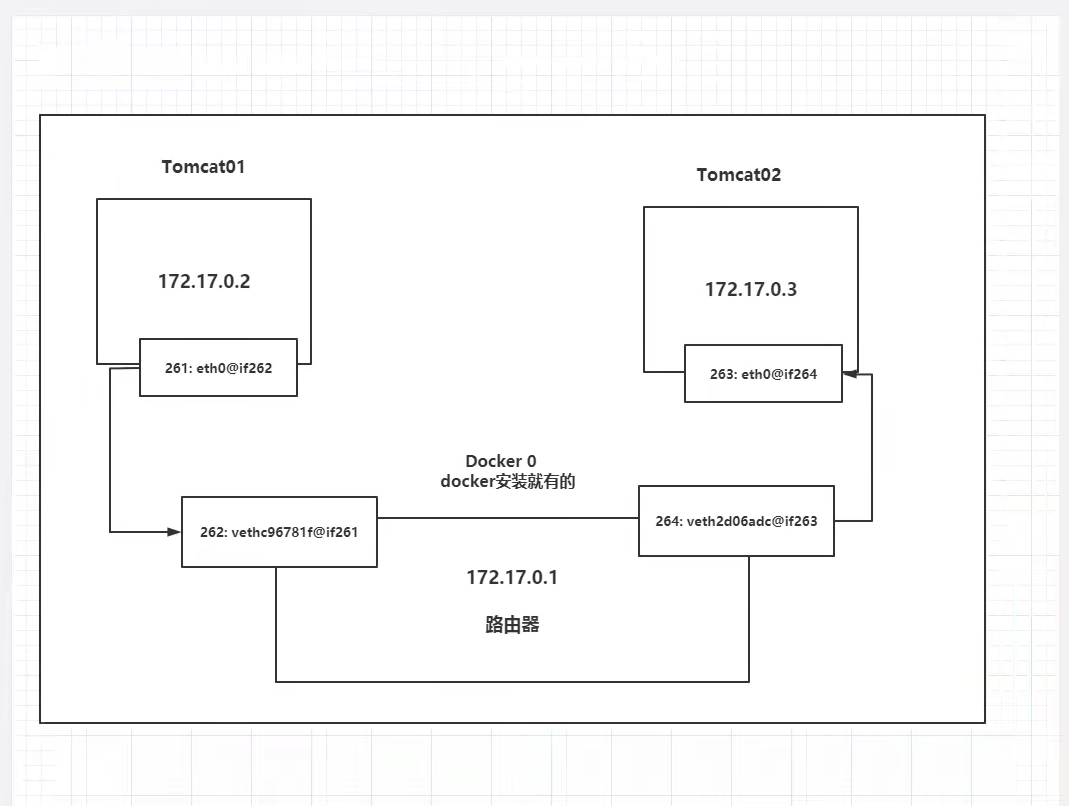
Conclusion: tomcat01 and tomcat02 are public routers, docker0.
All containers are routed by docker0 without specifying a network, and docker assigns our containers a default available IP
Summary: Docker uses a Linux bridge, and docker0 is the bridge for a Docker container in the host.
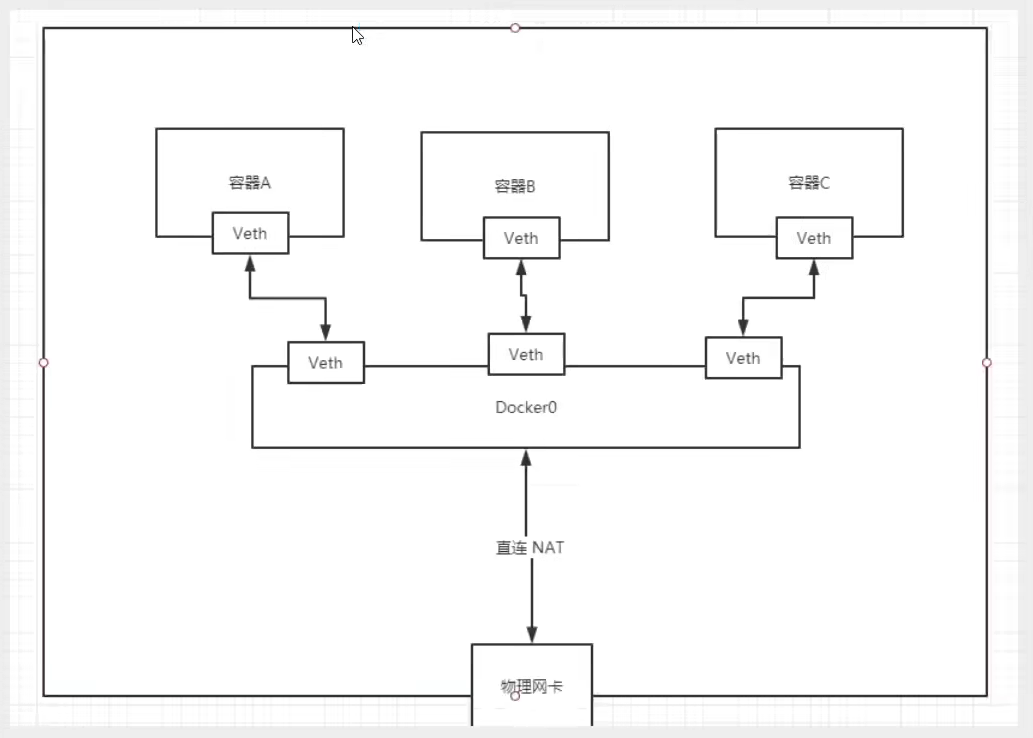
All network interfaces in the Docker are virtual amounts. Virtual transfer efficiency! (Intranet Delivery Files!)
As long as the container is deleted, the corresponding pair of bridges will be gone!
–link
Consider a scenario where we write a microservice, database url = ip:, the project does not restart, the database IP is replaced, and we want to be able to address this issue by name to access the container?
2. Container interconnection - link
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker exec -it tomcat02 ping tomcat01 ping: tomcat01: Name or service not known #How can I solve it? # --link solves the problem of network connectivity [root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -d -P --name tomcat03 --link tomcat02 tomcat
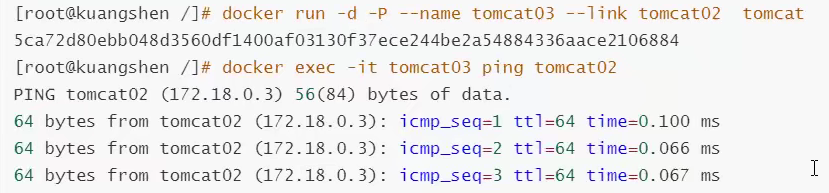
# Can directions be ping? Discovery is not possible, as shown below:

Explore: insepct!
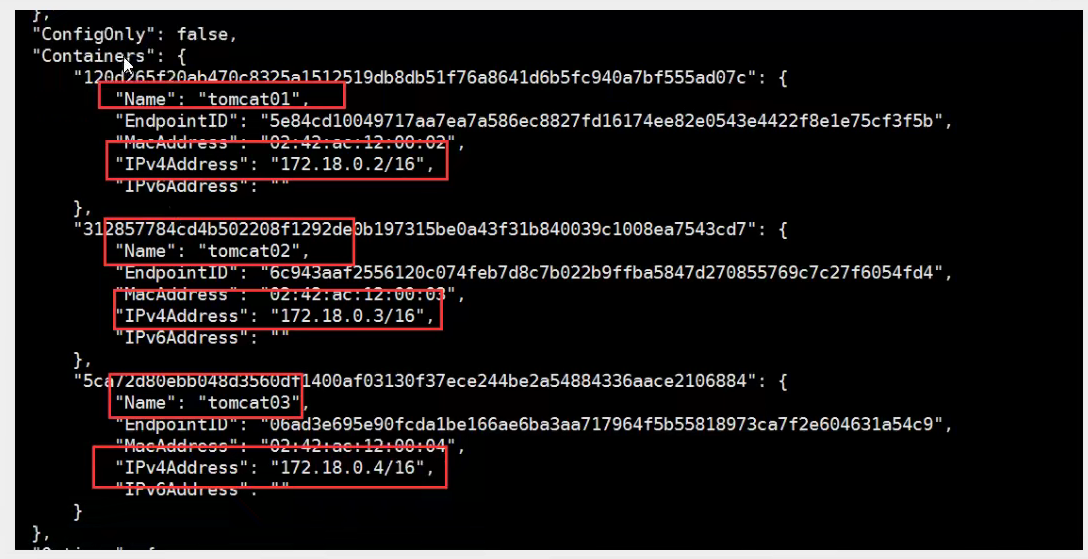
Actually, this tomcat03 configures tomcat02 locally?

Essential Exploration: - link is the addition of 172.18 to the host configuration. 0.3 tomcat02 312857784cd4
Docker is no longer recommended for us to use now - link!
Customize the network! Doker0 does not apply!
docker0 problem: it does not support container name connection access!
3. Custom network
View all docker networks
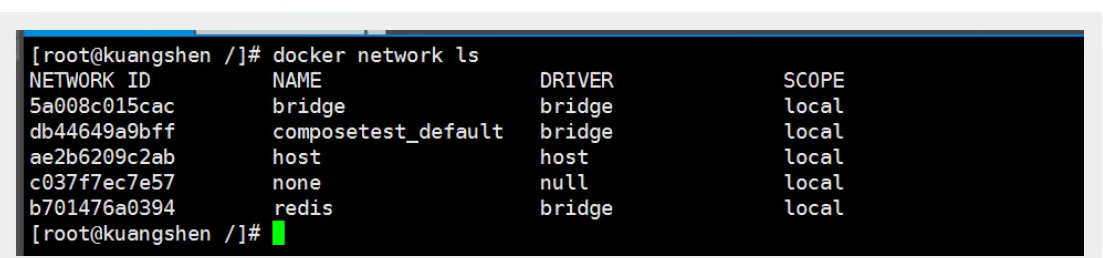
Network mode
- Bridge: Bridge docker (default, self-created also uses bridge mode)
- none: do not configure network
- Host: host mode, share network with host
- Container: the network inside the container is connected! (rarely used! Limited)
test
# The command we started directly--net bridge, which is our docker0
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 tomcat
docker run -d -P --name tomcat01 --net bridge tomcat
# docker0 features: by default, the domain name is not accessible, --link can make a connection!
# We can customize a network!
# --driver bridge
# --subnet 192.168.0.0/16
# --gateway 192.168.0.1
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker network create --driver bridge --subnet 192.168.0.0/16 --gateway 192.168.0.1 mynet
2a4e1f32c4f6f33a0e9c7138bcf49af47f2102e8f583d31eece9c6d3dbdd874d
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
f43965cd2489 bridge bridge local
99a84946d527 host host local
2a4e1f32c4f6 mynet bridge local
0d8ed1ed056b none null local
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -d -P --name tomcat-net-01 --net mynet tomcat
c65ed90c296b7dc3c2dce7d1583b19906bb726ea4e5b0a21370a43865f68c3f2
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker run -d -P --name tomcat-net-02 --net mynet tomcat
d5aaa4f721adca2f88302c7cae322ff76014ad977ce7f0251aba308a2cab3c90
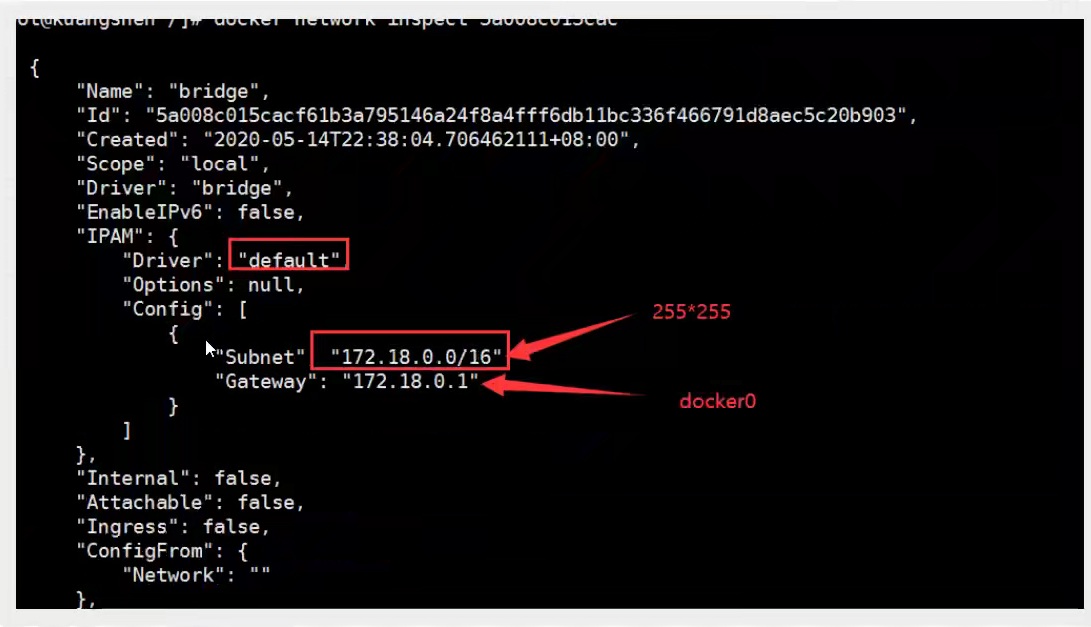
[root@izbp1ca5vr2fxjgbmapekkz ~]# docker network inspect mynet
[
{
"Name": "mynet",
"Id": "2a4e1f32c4f6f33a0e9c7138bcf49af47f2102e8f583d31eece9c6d3dbdd874d",
"Created": "2021-12-20T20:49:04.527045377+08:00",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "192.168.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "192.168.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {
"c65ed90c296b7dc3c2dce7d1583b19906bb726ea4e5b0a21370a43865f68c3f2": {
"Name": "tomcat-net-01",
"EndpointID": "837474d235b3693616cc2be7b630e61391da4518d3ec773d7dd9c24f9c7c956d",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:02",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.2/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
},
"d5aaa4f721adca2f88302c7cae322ff76014ad977ce7f0251aba308a2cab3c90": {
"Name": "tomcat-net-02",
"EndpointID": "d7c9af6e5e46f099bdad716db9e25dce9c6a83becae3d5588ddaa1226b1e53f4",
"MacAddress": "02:42:c0:a8:00:03",
"IPv4Address": "192.168.0.3/16",
"IPv6Address": ""
}
},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
# Test the ping connection in the book as follows:
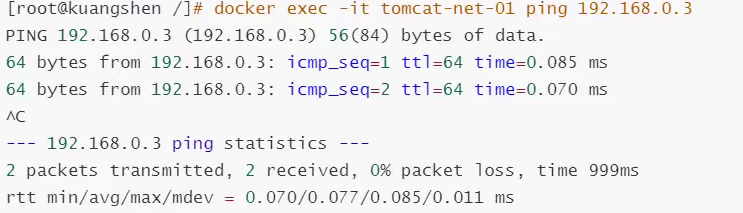
# Don't use it now--link can also ping!
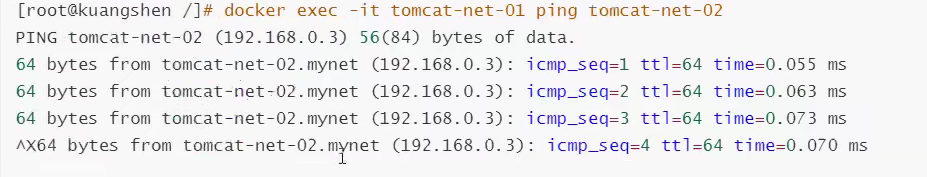
Find that all can ping!!!
Our customized web docker s have helped us maintain a good relationship. We recommend using the web as usual.
Benefits:
redis - Different clusters use different networks to ensure that the cluster is safe and healthy
mysql - Different clusters use different networks to ensure that the cluster is safe and healthy
4. Network Connectivity
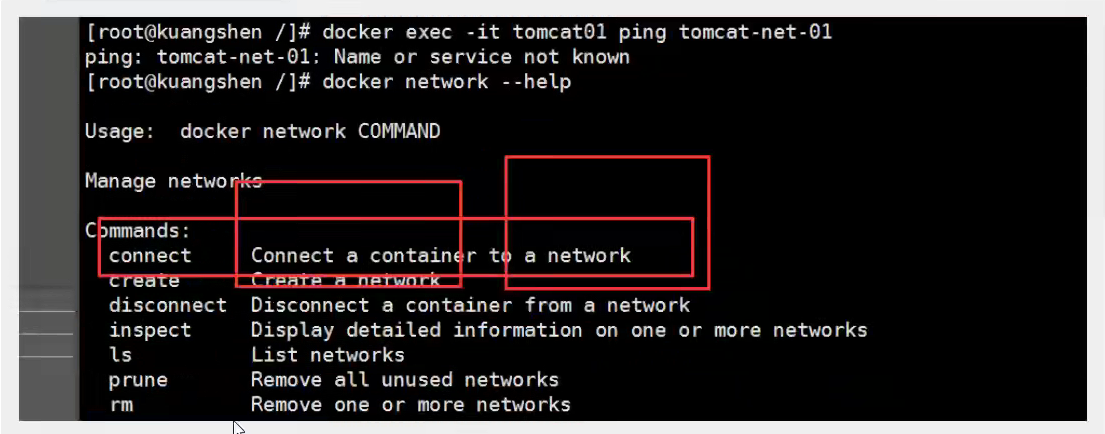
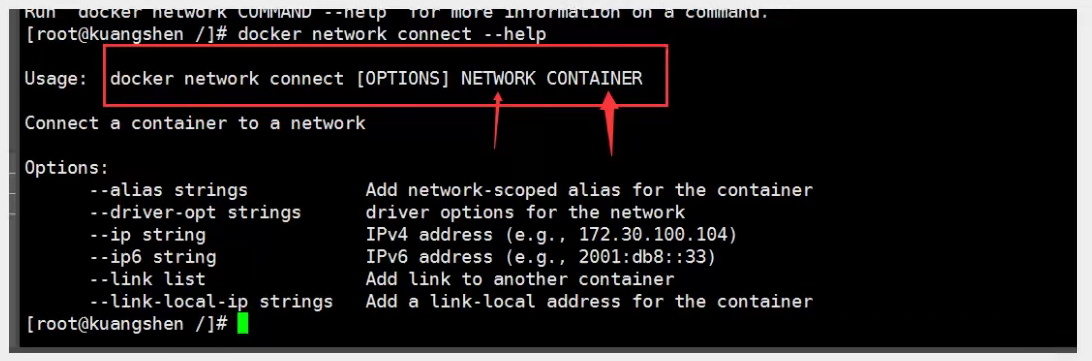
# Test to get through tomcat01 -> mynet docker network connect mynet tomcat01 # Once connected, tomcat01 is placed on the mynet network # Is a container with two IP addresses, listed as Ali Cloud Service, a public ip, a private IP
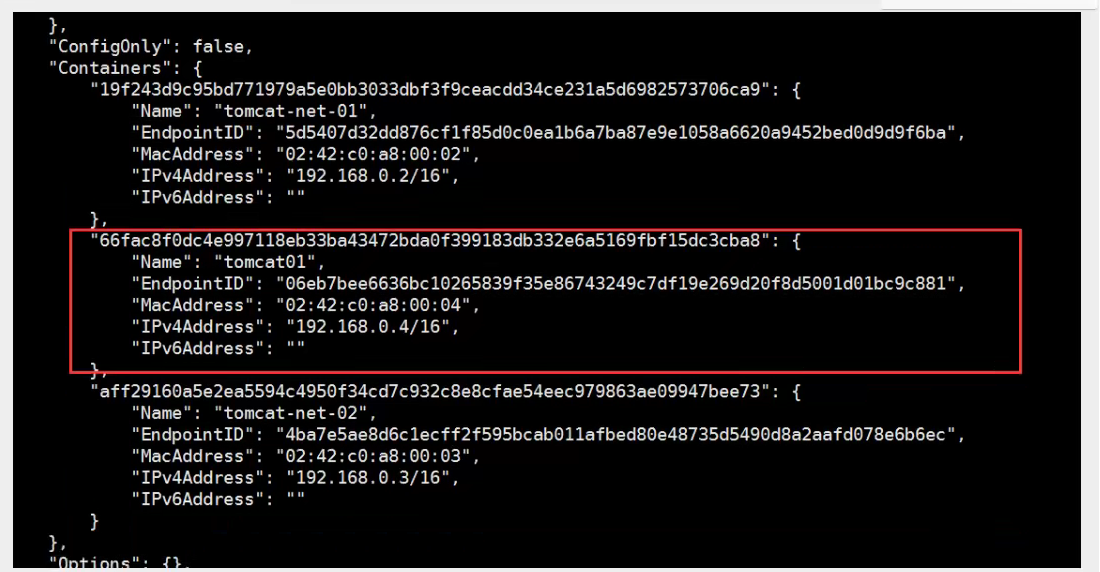
tomcat01 is connected to ok
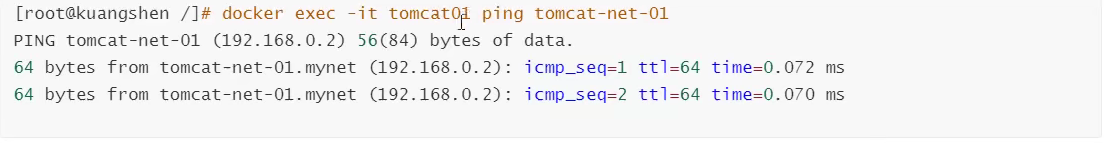
tomcat02 was found to be inappropriate. Repeat tomcat01 operation
 Conclusion: If you want to operate across networks, you need to use docker network connect ion to connect!
Conclusion: If you want to operate across networks, you need to use docker network connect ion to connect!
5. Actual Warfare: Deploying Redis Clusters
The following figure shows three hosts and three slave redis clusters
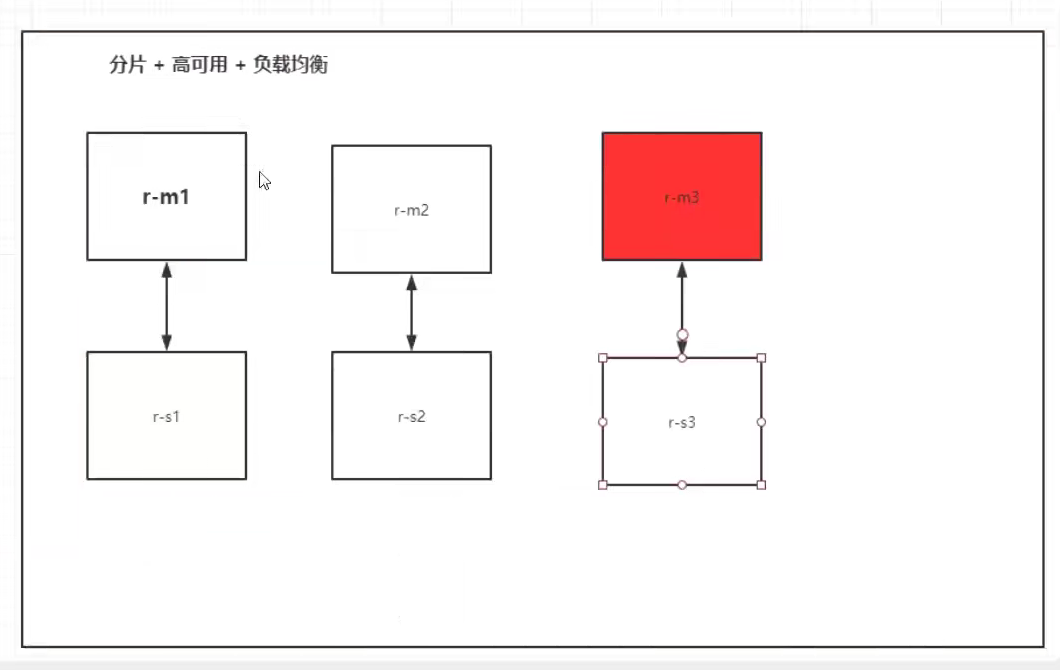
Create a custom network named redis
docker network create redis --subnet 172.38.0.0/16
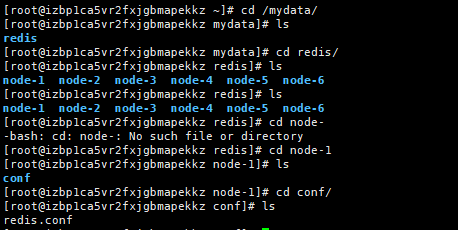
Create six Redis configuration information using the following script:
for port in $(seq 1 6); \
do \
mkdir -p /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf
touch /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
cat << EOF >/mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf
port 6379
bind 0.0.0.0
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
cluster-announce-ip 172.38.0.1${port}
cluster-announce-port 6379
cluster-announce-bus-port 16379
appendonly yes
EOF
done
Start six Redis containers below to set the corresponding container data volume mount
#First Redis Container
docker run -p 6371:6379 -p 16371:16379 --name redis-1 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-1/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-1/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.11 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
#Second Redis Container
docker run -p 6372:6379 -p 16372:16379 --name redis-2 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-2/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-2/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.12 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
#Third Redis Container
docker run -p 6373:6379 -p 16373:16379 --name redis-3 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-3/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-3/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.13 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
#4th Redis Container
docker run -p 6374:6379 -p 16374:16379 --name redis-4 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-4/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-4/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.14 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
#5th Redis Container
docker run -p 6375:6379 -p 16375:16379 --name redis-5 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-5/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-5/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.15 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
#6th Redis Container
docker run -p 6376:6379 -p 16376:16379 --name redis-6 \
-v /mydata/redis/node-6/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-6/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.16 redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
Or start six Redis containers at once through a script:
for port in $(seq 1 6); \
do
docker run -p 637${port}:6379 -p 1637${port}:16379 --name redis-${port} \
-v /mydata/redis/node-${port}/data:/data \
-v /mydata/redis/node-${port}/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \
-d --net redis --ip 172.38.0.1${port} redis:5.0.9-alpine3.11 redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf; \
done
Execute the above script with the following results:
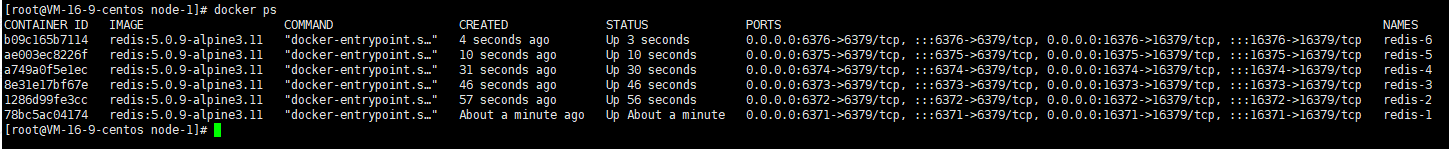
Enter below to create a cluster in the redis-1 container
redis-cli --cluster create 172.38.0.11:6379 172.38.0.12:6379 172.38.0.13:6379 172.38.0.14:6379 172.38.0.15:6379 172.38.0.16:6379 --cluster-replicas 1
View cluster information
redis-cli -c cluster info
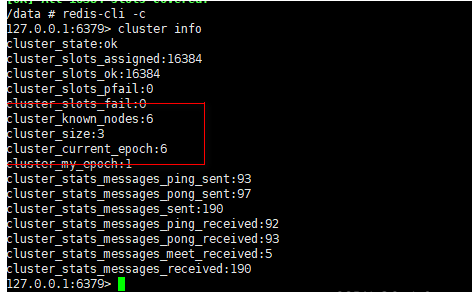
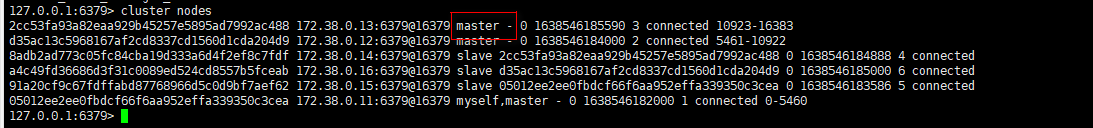
Looking at the node information cluster nodes, you can clearly see the master-slave relationship of the Redis node.
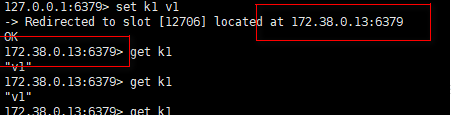
To test whether master-slave replication works, set a key and you can see that we have redirected to the Redis-3 node, which handles the operation.
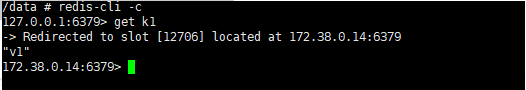
Create a new session, stop the Redis-3 container service, reconnect the Redis-cli client, retrieve k1 again, and redirect the processing from node Redis-4 to the Redis-3 node.
6. SpringBoot Micro Services Package Docker Mirrors
- Build a springboot project, write an interface, and start the project for local testing
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello World!";
}
}
-
Package applications, package Spring Boot projects with Maven's package, and generate jar packages
-
Write Dockerfile
FROM java:8 COPY *.jar /app.jar CMD ["--server.port=8080"] EXPOSE 8080 ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
-
Build a mirror to send the packaged generated jar package and the written Dockerfile to the server
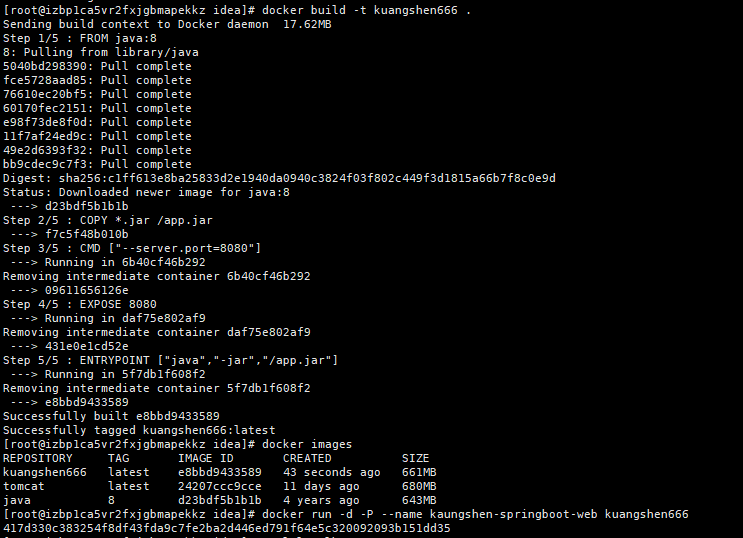
Use the build command to build the image:
docker build -t demo .
-
Publish Run! After you have finished building the mirror, run the mirror to test whether the / hello interface can be accessed properly. (Ports mapped by the host are randomly generated because -P was used for the previous run image)
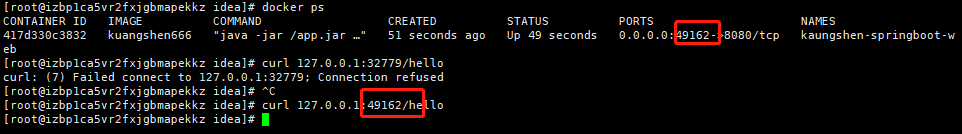
-
After we use Docker in the future, delivering it to others is a mirror!